Chapter 39: Tissue and Wound Healing
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1, 2, 3,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
The structure of the skin
largest organ in body
1.2-2.2 square meters
4-5 kilograms (9-11 pounds)
Function
Serves as first line of defense; waterproof barrier
Minimizes excessive water loss
Maintains thermoregulation
Contains receptors for somatic sensations
participates in metabolism and activation vitamin D
Two layers: epidermis and dermis
Epidermis
Upper layer of skin
Stratified squamous epithelial cells; keratinocytes
Meloncytes, dendritic (Langerhans) cells, tactile (Merkel) cells; sensory receptors for touch
Keratinization
Keratin is water-insoluble proteins, helps keep water in the body
Keratinocytes filled with keratin; dead at surface
Dermis
Contains
Blood vessels
Skin appendages
Sensory receptors for pain, touch, temperature
Smooth and skeletal muscle cells
Two layers
Papillary layer (superficial): less cells, more matrix
Reticular layer (thicker and deeper): connective tissue
Papillary layers
Loosely and irregularly organized connective tissue
Fibroblasts, macrophages, plasma cells, mast cellss, endothelial cells, adipose cells
Reticular layer
Dense connective tissue
Dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ)
Barrier against passage of substances into and out of body
Framework to restore architecture of the tissue
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
Ground substance
Tissue growth and wound healing
Fibrous structural proteins: collagen and elastin
Adhesive glycoproteins
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Cell-matrix and cell-cell interaction
Integrins
Transmit information bidirectionally
Bind extracellular substances
Adhesion molecules
Cytokines and growth factors: allow healing of the skin
Acute wound
Wound occurs suddenly or over brief period
Restoration of structural and functional integrity in 4 to 6 weeks
Chronic wound
Occurs over long period
Does not heal in organized and timely manner
Impairment of structural and function integrity
Partial thickness wound
Damage extends through epidermis; dermis intact
Reepitheliaization: Epithelial cells migrate to area and replicate by mitosis
Full thickness wound
Damage extends through epidermis and dermis
Possibly extends into subcutaneous tissue, muscle, bone
Scar formation
Wound healing phases
Hemostasis
Inflammation
Proliferation/granulation
Remodeling/maturation
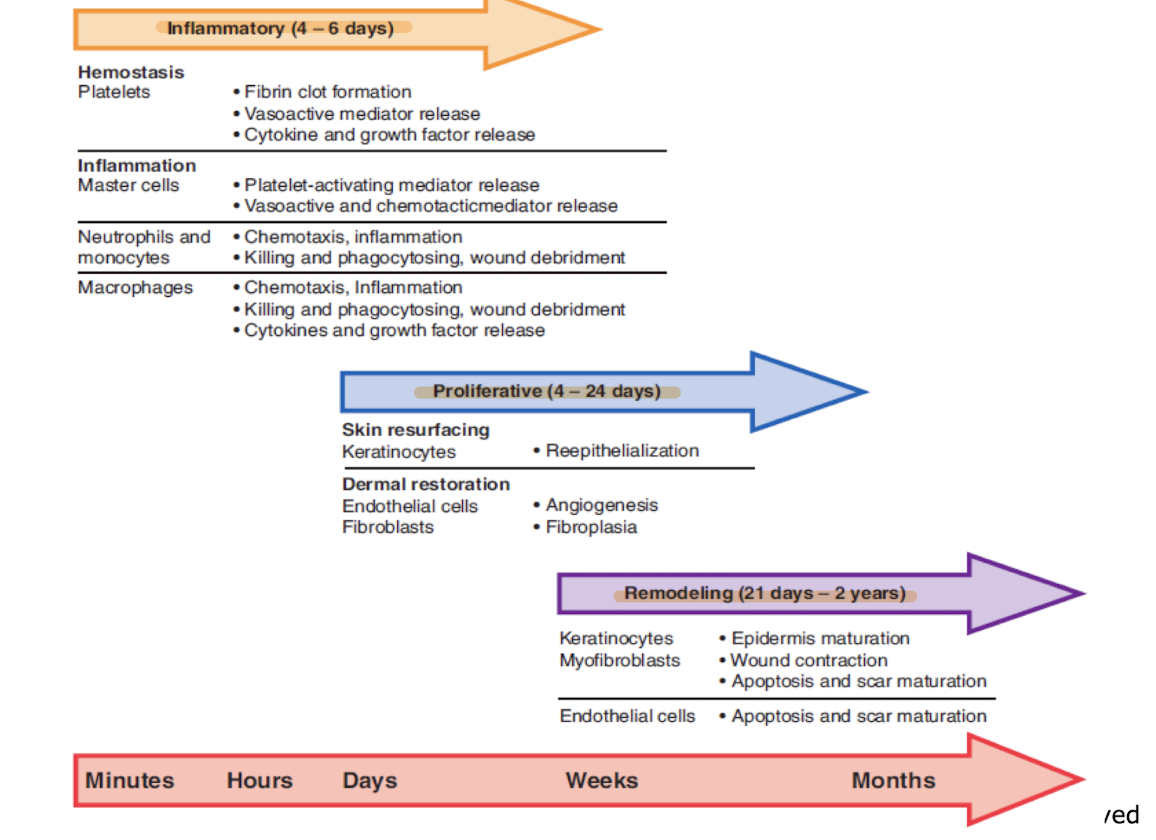
Chemical mediators
neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, platelets, keratinocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells
Growth factor
Stimulate growth, division, differentiation of other cells
Regulate intercellular communication
Cytokines
Initiate healing process
Produce growth factors and cytokines
Stimulate expression of growth factors
Develop the ECM
Coordinate intercellular communication
Nitric oxide
Direct effect: bacterial killing
Indirect effect: modulate cytokine and growth factor activity
Types of Wound Healing
Depends on:
Type of injury
Extent of tissue loss
Infection, necrotic tissue, or secondary tissue breakdown
Type of cells involved
Primary intention (primary closure)
Surgical closure of wound
Repair: formation of new ECM
Regeneration: reepithelialization
Little granulation tissue: small scar formation
Secondary intention (secondary or spontaneous closure)
Full thickness wound heals without closure attempt
Large amount of granulation tissue
Longer healing time; larger scar
Skin grafting; skin substitutes
Tertiary intention (delayed primary closure)
Combination of primary and secondary intention
Contaminated wound cleaned, left open drainage
Scarring> primary intention and < secondary intention
Hemostasis
Goals
Prevent additional tissue injury
Prepare wound for healing and regeneration
Phases
Platelet adhesion, platelet activation, platelet plus
Fibrin clot formation
Recruitment of phagocytic cells and wound debridement
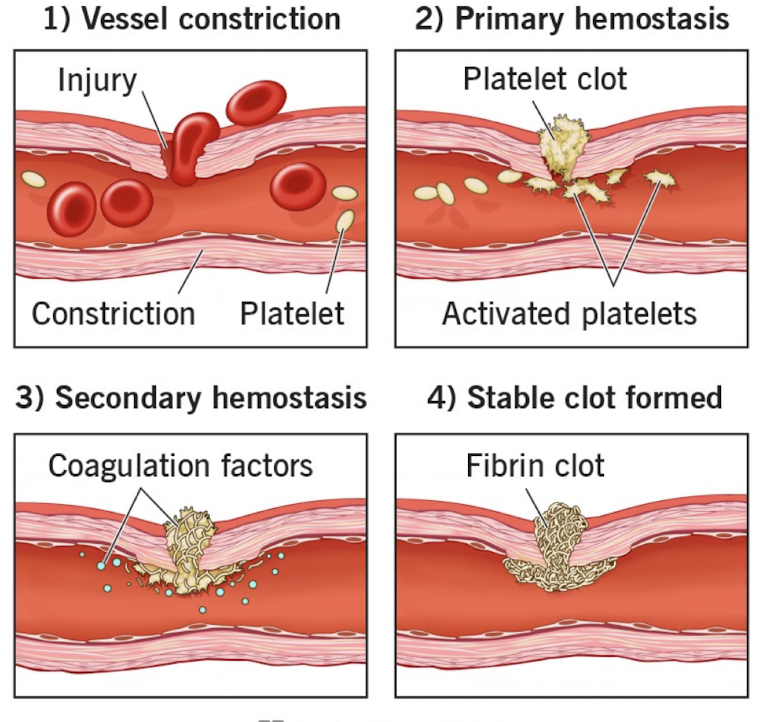
Inflammatory response
Goals
To clean the wound
Prevent additional tissue injury
Prepare wound for healing and regeneration
Recruitment of phagocytic cells and wound debridement
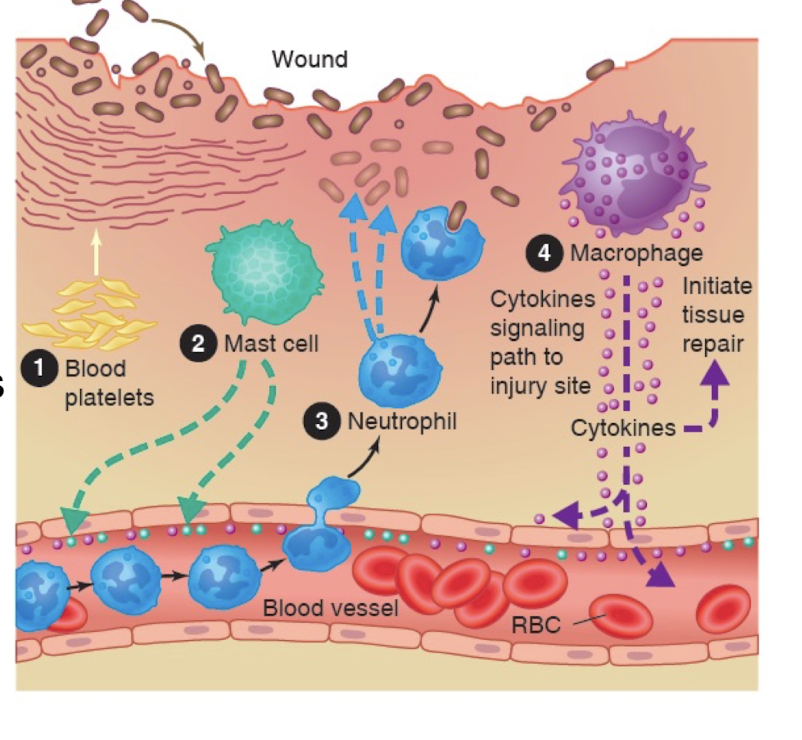
Proliferative Phase
Goal: wound healing guided toward tissue repair
Steps
Granulation tissue: foundation for collagen-based matrix that replaces fibrin-based provisional matrix
Fibroblasts: produce collagen, adhesive proteins for ECM
Myofibroblasts
Endothelial cells: angiogenesis (neovascularization)
Reepithelialization: regeneration of keratinocytes
Remodeling Phase
Restores structural and functional integrity of skin
Dermal matrix not regenerated; mended
Steps
Wound contraction and closure
Continuous turnover of collagen
Decreased capillary density
Declining cellular content
Mature scar tissue devoid of skin appendages
Maturation of scar tissue continues for minimum of one year
Factors that Impede Would Healing
Local
Blood flow and hypoxia
Infection and contamination
Movement/tension
Desiccation
Excessive edema
Denervation
Systemic
Advanced age
Malnutrtional status
Immune deficiency
Smoking
Medications
Metabolic status
Hypoxia
Tissue is not receiving enough oxygen
Delays or stops wound healing process
leading cause of wound infection
inhibits fibroblast activity
collagen deposition in matrix
Infection and Contamination
Badly contaminated wound may overwhelm host defenses
Surgical wound handling
Contamination: Necrotic tissue, foreign or exogenous material, endogenous substances
Nutritional Status
Major role in wound healing
Essential macronutrients: carbohydrates and fats
Effect of negative nitrogen balance
Impaired immune and inflammatory responses
Delayed wound healing; increased wound infection
Diminished angiogenesis
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies
Associated with chronic, non-healing wounds in nutritionally debilitated individuals
Medications
Corticosteroids
Promote breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, proteins
Anti-inflammatory action impedes inflammatory phase of wound healing
Various negative effects
Antineoplastic drugs
Potent immunosuppressants
Impair reepithelialization, granulation tissue formation, angiogenesis
Metabolic Status
Diabetes mellitus
Insufficient insulin, insulin resistance, or both
Hyperglycemia with untreated diabetes
Chronic macrovascular disease
Atherosclerosis; tissue ischemia and hypoxia
Thickening of basement membranes: diabetic lesions
With impaired perfusion
Impaired granulocyte function and chemotaxis
Reduced ability to fight infection
Sensory neuropathy
Reduces pain sensation associated with wounds
Abnormal Wound Healing: Excessive
Abnormally high connective tissue deposition resulting in altered tissue structure and function
Fibrosis
Replacement of normal tissue excessive with nonfunctional collagen or scar tissue
Excess synthesis and/or delayed degradation
Keloids
Lesions of dermal scar or fibrotic tissue
Hypertrophic scars
Excess fibrotic tissue
Raised above level of surrounding skin
Grow within boundaries of original injury; regress spontaneously
Contractures
Abnormal exaggeration of wound contraction
Shrinking scars severely deform wound; reduce mobility
Compromise mobility of involved joints
Abnormal Wound Healing: Deficient
Insufficient deposition of dermal connective tissue matrix weakens tissue to wound failure
Wound dehiscence
Extrafascial: partial or complete separation of outer layers of sutured wound; underlying fascial layer remains intact
Fascial: evisceration; separation of fascial layers
Clinical manifestations of impending wound disruption
Signs of infection
Absence of healing ridge by 5th to 9th postoperative day
Seroma or hematoma formation
Increase in serous discharge
Chronic nonhealing wounds
Do not proceed through healing process
Progress through healing process but cannot maintain structural and functional integrity
Arrest in inflammatory phase
Harbor bacteria; imbalance between neutrophilic proteolytic enzymes and their inhibitors
Increased levels of inflammatory mediators; chronic inflammation, necrosis, fibrosis