Fundamentals of market system
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What’s the type of market structure for many producers?
Monopolistic competition
What’s the type of market structure for a few producers?
Oligopoly
What’s the type of market structure for one producer?
Monopoly
What is perfect competition?
A market is perfectly competitive.
When is a market perfectly competitive?
Many buyers and sellers
Freedom to enter and exit market
Homogeneous product
Perfect information in product availability and prices. Producers and consumers know if a producer is selling at a higher or lower price than other sellers.
What is a homogeneous product?
All producers sell identical products in the eyes of consumers
What are examples of perfectly competitive markets?
Gold and silver market
Stock and bonds
Foreign exchange
Some of the agricultural products
When does the market mechanism perform ‘best’?
Under perfect competition (achieving efficiency in resource use). Having a goal or ideal.
What is the simplest market structure to analyse?
Perfect Competition
What does the height of D reflect?
The marginal utility of consuming each additional good.
What does the height of S reflect?
The marginal cost of producing each additional unit of the good.
What does supply equal?
Marginal Cost, Marginal Social Cost
What does demand equal?
Marginal Utility, Marginal Social Benefit

What happens at point E on the graph?
Marginal Utility = Marginal Cost, Marginal Social Cost = Marginal Social Benefit
What is demand called in ‘efficiency in resource allocation in a market’?
Marginal Social Benefit
What is supply called in ‘efficiency in resource allocation in a market’?
Marginal Social Cost
What is allocative efficiency?
It is achieved when we push the resource use to the point where the MSB of resource use is equal to the MSC.
When is it good to go ahead and use the productive resources?
So long as the additional benefit of resource use for society exceeds its additional cost
What is the market equilibrium?
It is allocatively efficient, when the price equals the marginal costs
What are property rights?
Rights of ownership, usage, and transfer of resources, good and services, including intellectual property (patents, copyrights, and trademarks).
What are the rule of law and property rights in the market economy: Private firms and individuals?
They own productive resources, and goods and services to be consumed.
When does the market system work?
Only if the government protects and enforces property rights.
Is the market system always successful
No, it is not always successful in providing goods and services for society.
What goods and services are often traded in markets?
Private Goods.
What are (pure) public goods?
The kind of goods that the market system will not provide, at the efficient level.
When is a good rival (depletable)?
If a person’s consuming a given quantity makes it impossible for others to enjoy (i.e. ones consumption decreased the supply available to others). e.g. most tangible goods, my laptop, my shoes.
When is a good nonrival?
If a given amount of the goos can be enjoyed by multiple consumers without decreasing the enjoyment of each other. e.g. TV and radio programmes, national parks, roads (up to congestion point).
When is a good nonexcludable?
If, due to the physical/ technological nature of the good, it is too costly or nearly impossible to prevent those who refuse to pay for it from enjoying the benefits of a given amount of the good. e.g. a large natural park, a defence system for a region, roads.
Are pure public goods nonrival and nonexcludable?
Yes
Why does the market system fail to provide public goods efficiently, or at all?
The free-rider problem as a result of the good being non-excludable.
What are negative (or detrimental) externalities?
Are costs to third parties as a result of production and/or consumption activities in a market, no reflected in the market price of the good.
or
They emerge when market actitives impose external costs on other people without compensating them?
e.g. cigarettes, fossil fuels, fertilisers.
What cost exists when a negatively
What is the Marginal External Cost?
Marginal external cost of a good is the cost to third parties by producing and consuming one more unit of good.
What is only partially represented in the marginal cost of resource use for society?
Producers’ Marginal codt of production, which we now call Marginal Private Cost.
What makes up Marginal Social Cost?
Marginal Private Cost + Marginal External Cost
What does a Marginal External Cost graph look like?
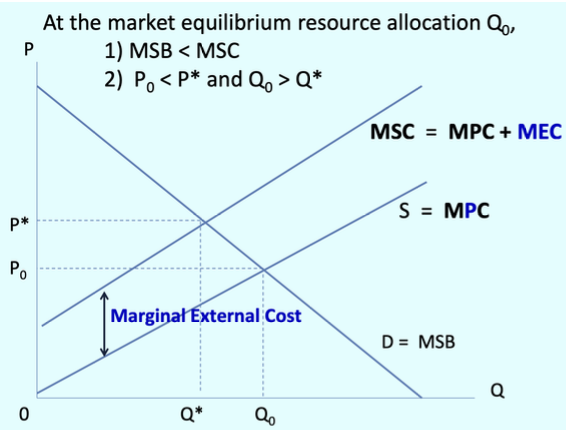
What happens when the price is ‘too low’?
We observe an over-production and consumption.
How do you internalise the externality?
By making the goods more expensive through taxation
What can we do about the inefficient resource allocation in such a market?
Taxation e.g. Cigarette tax, Fuel tax, Dog poop
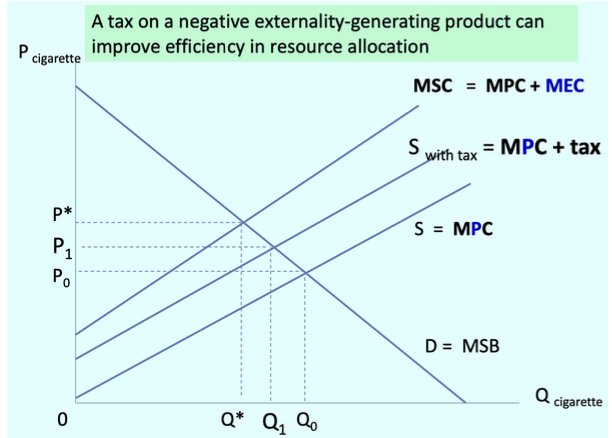
What happens when tax is added on a negative externality-generating product?
It can improve the efficiency in resource allocation
How is supply with tax calculated?
Marginal Private Cost
What does the graph including Supply with tax look like?