Developmental Psych Exam 2
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Social Reflexes
How infants are prepared for social exchanges
Signaling needs
Tracking cause in effect (when I cry, does someone help?)
Attracted to social stimuli
Synchronized with caregiver’s behavior (serve and return)
Social Smiling
Baby smiles on reflex
Caregiver assigns meaning to it
Baby recognizes that smiling is a good thing to the caregiver, and it becomes intentional around two months
Temperament
An individual infant’s general style of behavior across contexts.
How much stimuli can you take before getting overwhelmed?
High Temperament
More reactive to stimuli
Low temperament
Less reactive to stimuli
Differential susceptibility/Biological sensitivity to context
Stress reactivity up-regluates under high stress with little support, OR in high support with little stress
In a middle ground, it down-regulates
Both genes and the environment interact to determine this
Make sure we aren’t super reactive in an environment where we don’t need to be, or are super reactive when that’s to our advantage
Harlow’s Monkey Research
Freud thought infants only engage with their caregivers for drive reduction
However, Harlow showed that even though the wire mom provided food, they found comfort in the cloth mom, showing that they loved them.
Infant contribution to attachment
Singals (crying, smiling, reactions)
Proximity seeking (reaching, facing toward caregiver)
Secure base exploration (Exploring new environments close to caregiver, showing them their new experience)
Caregiver Contribution to attachment
Sensitive care
Attunement
Sensitivity
Caregiving style that responds and attends to infant's needs promptly and effectively
Attunement
Caregivers adjust stimulation in response to signs from the infant
What kind of support does the child need?
Recognizing when the child is about to get dysregulated before it starts
The Strange Situation Procedure
Series of separations and reunions between caregiver and child
Measures quality of:
Child’s play and exploration
Child’s distress behaviors
Caregiver’s soothing (sensitivity and attunement)
Reunion behaviors
Secure Attachment
Infant is confident that CG will be available and responses
CG is base for exploration
CG is sensitive and attuned
Anxious-Resistant Attachment
Infant separates reluctantly but shows ambivalence afterward
CG is inconstant, soothing is sometimes ineffective
Infant tries to figure out how to get CG to respond, usually by crying louder
Anxious-Avoidant Attachment
Infant reaily separates, and avoids contact afterwards
CG is indifferent, emotionally unavailable, or harsh
Infant learned not to show emotion if they want to be close
Romantic Relationship: Anxious
Fears of rejection and abandonment
Hypervigilant of low partner support
Needs reassurance, care, and availability
Romantic Relationship: Avoidant
Fears of vulnerability and dependence
Hypervigilant of emotional demands and lack of autonomy
Need space, low stakes, low drama
Preoperational Period Limitations
Unable to use logical operations
Appearance Reality Distinction
Centration
Attention and Memory
Appearance Reality distinction
Defines reality on superficial terms
ex) it looks like that thing, so it is. Why would it be more complex? That’s not a spiderman costume, that IS spiderman.
Centration
Lack of ability to see things from multiple perspectives
Takes one piece of info into account at a time
Attention and memory
Info. processing problems
Small neurological bandwidth and attention span
Cant store a lot of things in long term memory or process quickly.
Conservation errors
Caused by preoperational period limitation
The same amount of water in two different containers, but they think it changed
When items are moved farther apart, there must be more of them
Splitting cracker in half makes two crackers, not two halves
Egocentrism
tendency to focus on own vs. others perspectives
Perceptual Egocentrism
Not differentiating own perceptual experience from someone else’s.
ex) everyone else has the same thoughts and sights that I have
Cognitive Egocentrism
Failing to take into account someone else’s cognitive perspective
ex) a kid getting a pony for their dads birthday because thats what they would want themselves
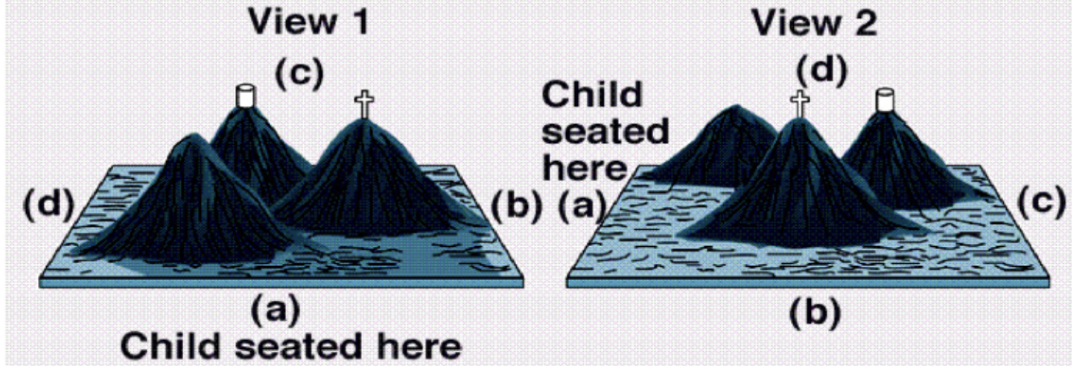
Three Mountain task
Can they tell if someone at a different point in the table sees a different view than what they see?
Used to test perceptual egocentrism
Theory of Mind
An understanding of the mind & mental operations.
Development of Self-constancy
A sense that the self endures despite temporary disruptions in relationships.
ex) I am myself. People can come and go, but I am the same person no matter where they are and what I do
Early Childhood
Gender Socialization
Parents, teachers, and peers supporting “gender-appropriate” play and disapprove of “gender-inappropriate” play
Behaviors such as gender related toy preferences and behavior are learned
Self regulation
I can manage and direct myself based on environmental and internal cues
ex) knowing when I can yell and scream, and when I can be quiet and calm
Effortful control
Ability to suppress strong impulses
Part of self regulation
Emotional Development (Early Childhood)
After realizing themselves in a social context, they can now feel the emotions of jealousy, pride, embarrassment, and shyness
They still have trouble telling others genuine vs false emotions (appearance-reality distinction)
Emotional Regulation
Promoted by
Brain
Cognitive
Social
Early childhood kids cant hide their own emotions
Middle Childhood Dev. Achievements
No more centration, egocentrism, or appearance-reality distinction
Theory of Mind -> Metacognition
Overcoming centration -> Classification
Memory advances
Metacognition
Thinking about thinking
Appears in middle childhood
Theory of mind makes it possible
Paves the way for new cognitive complexity
Understand:
Different viewpoints
Reality and appearance may differ
Different problem-solving and memory strategies
Metamemory
knowledge about memory and memory processes
How to remember
Your own strengths and weaknesses
Monitoring your memory performance
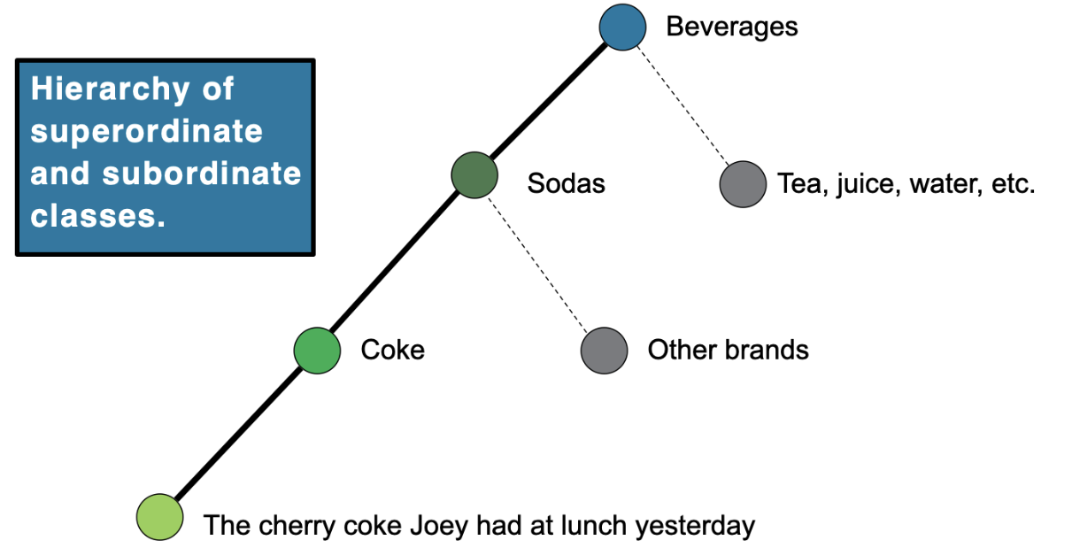
Hierarchical classification
Hierarchy of superordinate and subordinate classes.
Matrix Classification
Categorized simultaneously along two independent dimensions, such as shape and color.

Friendships
Reciprocal (both like each other)
Frequent interactions
Coordinated Behaviors (interdependence)
Peer Groups
A network of several kids
Clusters of friendships
They know each other and aren’t strangers, but not quite friends
Friendship Quality Predicts:
Quality of romantic relationships
Conflict resolution skills
Attachment behaviors with romantic partners
Peer Competence predicts:
Number of romantic relationships
Dating opportunities
Job competence (working in groups)
Sociometric
Measuring peer status
Accepted Children
Well-liked, accepted by peers
Rejected Children
Disliked; viewed as aggressive or mean
(Socially) Neglected Children
Overlooked; neither liked nor disliked
Controversial Children
Liked by peers; also viewed as anti-social or aggressive. Popular kids often fall into this.
Erikson’s theory of social development
Psychosocial crises drive developmental change
Industry vs. inferiority
Children gain skills that they work hard and try to get better at, that are valued by society
When encouraged, they develop ____
When they are discouraged and criticized, they struggle with _____