CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 13: Excretion
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
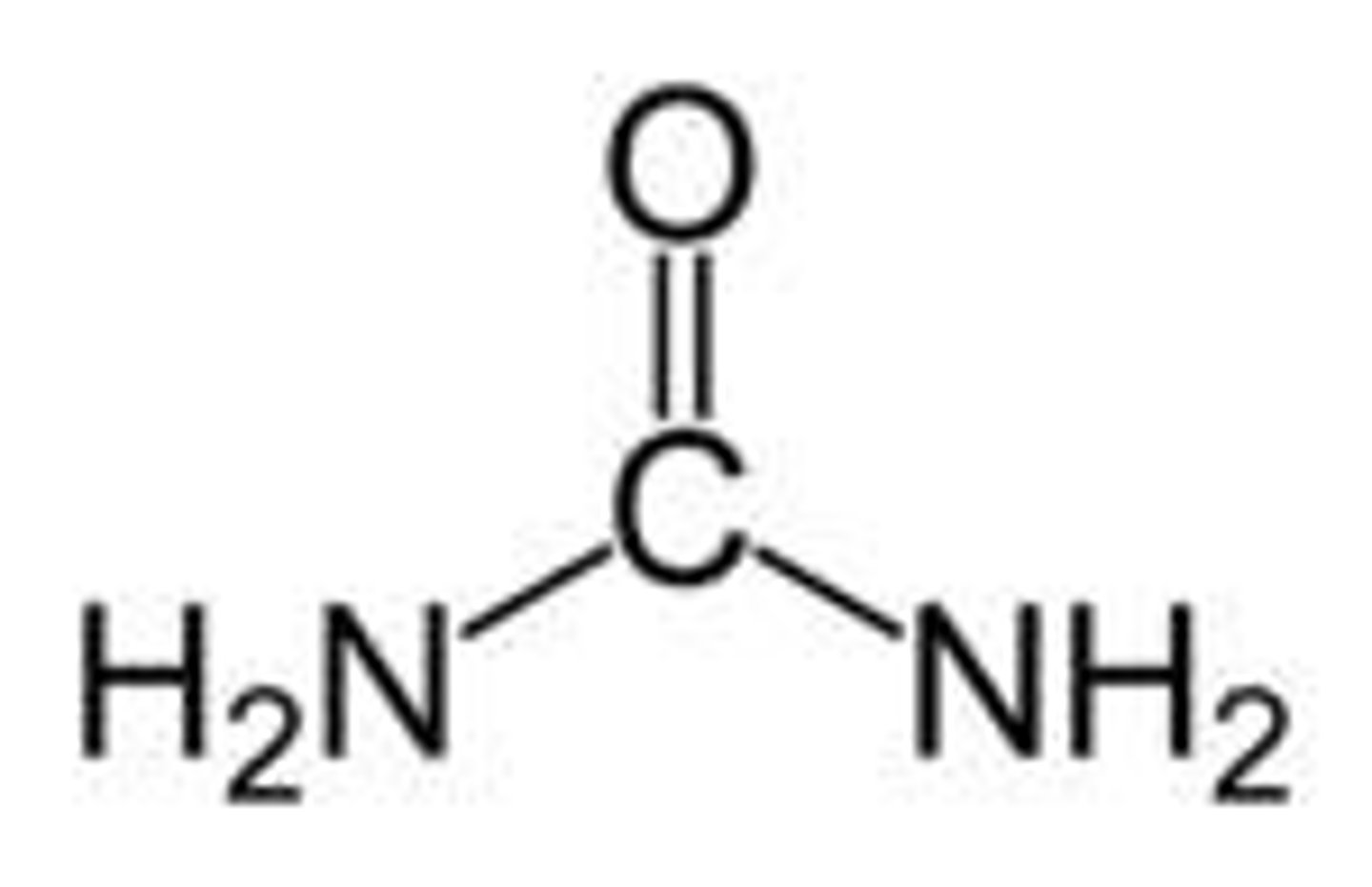
urea
formed in the liver from excess amino acids( deamination )
carbon dioxide
excreted through the lungs
role of the liver in the assimilation of amino acids
converting them to proteins, including plasma proteins, e.g. fibrinogen
deamination
the removal of the nitrogen-containing part of amino acids to form urea
kidneys
excrete urea and excess water and salts
volume and concentration of urine
affected by water intake, temperature and exercise
structure of kidney
cortex: brown outer layer
medulla: reddish inner area
pelvis: white area

Function of glomerulus
Filtration from the blood of excess water, glucose, urea and salts.
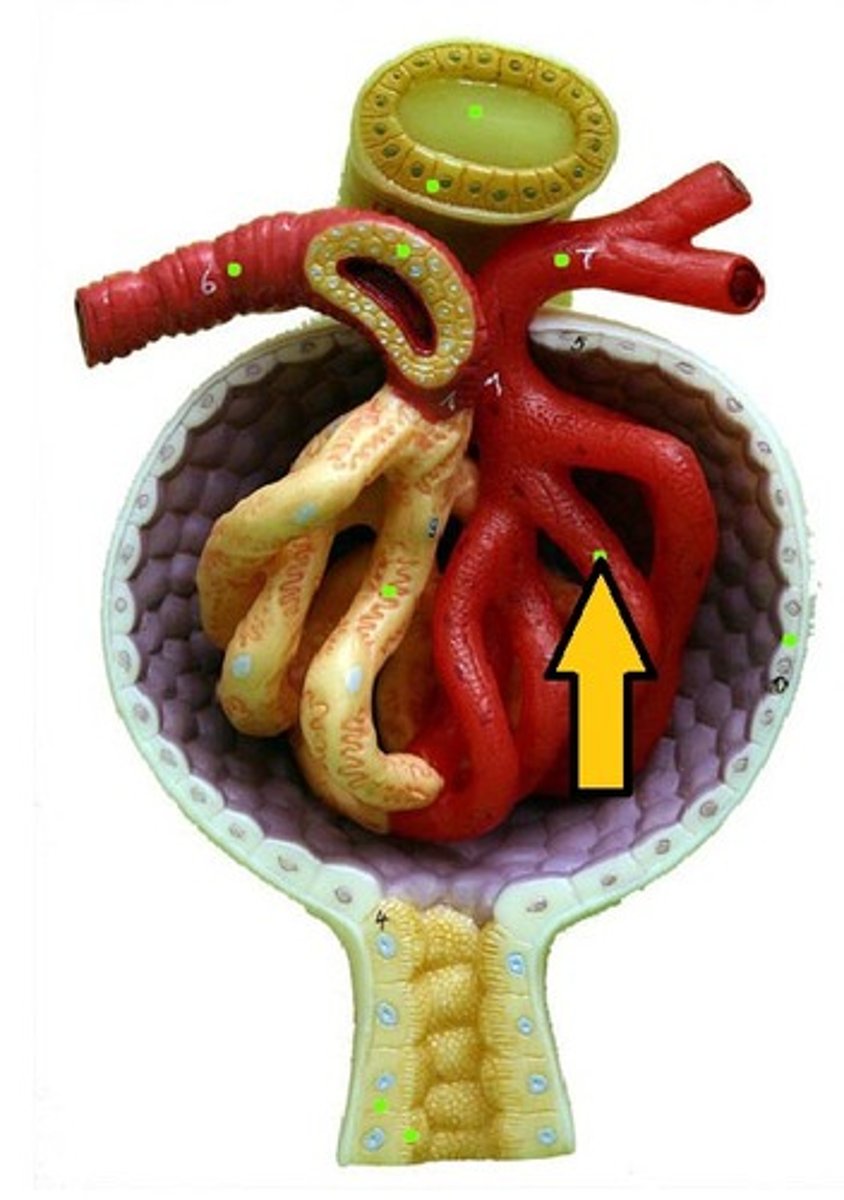
Ultrafiltration
The process where small molecules are forced from the blood out of the capillaries of the glomerulus, under high pressure, into the Bowman's capsule.
Function of kidney tubule
The reabsorption of all of the glucose, most of the water and some salts back into the blood, leading to the concentration of urea in the urine as well as loss of excess water and salts
ureters
transport urine from the kidney to the bladder where it is stored
bladder
stores urine before passing out through the urethra
urethra
allows urine to leave body, excretion
Kidney failure
when kidneys can no longer cleanse the blood and maintain homeostasis
the need for excretion
toxicity of urea and carbon dioxide
dialysis
a procedure to remove waste products from the blood of patients whose kidneys no longer function
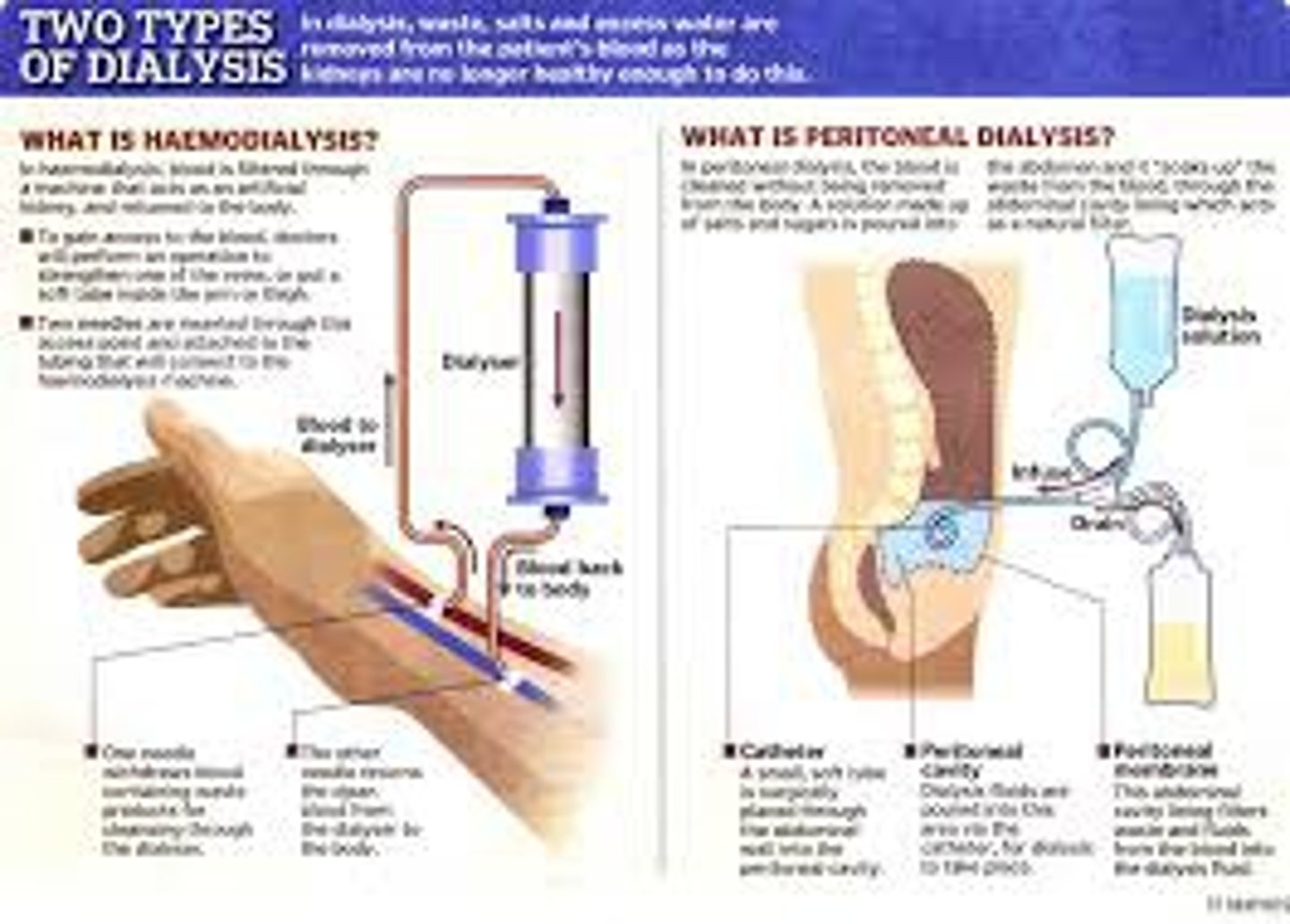
The use of dialysis in kidney machines
to remove toxins, excess amino acids and mineral salts
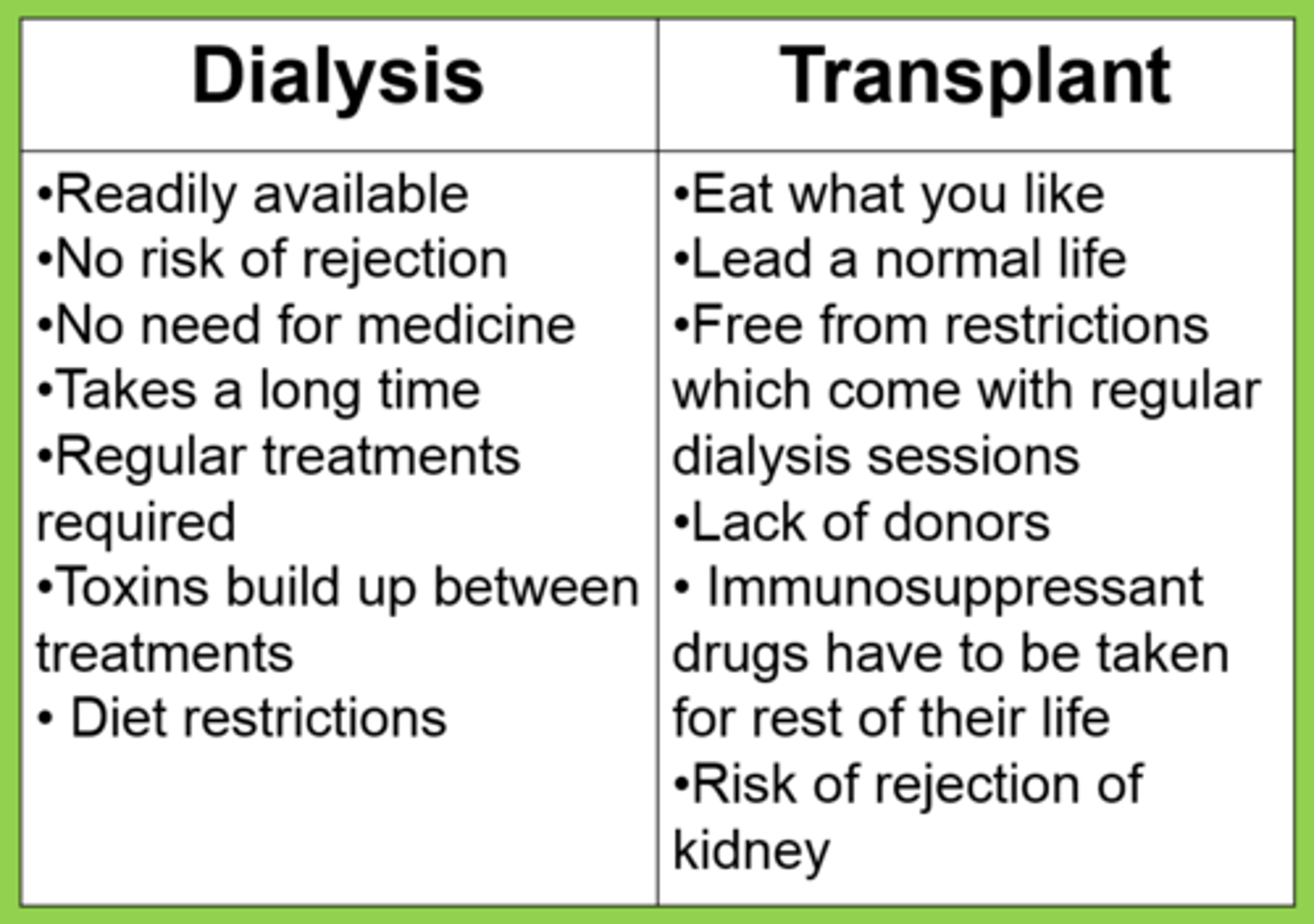
The advantages and disadvantages of kidney transplants, compared with dialysis
Advantage: do not need dialysis treatment after kidney transplant
Disadvantage: chance of rejection from body