Terms-Art History Post 1300s
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Mannerism
bridged the High Renaissance and Baroque periods. Defined by its emphasis on complexity, artificiality, and virtuosity over the naturalism of the High Renaissance. Key characteristics include elongated figures, complex and crowded compositions, distorted perspectives, and an unconventional and often jarring color palette.
Protestant Reformation
Emphasized individual faith and rejected religious imagery that could lead to idolatry. Resulted in a significant reduction of religious art, particularly in churches, and a dramatic shift in subject matter toward secular themes such as landscapes, portraits, and still life, reflecting the Protestant belief that all vocations and everyday life hold spiritual significance.
Iconoclasm
The deliberate destruction of religious images, often driven by the belief that the images are idolatrous or violate religious principles.
Counter Reformation
Was a Catholic revival in the 16th and 17th centuries that used art to reassert Catholic doctrine and inspire devotion in response to the Protestant Reformation. Promoted Baroque art style.
Council of Trent (1545-63)
An ecumenical council of the Catholic Church that defined new guidelines for religious art as part of the Counter-Reformation.
Vanitas
A style of still-life painting that uses symbolic objects to remind viewers of their mortality and the fleeting nature of earthly life.
Anamorphic image
A distorted projection that appears distorted but can be viewed as normal from a specific angle. (ex. The Ambassadors)
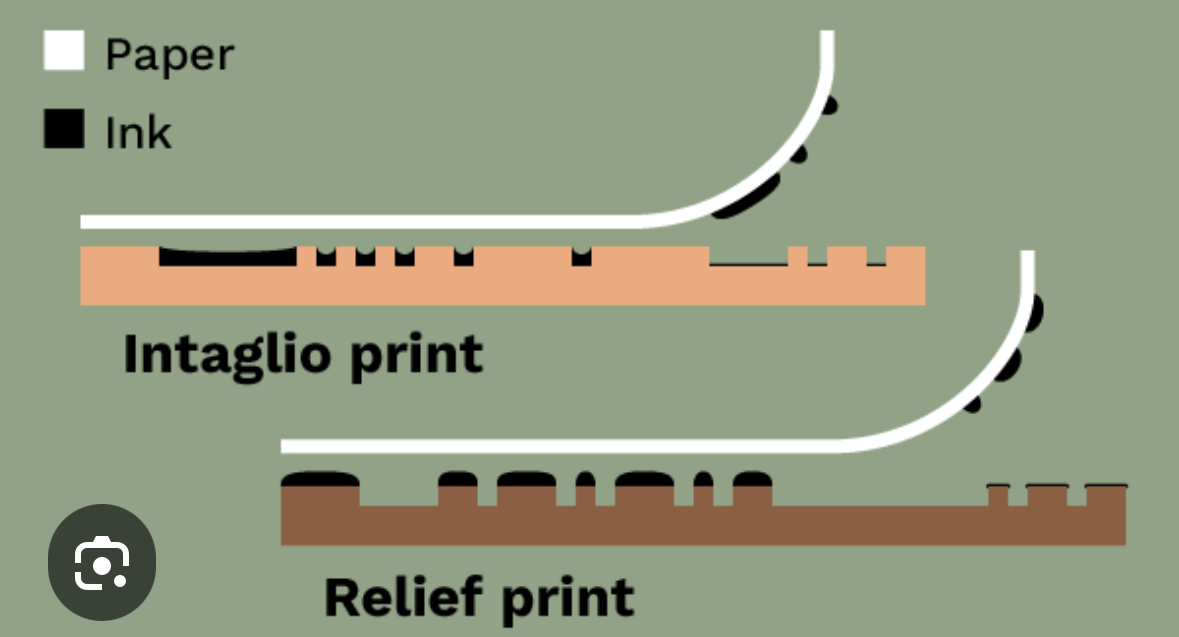
Relief and Intaglio printing processes
Relief printing uses a raised surface to print, while intaglio printing uses incised (cut) grooves.
Chiaroscuro
Technique that uses strong contrasts between light and dark.
Allegory
A narrative or visual representation that uses symbolic figures, actions, and imagery to convey deeper moral, spiritual, or political meanings beyond the literal story.
Personification
The artistic device of representing an abstract concept, idea, or non-human entity as a human figure, often with symbolic attributes.
Art Market
The economic system for buying and selling art.
Camera Obscura
A darkened room or box with a small hole that projects an inverted image of the outside world onto a surface, and was used by artists as a tool to aid in achieving realism and accurate perspective in their work.
Baroque
An artistic and architectural style that flourished in Europe from the late 16th to mid-18th centuries, characterized by grandeur, drama, movement, and emotional intensity.
Tenebrism
A style of painting characterized by the dramatic use of extreme contrasts between light and dark, where the light is often used to illuminate a specific subject against a background of plunging darkness. More extreme version of chiaroscuro.
Poussinists and Rubenists
Two opposing factions in a late 17th-century debate within the French Royal Academy over whether drawing or color was the most important element in painting.
Hierarchy of Genres
1) History painting
2) Portraits
3) Genre (everyday life)
4) Landscape
5) Animal paintings
6) Still-life
The Sublime
An aesthetic quality that evokes feelings of awe, terror, and wonder, often through vast, powerful, or overwhelming subjects like dramatic landscapes or monumental art.
Neoclassicism
Architecture style that emerged in the 1750s and was inspired by ancient Greek and Roman models. The term "neo" means "modern" or "new", and the style is known for its simplicity, discipline, and unemotional grandeur.