ASU BIO 201: Chapter 9 - Joints
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Define "joint"
a point at which parts of an artificial structure are joined
Name the term that is synonymous with joint
Articulations
Define arthrology
the study of joints
Define kinesiology
the study of musculoskeletal movement
Explain how joints are named
they are derived from the names of the bones involved
Define diarthrosis
freely movable
ex: carpals, elbow, knee
Define amphiarthrosis
slightly movable
ex: joints between the skull bones surrounding the brain,pubic symphysis or an intervertebral cartilaginous joint., the elbow joint
Define synarthrosis
little or no movement
ex: fibrous joints of the skull sutures and the cartilaginous manubriosternal joint
List four types of joints based on the way they adjacent bones are joined
bony, fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial joints
Explain the discrepancy between the number of bones in infants and adults
the frontal and mandibular bones in infants, cranial sutures in elderly, attachment of first rib and sternum with old age
Describe a synostosis and give examples of where they are located
bony joint in the fibrous or cartilaginous joints
List and describe the three types of fibrous joints
sutures, gomphoses, syndesmoses
Examples of sutures
cranial sutures
Examples of gomphoses
the roots of the teeth (the pegs) fit into their sockets in the mandible and maxilla
Examples of syndesmoses
manubriosternal joint or the joints between the skull bones surrounding the brain, in-between the radius and ulna as well as the tibia and fibula
Recognize three types of sutures
serrate, lap (squamous), plane (butt)
Examples of serrate sutures
coronal, sagittal, lambdoid
Examples of lap (squamous)
temporal and parietal bone, squamous suture
Examples of plane (butt)
palatine processes of the maxillae, intermaxillary suture
Define interosseous membrane
2 bones are bound by longer collagenous fibers than in a suture or gomphosis
Where are interosseous membranes are located in the body
in between radius to the ulna and the tibia to the fibula
List the two types of cartilaginous joints
synchondroses and symphyses
Describe the two types of cartilaginous joints
synchondroses: Connecting material is hyaline cartilage---epiphyseal plate of a growing bone and between 1st rib and sternum
symphyses: bones are separated by a pad of cartilage-- intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis
Examples of synchondroses
first sternocostal joint (where the first rib meets the manubrium)
Examples of symphyses
pubic symphysis; the symphyses between the bones of the skull, most notably the mandible
Explain the significance of synovial joints
most structurally complex, most likely to have complications
Draw and label a synovial joint
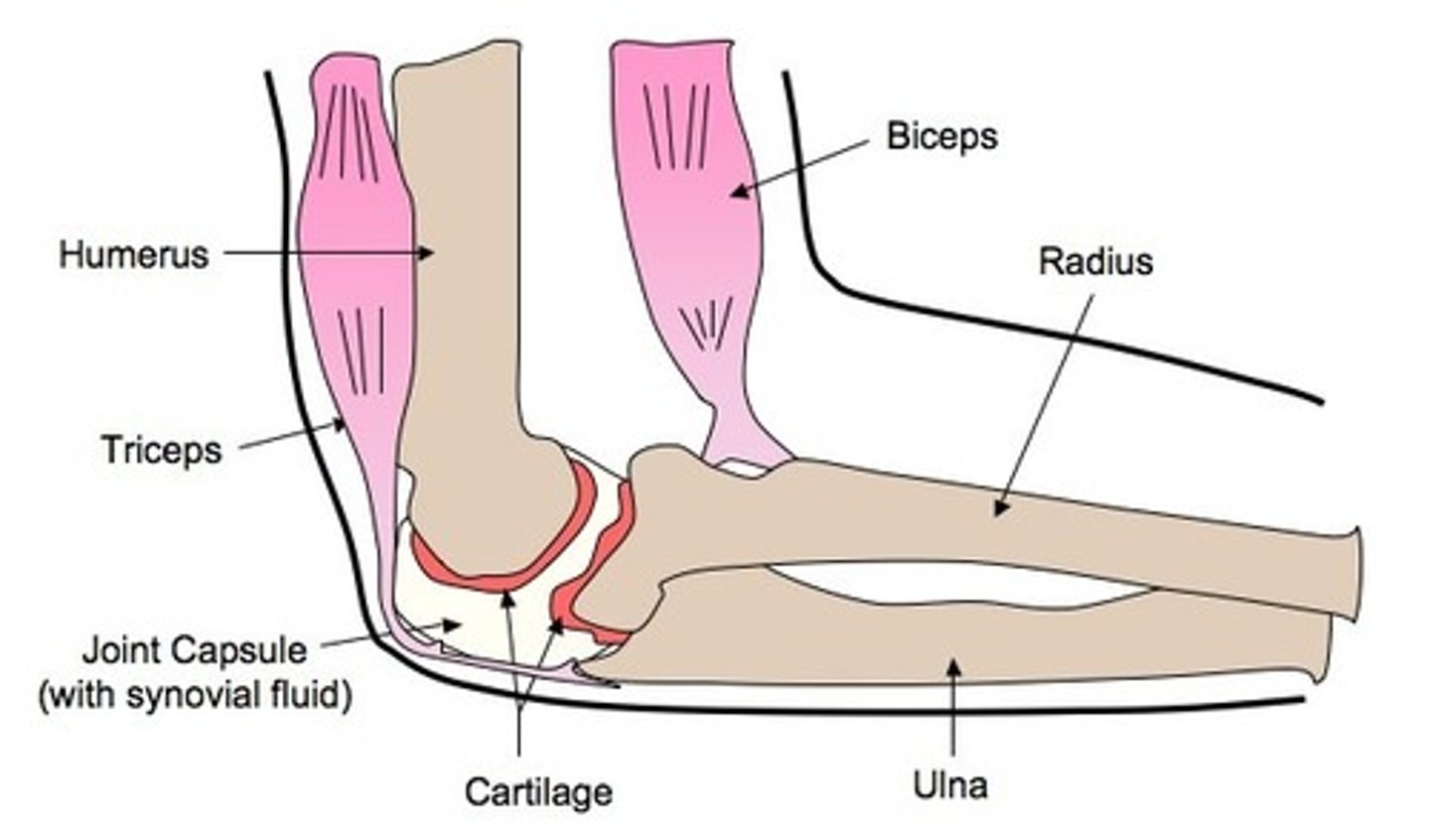
What is the function of the synovial joint
absorb shock and reduce friction during movement
What is fibrocartilage?
growth inward from joint capsule in a few synovial joints
Describe fibrocartilage that is associated with synovial joints
articular disc, meniscus
Characterize the accessory structures of joints
tendons, ligaments, tendon sheaths, bursae
Why warm-up exercises are so important?
warm-up period before vigorous exercise helps protect cartilage from undue wear and tear
Explain the effects of exercise on synovial joints
exercise warms synovial fluid
Define axis of rotation
the straight line through all fixed points of a rotating rigid body around which all other points of the body move in circles
Describe a monoaxial joint
this joint has one degree of freedom or axis of rotation
Describe a biaxial joint
this joint has two degrees of freedom or axes of rotation
Describe a multiaxial joint
this joint has three degrees of freedom or axes of rotation
List, describe and give examples of the 6 types of synovial joints
ball and socket joints, condyloid (ellipsoid) joints, saddle joints, plane (gliding) joints, hinge joints, and pivots joints
Explain "range of motion"
the degrees through which a joint can move
Explain what is really meant if someone is described as "double-jointed"
people have long or slack ligaments
Define zero position
the position of a joint when a person is in standard anatomical position
List the following movements:
fexion, extension, hyperextension, abduction, adduction, elevation, depression, protraction, retraction, circumduction, medial/lateral rotation, pronation, supination, lateral/medial excursion, inversion, eversion, opposition, reposition, dorsiflexion, plantar flexion
Flexion movement
movement that decreases the joint angle (common in hinge joints)
Extension movement
movement that straightens a joint and generally returns a body party to the zero position
Hyperextension movement
further extension of a joint beyond the zero position
Abduction
movement of a body part in the frontal plane away from the midline of the body
Adduction
movement in the front plane back toward the midline
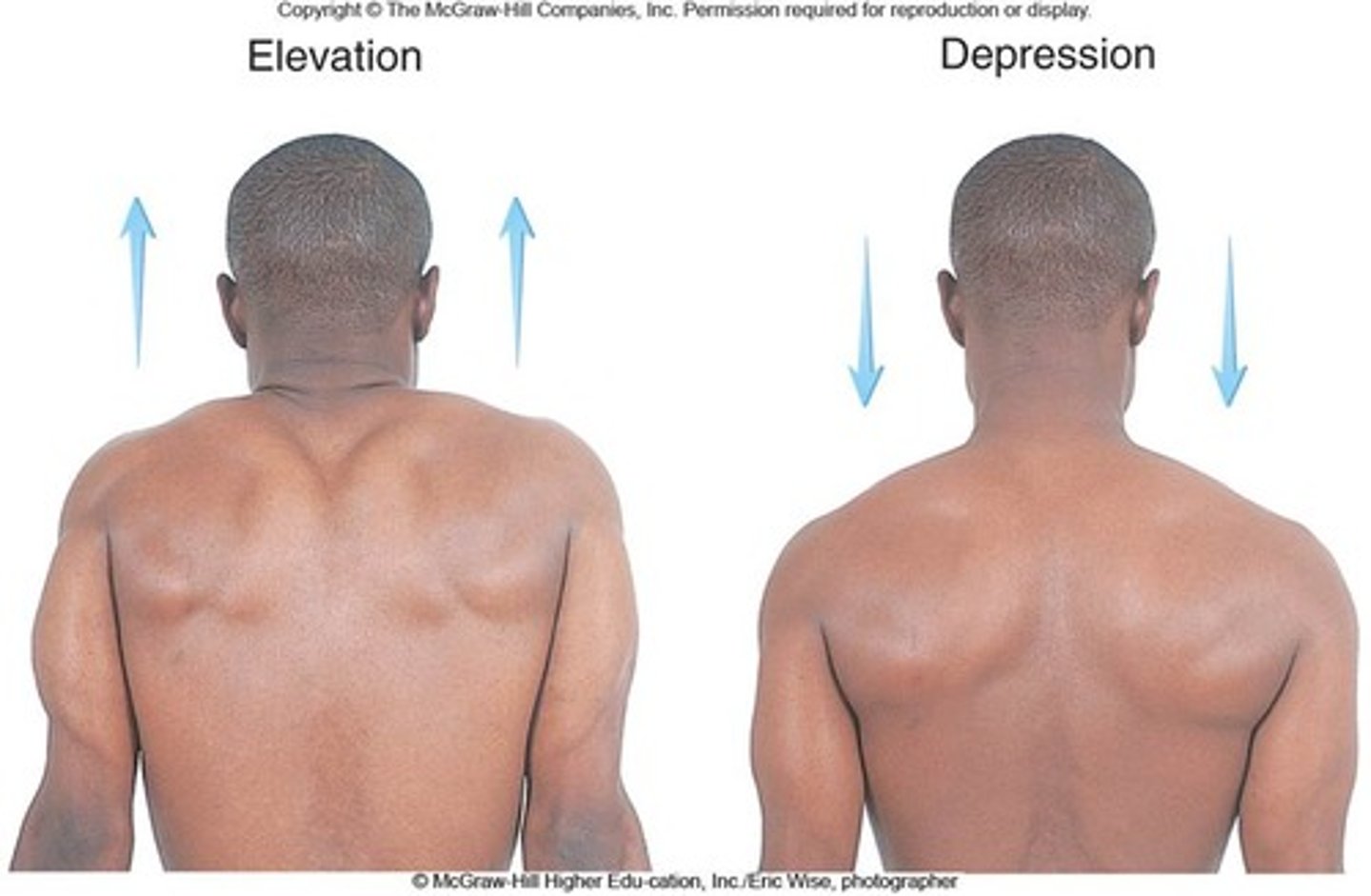
Elevation
a movement that raises a body part vertically in the frontal plane
Depression
lowers a body part in the same plane
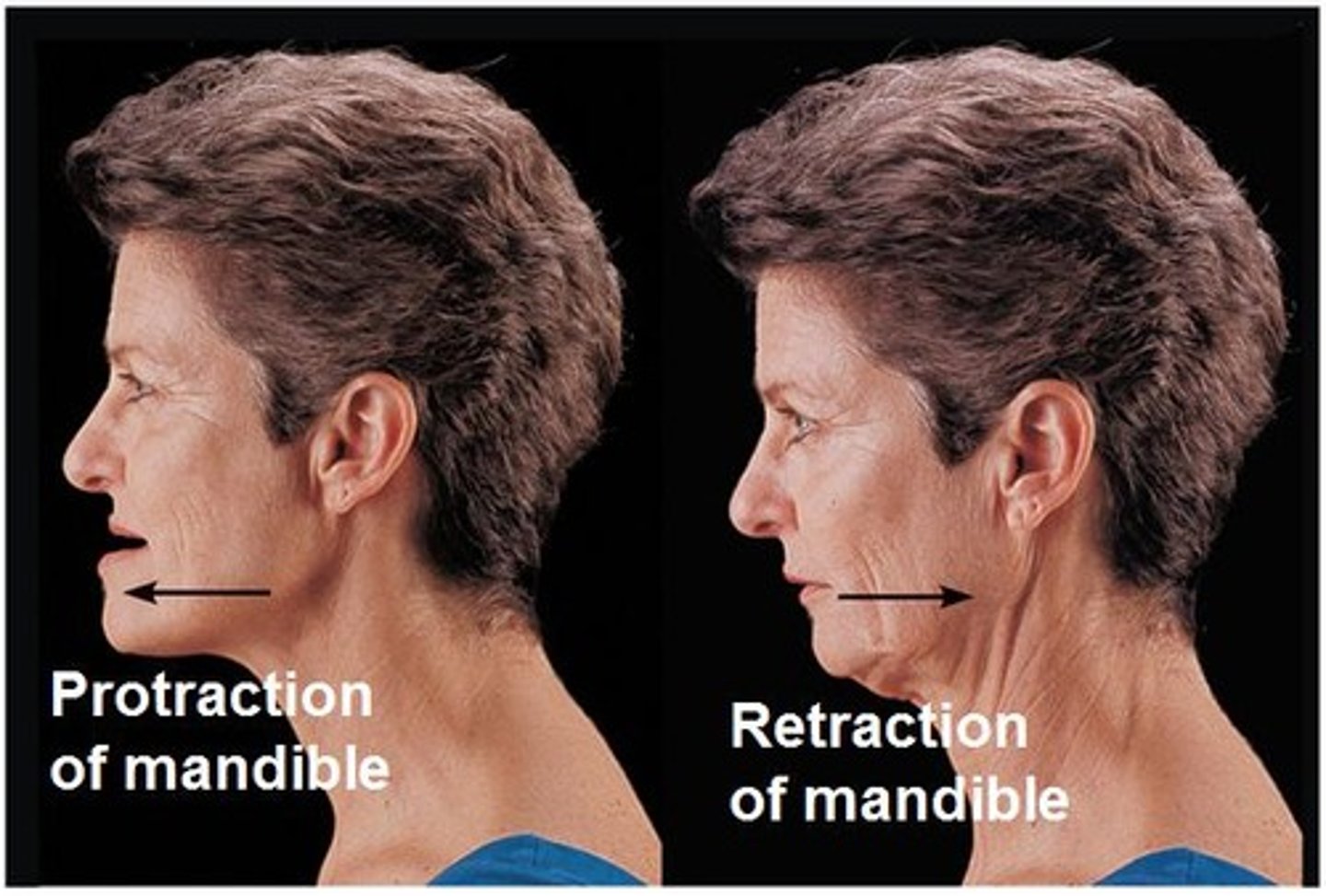
Protraction
anterior movement of a body part in the transverse (horizontal) plane
Retraction
posterior movement
Circumduction
end of the appendage remains stationary with other end makes a circular motion
Rotation
movement in which a bone spins in its longitudinal axis
Medial Rotation
turns the bone inward
Lateral Rotation
turns the bone outward
Supination
forearm movement that turns the palm to face anteriorly and upward
Pronation
forearm movement that turns the palm to face posteriorly or downward
Lateral Flexion of the head and trunk
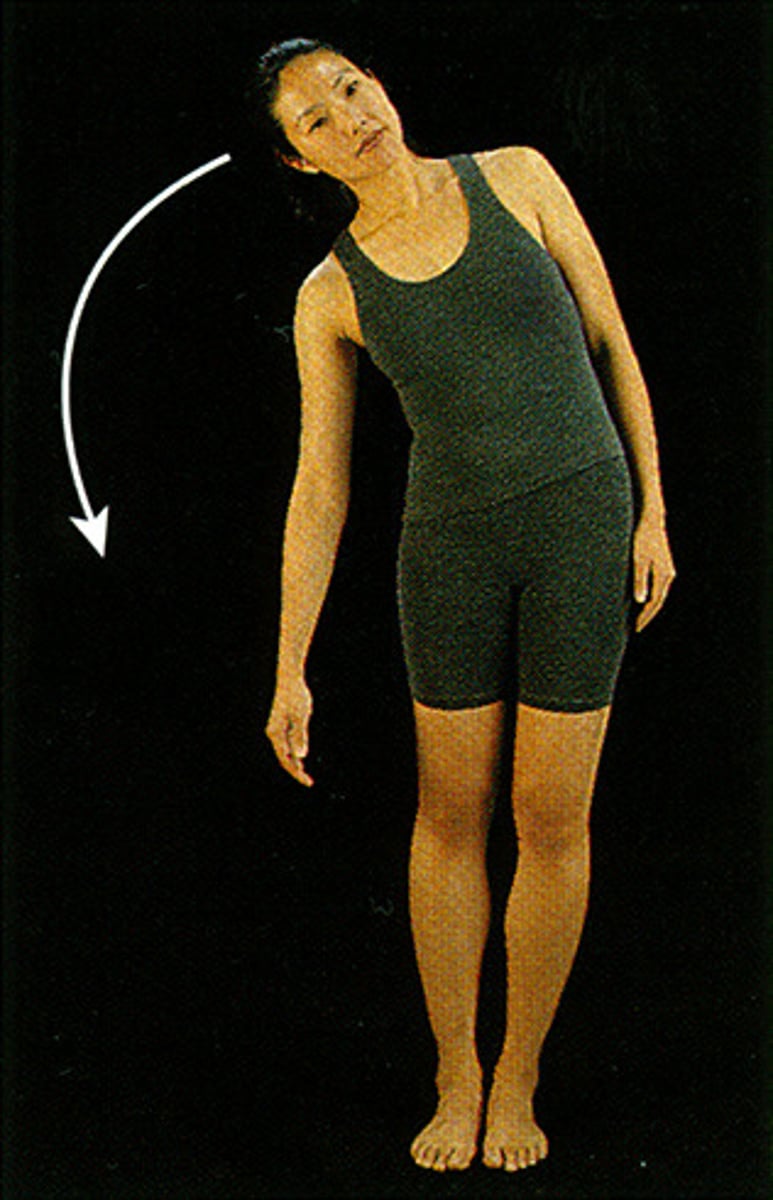
Flexion of trunk

Hyperflexion of the vertebral column
Rotation of the head
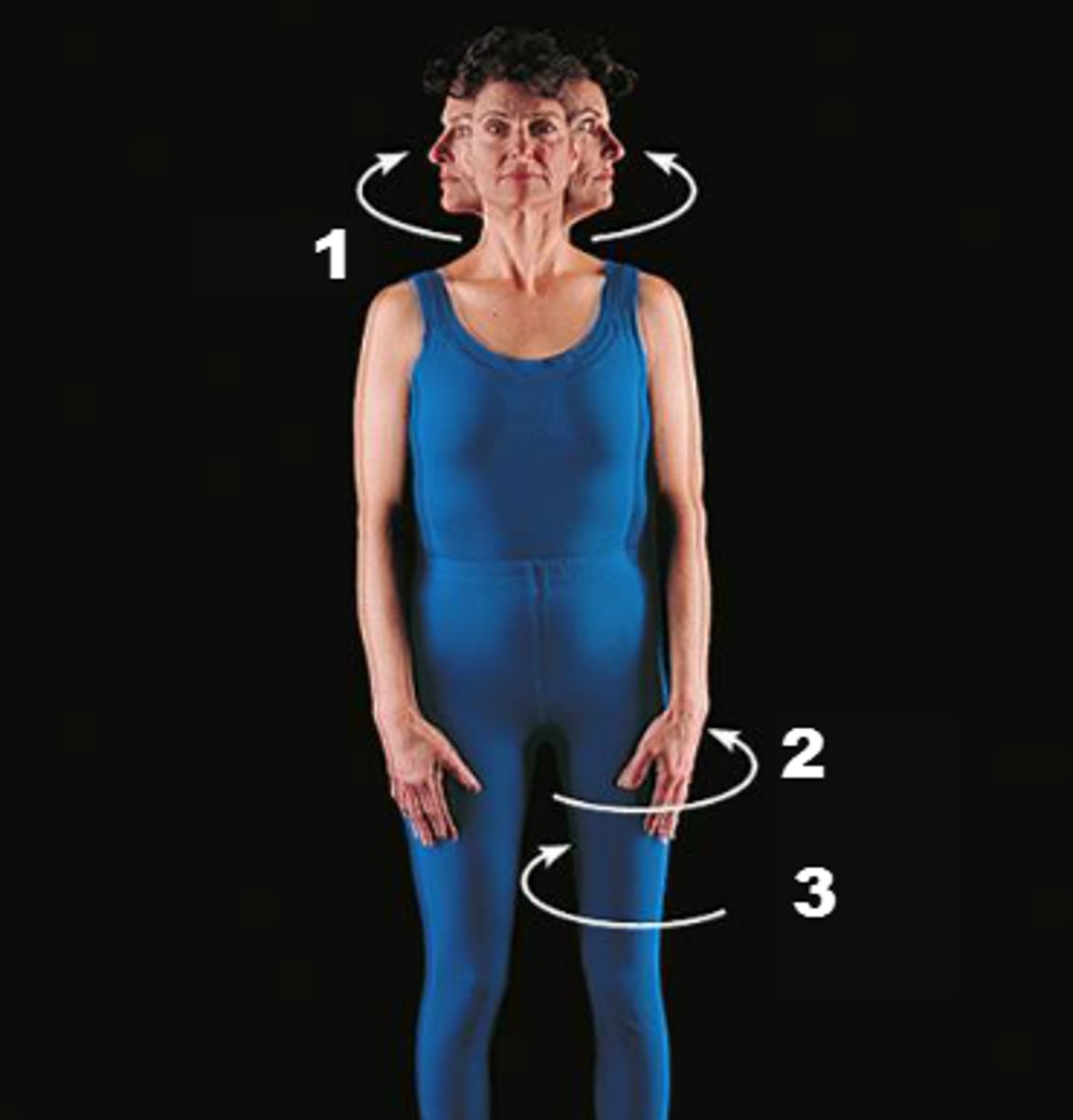
Specific movements of the mandible
Protraction-retraction, elevation-depression, lateral excursion, medial excursion
Protraction-Retraction
protract when you prepare to take a bite
Elevation-Depression
depress the mandible to take a bite
Lateral excursion
right or left movement from zero position
Medial excursion
movement back to the median, zero position
Ulnar flexion
tilts the hand toward the little finger
Radial flexion
tilts the hand toward the thumb
Flexion of fingers
curling them
Extension of fingers
straightening them
Abduction of the fingers
spread them apart
Adduction of the finger
bring them together again
Flexion of the thumb
tip of thumb directed toward palm
Extension of the thumb
straightening the thumb
Radial abduction
move thumb away from index finger 90°
Palmar abduction
moves thumb away from hand and points it anteriorly
Adduction of thumb
moves it to the zero position
Opposition
move the thumb to touch the tips of any of the fingers
Reposition
return the thumb to the zero position
Dorsiflexion
elevation of the toes as you do while swinging the foot forward to take a step (heel strike)
Plantar flexion
extension of the foot so that the toes point downward as in standing on tiptoe (toe-off)
Inversion
a movement in which the soles are turned medially
Eversion
a movement in which the soles are turned laterally
Supination of foot
complex combination of plantar flexion, inversion, and adduction
Pronation of foot
complex combination of dorsiflexion, eversion, and abduction
Describe the cause of sprains
ligaments are torn or stretched
Treatment for sprains
Heal slowly - poorly vascularized
Completely torn - surgery or replacement
Describe torn cartilage
remain due to avascularization
Treatment for torn cartilage
Arthrosctorn opic surgery to remove damaged tissue.
Joint is less stable after removal
Describe a joint luxation (dislocations)
bones are forced out of alignment
Treatment for laxations (dislocations)
must be reduced
Explain which joint of the body is the most complex, and therefore most vulnerable to injury
knee joint
List the injuries that are most common to the knee
meniscus and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Define arthroscopy
a procedure in which the inferior of the joint is viewed with a pencil-thin arthroscope inserted through a small incision
Characterize the three types of arthritis
osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gouty arthritis (Gout)
Causes and treatments of osteoarthritis (OA)
causes: years of joint wear
treatments: acetaminophen
Causes and treatments of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
causes: autoimmune, attack against the joint tissues
treatment: steroids and aspirin control inflammation
Causes and treatments of Gouty Arthritis (Gout)
causes: hereditary
treatment: anti-inflammatory
Characterize TMJ syndrome - including signs, symptoms, causes and treatments
the articulation of the condyle of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone.
signs and symptoms:
can cause moderate intermittent facial pain
clicking sounds in the jaw
limitation of jaw movement
often severe headaches
Vertigo (dizziness)
tinitis (ringing in the ears)
pain radiating from jaw down the neck, shoulders, and back
cause of syndrome:
caused by combination of psychological tension and malocclusion
(misalignment of teeth)
treatment:
psychological management, physical therapy, analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs, corrective dental appliances to align teeth properly
List the bones that participate in the shoulder joint
glenohumeral (humeroscapular) joint
head of the humerus articulated with the glenoid cavity