Geosystems: Ch 2~ Earth's Atmosphere
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What does the Earth’s Atmosphere do?
Contains gases to sustain life, helps with biological processes, blocks UV radiation, moderates climate, and redistributes water
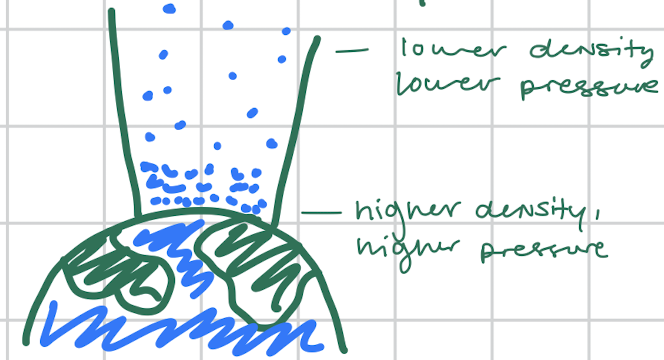
What does gravity do density and pressure?
It makes them decrease when distance or altitude is increased
What is the heterosphere?
Highest in atmosphere and it contains a top (H2, He2) and bottom (N2, O2) layer
What is the homosphere?
It is uniformly mixed gases, except for Ozone (O3) and contains the “Ozone Layer”
What are the three highest gases of the homosphere?
Nitrogen (N2) 78%, Oxygen (o2) 20%, and Argon (Ar) 9%
What are the top two variable gases that affect Earth’s temperature?
Water Vapor (H2O) and Carbon Dioxide
Where does water vapor (H2O) come from?
Evaporation, photosynthesis, and volcanic eruptions
Where does carbon dioxide (CO2) come from?
Fossil fuel combustion, volcanic eruptions, and plant repiration
What is the outermost layer of the atmosphere?
Exosphere
What is the hottest layer of the atmosphere?
Thermosphere
What is the middle layer of the atmosphere?
Mesosphere
Which layer of the atmosphere is the “ozone” layer?
Stratosphere
Which layer of the atmosphere is where weather occurs?
Troposphere
What does the Ionosphere do>
It absorbs cosmic rays, Gamma rays, X-rays, and some UV rays
What does the Ozonesphere do?
It absorbs UV rays
When was the ozone depletion first identified?
In antartica in 1985
When is the ozone most depleted throughout the year?
September - November
What caused the ozone depletion?
Humans produced bromine and chlorine containing chemicals
What are CFCs or chorofourocarbons?
Used in cooling systems, blowing agents, or medicinal applications
EX: Freon
What are some effects of ozone depletion?
Higher UV radiation which causes eye cataracts, skin cancer, and weakened immunity and it may cause damage and disruption to ecosystems, crops, and forests
What was the Montreal Protocol of 1987?
Called for a reduce of CFC’s and started the use of HCFC’s
What is air pollution?
When substances are added to the atmosphere in enough concentrations to be harmful
What are some examples of natural air pollution?
Wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and soil
What are some examples of human air pollution?
Transportation 57%, fuel combustion 21%, industrial processes 12%, miscellaneous 10%
What is a primary air pollutant?
Harmful substance that is emitted directly into the atmosphere; no change
Ex: CO2 and NO2
What is a secondary air pollutant?
Formed in the atmosphere when a primary air pollutant reacts with substances normally found within the atmosphere; change
EX: Sulfuric acid, Nitric Acid, Nitric Oxide, and Ozone
What are photochemical reactions?
Produced chemicals through the aid of sun rays/UV
What is tropospheric ozone?
A man-made pollutant in the lower atmosphere; photochemical smog
Causes lung irritation, asthma issues, and respiratory illnesses
What is stratospheric ozone?
Essential component that helps screen out UV rays; however mad-made pollutants damage it
What was the Clean Air Act of 1970 and what did it do?
Created EPA and set limits on amount of specific air pollutants permitted
Ex: Lead, particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, and ozone
What is a pH scale?
Detects when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide reacting with water vapor in atmosphere create acids