3. Structure and Functions of Immune System - Primary Lymphoid Organs
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the primary/central lymphoid organs? What do they serve as?
Thymus and bone marrow
Lymphocyte educational centers
Although all lymphocytes originate within the ____ ______, some are sent to the ______ for _____________ and __________ of T-lymphocytes. Other lymphocytic lineages are “home-schooled” and remain within the ____ ______ to become B-lymphocytes.
bone marrow
thymus
proliferation
maturation
bone marrow
______ cells within the thymus and bone marrow closely ________ the development of T and B cells.
Stromal cells
regulate
How many lobes does the thymus have?
2 (bilobed)

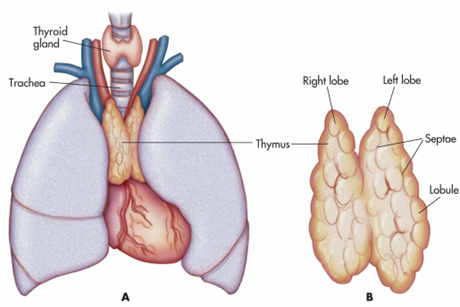
Where does the thymus anlage (foundation) develop from? What week of gestation does it develop?
Develops from the epithelium of the 3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouches
6th week of gestation
Describe how mesenchymal stem cells differentiate in the thymus.
By 8th week of gestation, mesenchymal stem cells (precursors of lymphocytes) from the yolk sac, fetal liver, and bone marrow, reach the thymus and differentiate into the thymic lymphoid cells (thymocytes)
The thymus is the first organ in all animal species to become predominantly ________.
lymphoid
When does the thymus increase in size in humans?
During fetal and neonatal life, and progressively involutes (returns to normal size) following puberty
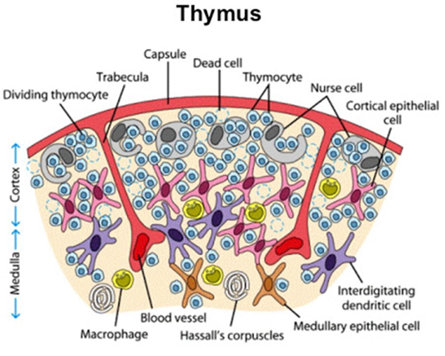
Describe the structure of the lobes of the thymus.
Thymus surrounded by a fibrous capsule
Septa arising from the capsule divide the thymus into 2 lobes
Each lobule is differentiated into an outer cortex and inner medulla
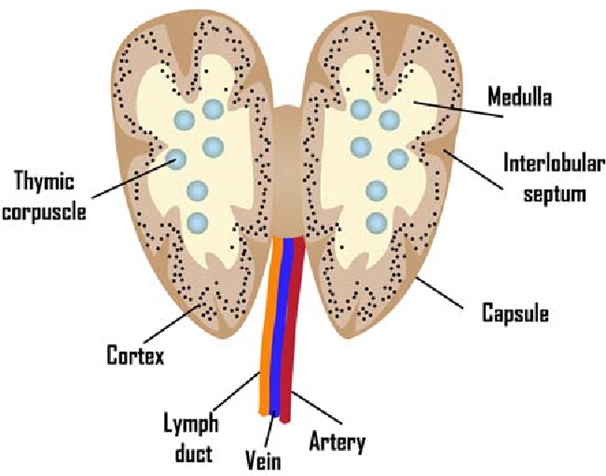
Describe the cortex of the thymus.
Densely populated
Contains thymocytes (lymphocytes of thymus)
Immature and many in number
Contains cortical epithelial cells and nurse cells
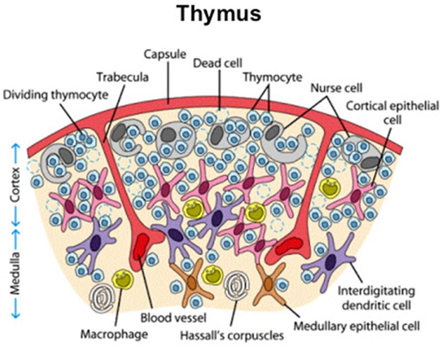
Describe the medulla of the thymus.
Sparsely populated
Contains thymocytes
Medullary thymocytes are relatively more mature and fewer in number
Contains medullary epithelial cells, interdigitating dendritic cells, and Hassall’s corpuscles
Several thymic hormones are produced from the epithelial cells of the thymus. List some hormones.
Thymulin
Thymopoietin
Thymosin
What is the role of thymic hormones?
Believed to attract precursor T cells (progenitor T cells) from bone marrow
The interaction between __________ and ______ _______ cells (epithelial cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages) and the effect of thymic hormones, help in the __________ of T cells in the thymus.
thymocytes
thymic stromal cells
maturation
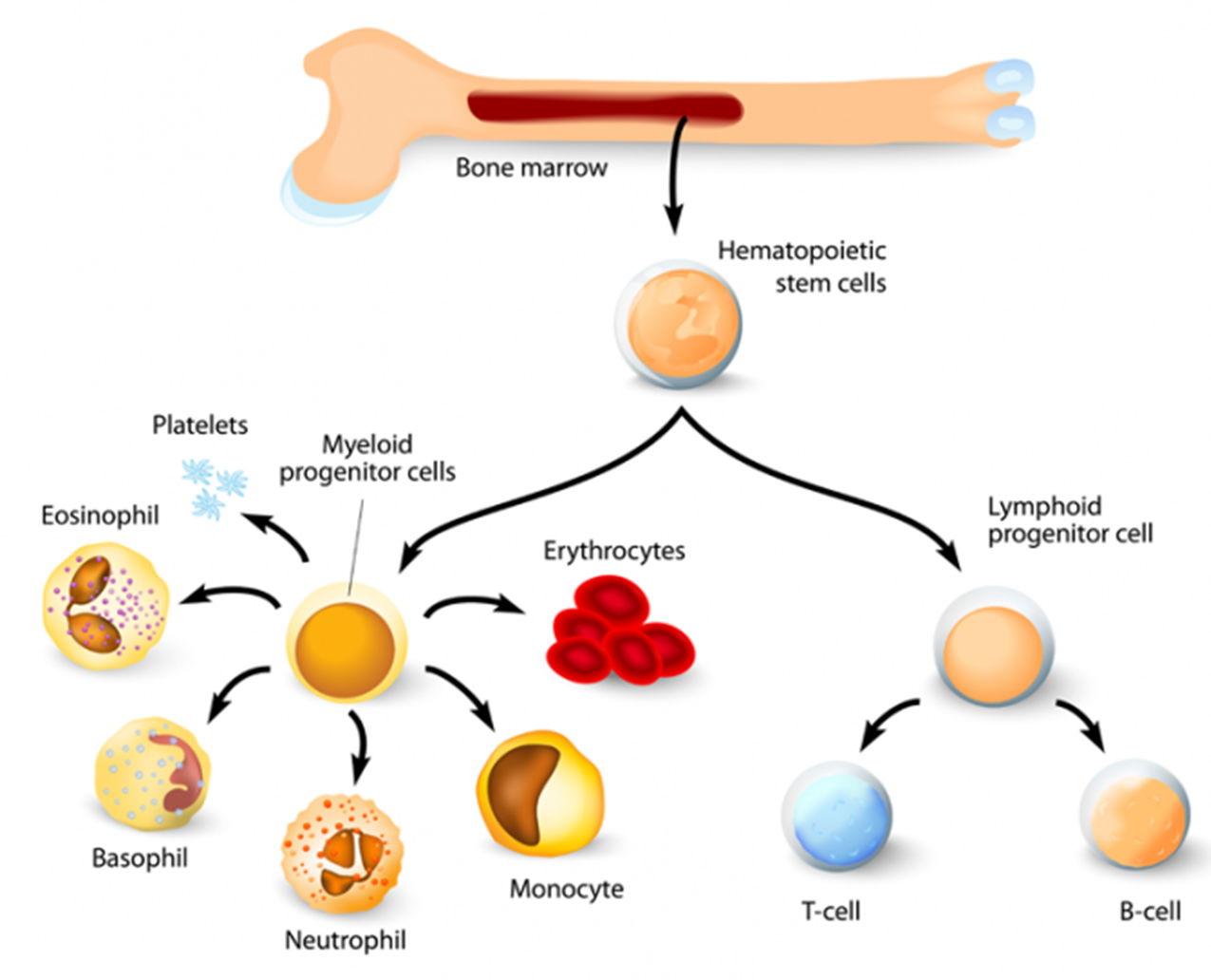
Almost all the cells in blood have originated from ___________ hematopoietic stem cells of bone marrow; the process is known as _____________.
pluripotent
hematopoiesis
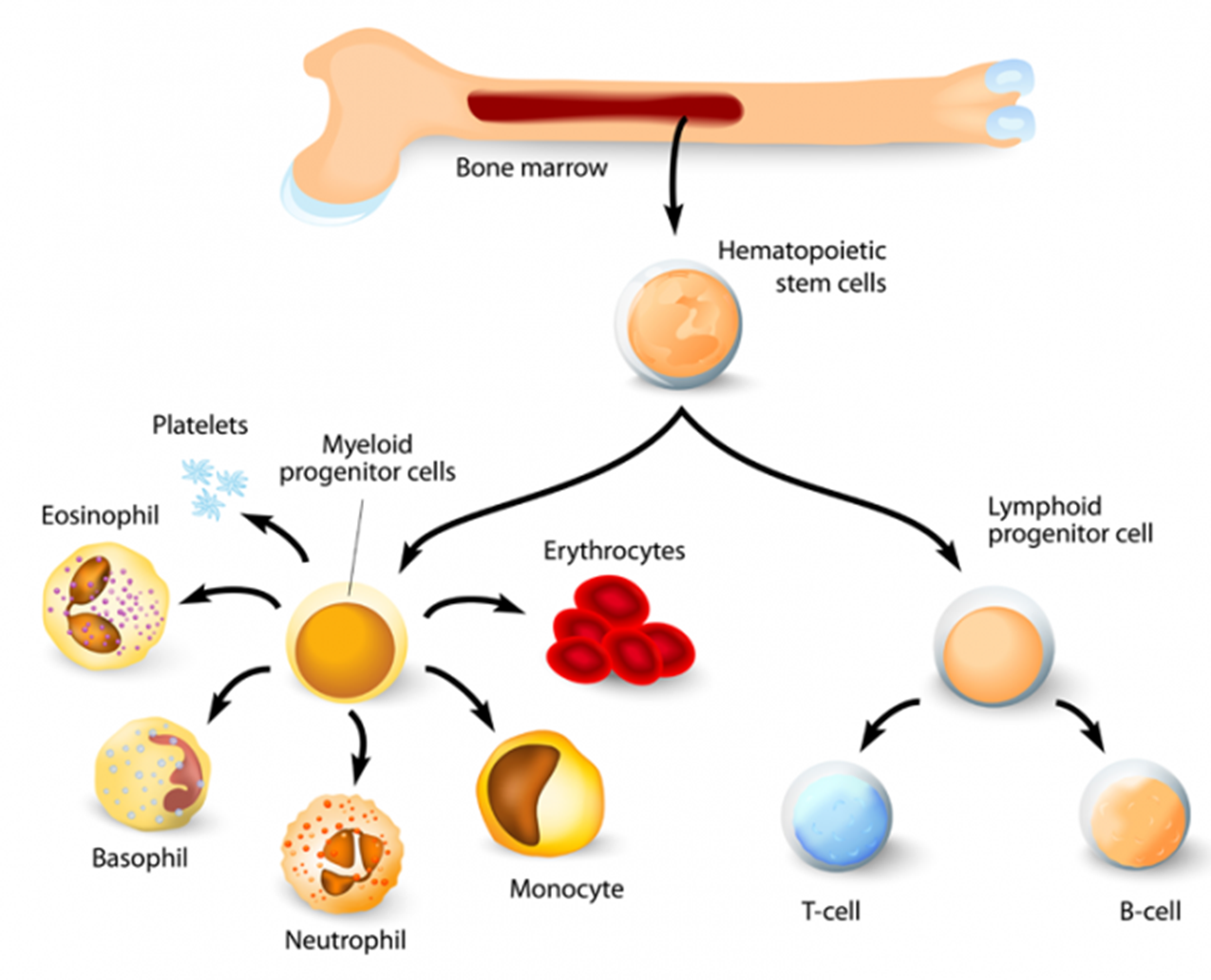
Where does hematopoiesis occur in early fetal life?
Liver (gradually stem cells migrate to bone marrow)
By birth, stem cells occupy most of the bone marrow space of _____ bones.
large
As an individual ages, hematopoietic activity in large bones will be __________.
decreased
Where does hematopoiesis occur after puberty?
Mostly confined to axial bones (pelvis, vertebrae, sternum, skull, ribs)
The __________ T and B cells originate in bone marrow. Lymphocytic lineage cells fated to become immunoglobulin-producing lymphocytes (progenitor B cells), undergo their early stages of ________________ within the bone marrow, whereas progenitor T cells migrate to ______ for further ______________.
progenitor
differentiation
thymus
proliferation