Extracellular Matrix and Cell-Cell Junctions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
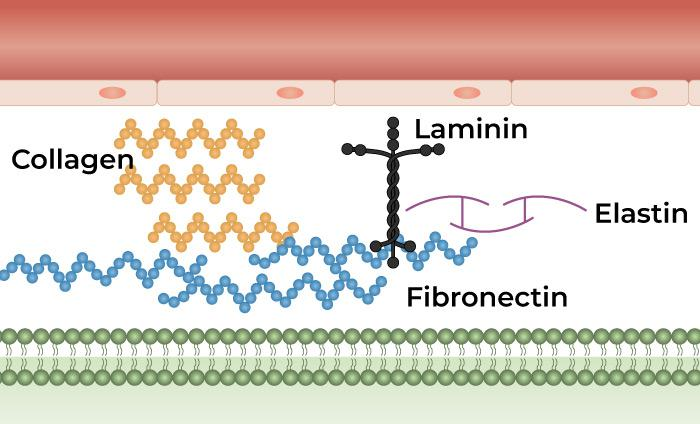
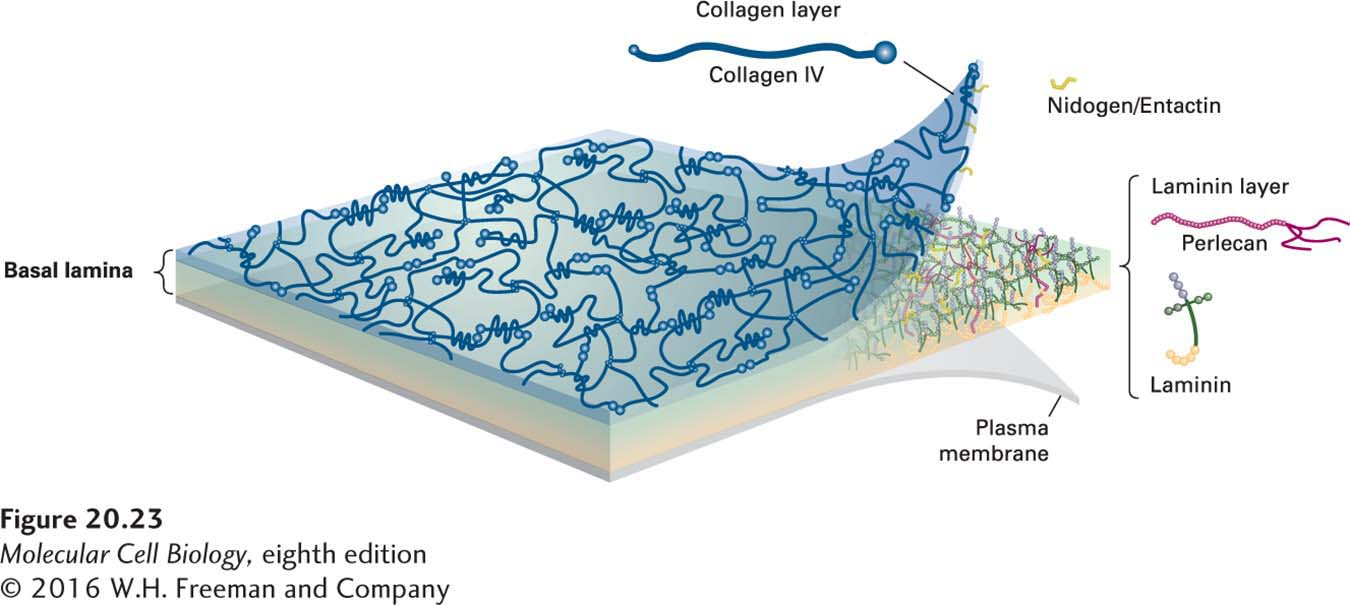
Basal Lamina/ Basement Membrane
Layer 40 nm to 120 nm thick composed of laminin and type IV collagen that is tethered to the ECM by lamina and type VII collagen fibrils. Serves as a scaffold for regrowth following injury.
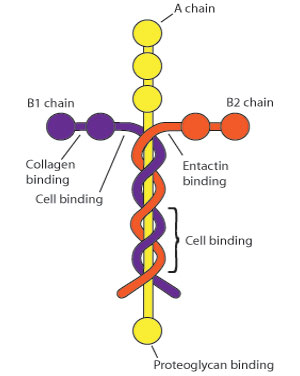
Laminin
Extracellular component that composes the basal lamina.
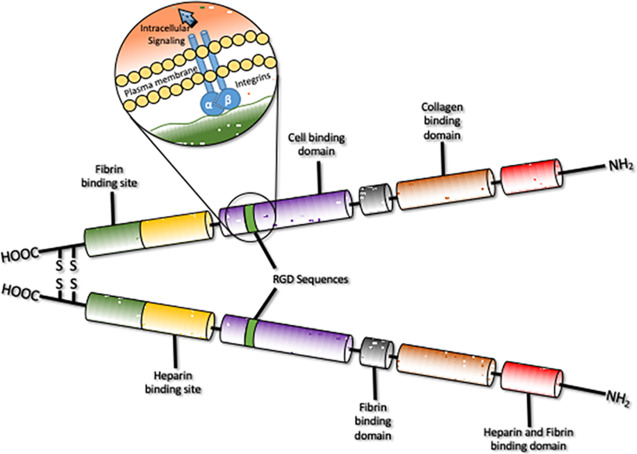
Fibronectin
A dimer that is held together by disulfide bonds at one end that bind to integrins on the cell surface. Each arm has functionally distinct domains linked with flexible polypeptide chains.
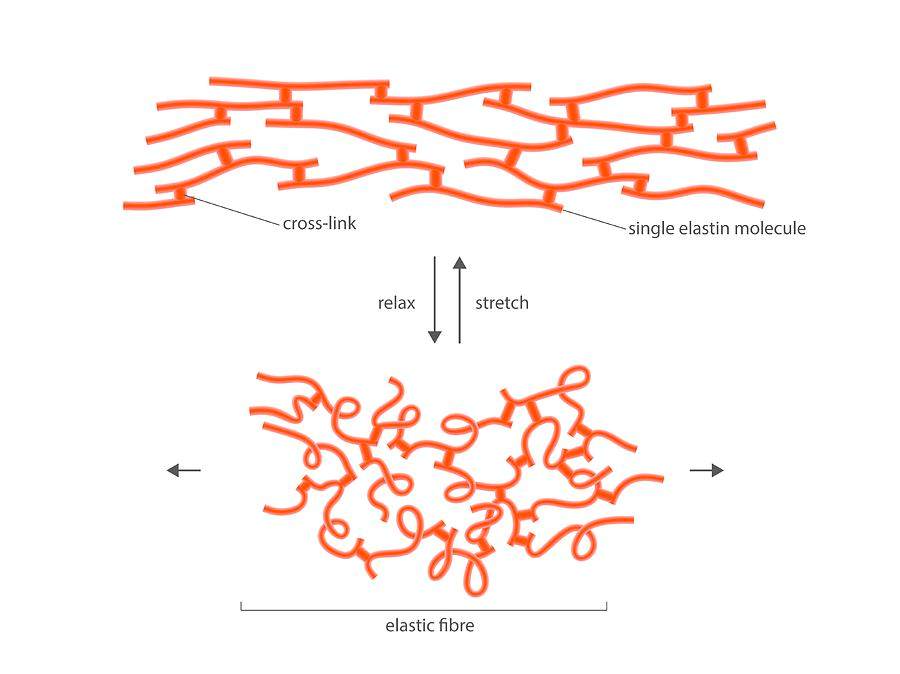
Elastin
A hydrophobic protein that has proline and glycine. Protein is made in ER and secreted in the ECM as tropoelastin and then cross-linked.
Collagen
Most abundant protein in mammals with 20 types. Provides tensile strength to tissues.
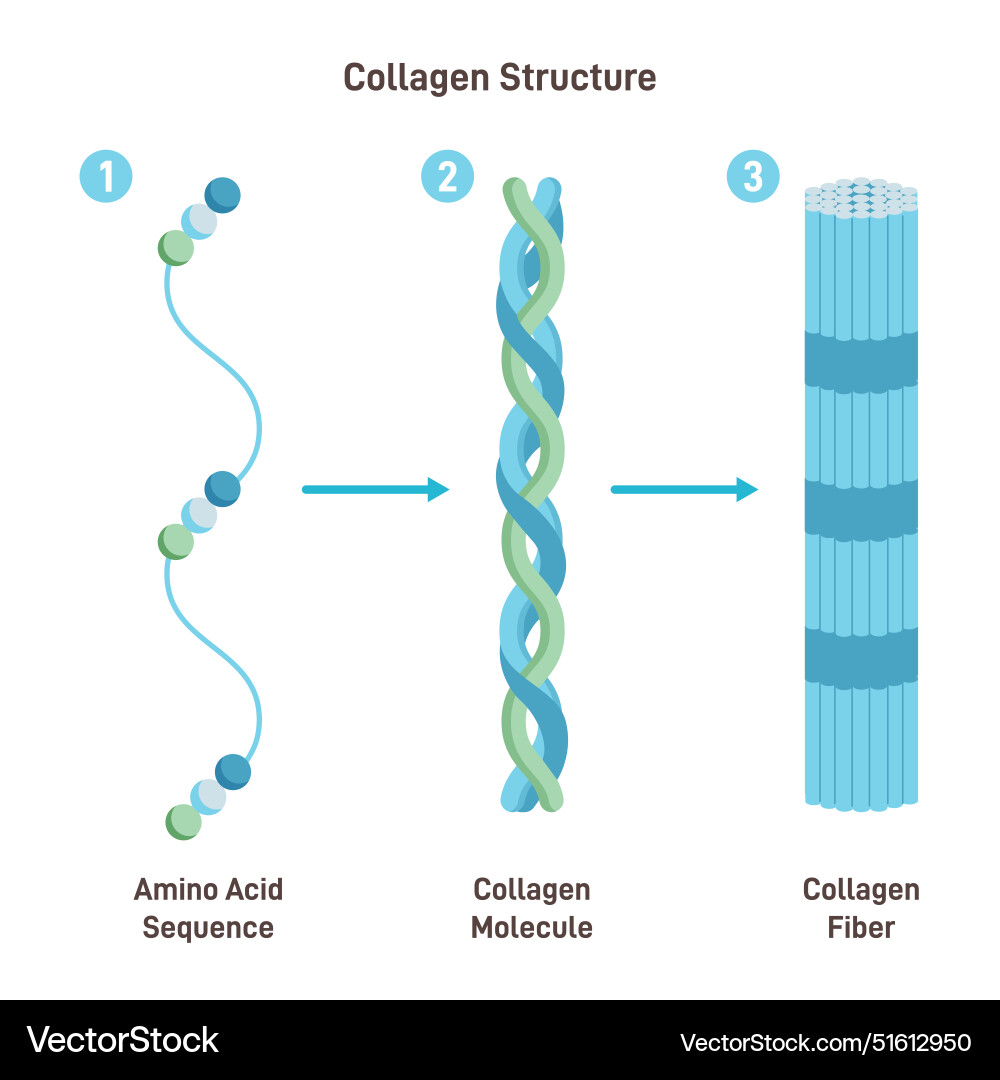
Pro-alpha chain
Component that composes Collagen that are produced by ribosomes. Undergoes hydroxylation and glycosylation and cross-linked with 2 other chains by hydroxyprolines and hydroxylysines. Secreted out of the cell as fibrils (0.5 um) or fibers (300 um)
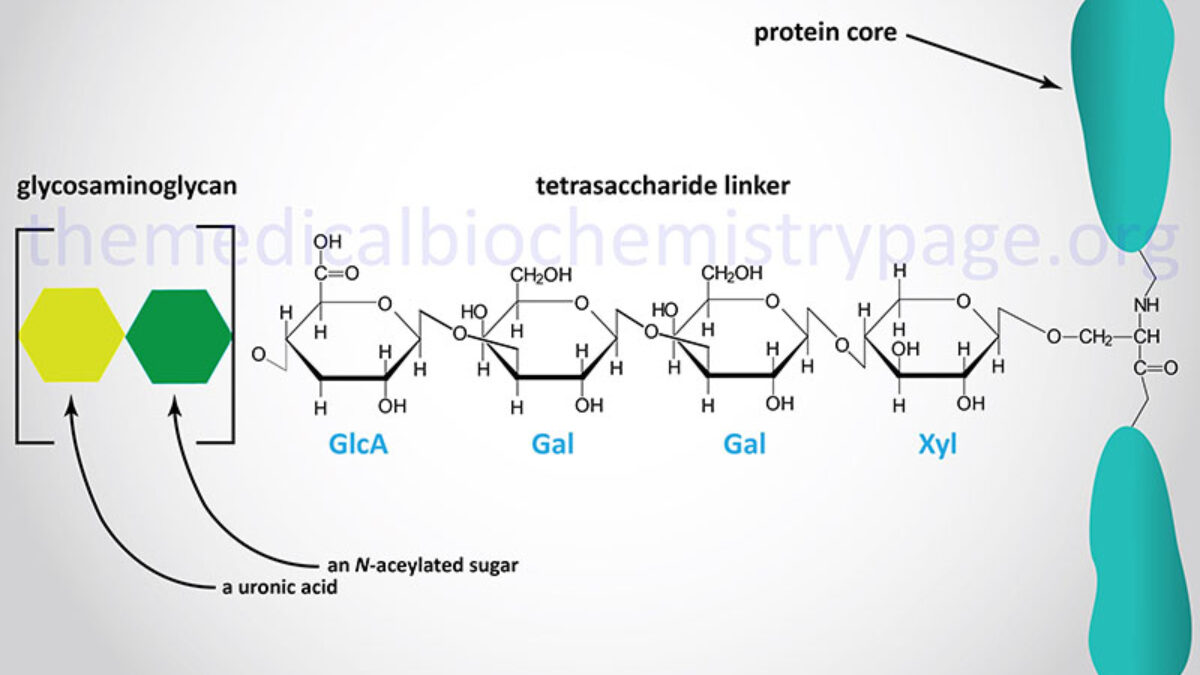
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Macromolecule of the extracellular matrix. Resist pressure and provides tensile strength and makes hydrogel.
Proteoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans that are linked to proteins. Gel formed acts as a sieve and influences what makes it to the apical and basal surface. Plays role in cell signaling and binds to enzymes or proteins.
Hyaluronan
GAG not linked to core protein and found in all tissues and fluids of adults. It is produced at the cell surface by an enzyme complex in the cell membrane. Also serves as space filler during embryonic development.
Chondroitin, Heparan, and Keratin Sulfate
GAGs made in the ER and polysaccharides are added by the Golgi Apparatus. Up to 95% carbohydrate by weight and function is determined by core protein and GAG chains.
Fibroblasts
Cells that secrete the majority of the ECM molecules/proteins.
Cell Junction
Either Cell-Cell or Cell-Matrix contact. Three types: occluding, anchoring, and communicating junction.
Occluding Junctions
Prevents molecules from moving from apical to intracellular space. Includes the tight junction.
Anchoring Junction
Provides mechanical attachments. Includes Adherens junction, desmosomes, focal adhesions, and hemidesmosomes
Communicating Junction
Junction that allows for chemical and electrical signals to move between cells. Includes the Gap Junction.
Tight Junction
Type of Occluding Junction that prevents liquids from escaping between cells. Composed of the proteins claudins, occludins, and ZO proteins that are attached to actin.
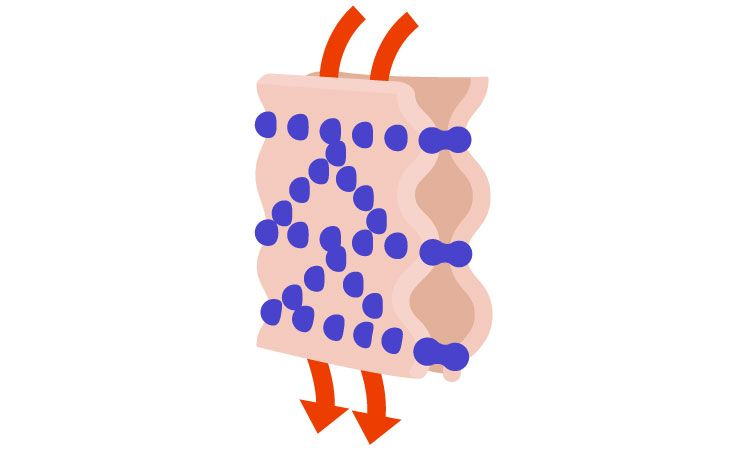
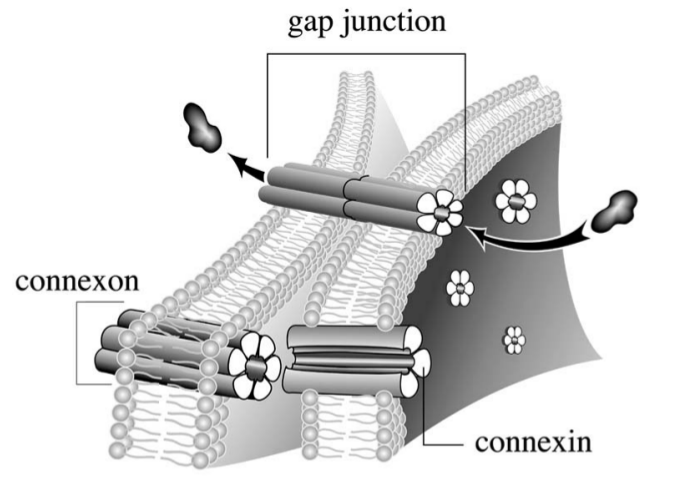
Gap Junction
Type of communicating junction that allows for transport of ions, water, and other substances between cells. Composed of 6 connexin proteins that form connexons.
Adherens Junction
Type of anchoring junction that attaches to cell to cell. Composed of the proteins Cadherins and vinculin and alpha-actinin that are are attached to actin.
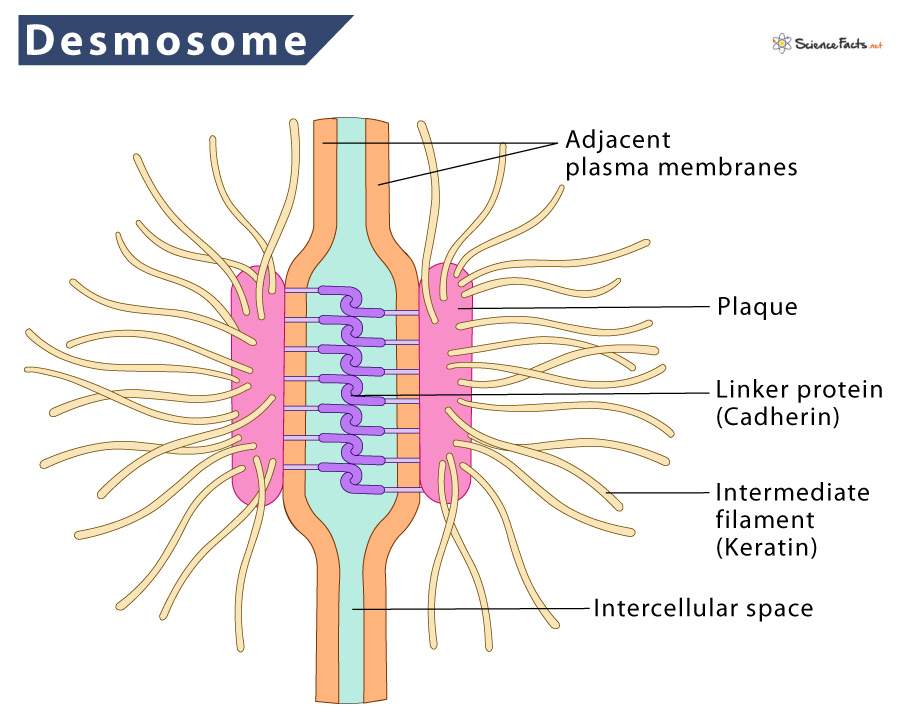
Desmosomes
Type of anchoring junction that attaches to cell to cell. Composed of the proteins cadherins and desmoplakin or plakoglobin that are either attached to the intermediate filaments keratin (in skin) or desmin (in the heart)
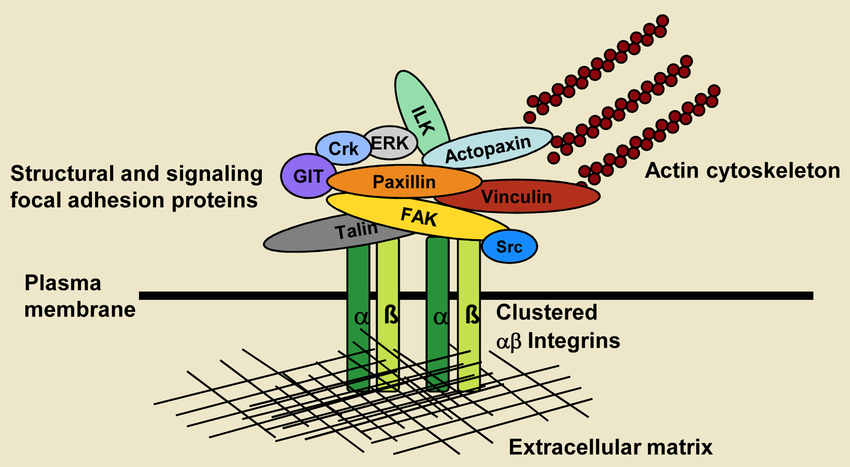
Focal Adhesions
Type of anchoring junction that hold cells to the extracellular matrix. Composed of the proteins vinculin, talin, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and integrins that are attached to actin and laminin or fibronectin.
Hemidesmosomes
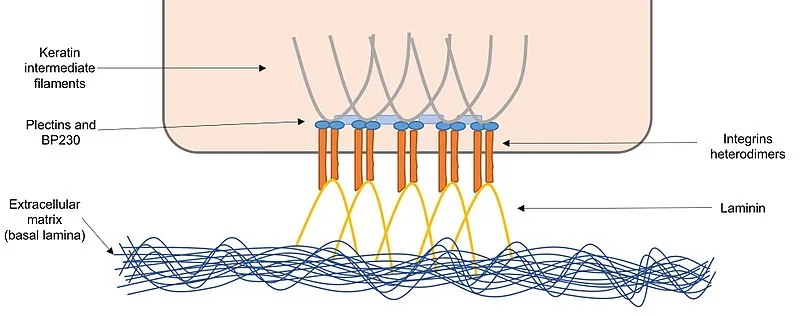
Type of anchoring junction that hold cells to the extracellular matrix. Composed of the proteins plectin and (beta and alpha) integrins that are attached to the intermediate filaments keratin and laminin.
Extracellular Matrix
The connective structure beneath and in between cells that they build. Unique to each tissue type.