DMT W4 Preventive and Desensitizing Materials
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Define Fluorapatite
Tooth mineral that results when fluoride is incorpated into the tooth
Define Substantivity
Proper of a material that has prolonged therapeutic effect after its initial use.
What are the 4 main preventive measure for caries management?
Fluoride
ANtibacterial mouth rinse
Sealants
SIlver diamine fluoride
What is CAMBRA?
Caries Management by Risk Assessment → common practice in many dental offices; evidence-based approach to preventing and managing cavities at the earliest stages
OTC toothpaste with fluoride 2x daily is recommended for which level of risk based on CAMBRA?
Low Risk
OTC fluoridated toothpaste 2x daily
OTC fluoride rinse (0.05% NaF) daily
Xylitol candy/gum 4x daily
Is the recommended treatment for this level of risk based on CAMBRA?
Moderate Risk
What is CAMBRA’s alternate recommendation for Moderate risk?
Xylitol candies 4x daily with Rx 5000ppm fluoride toothpaste 2x daily (PreviDent5000)
What is the CAMBRA recommendation for individuals with High risk?
Xylitol candies or gum 4x daily
Rx 5000ppm fluoride toothpaste 2x daily
Chlorohexidine gluoconate (0.12%) rinse 1x daily for 1 week and then monthly until next oral evaluation for reassessment
Fluoride varnish applied at initial appt and then at each re-call
What is CAMBRA’s recommended treatment for Extreme risk individuals?
Xylitol candies/gum 4x daily
Rx 5000ppm fluoride toothpaste 2x daily
Chlorohexidine gluconate rinse (0.12%) 1x daily for 1 week and then monthly until next recall for reassessment
Fluoride varnish at initial appt and then at recall
Baking soda rinse 2tsp in 8oz of water 4-6x daily
Which statement is false about Fluoride?
Fluoride is a naturally occuring mineral
Fluoride occurs naturally in almost all foods and water supplies
Fluoride is safe and effective when used appropriately
Fluoride contributes to demineralization of the teeth making the teeth more resistant to acid attacks.
4 is FALSE - it contributes to RE-mineralization
What component of tooth crystals make them soluble in acid?
carbonate in tooth crystals
tooth crystals composed mainly of hydroxyapatite but not purely.
At 5.5 pH tooth mineral dissolves. What is the pH needed to dissolve tooth mineral converted to fluorapatite?
4.5 - Fluoride makes it more difficult for acids to demineralize tooth strucutre
What is the difference between the acid attacks on teeth from erosion versus fermemnted CHOs
Erostion acid attacks are not caused by bacteria, medical conditions or highly acidic food/drink cause erosion
Canned fish has high ____?
Fluoride

What are the 2 types of Fluoride?
Acidulated Phosphate fluoride (APF 1.23%)
Stannous fluoride (SNF2)
Sodium Fluoride (NaF 2%)
How much fluoride is given to a child/adult?
Child = 2ml per tray (total 4ml)
Adult = 2.5ml per tray (total 5ml)
Self adminstered fluoride is recommended for who?
clients who are moderate to high-risk for dental caries
Elderpatients on medications that cause xerostomia
Patients under active ortho treatment
In cases of acute fluoride poisoning, what can be done?
induce vomitting
protect the stomach using milk
maintain blood calcium by administering IV/orally (CaCl or Calcium gluconate)
What is the recommended daily intake for fluoride?
0.05-0.07mg per kg per day
5mg per kg of fluoride causes ?
Probably toxic dose
What is the certain lethal dose of fluoride?
32-64 mg per kg
Acceptable levels of fluoride in drinking water is ___
0.7mg/L or ppm
T or F - Prophylaxis paste containing fluoride (APF 1.23%) is an adequate replaecment for fluoride treatment
FALSE - it does not have ADA approval as an effective preventative against caries.
T or F Chlorhexidine rinses can be used occaisionally to prevent bacterial colony growth.
FALSE - it must be used consecutively for 2-weeks. After a 2 week treatment, the bacterial colonies will not regrow for 4-6 weeks
Why does Chlorohexidine rinse have the greatest substantivity?
It can be retained on oral structures and continue to be released over an extendedperiod of tiem without losing its potency and effectiveness
reduces plaque by 55% and gingivitis by 45%
What are some side effects of Chlorohexidine rinses?
allergy
staining teeth, restorations and tongue
increased supragingival calc due to increasing thickness of pellicle
lingering taste of the rinse may alter taste perception
not recommended for pregnant or nursing clients
What is the antibacterial component of Listerine?
Phenolic compound that alters the bacterial cell wall
reduces plaque scores by 25% and gingivitis by 50%
Where can you find pits and fissures?
occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth max and mand
buccal of mand molars
lingual of max molars
lingual of max incisors
What are some contraindications for sealants?
proximal caries present
carious pits and fissures
poorl oral hygiene, cariogenic diet
well fused enamel so that pits and fissures are shallow or non existent
bis-GMA (Bisphenol A-glycidyl methacrylate) is a monomer found in the resin component of ____?
Sealant
What contributes to an unsuccessful sealant? (3)
Inadequate isolation (rubber dam, cotton rolls)
Contamination by moisture, saliva, air/water syringe, patients breath
part of the fissure is left uncovered → repair is recommended
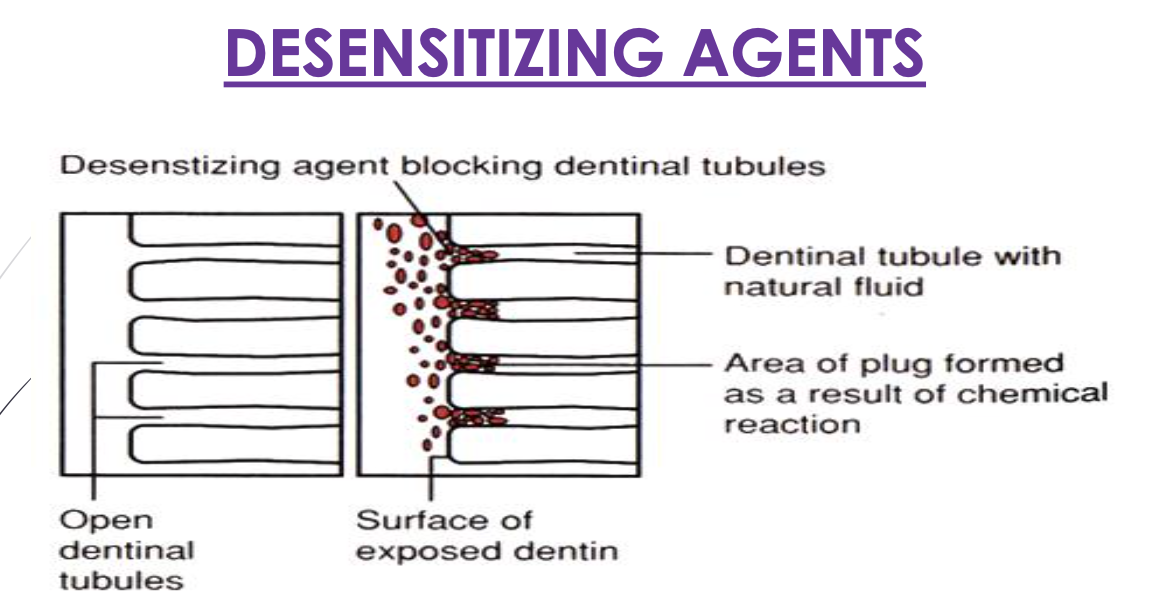
How does aggressive brushing contribute to tooth hypersensitivity?
Aggressive/excessive pressure applied when brushing wears away enamel or cementum and causes dentin to be exposed
How does gum recession contribute to tooth hypersensitivity?
Gums moving away from the tooth will exposure root surface
How does gum disease contribute to tooth hypersensitivity?
inflamed and sore gum tissue may cause sensitivity due to the loss of supporting ligaments exposing root surface
How does cracked teeth contribute to tooth hypersensitivity?
Chipped or cracked teeth may fill up with bacterial from plaque and enter the pulp causing an inflammatory reaction
How does bruxism (grinding teeth) contribute to tooth hypersensitivity?
Grinding/clenching wears down enamel and exposes underlying dentin
How does plaque contribute to tooth hypersensitivity?
Presence of plaque on the root surface can cause sensitivity
What are 6 common causes of root sensitivity?
root caries
tooth brush abrasion
erosion by acids
abfraction associated with bruxism
scaling and root planing
leaing restorations on the root
What professional treatments can be done to help reduce tooth sensitivity?
white fillings to cover exposed root
Fluoride varnish to exposed root
dentin sealer applied to exposed root surfaces
Potassium nitrate, strontium chloride, zinc chloride are all ______ agents.
desensitizing agents