Vaccination
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Vaccination
Successful and frequently-used manipulation of the immune system
Routine medical procedure
Provides immunological memory without the infection
Vaccine = non-infectious material with the pathogen’s antigens
Best given in youth to protect the individual and the population
Back to Jenner in late 1700s
First human vaccines were based upon weaker/attenuated viruses
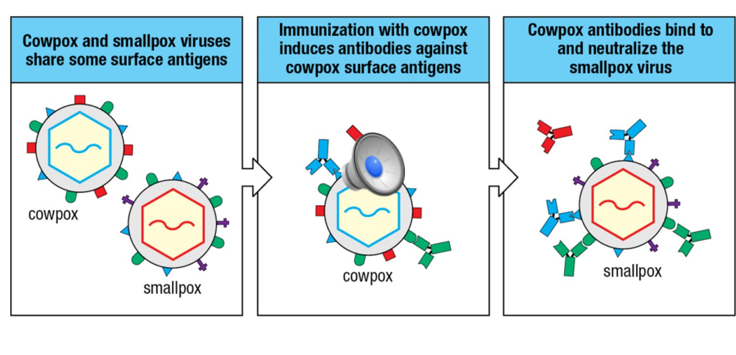
Smallpox vaccine used cowpox
Cowpox virus similar enough to induce an immune response, but did not cause the serious illness of smallpox
Rabies was the first virus that was attenuated in the lab to create a human vaccine
Why was the first vaccine (smallpox) so successful?
Slow virus evolution – epitopes conserved
Live vaccine – impacts skin and is a good mimic of the real infection
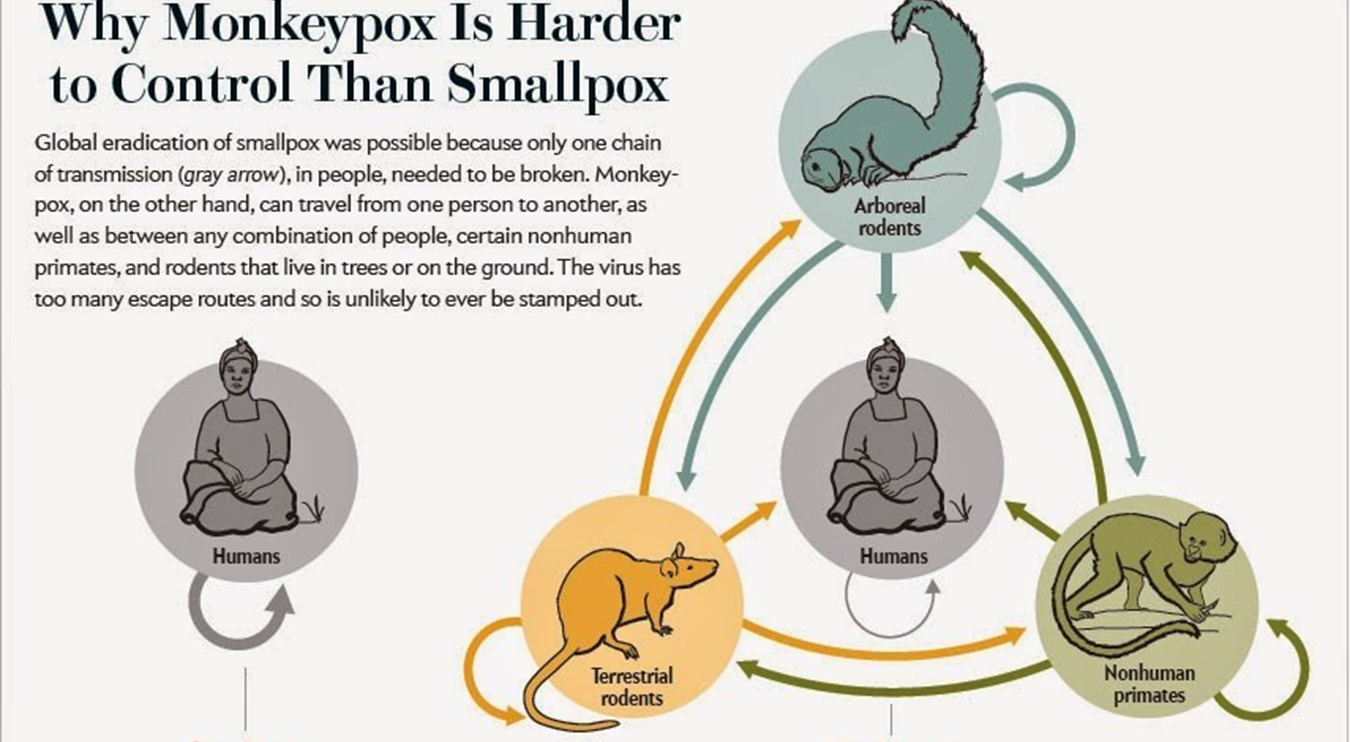
Virus cannot survive outside of humans (no animal reservoirs)
Why have we recently seen incidences of cowpox and monkeypox?
Killed or Inactivated Vaccines
Typically use heat or chemicals, like formaldehyde or formalin
Stops pathogen replication but keeps it intact and recognizable
Pros
Cannot revert to a more virulent form
Cons
Shorter length of protection, require boosters
Live, Attenuated Vaccines
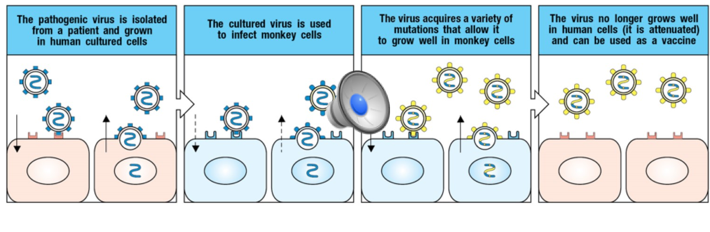
Can be made in several ways
Series of cell cultures or animal (chick) embryos
Virus grown in series and becomes better at replicating in non-human host and loses ability to replicate in humans
May require up to 200 passes through non-human host cells
Has potential to revert to a virulent form through mutation
Why oral polio vaccine replaced by the inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) in the U.S.
Inactivated toxins bacterial vaccine
– for bacterial diseases where the toxoids generated by the bacteria cause the illness and not the actual bacteria themselves
Toxoids
Disease caused by the toxin produced by the bacterium and not the bacterium itself.
Ex. Tetanus caused by a neurotoxin produced by Clostridium tetani bacteria
Need to inactivate/neutralize the toxin…turn the toxin into a toxoid (an inactivated protein)
Subunit or Conjugate Vaccines
Both contain only pieces of the pathogens they protect against
Subunit vaccine – isolates one specific piece of pathogen to provoke a response (e.g. flu shot)
May be a recombinant vaccine – made through genetic engineering (e.g. Hepatitis B, HPV)
Conjugate vaccine – similar but a combination of 2 different components of bacterial coats
Components bound to carrier proteins
Small pieces of bacterial coat don’t evoke a strong response, but carrier proteins do
Conjugate vaccines (like for meningitis) will activate BOTH B and T cells! Helps to boost Ab production through plasma cells and TH cells that inspire/support them in the lymph nodes.
Vaccine types
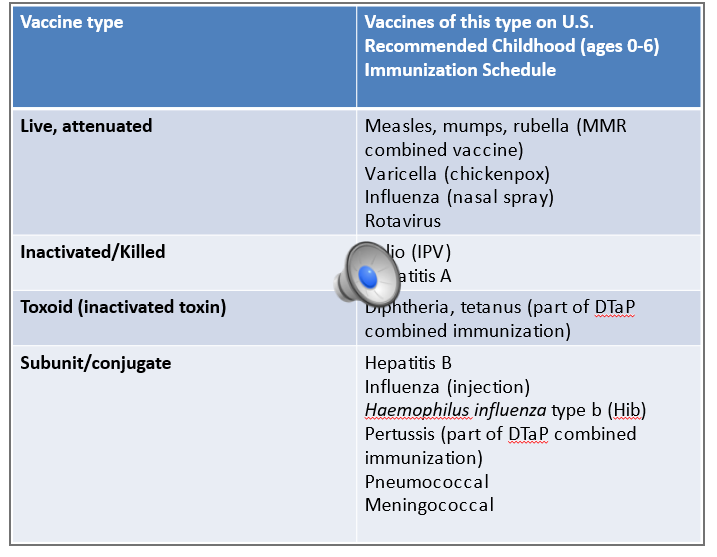
What is an adjuvant?
“Helper” additive
Trigger the innate immune response to start inflammation. The inflammation helps start the adaptive immune response
Allows for a smaller amount of vaccine to produce the same effect.
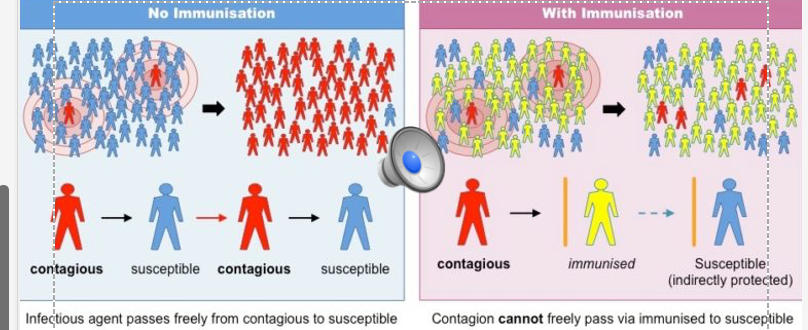
Herd Immunity