Advertising Exam #2
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
marketing
the activity, set of institutions and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers
Larger marketing context of advertising
Advertisers must understand the relationship between the product and the marketplace; this means a company must be able to locate perspective customers, understand their needs, wants and desires, and communicate that information in a powerful, clear, compelling way
Key drivers of marketing decision
Establishing a target market(s)
Classifying your product
Setting your pricing
Determining placement (distribution) approach
Choosing types of promotion
market segmentation
Marketers select specific markets that offer the greatest potential
Key steps to creating segments to target
identifying groups with shared needs and characteristics and combining the groups into larger larger segments through a marketing mix
Types of markets
Consumer and business
Consumer markets
Target of most advertising; advertising to individual consumers
Consumers
people who buy the product for their own or someone else’s personal use
Consumer segmentation
Consumers are segmented by:
Demographic
Geographic
Psychographic
Behavioristic
Demographic
Based on a population’s statistical characteristics with quantifiable factors
Ex. Gender, age, ethnicity, occupation, income, etc.
Geographic
Based on geographic regions with shared characteristics: culture, traditions, lifestyles
Ex. Country, region, neighborhood
Psychographic
Defining consumer markets based on psychological variables (psychographics) including values, attitudes, personality, lifestyle and activities
Ex. Runners, vegans, values good quality food and fabrics
Behavioristic
Grouping of consumers by their purchase behavior- how they buy and use products and brands
Ex. Sole users, discount user, aware nontriers
Sole users
Most brand loyal and require the least amount of advertising and promotion
Semisole users
Typically use Brand A but have an alternative selection if it is not available or if the alternative is promoted with a discount
Discount users
Semisole users of competing brand B; they won’t buy Brand A at full price but perceive it well enough to buy it at a discount
Aware nontriers
use competitive products in the category but haven’t taken a liking to Brand A but aware
Trial/rejectors
Tried Brand A because of its advertising message but didn’t like the product
Repertoire users
Perceive two or more brands to have superior attributes and will buy at full price; these are brand switchers; therefore they are the primary target for brand advertisers
Behavioristic Considerations
Usage rate: defining consumers as light, medium or heavy users of a product
Purchase occasion: segmenting markets on the basis of whe consumers buy/use good or service
Benefits sought: segmenting consumers based on the benefits being sought such as high quality, low price, symbolism
Business markets
organizations that buy natural resources, component products, and services that they resell, use to conduct their business, or use to manufacture another product
B2B Marketing
Marketing directed at people who buy good and services for resale, for use in a business or organization or for manufacturing other products
B2C Marketing
Marketing directed at consumers who buy goods and services
Product classification
Consumer need and product utillity: determining what role the product plays
Utility
product’s ability to satisfy both functional needs and/or psychological wants
Five types of functional utility
Form: provides a tangible good
Task: performs a task
Possession: Available for purchase
Time: Available when wanted
Place: Available where wanted
Psychological utility
Offers symbolic or psychological desire satisfaction, such as status or makes the consumer feel a certain way like confident
Product life cycle
Progressive stages in the life of a product that affect the way a product is marketed and advertised
Introduction stage
initial phase of the product life cycle when a new product is introduced, costs are highest, and profits are lowest
Growth stage
period in the product life cycle marked by market expansion as more and more customers make their first purchases while others are already making their second and third purchases
Maturity stage
point in product life cycle when the market becomes saturated with products, the number of new customers has dwindled, and competition is most intense
Decline stage
stage in the product life cycle when sales begin to decline due to obsolescence, new technology, or changing consumer tastes
product position
ranked in the way consumer’s mind by the benefits it offers
Brand
core feeling about a product
Price
the amount charged for a good or service, influences consumer perceptions of a brand
Key factors influencing price
Market demand (law of supply and demand)
Production and distribution costs
Competition
Corporate objectives (how much profit they want)
Psychological pricing
using prices as a means to influence customer behavior or perceptions (higher prices=higher quality?)
Place
The place or distribution element of the ad itself; its important for marketers to understand that the method of distribution must be consistent with the brand’s image
Direct distribution
Sell directly to consumer from a manufacturer; the advertising burden is entirely on the manufacturer without any assistance from other members
Indirect distribution
A network of resellers and retailers that operate between the producer and user; most companies market their product this way
Intensive distribution
Distribution strategy based on making the product available to consumers at every possible location
Selective distribution
Distribution method limits the number of outlets or creating demand
Exclusive distribution
Exclusive right to one wholesaler/retailer in one geographic region
Promotion
All marketing-related communications between the seller and buyer
Marketing mix
The written document that details all of the various elements of the marketing decision
Key components of the marketing plan
Situation analysis
Marketing objectives
Marketing strategy
Marketing tactics
Situational analysis
Factual statement of the organizations current situation and how it got there, including a SWOT, the company, the product, and the competition
Marketing objectives
what marketing is intending to achieve, could be corporate objectives, brand objectives, or even need-satisfying objectives
Marketing strategy
How the marketing will achieve its marketing objectives
Marketing tatics
The specific actions that will be taken to achieve its objectives
SWOT Analysis
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
SWOT: Strengths
Internal; Positive characteristics or facts about the brand/product/company itself
SWOT: Weaknesses
Internal; Negative characteristics or facts about the brand/product/company itself
SWOT: Opportunity
External; Societal/culture/business trends that provide growth and great possibility for the brand
SWOT:Threat
External; Competitive pressures, societal/culture changes, business realities that my hinder growth and negatively affect brand
Advertising plan
With advertising research as a basis, a full ad plan is created that includes these main parts: advertising strategy which is comprised of two drivers: creative strategy (which guides creative ideas) and media strategy (which guides media decisions where to place/put creative)
Advertising research
Comprised of creative and media strategy; companies use advertising strategy research to gain understanding and key insights, and inform on the brand, the target audience, the message, the creative, and the media
Steps in advertising research
Analyze the situation/define the problem
Conducting secondary research (both primary and secondary data)
Establishing research objectives
Conducting primary research (Both qualitative and quantitative)
Interpret and report findings
Primary data:
Customized information that often comes from the company/client itself
Secondary data
information previously gathered and published, by another firm or organization
Qualitative research
Uses in-depth studies of small, non-random samples to explore behavior, perceptions, needs and motivations of a target audience; provides a deeper impression of the market
Ex. in-depth interviews, focus groups, etc.
Quantitative research
Larger, representative samples and surveys to quantify hypotheses and measure specific market variables; provides a full breath of data
Ex. Surveys, observations, experiments
Consumer behavior
The mental/emotional processes and the physical activities of people that purchase/use goods and services to satisfy particular needs and wants
Consumer influences
Interpersonal influence: family, society, and culture
Non-personal influence: time, place, and environment
Personal process: perception process, motivation process, learning and persuasion process
Stimulus: something we perceive through our senses
Screens: perceptual or physiological screens
Perceptual Screens
subconscious filters that shield us from unwanted messages before any data can be perceived; stimuli must penetrate a set of perceptual screens
Physiological screens
Comprise the five senses, detect incoming data, and measure the dimension and intensity of the physical stimuli
Cognition
point of awareness and comprehension of stimulus
mental files
Long-term memory storage that is ranked in order of importance, quality, features, etc.
Motivation
Refers to the underlying forces (or motives) that foster actions, which stem from the conscious or unconscious goal of satisfying our needs and wants
Needs
basic, often-instinctive, human forces that motivate a person to do something
Wants
“needs” we learn during our lifetime
Creative brief
Made to inform creatives on what their ideas must do to be successful for the brand, inspire creative to create amazing ideas that both resonate and are relevant the audience, and hold both agency and clients accountable on the focus of creative ideas
Creative brief key components
Challenge
Objectives
Target Audience
Key Message
Reasons to believe
Tone/feel
Creative brief: Challenge
One key challenge or opportunity that advertising can solve; it briefly sets up context, the stakes and the mission for advertising
Advertising objectives pyramid
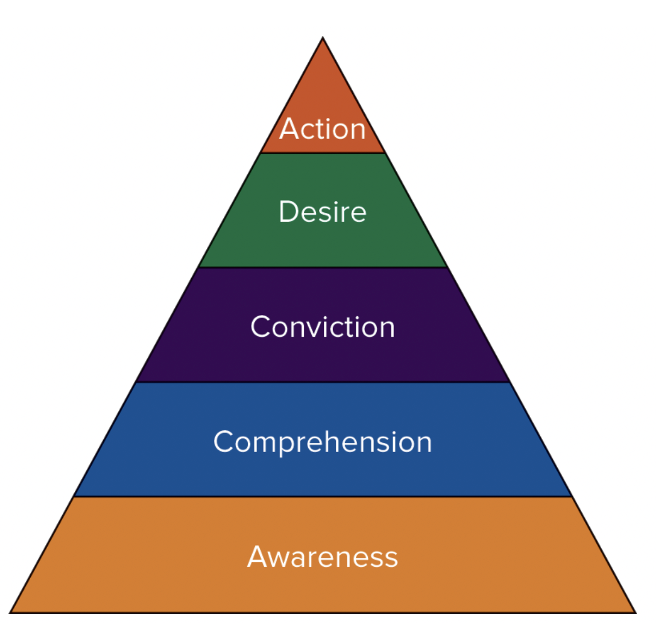
Objectives Pyramid: Awareness
To acquaint people with the company, product, service, and/or brand
Objective pyramid: Comprehension
To communicate enough information so that some percentage of the aware group recognizes the product’s purpose, image or position, and perhaps some of its features
Objectives pyramid: Conviction
To persuade a certain number of people to believe in the product’s value
Objectives Pyramid: Desire
Creating a desire for the product by emphasizing its value and how it can fulfill a need
Objectives pyramid: Action
request additional information, visit a store or buy it
Creative Brief: Target audience
A clear and full picture of who the advertising is trying to speak to- using the various ways to look at and define an audience; a good target audience is robust, diverse, and paints a clear picture of who you are talking to
Creative brief: key message
A singular message you want to convey to your target audience- the one thing you want to say about the brand product/service (often the main benefit- whether functional or image); a good key message is singular, clear, focuses on a benefit of the brand
Creative Brief: Reasons to believe
Support points that communicate why your target audience should believe the main message about the product/brand; points about the product/brand itself; a good reason to believe is brand/product focused, it truly ties to the key message, focuses on 2-3 points most important points
Creative brief: Tone
How the ad should feel and often driven by the personality of the brand itself- the brand voice; a good tone uses emotional words, makes it clear how work should feel, no conflicting words
Role of creativity in advertising
Creativity helps advertising inform
Creativity helps advertising persuade
Creativity helps advertising remind
Creativity puts the boom in advertising
Fact- based vs. value-based thinking
Fact-based: linear thinkers, preferring facts/figures over soft concepts; they use creative thinking but in a more logical and analytical way
Value-based: make decisions on intuition, morals, and values; they tended to be more imaginative
Creative
Come up with ideas for advertising and oversee the execution of the creative idea to its final form; responsible for developing imaginative, smart ideas that follow the strategy and make effective advertising
Creative team
Copywriters, art directors, and creative directors
Copywriters
develop the verbal message- the copy (words) within the advertising
Art directors
Responsible for the visual aspect of the message that determines the look and feel of the ad
Creative directors
supervise the copywriters and art directors
Creatives
the people in all specialities who work in the creative department as a group
Creating great advertising includes two dimensions
Audience resonance and strategies relevance
Audience resonance
A great ad echos through society
Relevance
Measures how well the message strategy relates to the audience’s needs and wants
Creative journey roles
Explorer, artist, judge, and warrior
Explorer
Creatives examine the information they have, and work with their strategic planners
Artist
Creatives develop the big idea and implement the big idea
Judge
Creatives evaluate the practicality of their big ideas and decide whether to implement, modify, or discard them
Warrior
Creatives fight for their ideas and sell their idea to clients