Hearing Science - Oscillations & Vibrations
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Define Oscillations:
Back and forth movement (“swing”) around equilibrium (point 0).
Define Vibrations:
Back and forth movement around equilibrium due to the force of elasticity.
Why does a pendulum swing back and forth?
It’s an interaction between inertia and gravity. It eventually stops due to Internal Friction, giving off thermal energy and eventually the pendulum will burn through it all.
The oscillation made by the pendulum is a ____ function.
Sine (it’s a sinusoidal motion)
Define Periodic Motion:
Same thing every swing, predictable and repeatable pattern.
Max Velocity is placed where it ______ equilibrium.
Passes
A sine wave represents the movement of a ________.
Pendulum
What does the X-Axis on a sine wave represent?
Equilibrium or Time
What does the Y-Axis on a sine wave represent?
The length or how far it traveled or the amplitude.
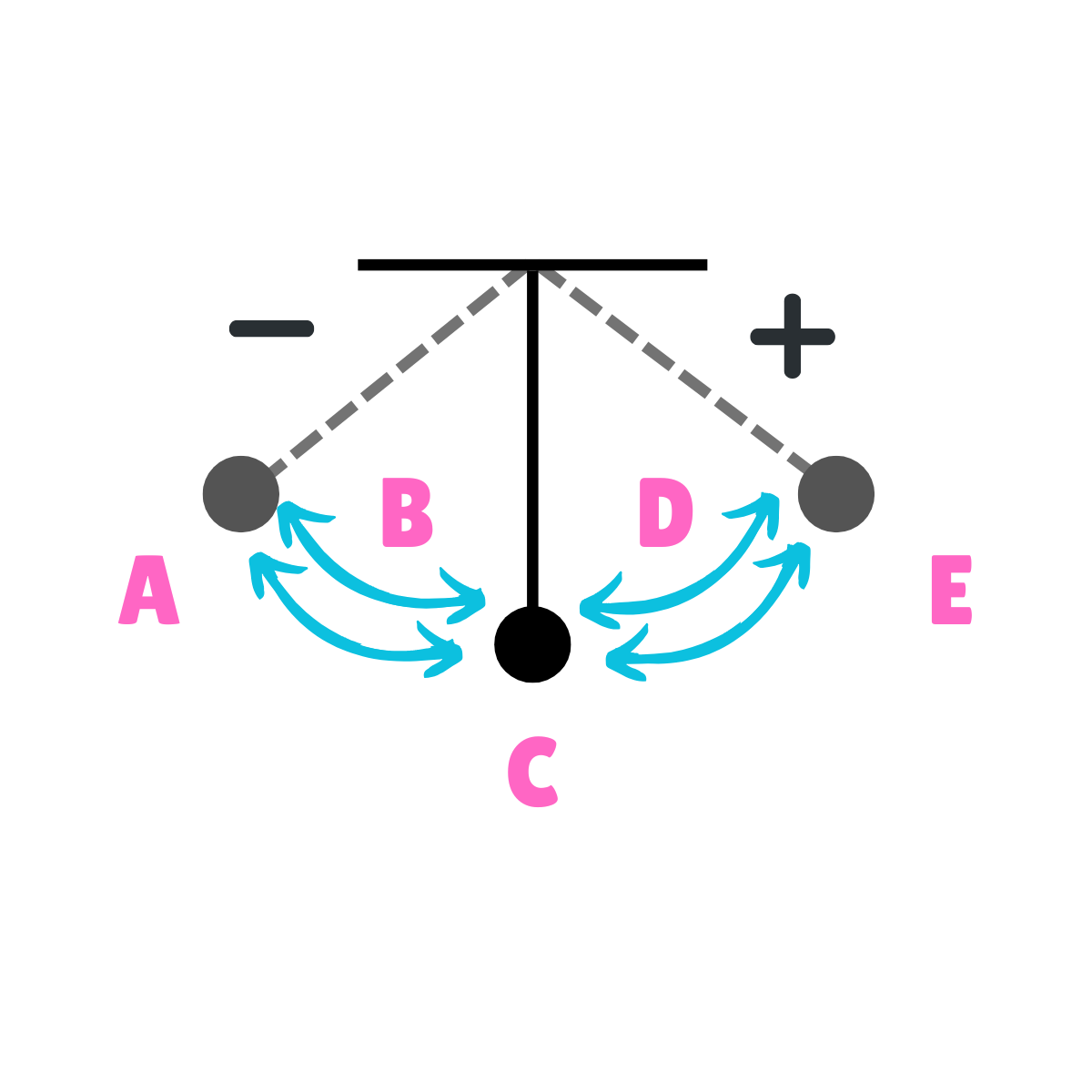
What does this drawing represent?
Oscillation
On this drawing, what does C represent regarding energy?
Potential Energy
On this drawing, what does C represent regarding inertia?
Inertia at rest
On this drawing, what does C represent regarding movement?
Equilibrium
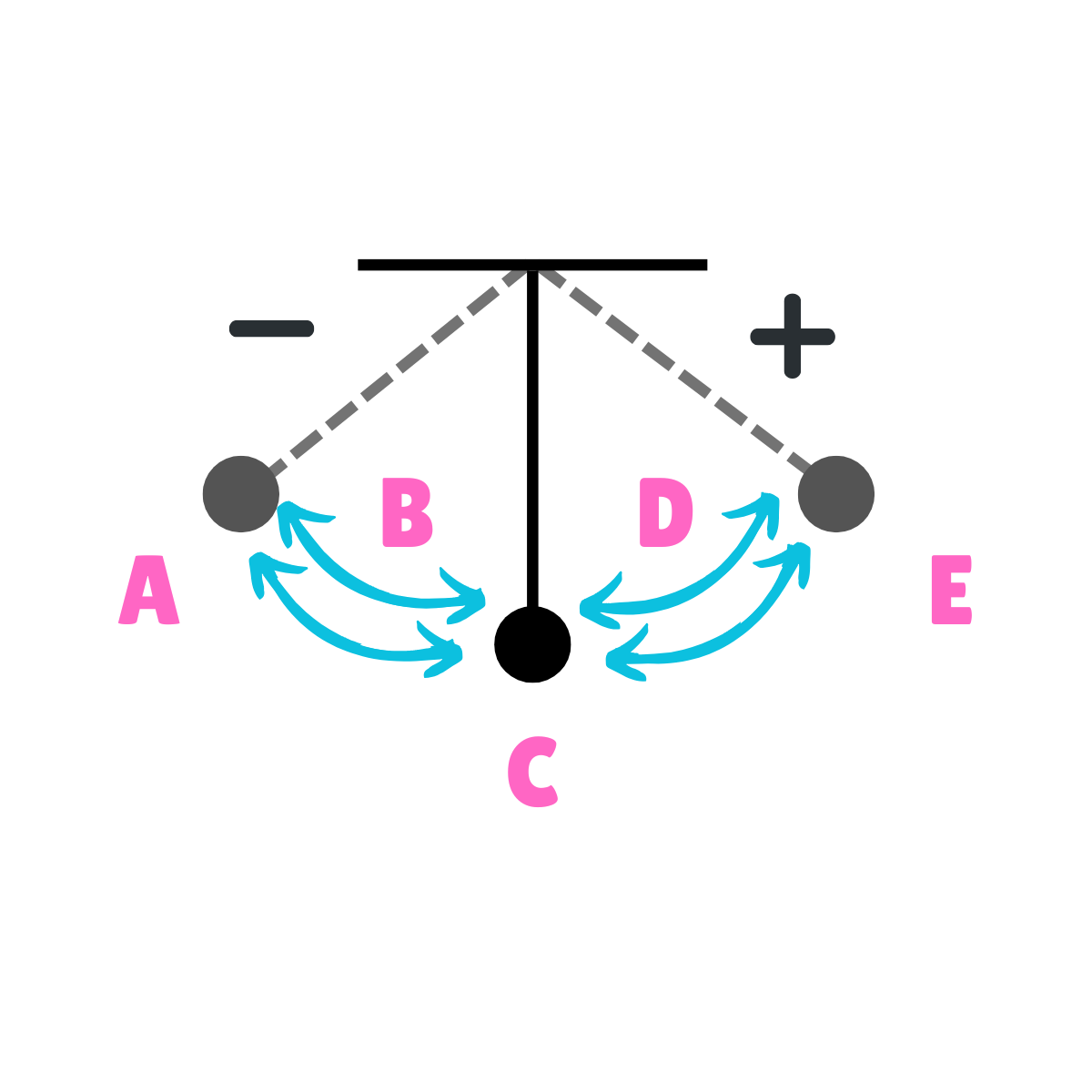
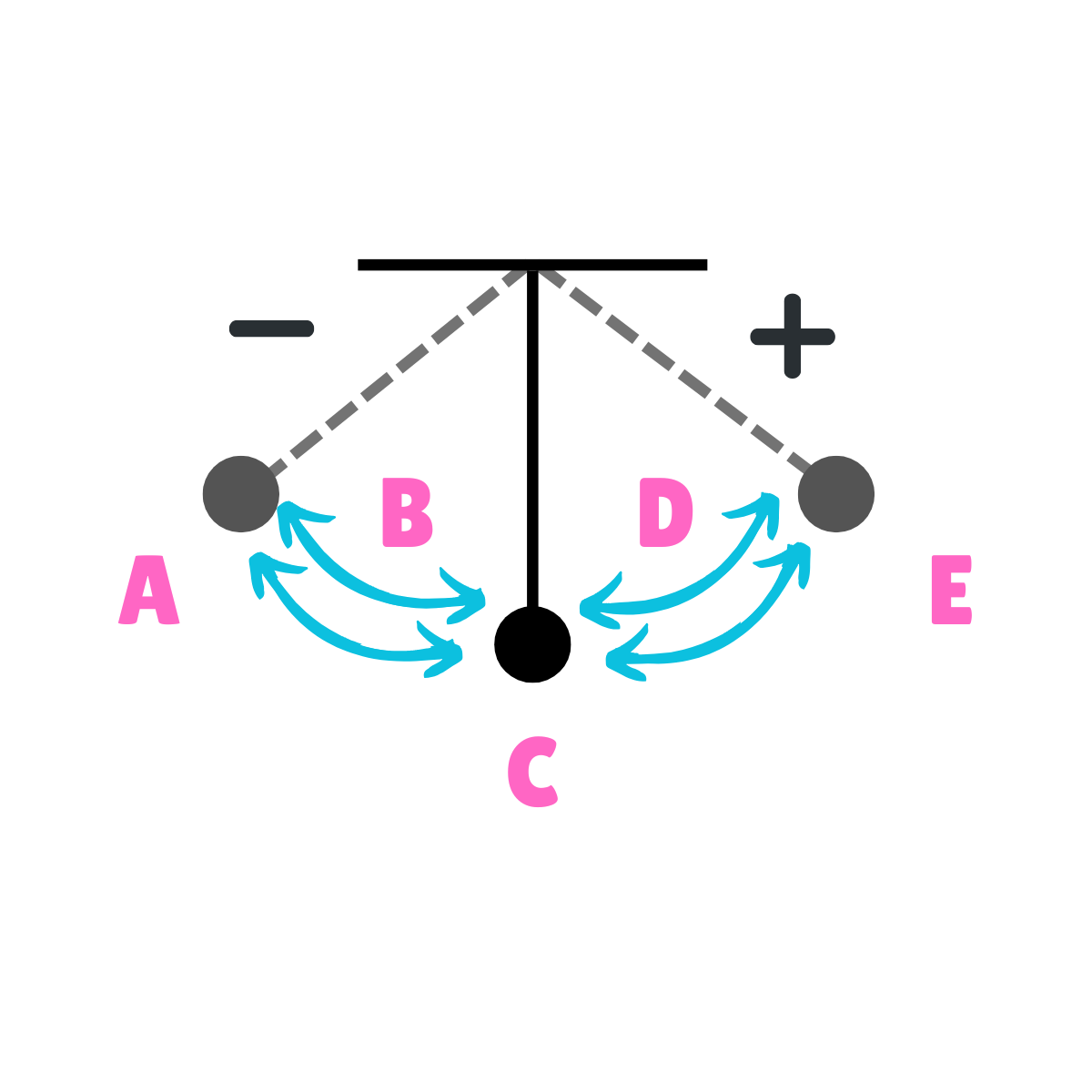
On this drawing, what does C represent regarding velocity?
Maximum Velocity
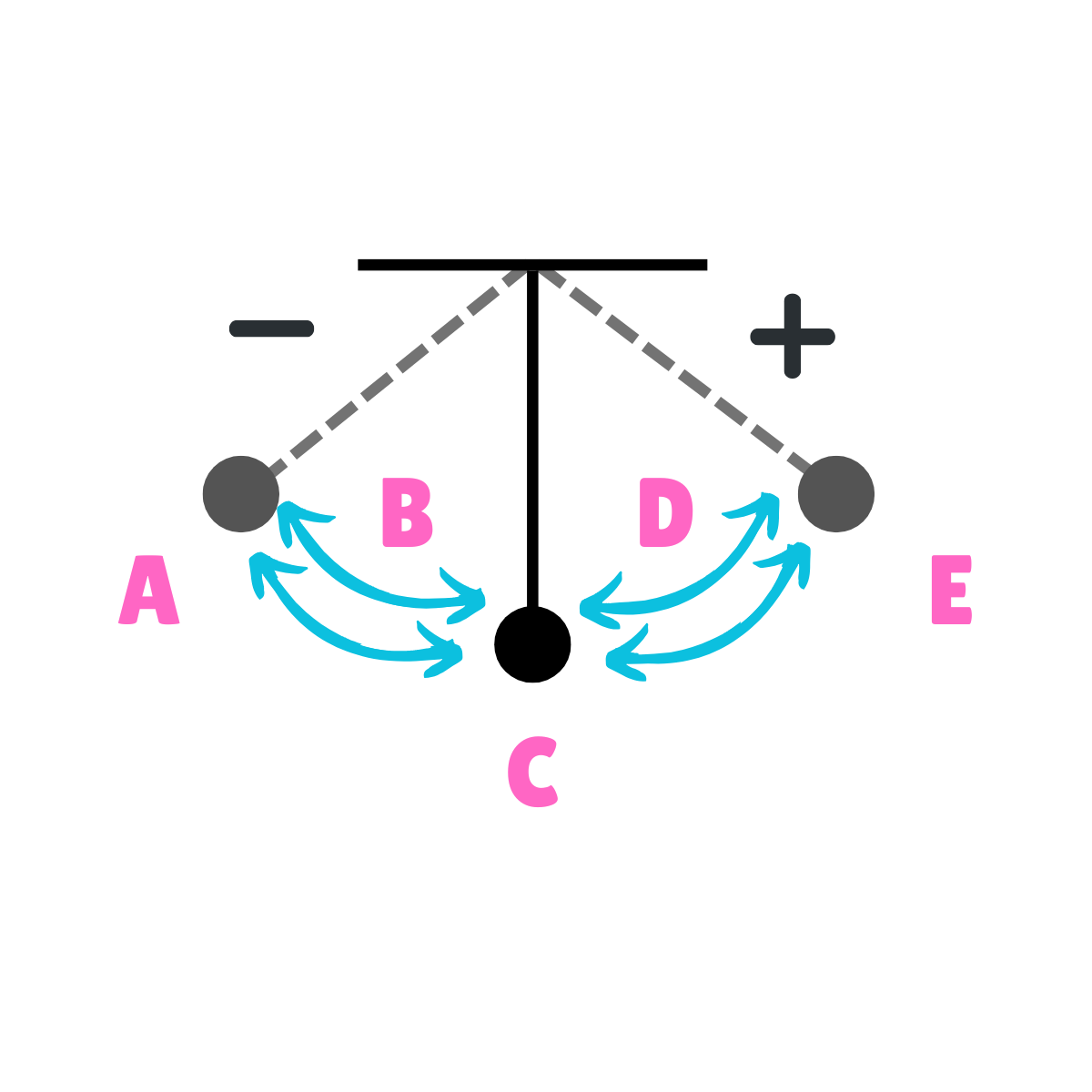
On this drawing, what does C represent regarding acceleration?
Minimum Acceleration
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding energy?
Potential Energy
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding inertia?
Inertia at rest
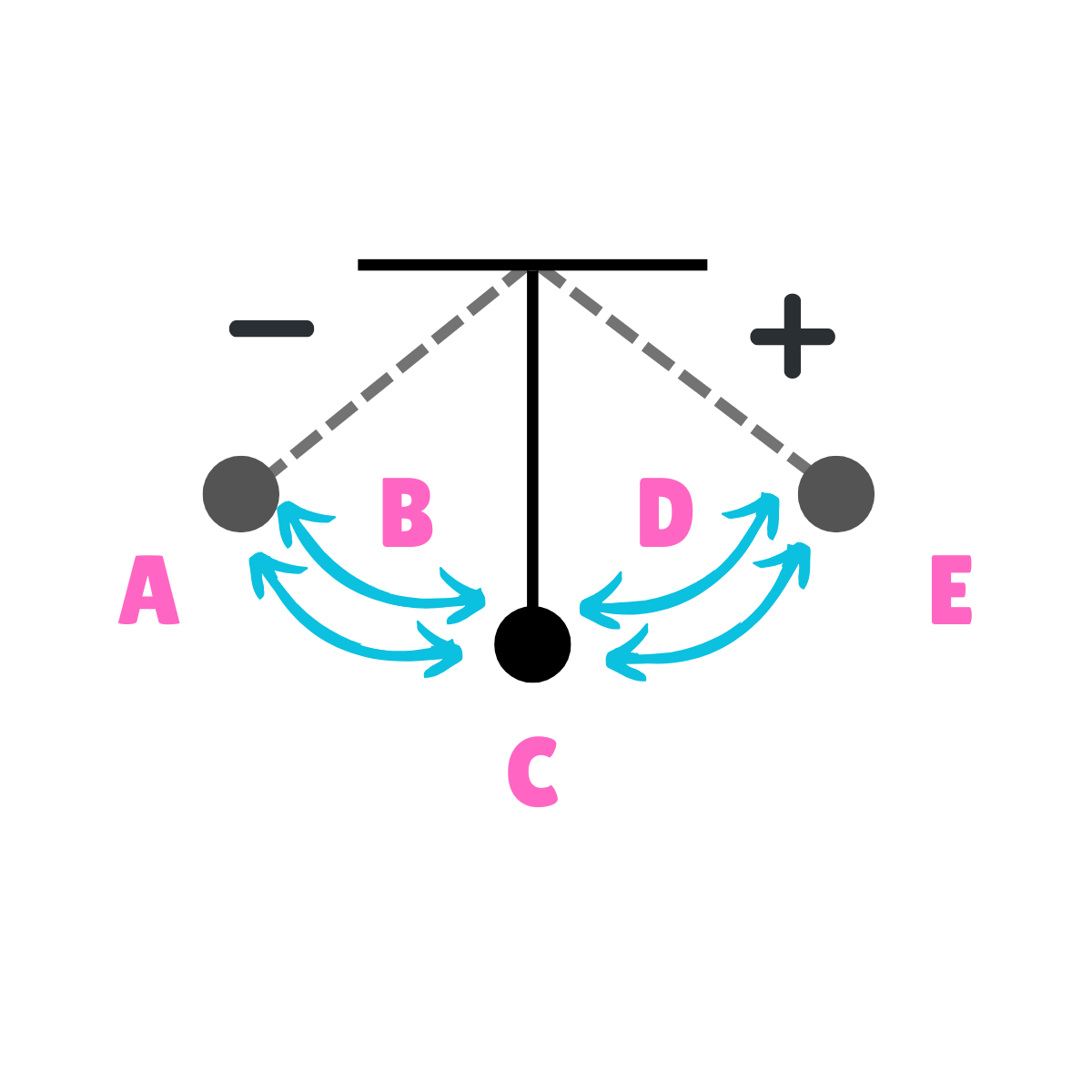
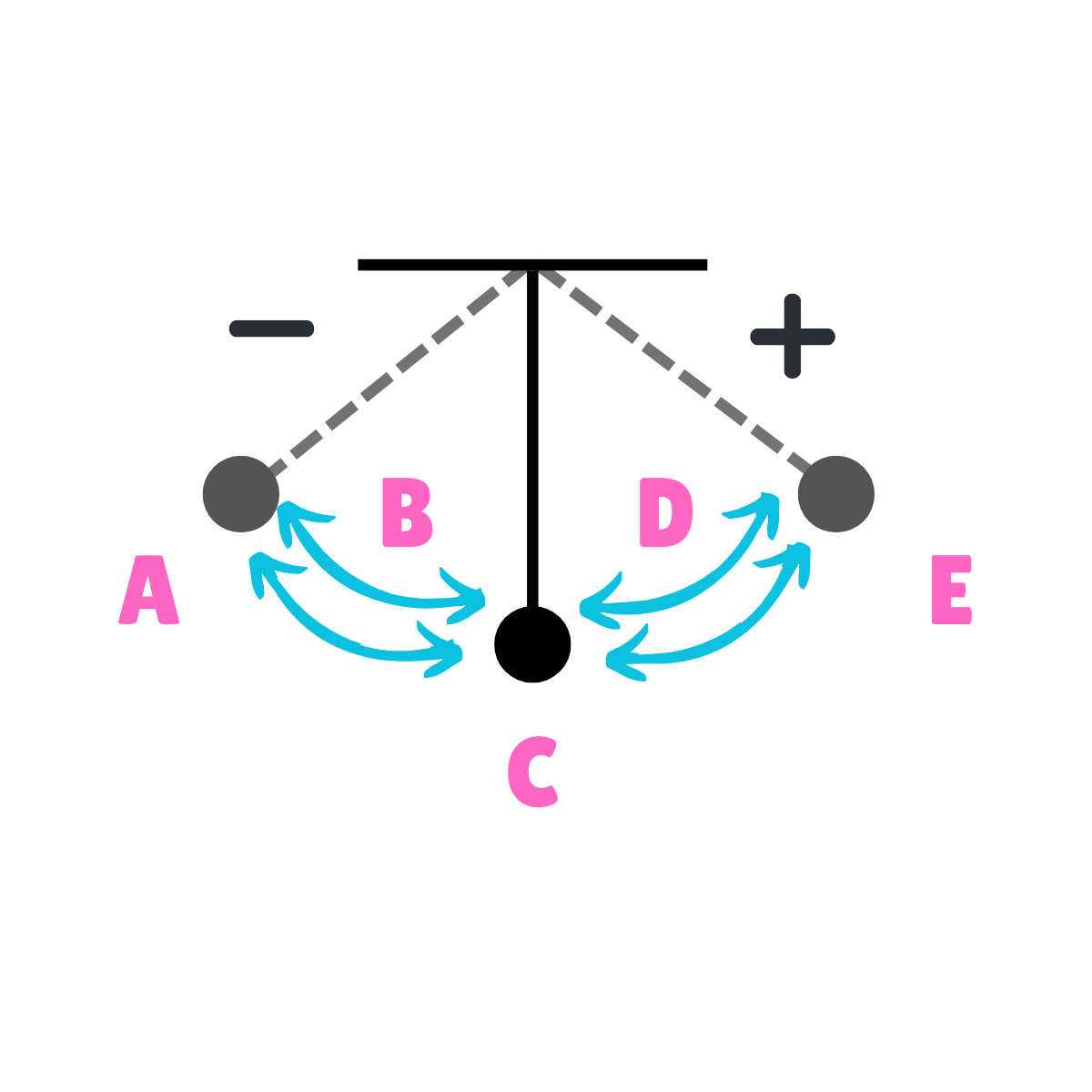
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding movement?
Max displacement
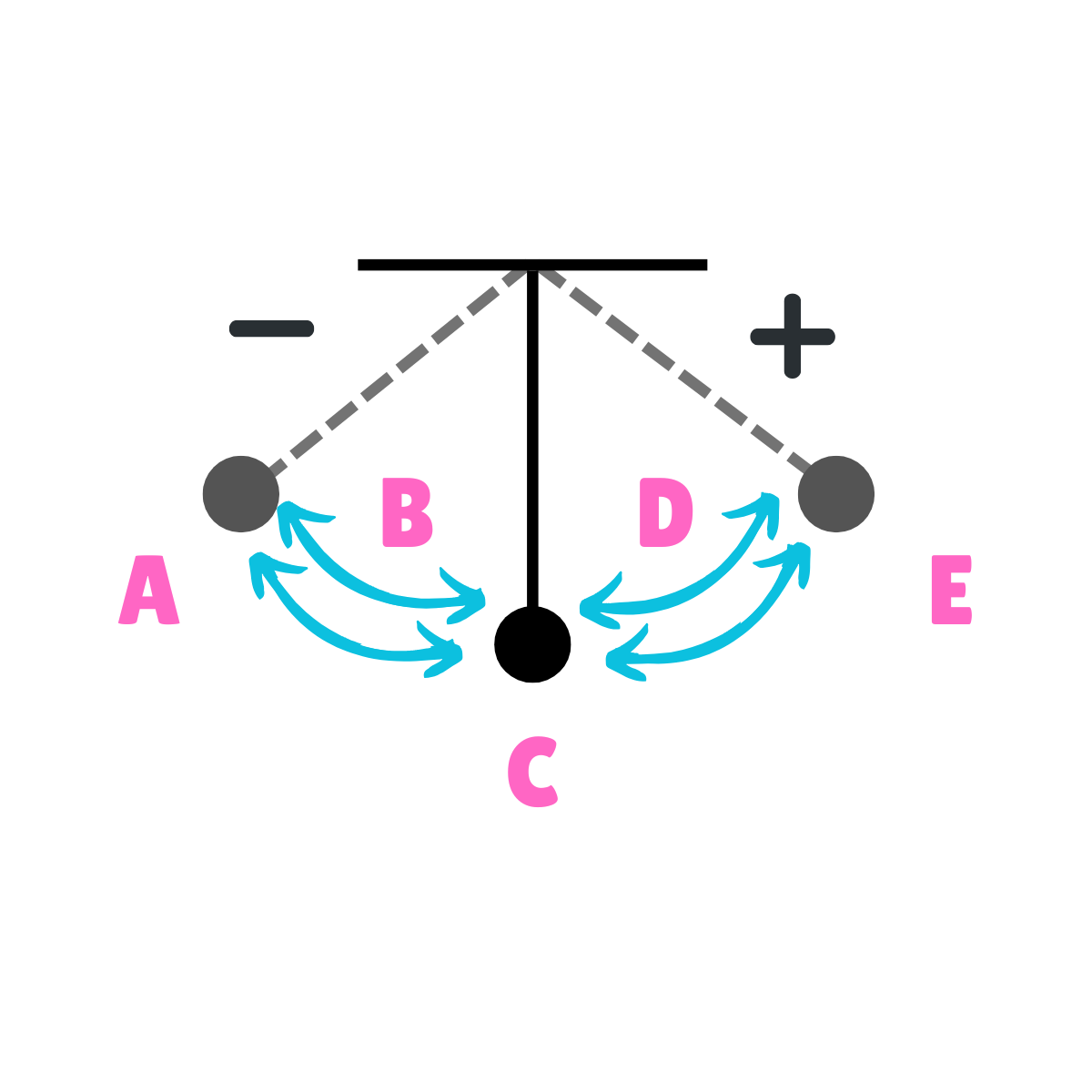
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding gravity?
The force of gravity is greater than the force of inertia.
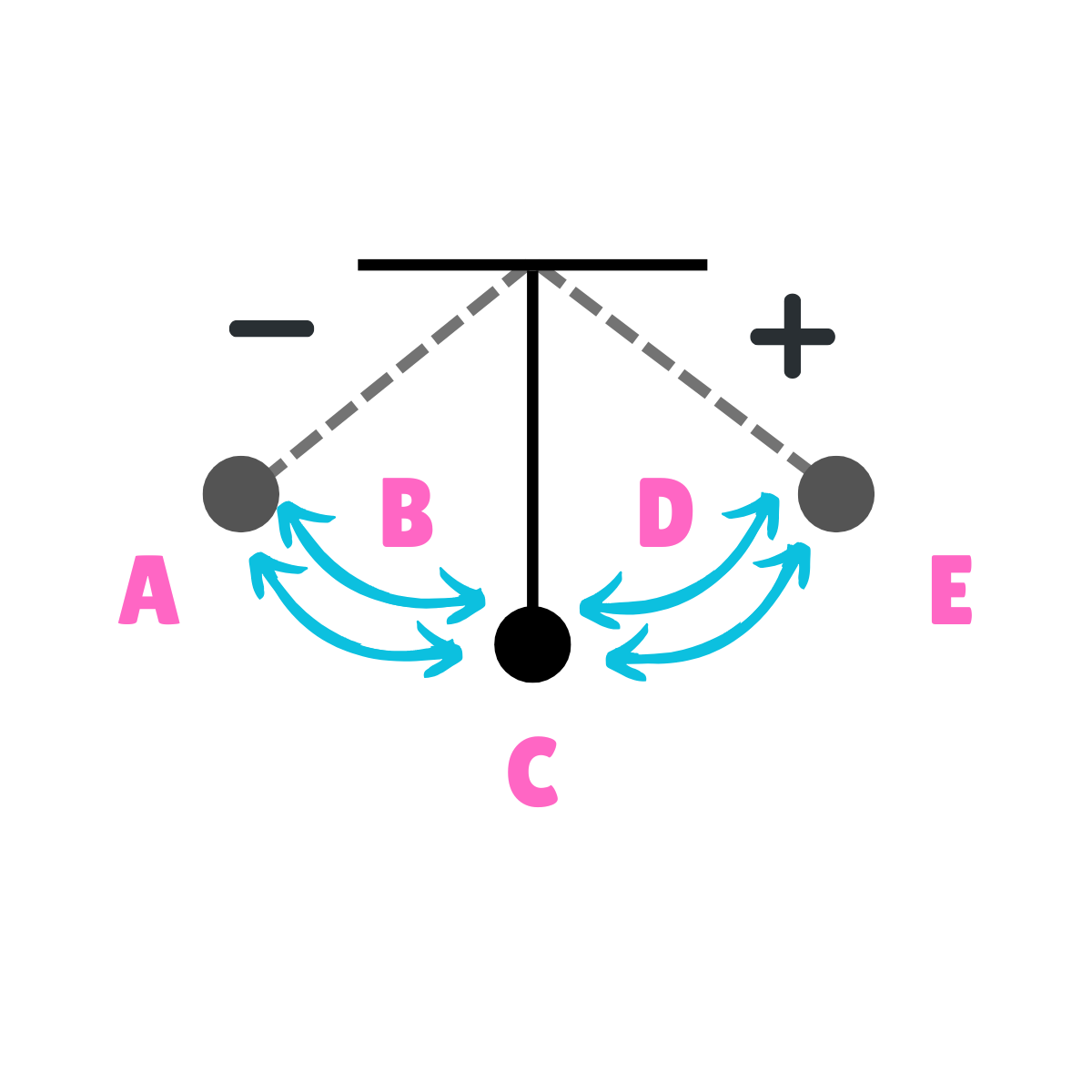
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding velocity?
Minimum Velocity
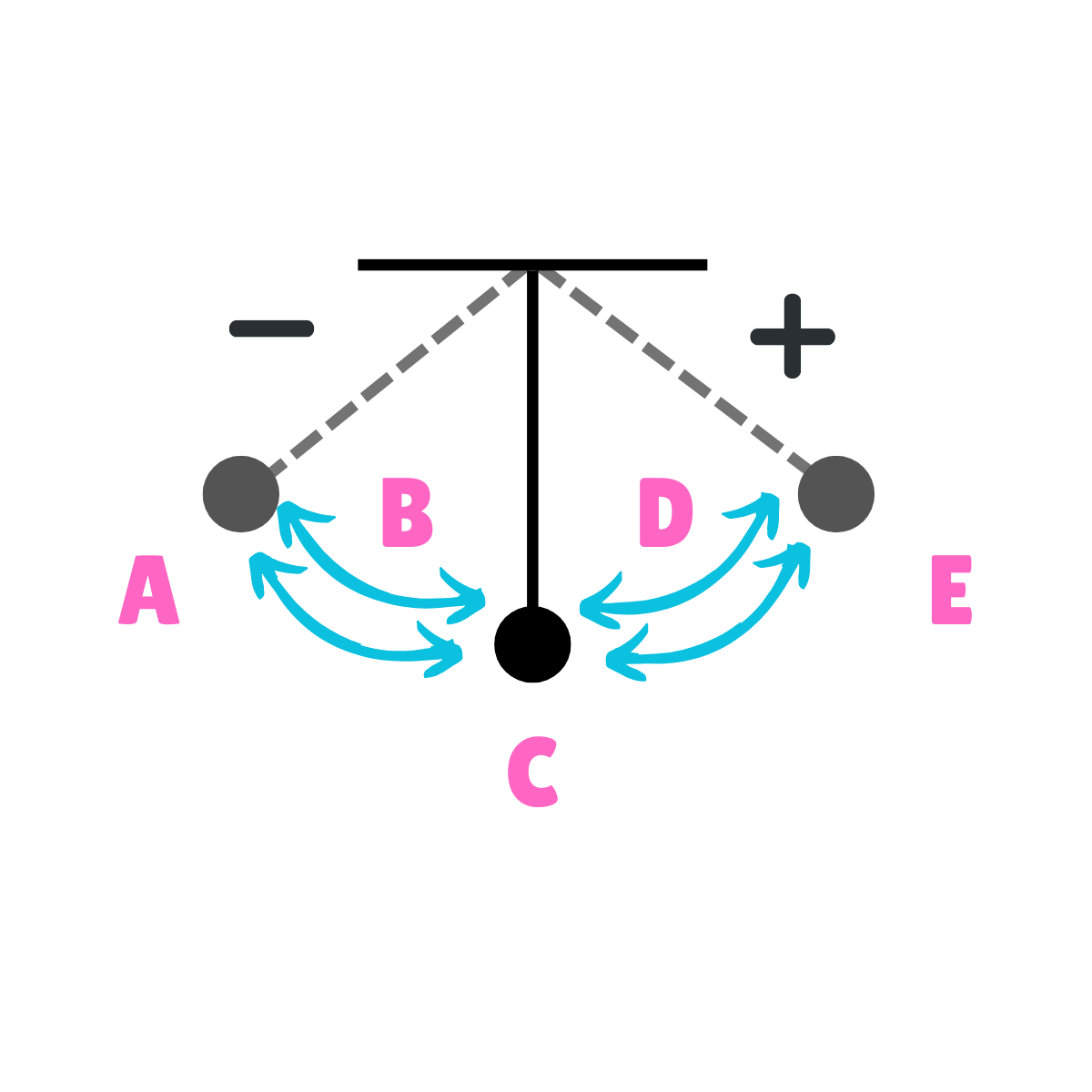
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding acceleration?
Maximum Acceleration
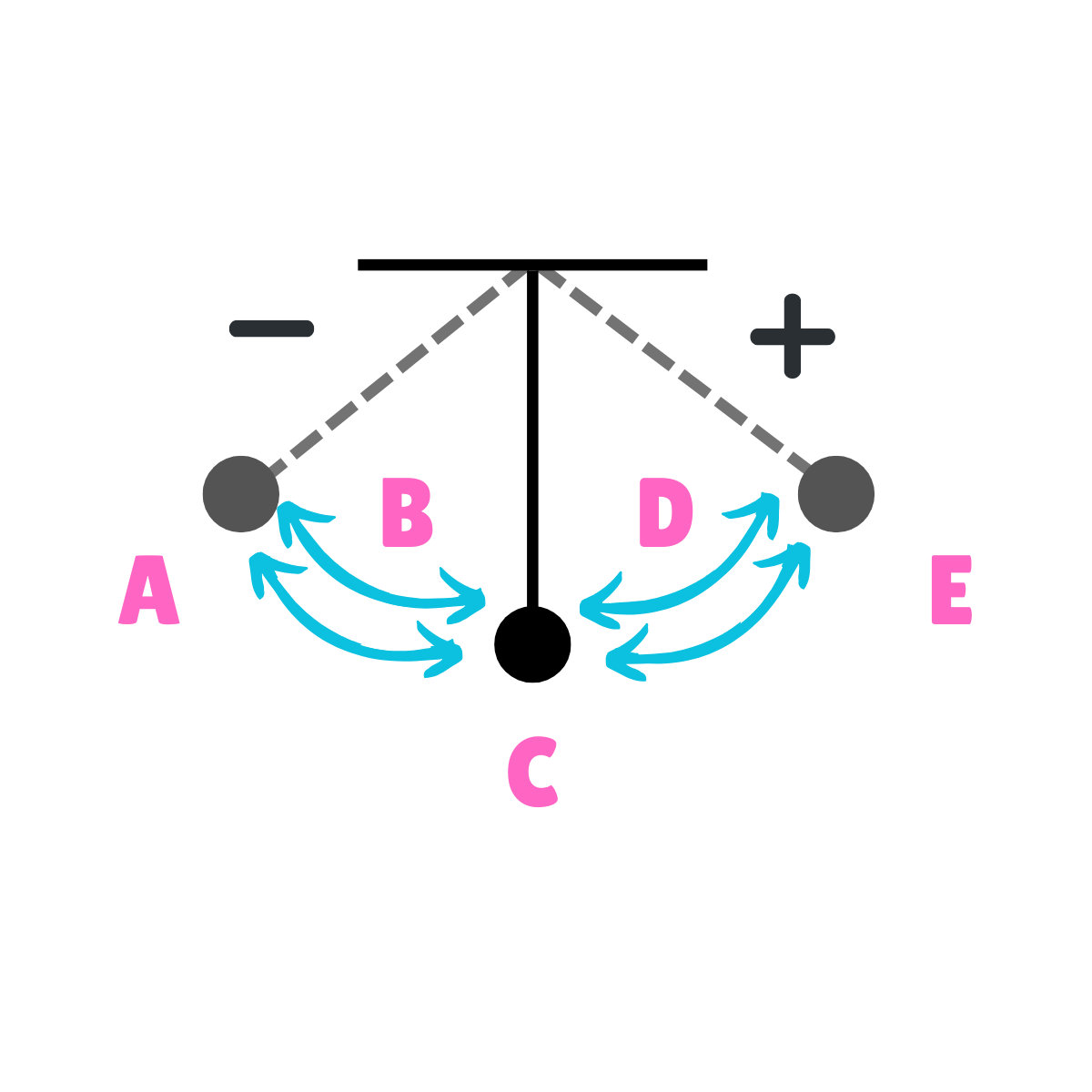
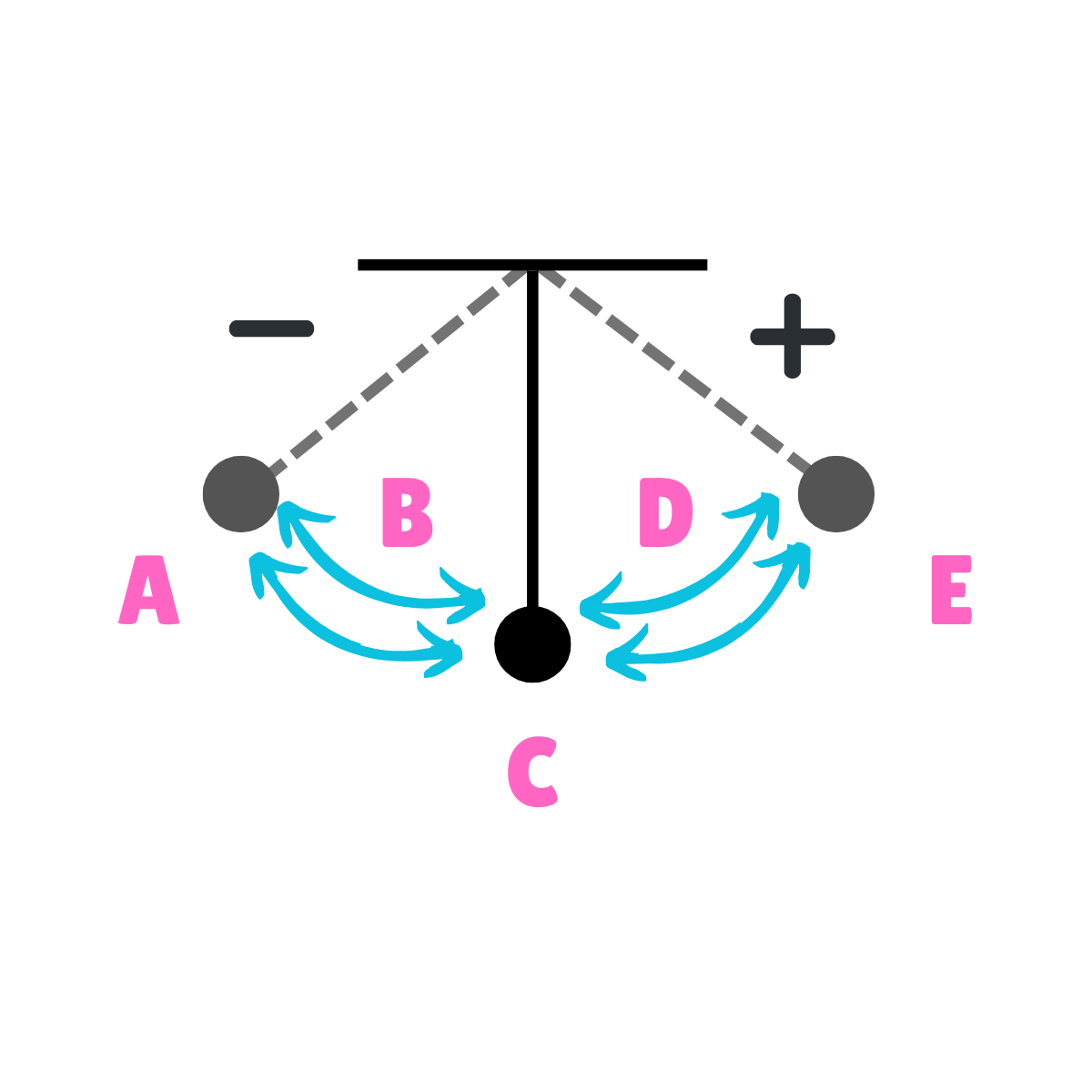
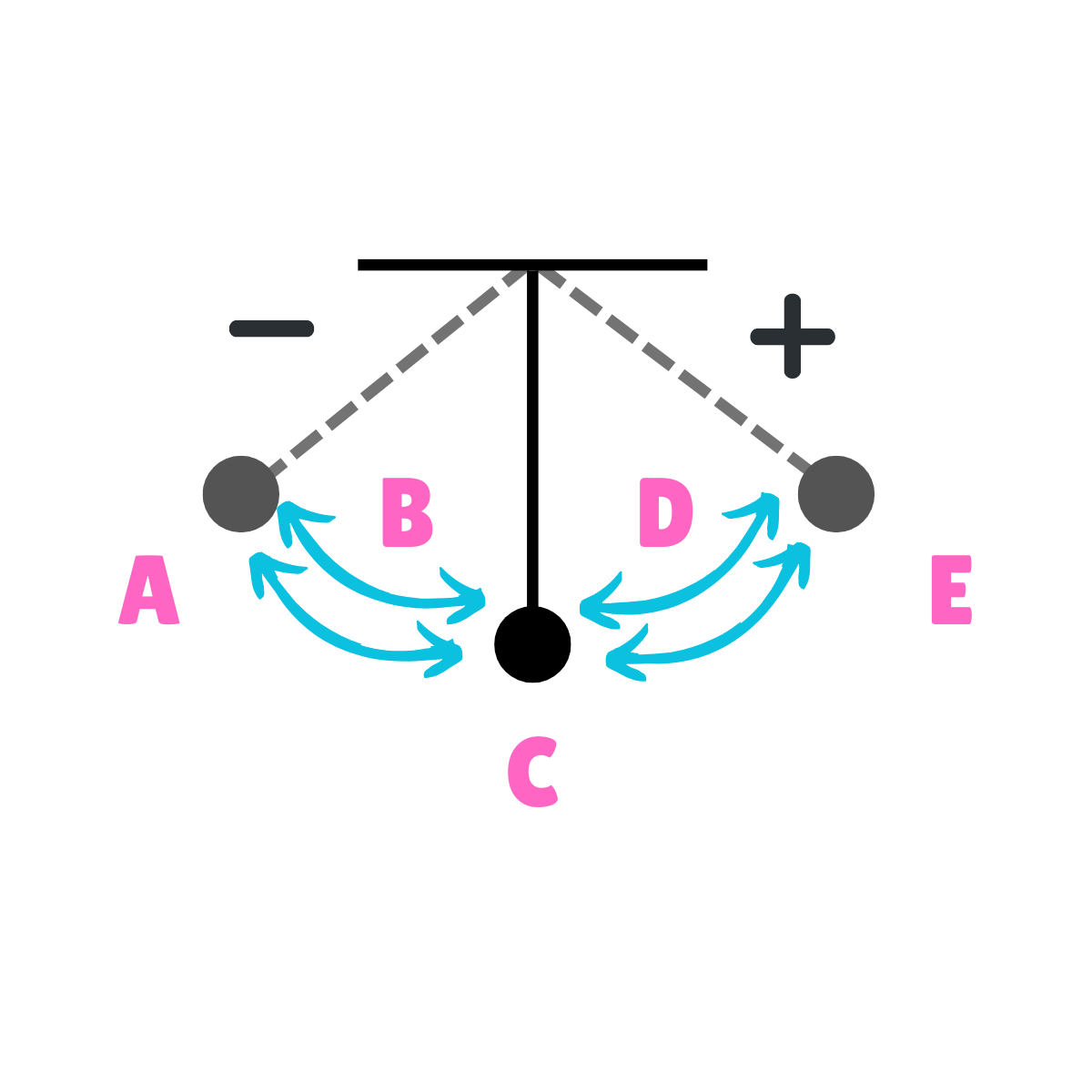
On this drawing, what does E represent regarding energy?
Potential Energy
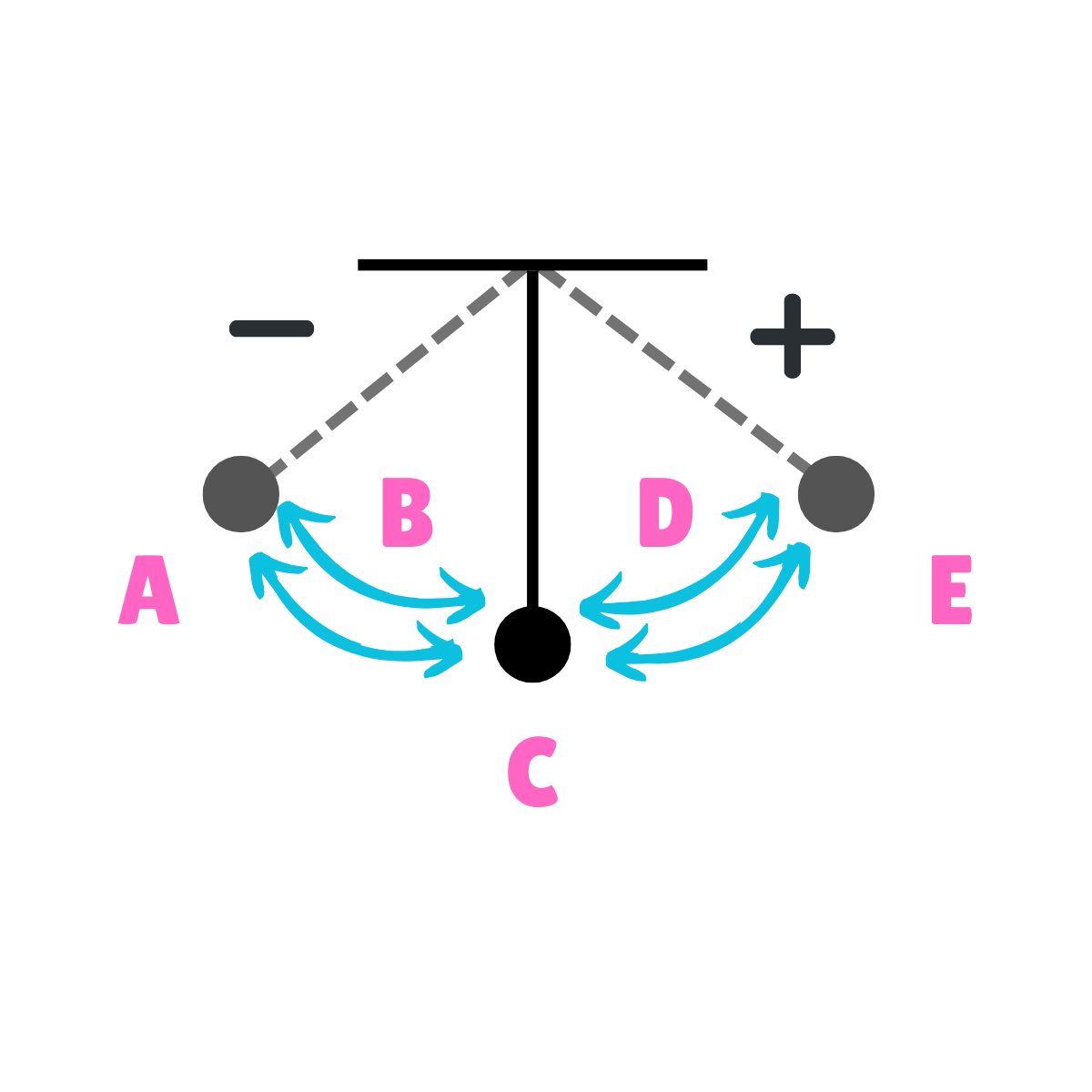
On this drawing, what does E represent regarding inertia?
Inertia at rest
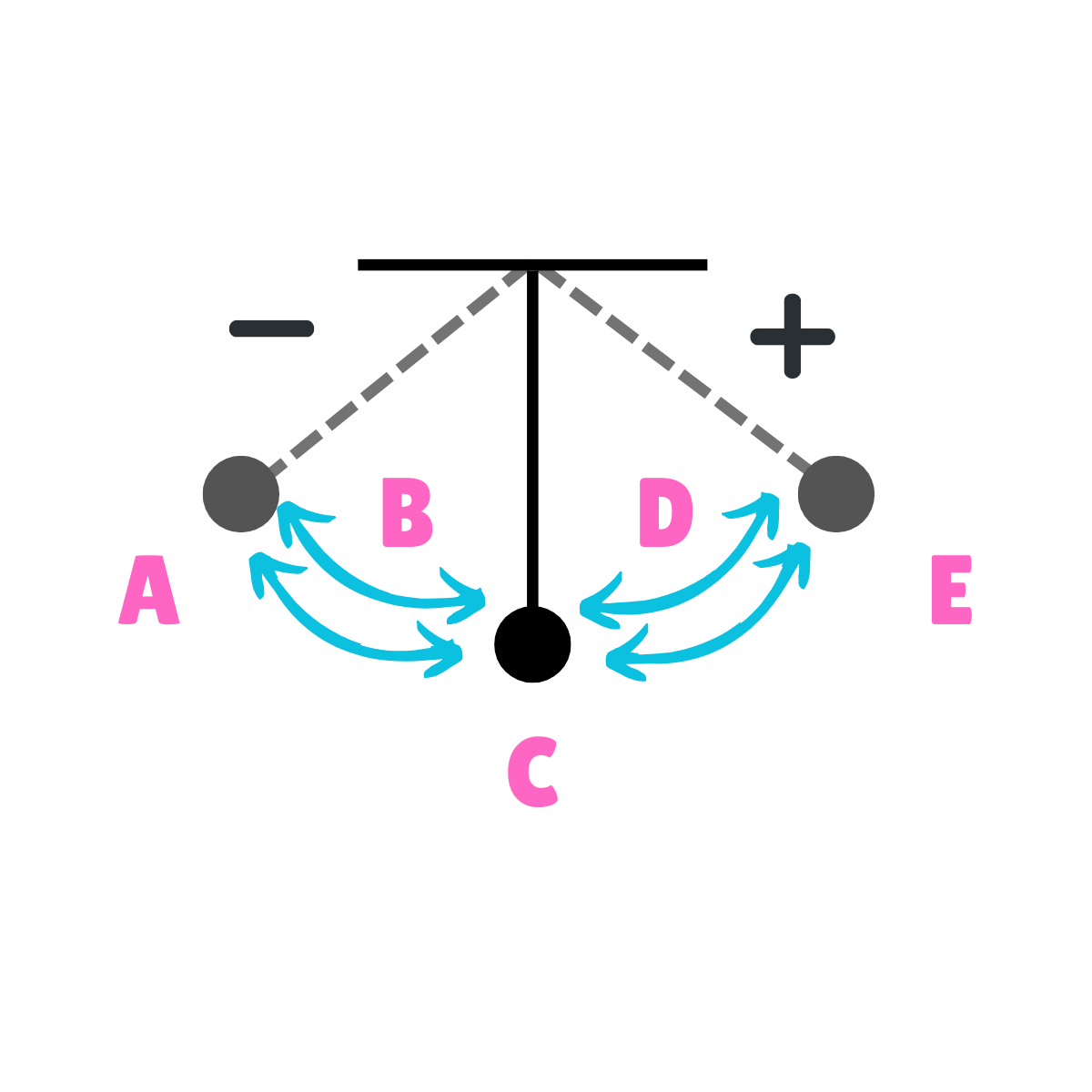
On this drawing, what does E represent regarding movement?
Max Displacement
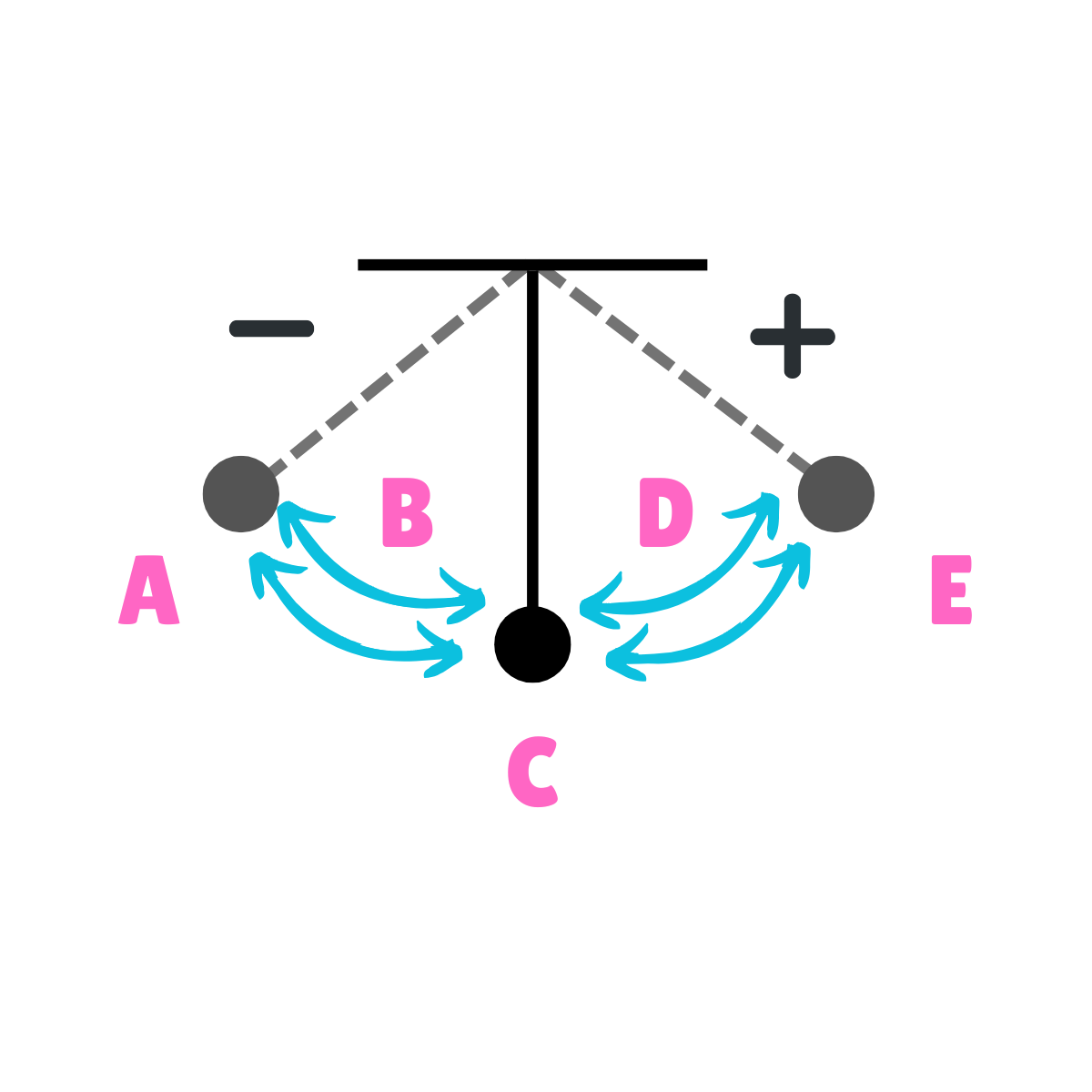
On this drawing, what does E represent regarding gravity?
The force of gravity is greater than the force of inertia.
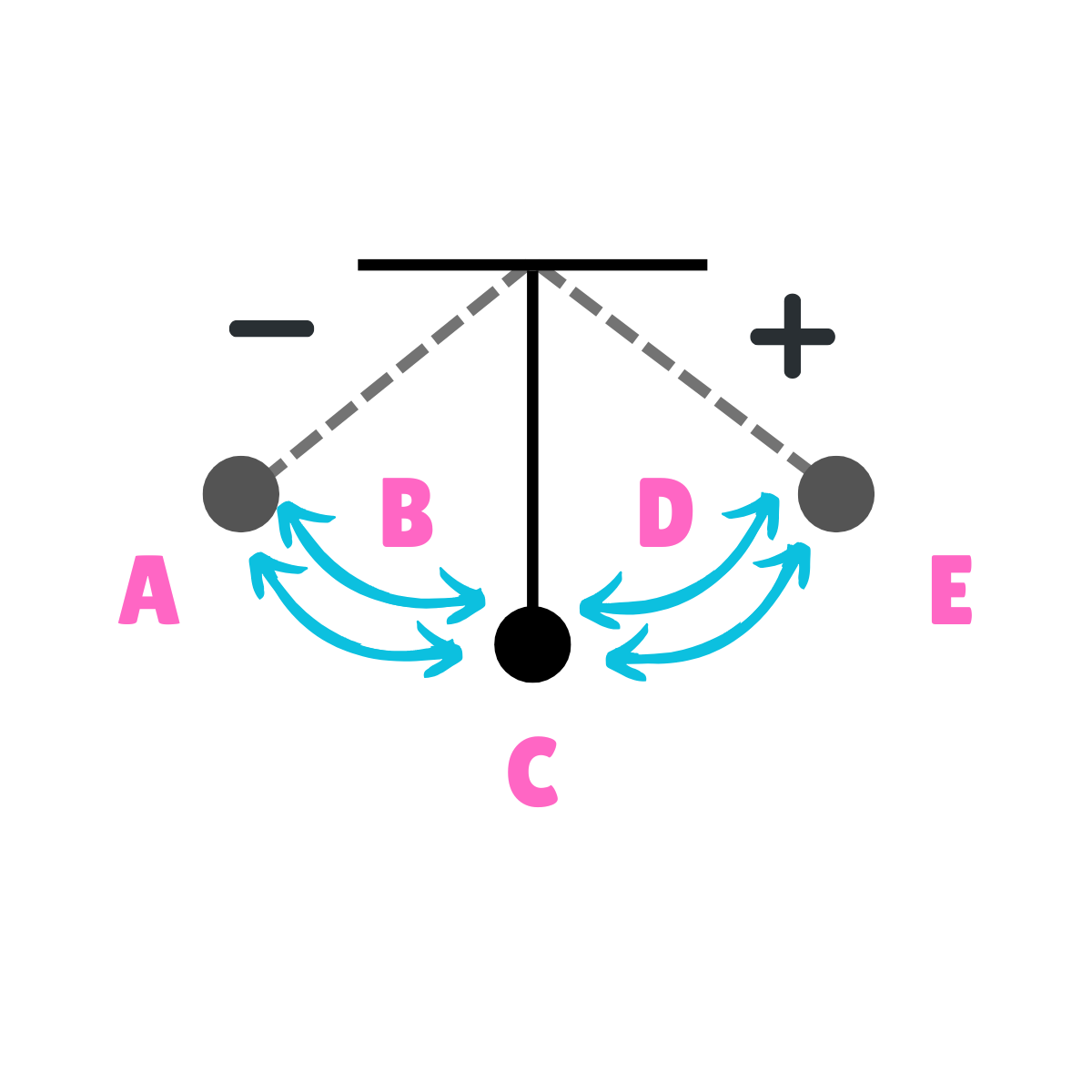
On this drawing, what does E represent regarding velocity?
Minimum Velocity
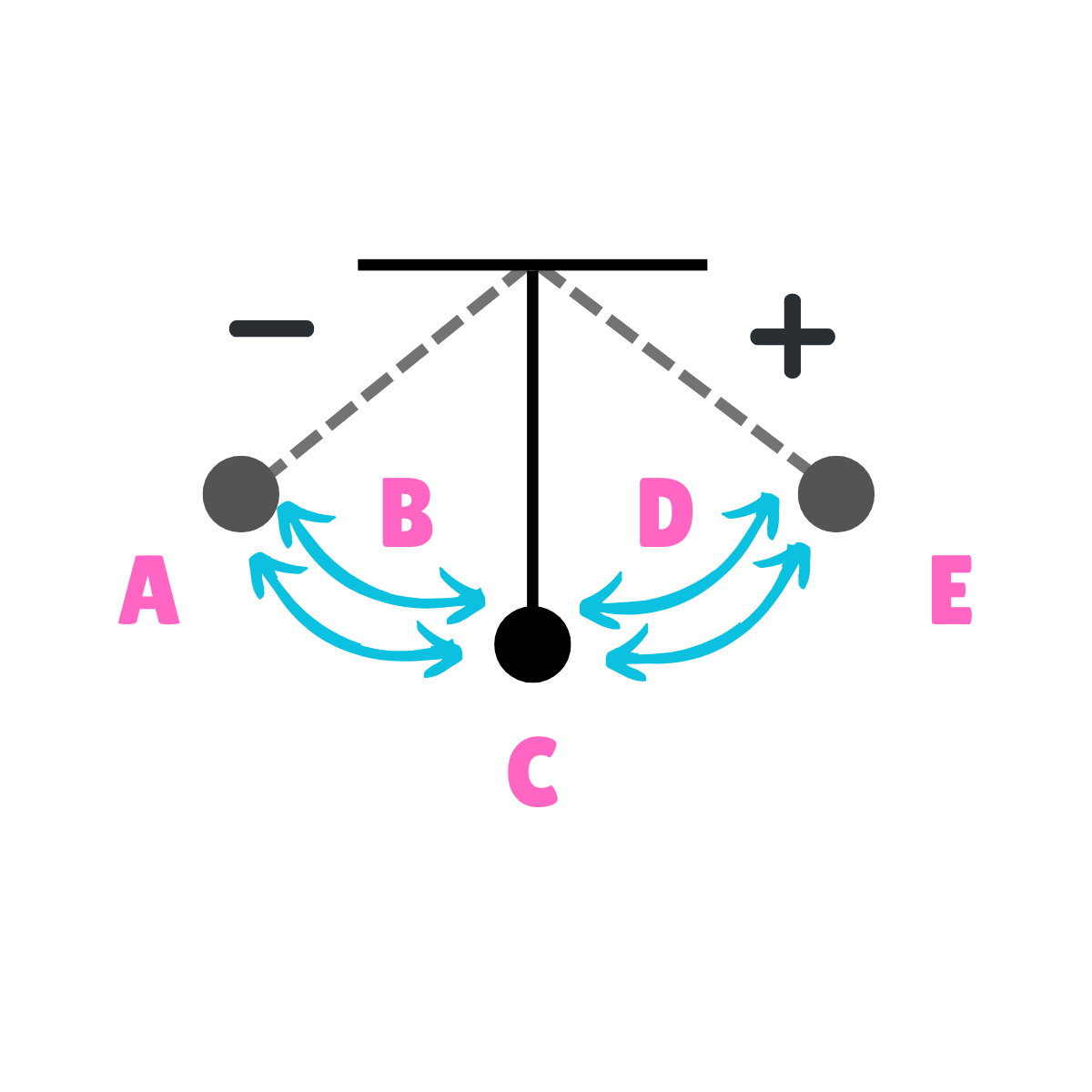
On this drawing, what does E represent regarding acceleration?
Maximum Acceleration
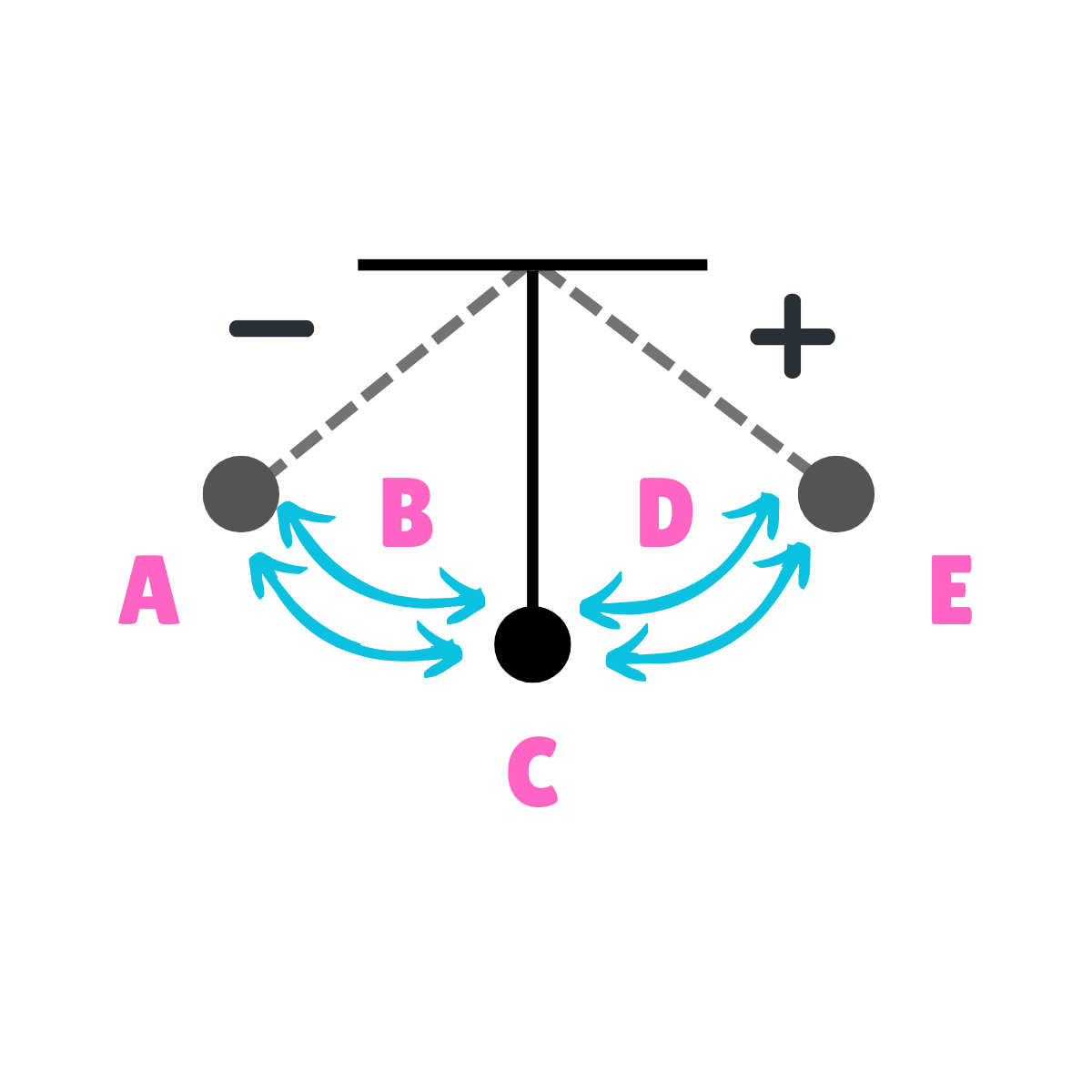
On this drawing, what does B represent regarding energy?
Kinetic Energy
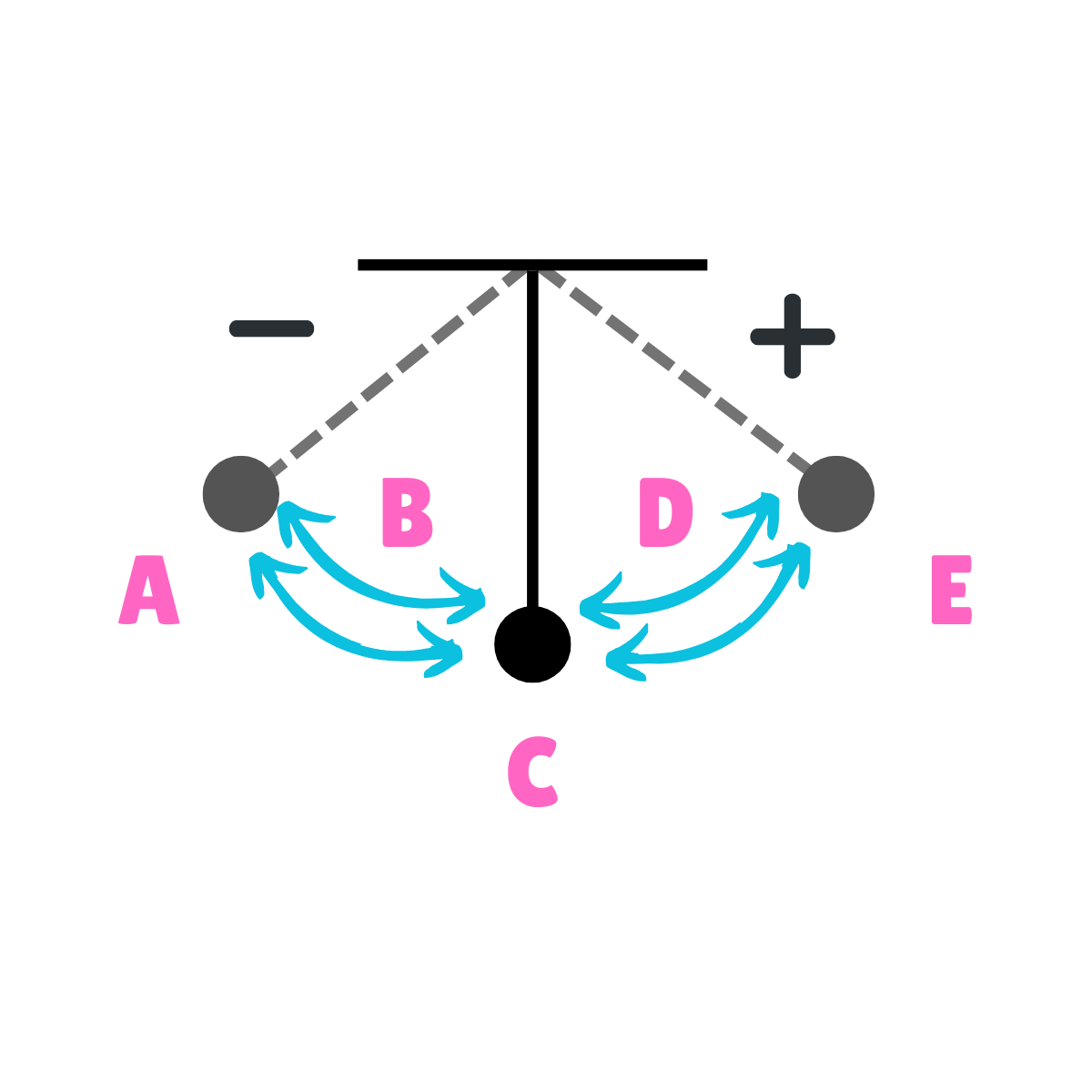
On this drawing, what does B represent regarding inertia?
Inertia in motion
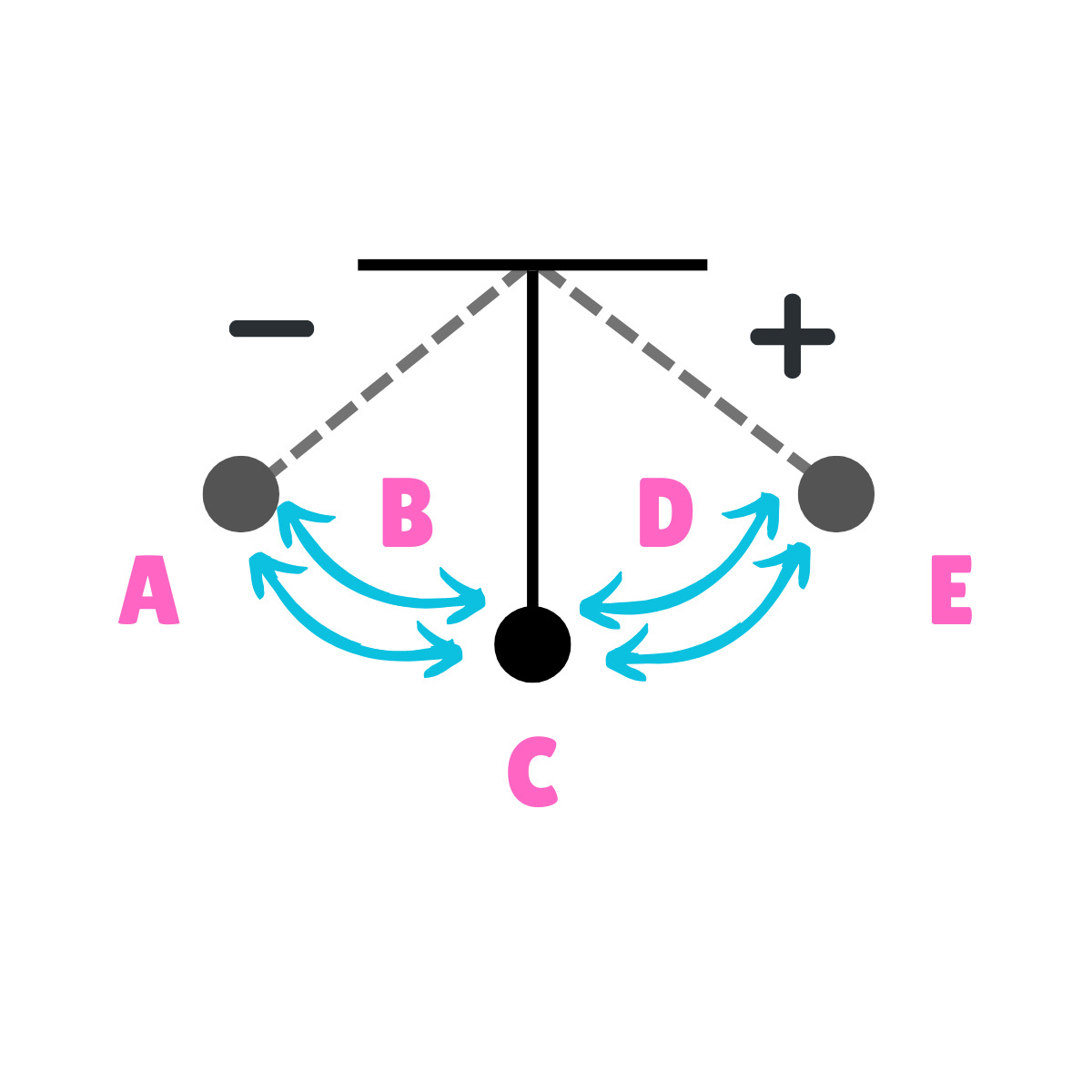
On this drawing, what does D represent regarding energy?
Kinetic Energy
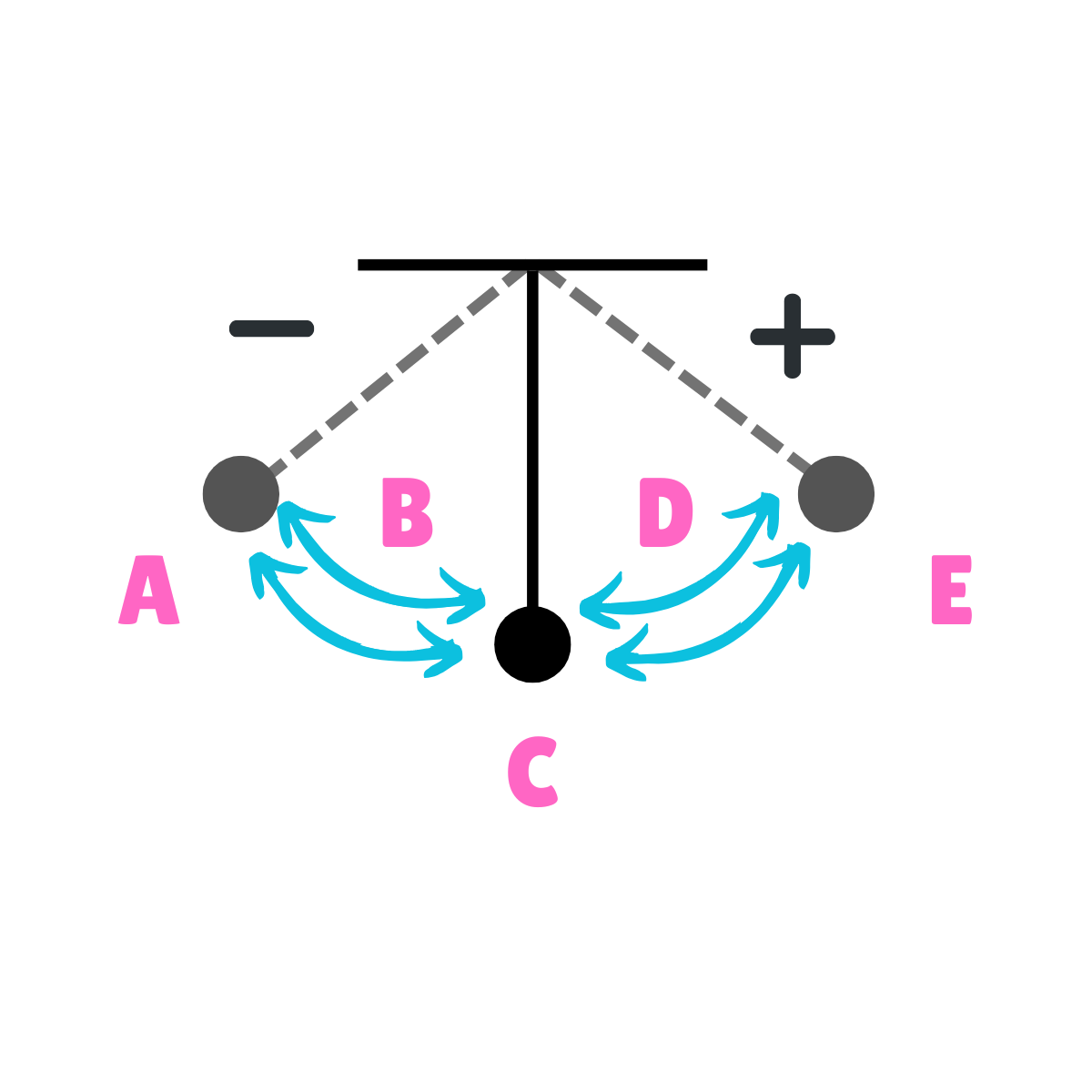
On this drawing, what does D represent regarding inertia?
Inertia in motion
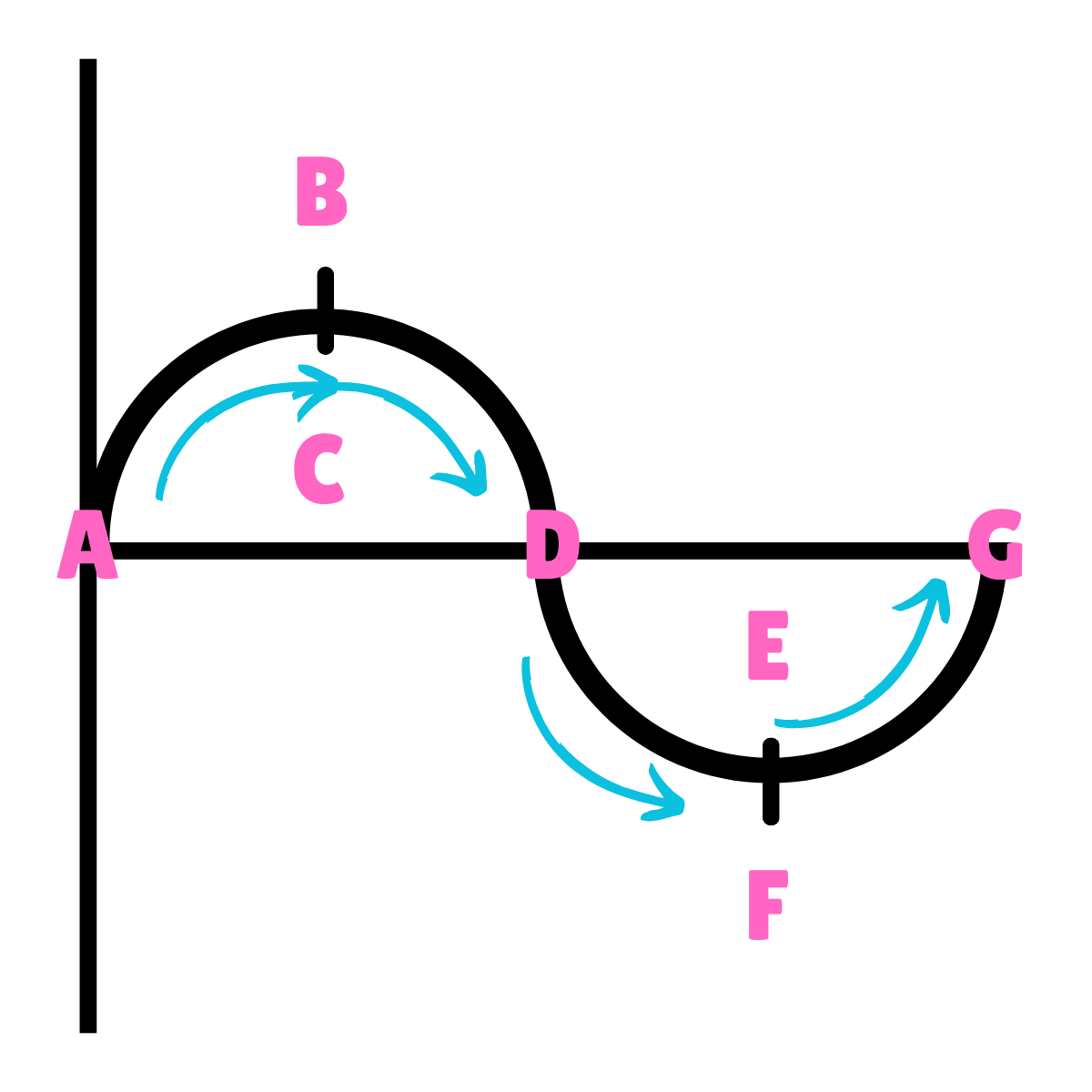
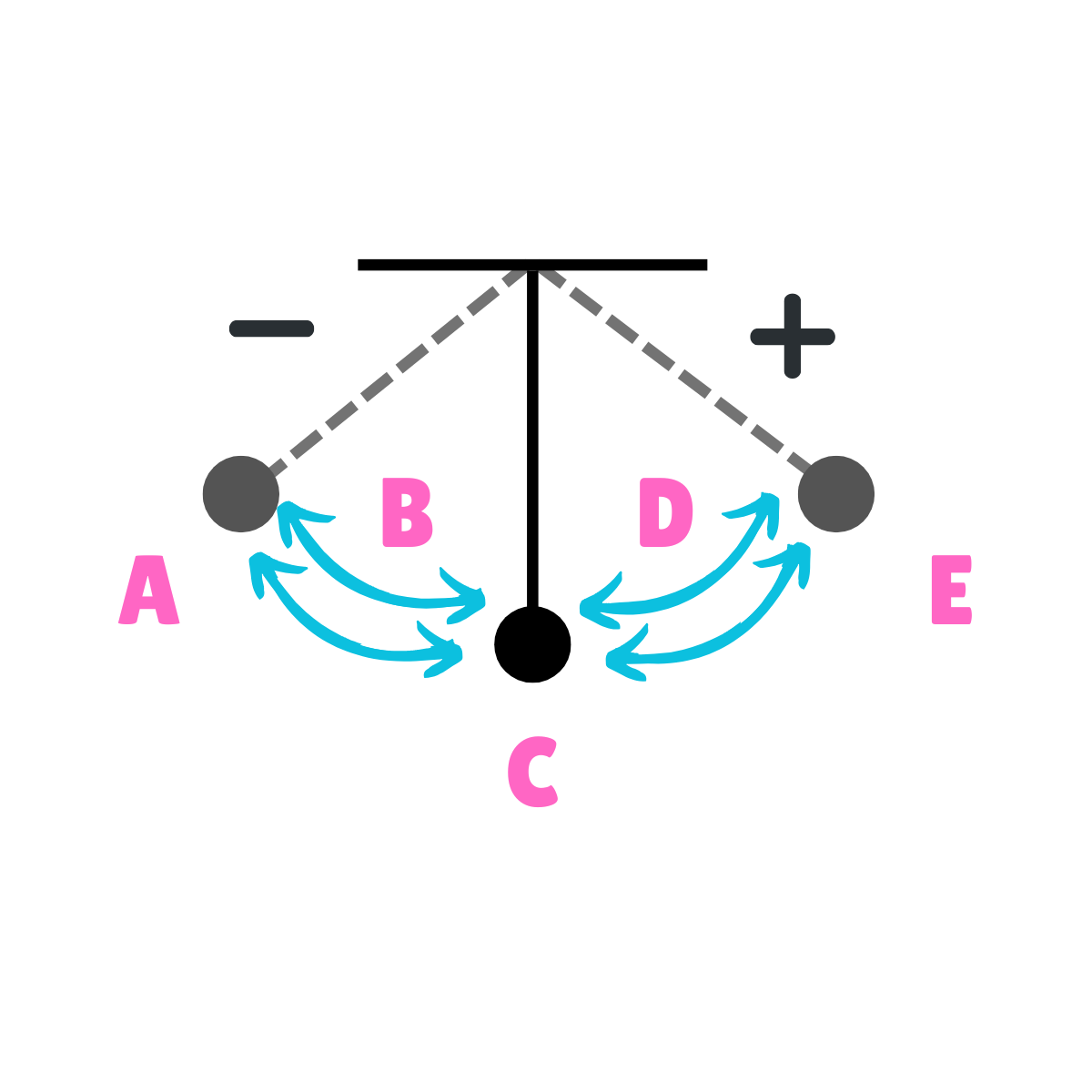
On this drawing, what does A represent regarding inertia?
Inertia at rest
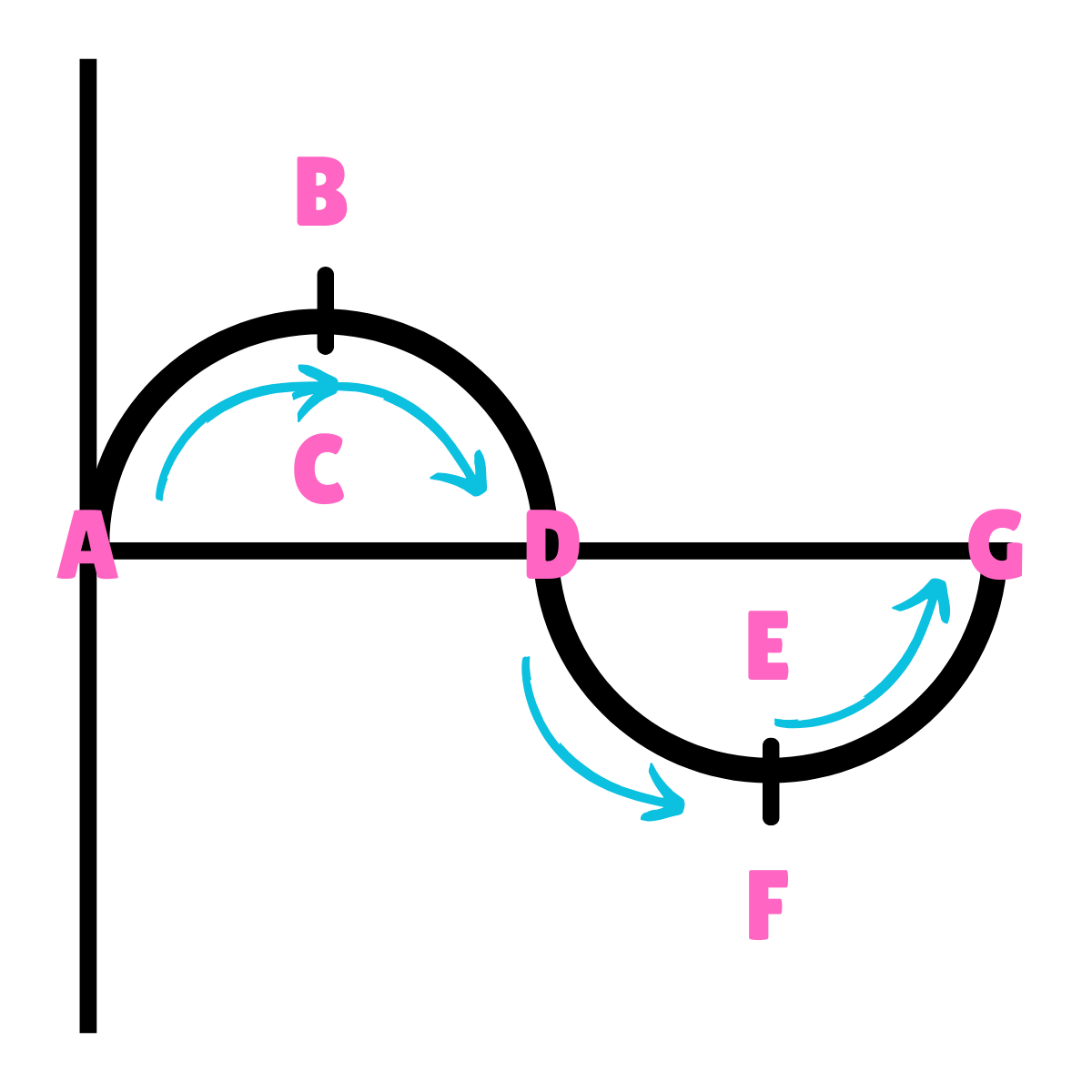
On this drawing, what does A or G represent regarding movement?
Equilibrium
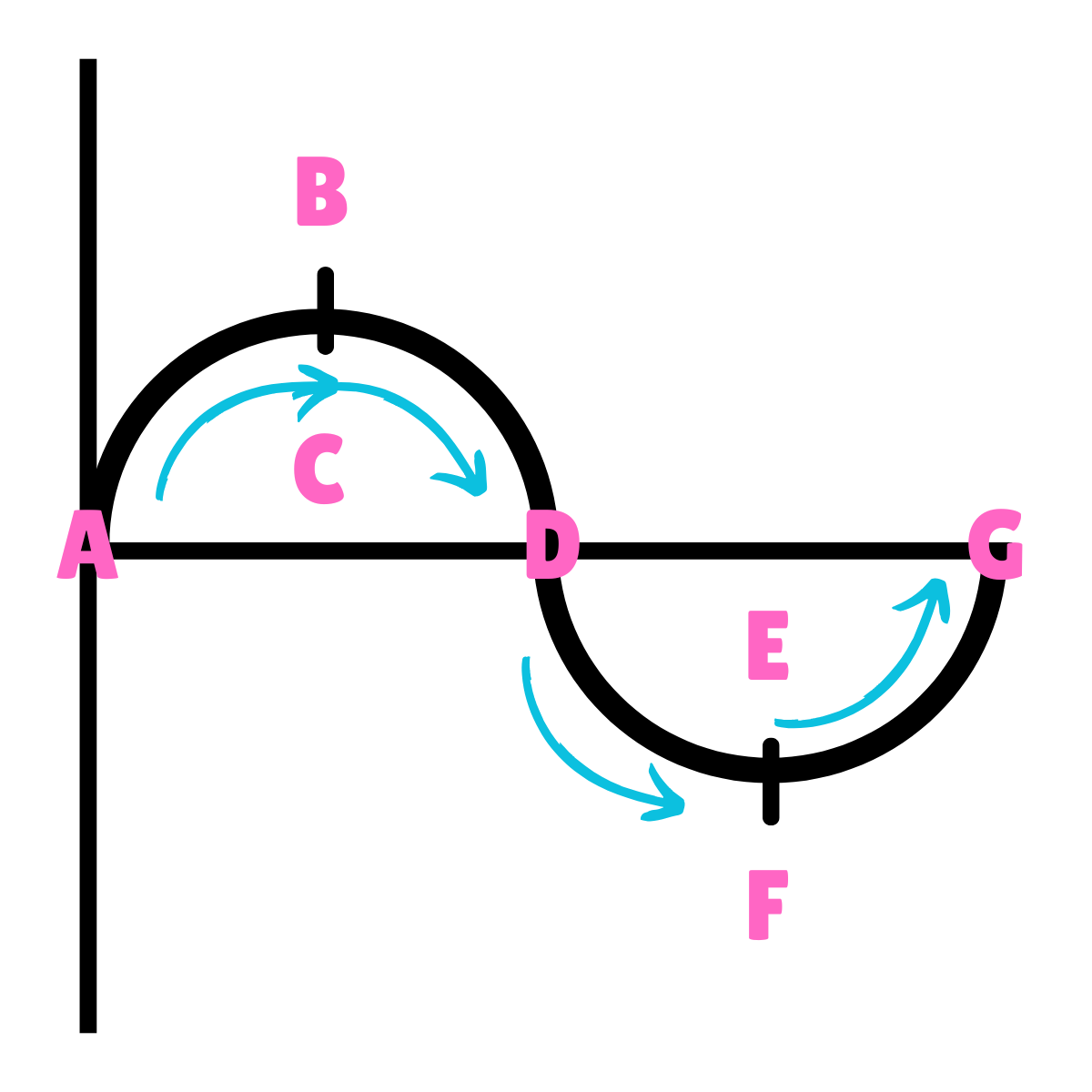
On this drawing, what does B or F represent regarding energy?
Potential Energy
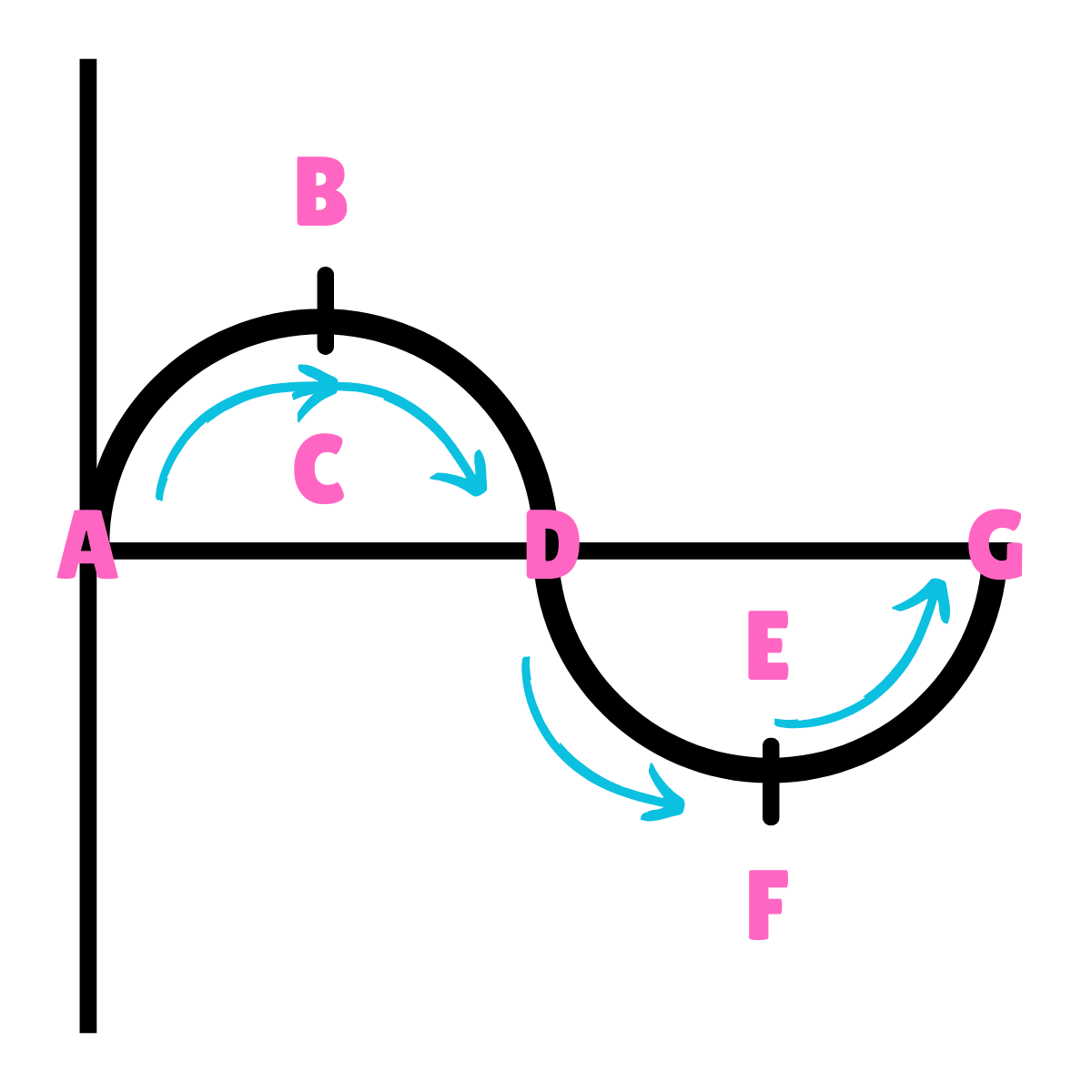
On this drawing, what does B or F represent regarding inertia?
Inertia at rest
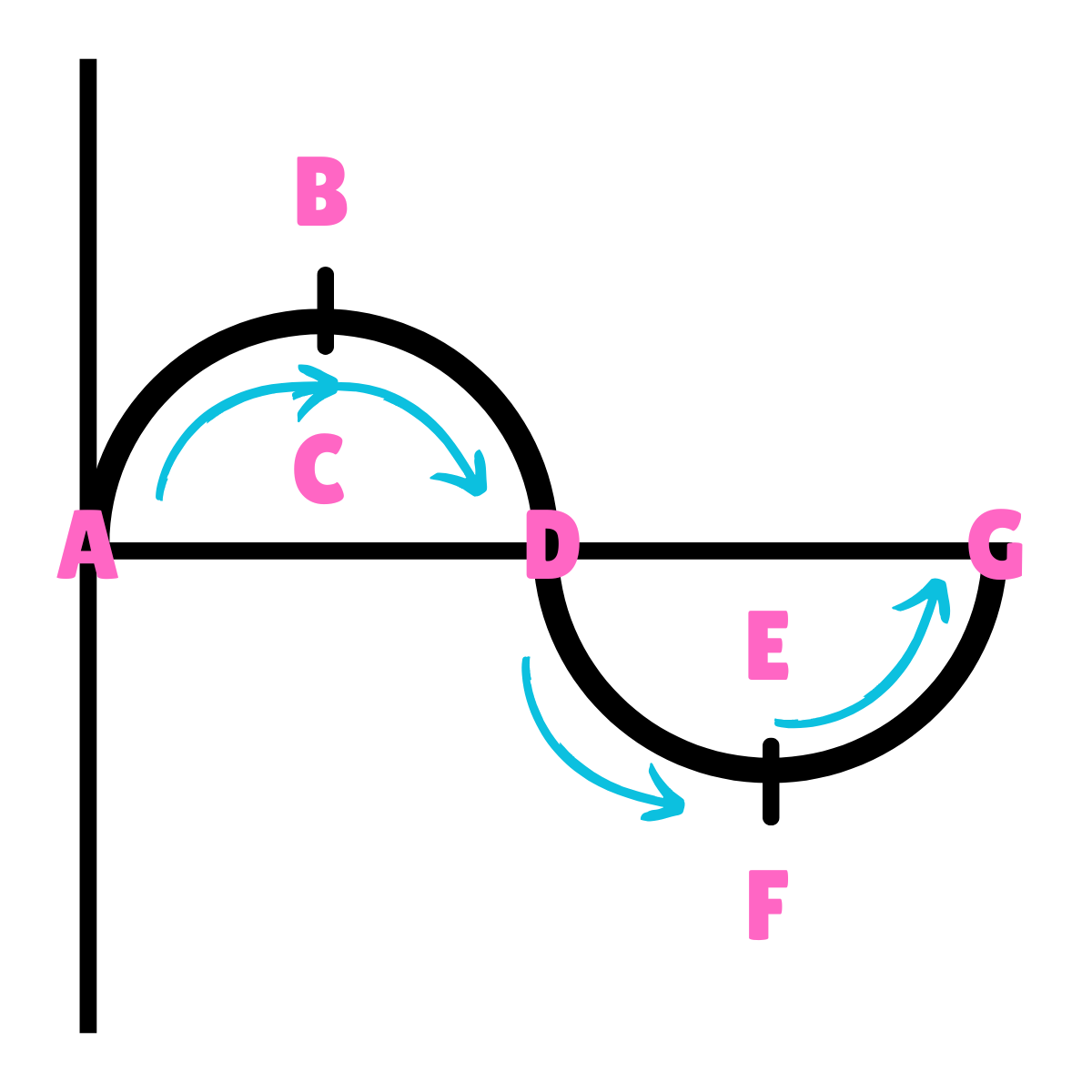
On this drawing, what does B or F represent regarding movement?
Max Displacement
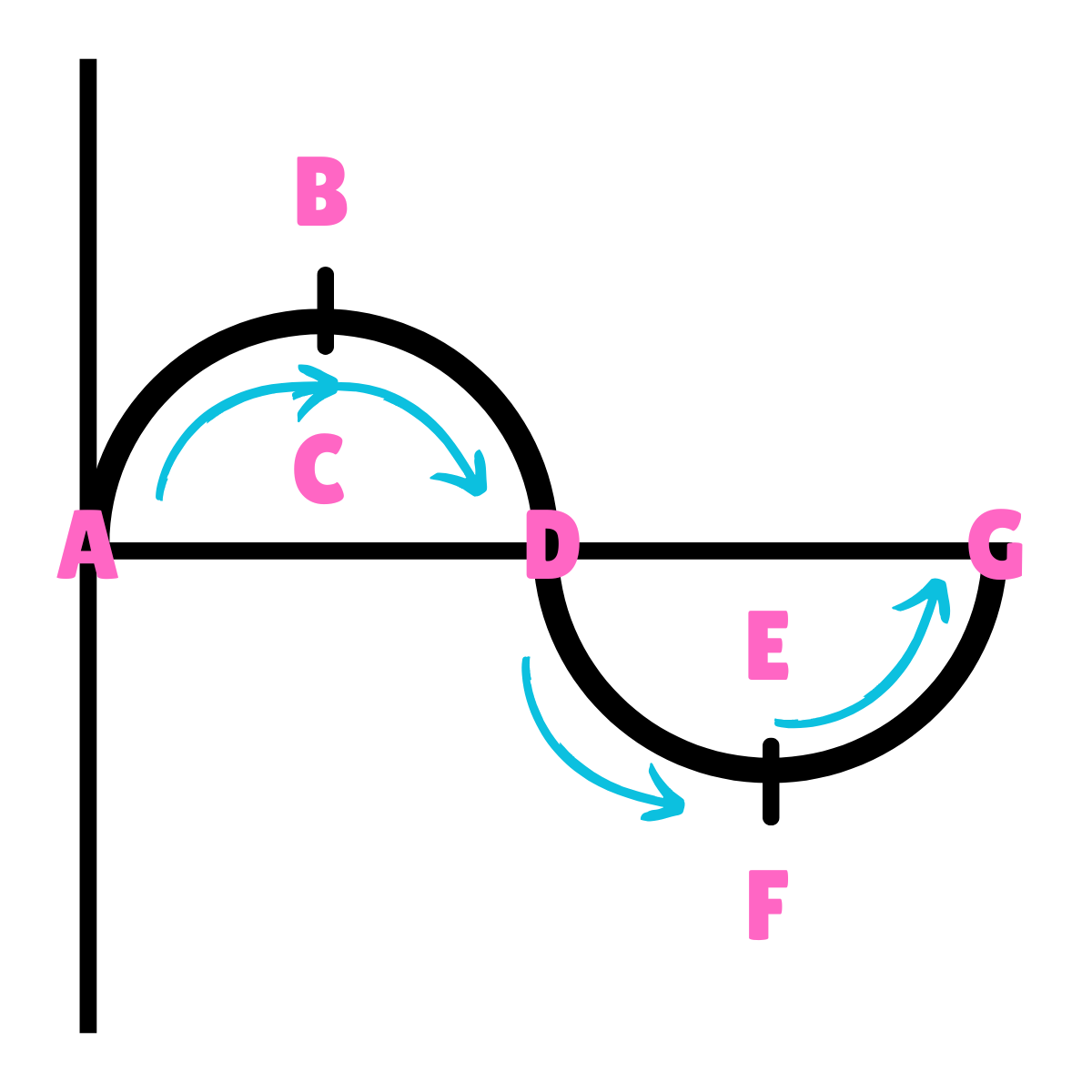
On this drawing, what does B or F represent regarding gravity?
The force of Gravity is greater than the force of inertia.
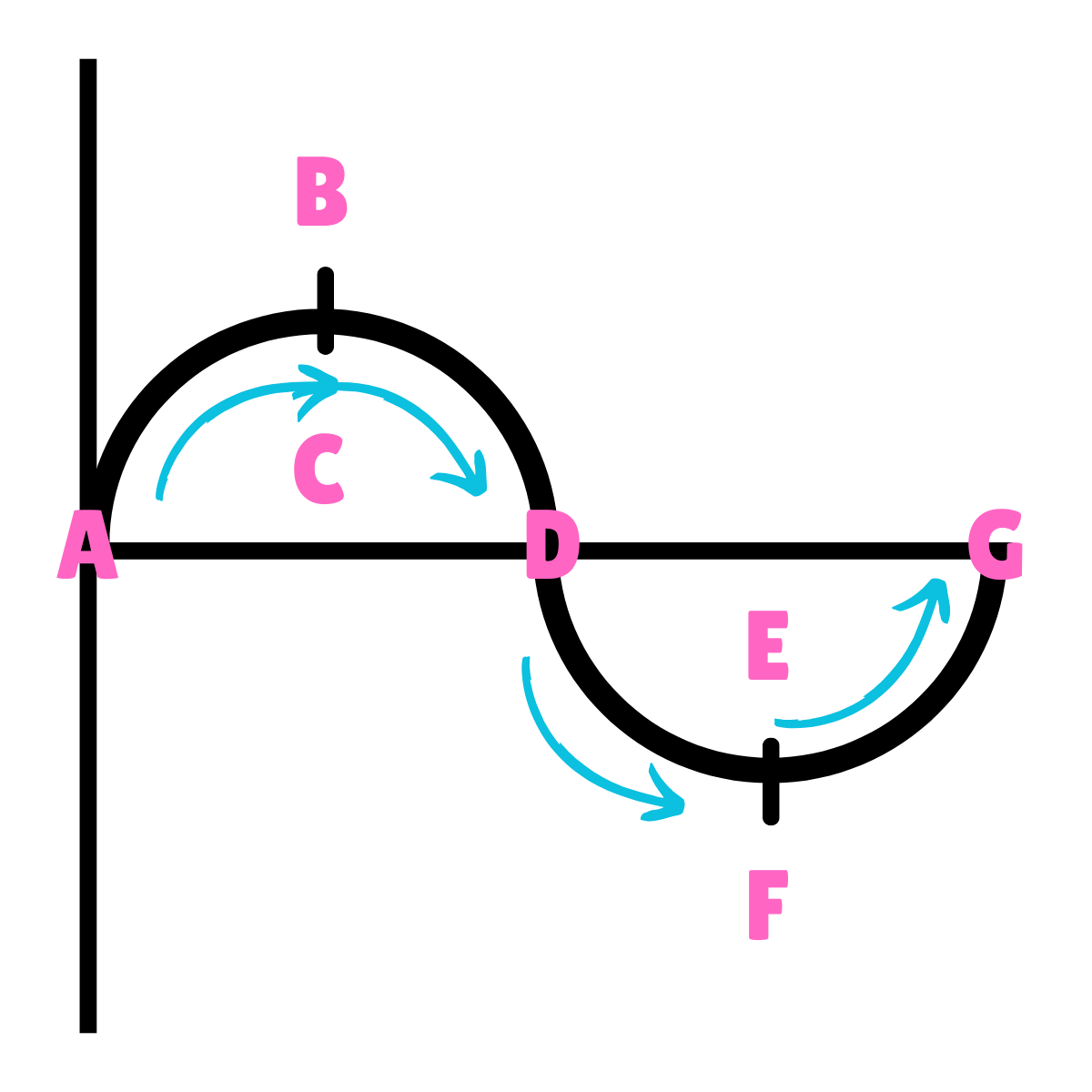
On this drawing, what does B or F represent regarding acceleration?
Maximum Acceleration
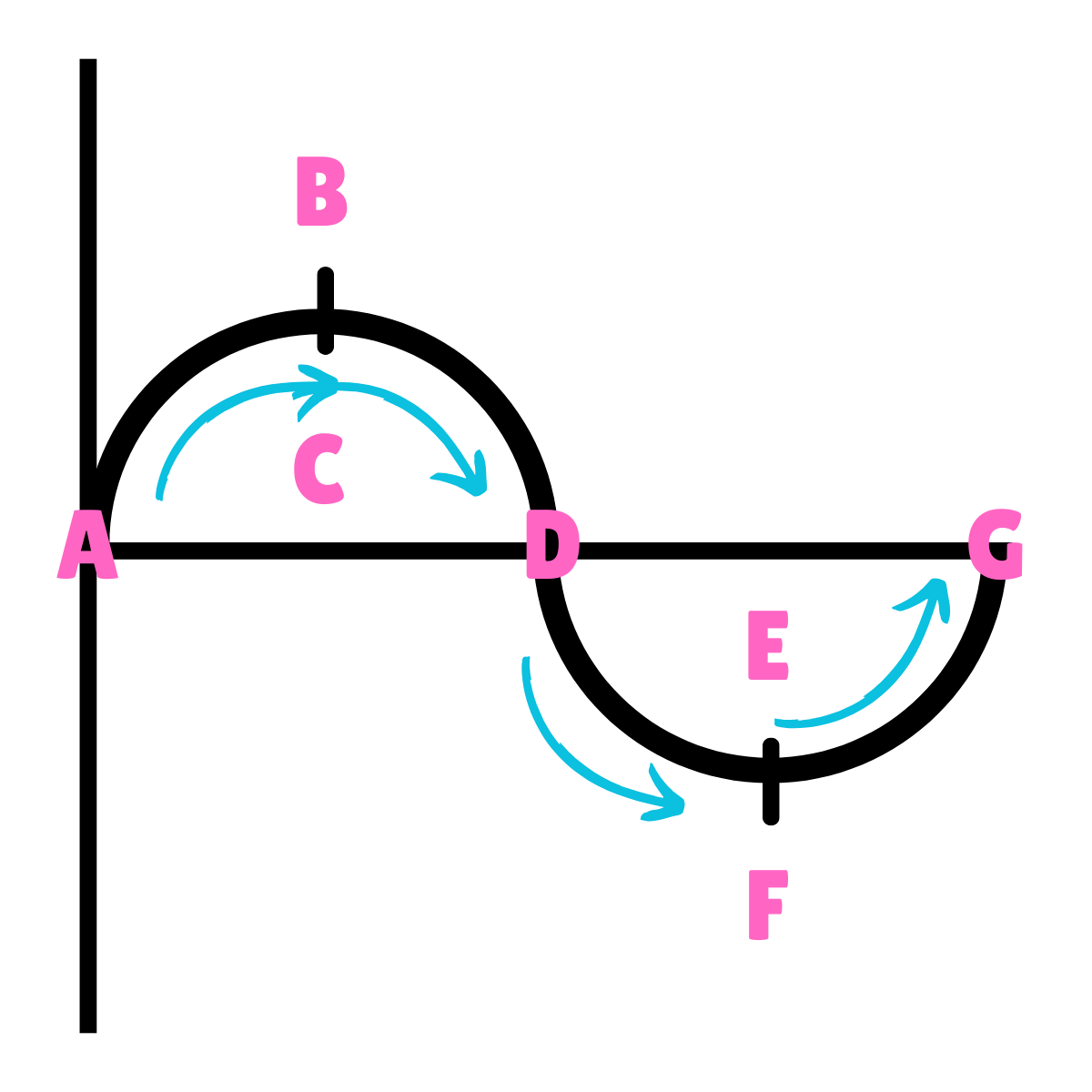
On this drawing, what does B or F represent regarding velocity?
Minimum Velocity
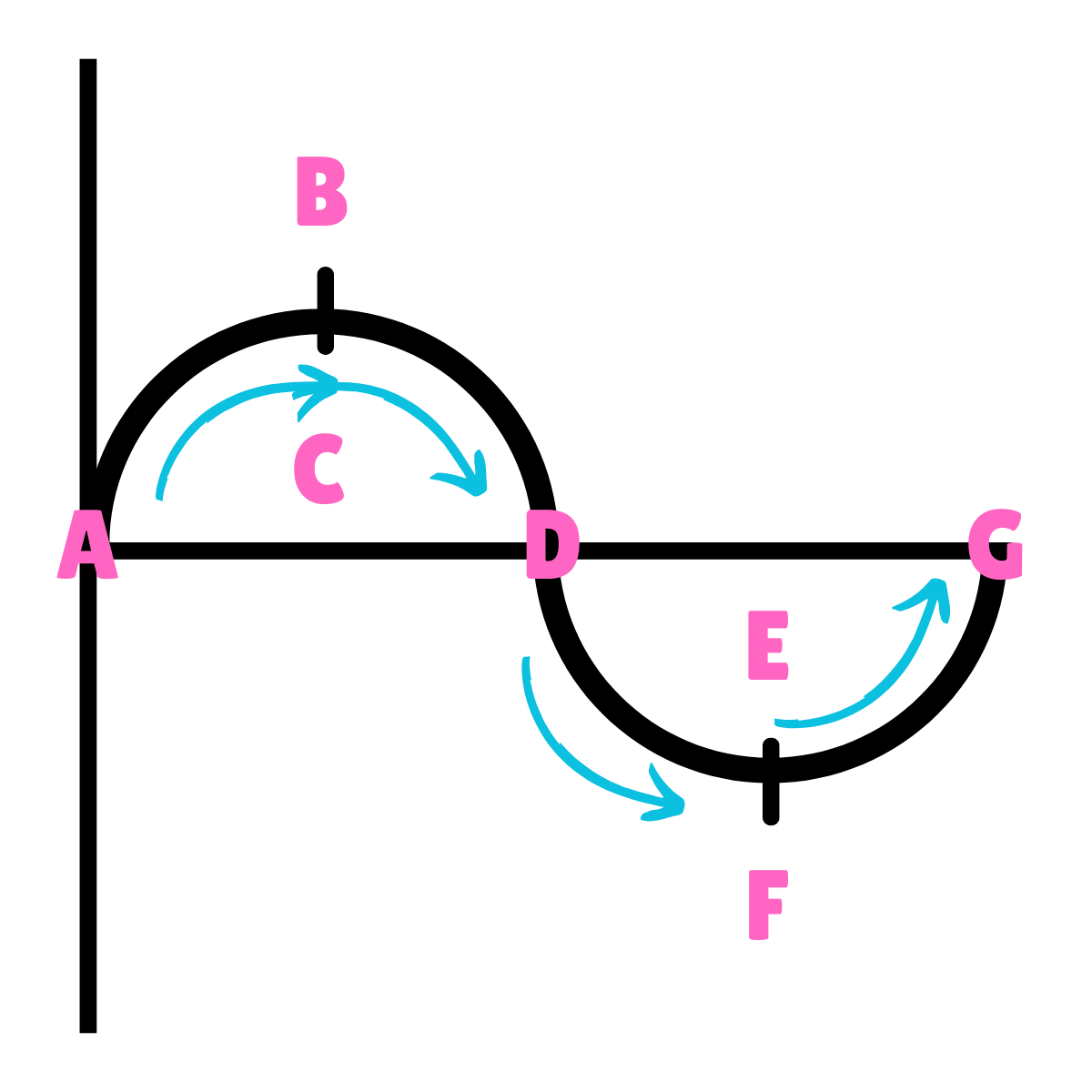
On this drawing, what does C or E represent regarding energy?
Kinetic Energy
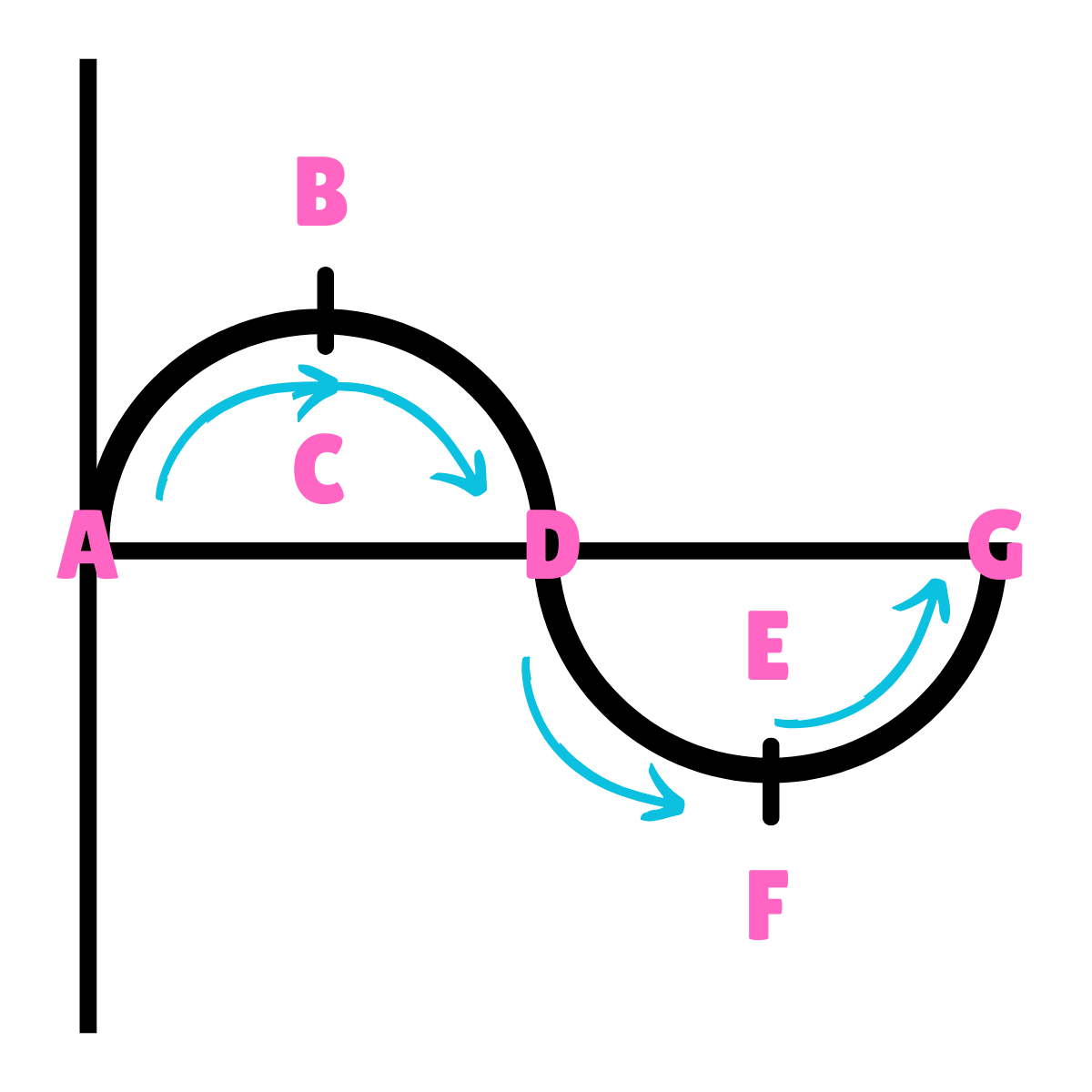
On this drawing, what does C or E represent regarding inertia?
Inertia in motion
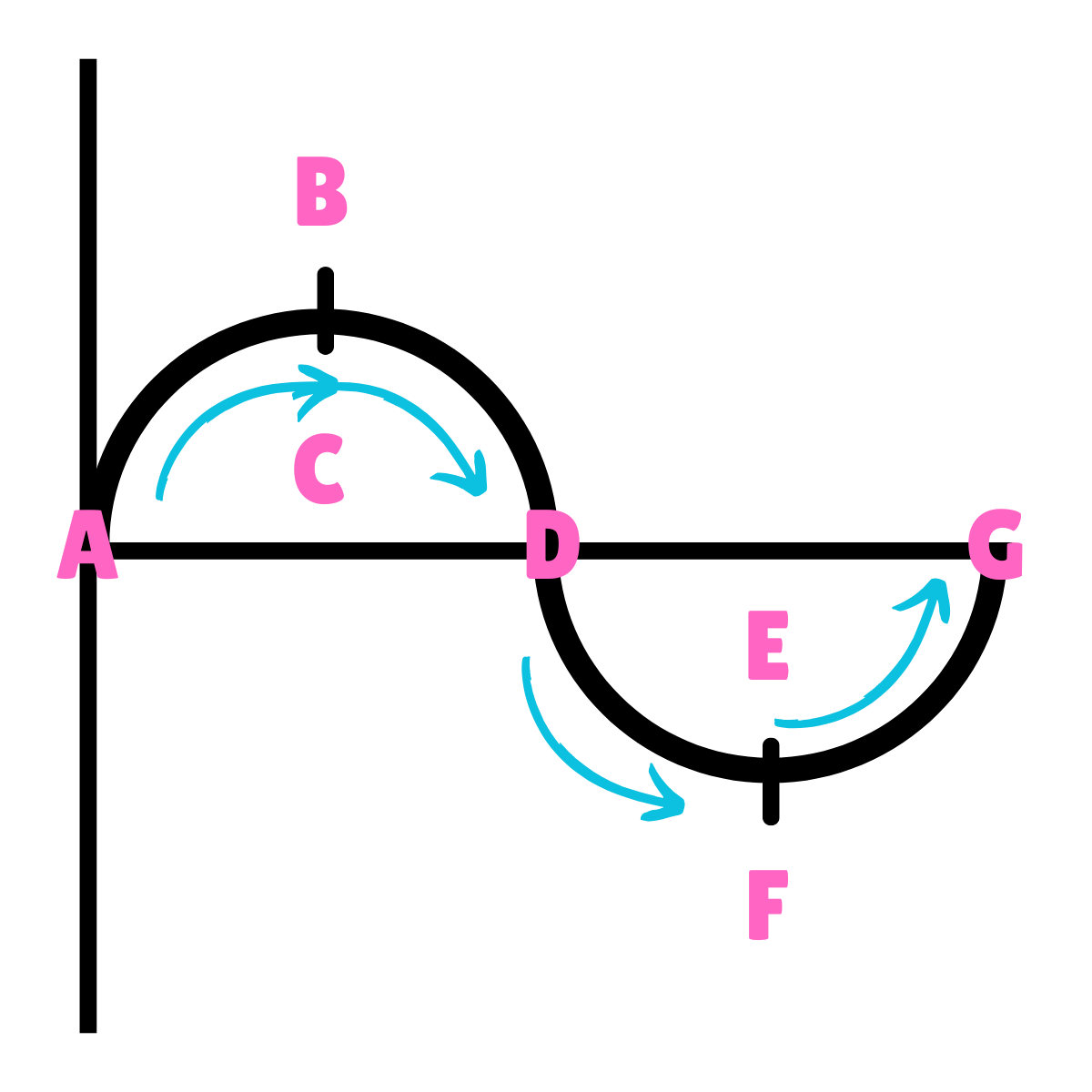
On this drawing, what does D represent regarding velocity?
Maximum Velocity
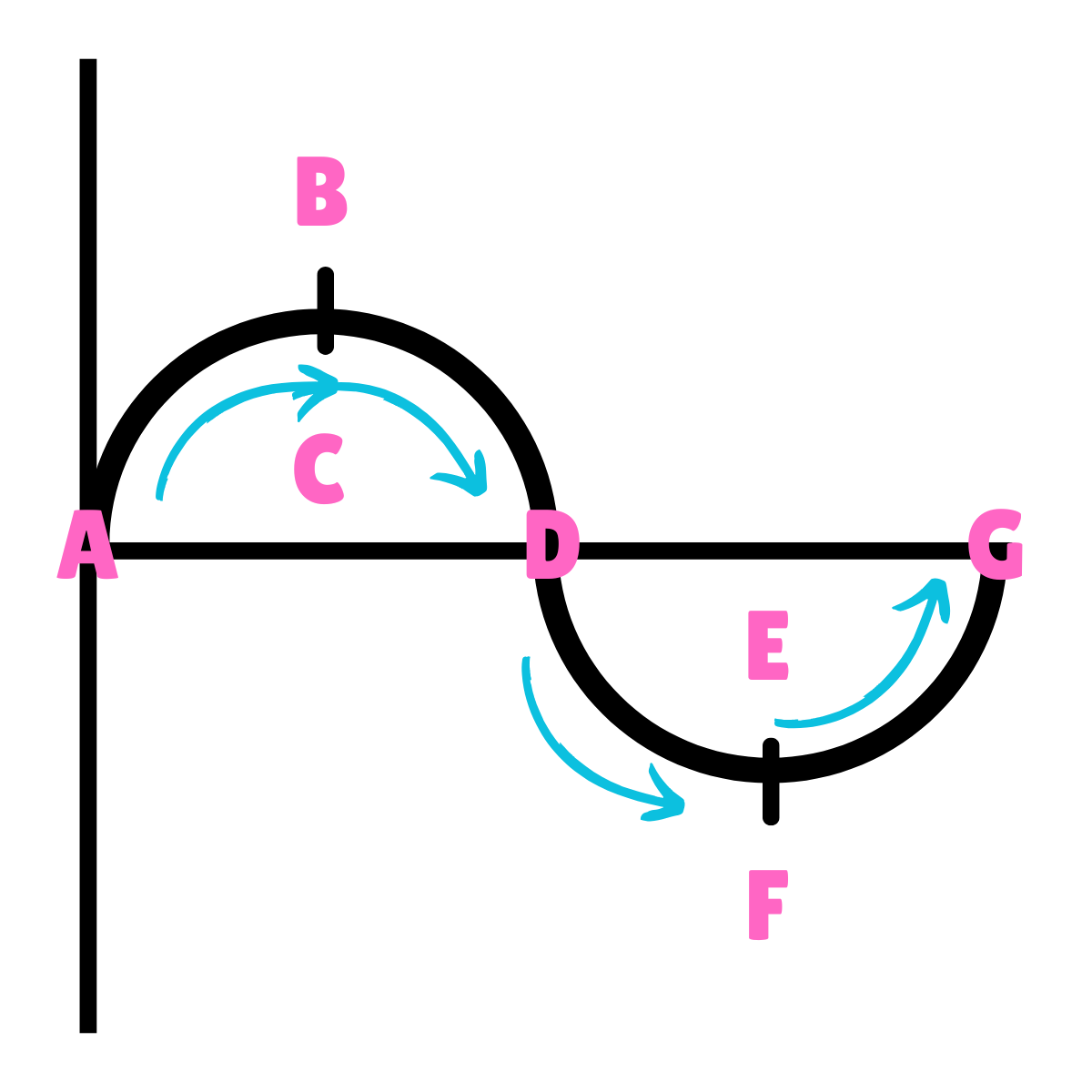
On this drawing, what does D represent regarding acceleration?
Minimum Acceleration
Define Cycle:
The movement from start to finish that can repeat (one complete sine-wave is a cycle).
“Peak, Trough, Stop!”
Define Waveforms:
Behavior of sound as a function of time.
How many times does a wavelength deal with equilibrium?
3 times.
Define Frequency:
The number of cycles per second, measured in Hz; physical measure of a sound.
What is the formula for frequency?
f = (# of cycles) / (time [seconds])
What must be converted when calculating frequency?
Time if it’s not automatically measured in seconds
Why is there maximum velocity and minimum acceleration on equilibrium?
It’s at a constant state of speed without slowing down or stopping.
Why is there minimum velocity and maximum acceleration on maximum displacement?
It is not at a constant state of speed, it’s slowing down or stopping.
Define Period:
The time it takes to complete one cycle of vibration.
What is the formula(s) for period?
T = (time [ms or seconds]) / (# of cycles)
OR
T = 1 / frequency
Define Phase:
Indicates a particular stage in the cycle of motion using the angles of the cycle.
One full rotation of the radius around the circle (0* to 360*) results in one completion of a ____ ____.
Sine wave.
What does it mean when the frequency is higher and the period is shorter in a sine wave?
It takes less time to complete that cycle.
What does it mean when the frequency is lower and the period is longer in a sine wave?
It takes more time to complete that cycle.
Define Phase Relationships:
They describe the difference between phases of two periodic waveforms.
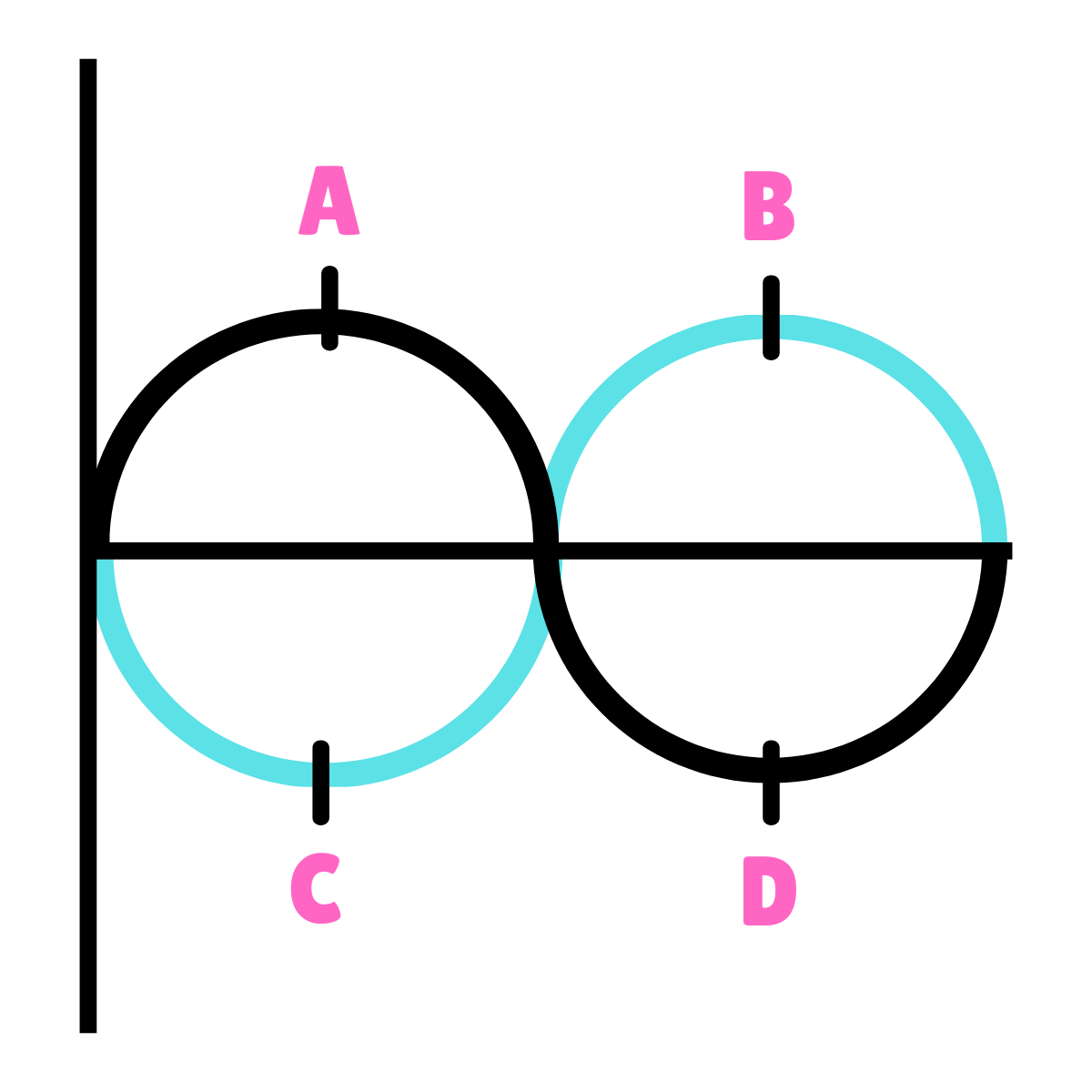
What type of phase relationship is this drawing representing?
180* Out-Of-Phase
They are mirror images; one starts at 0*, the other starts at 180*; adding these together could cancel them out.
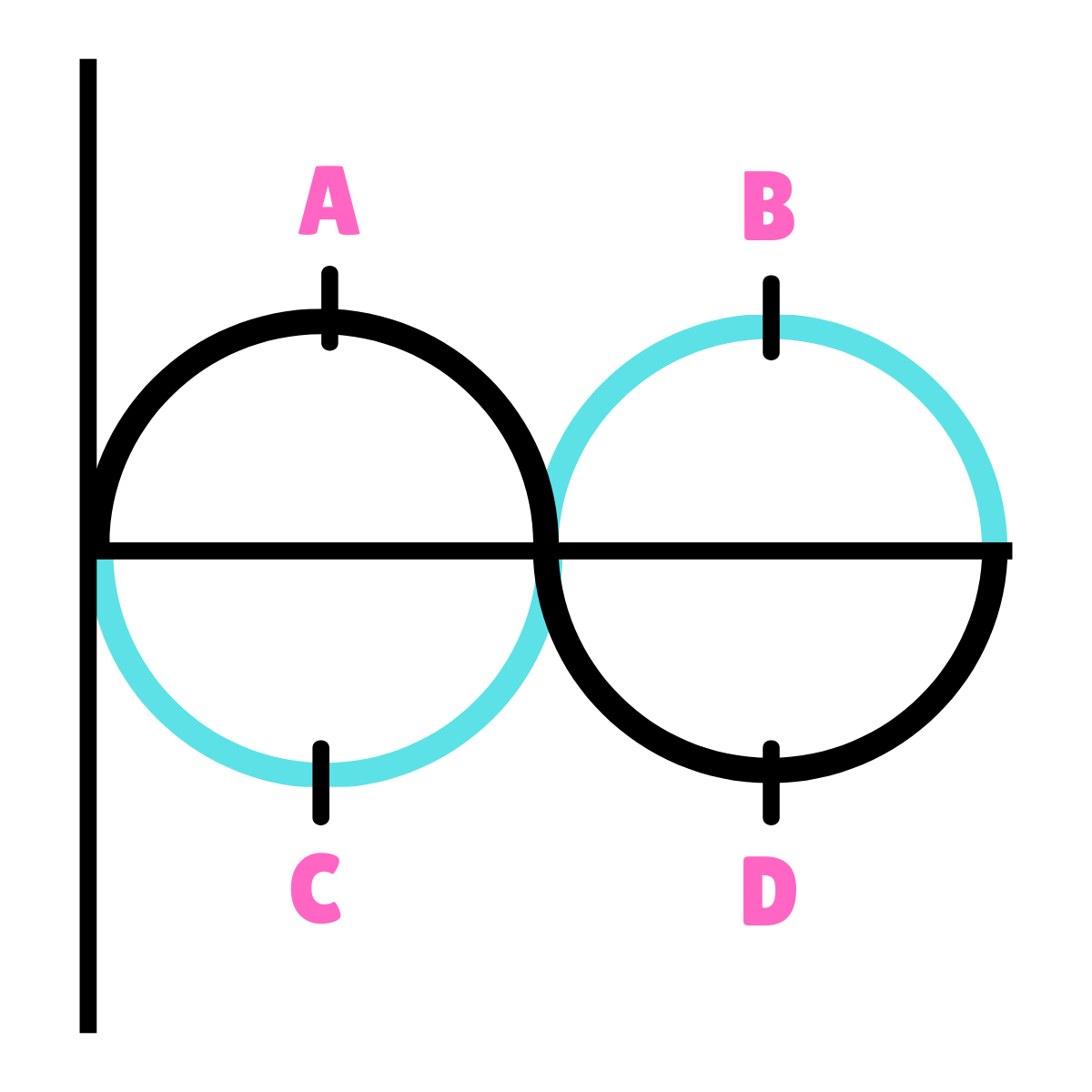
On this drawing, what do point A and B represent?
90*
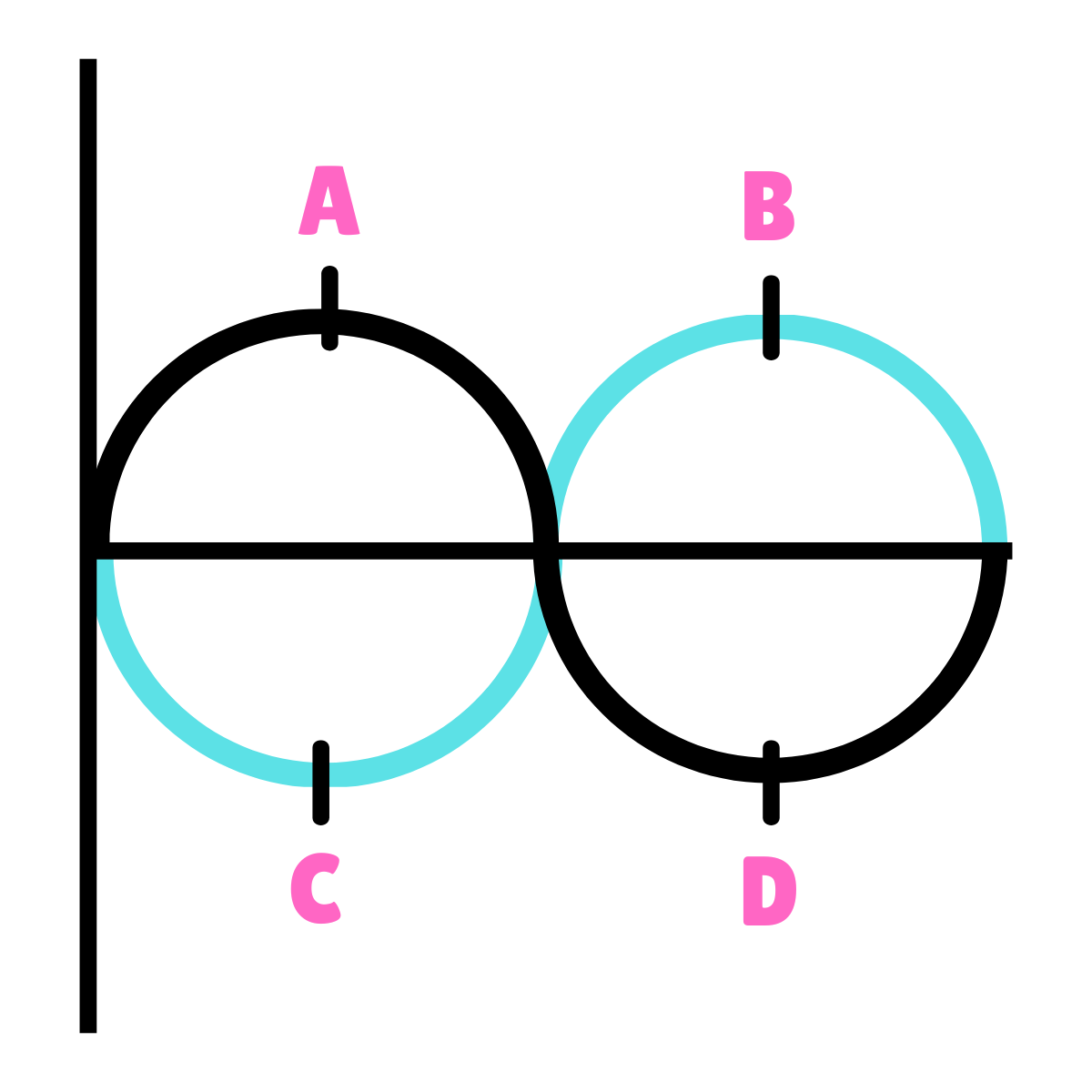
On this drawing, what does point C represent?
270*
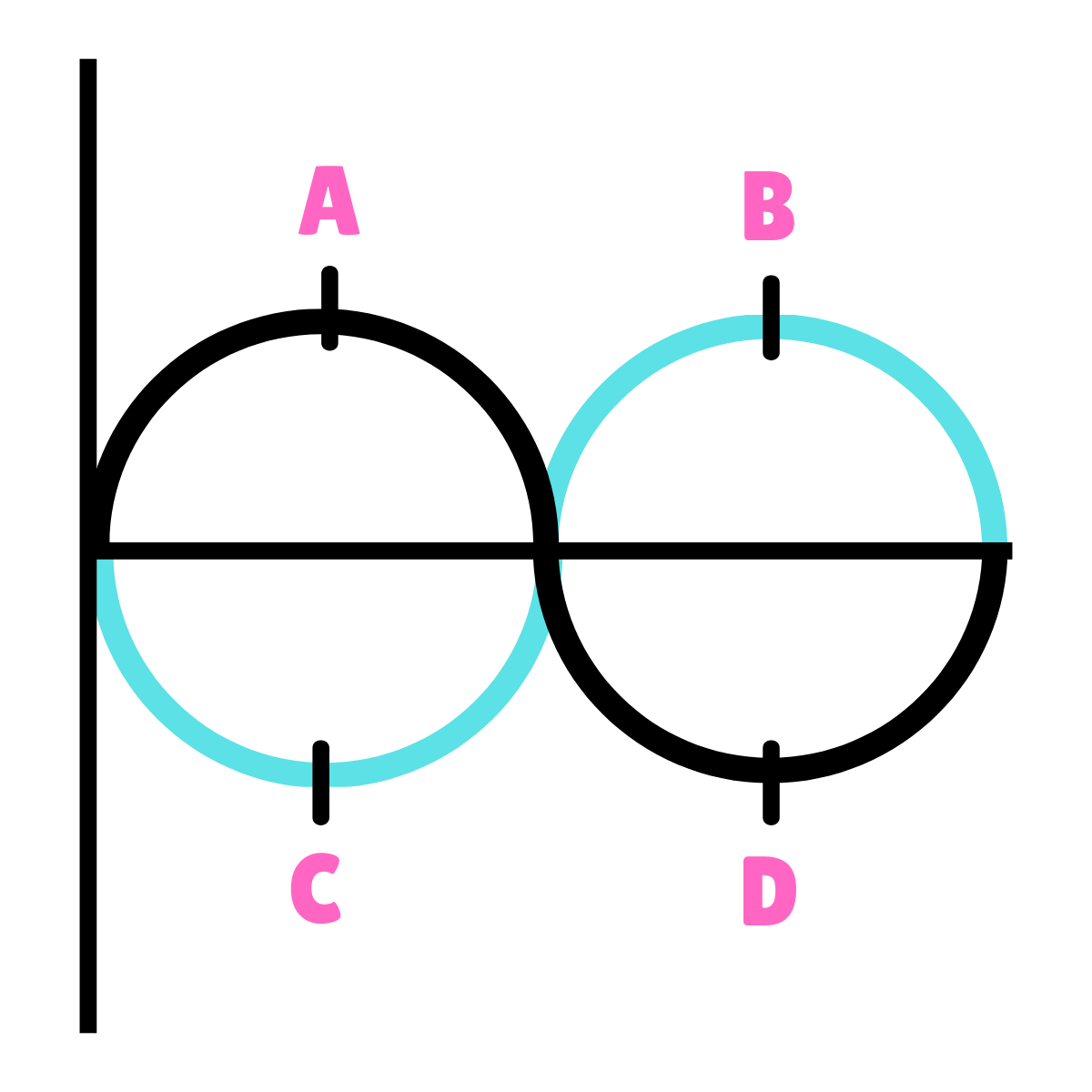
On this drawing, what does point D represent?
270*
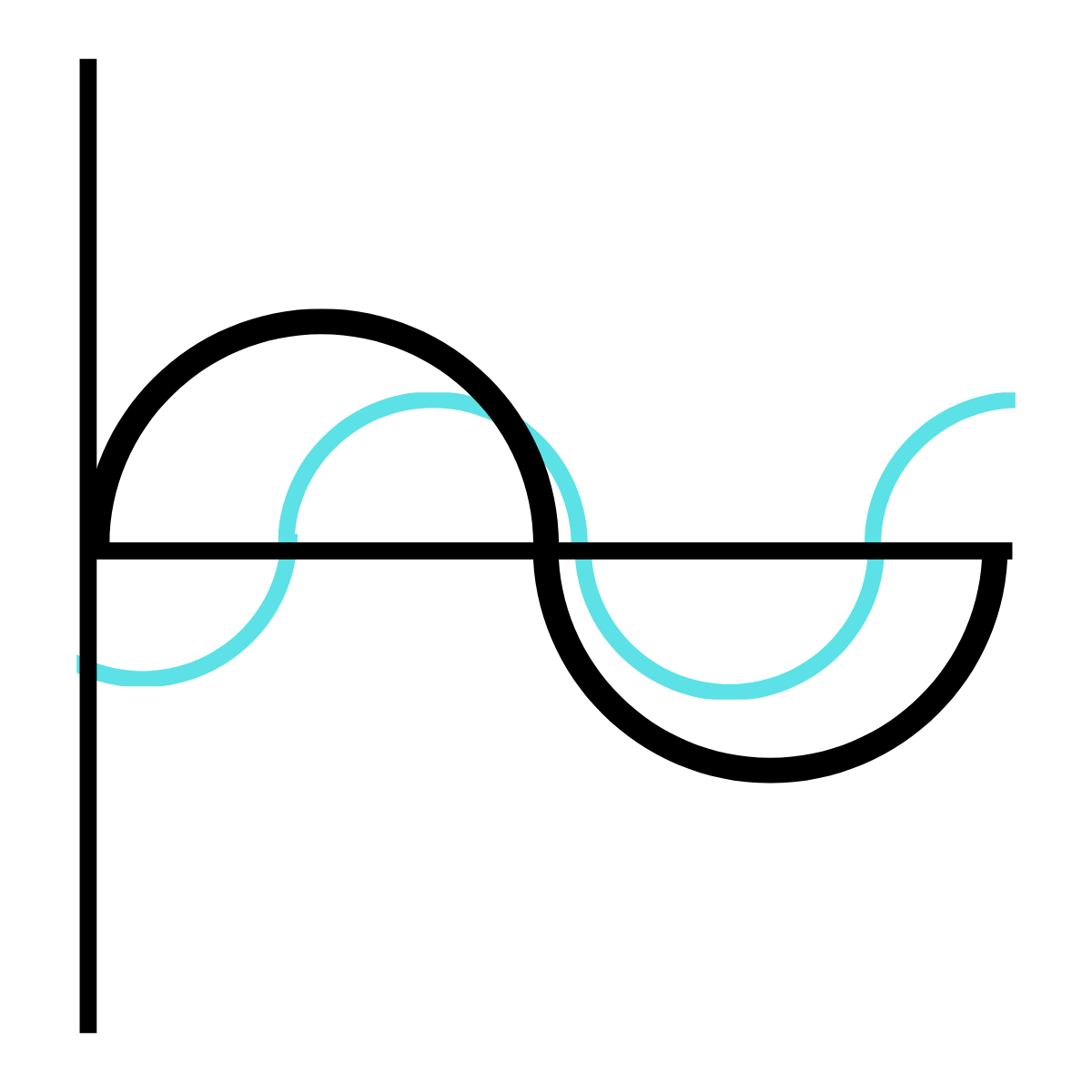
What type of phase relationship is this drawing representing?
Out-Of-Phase
They don’t start or cross equilibrium at the same time.
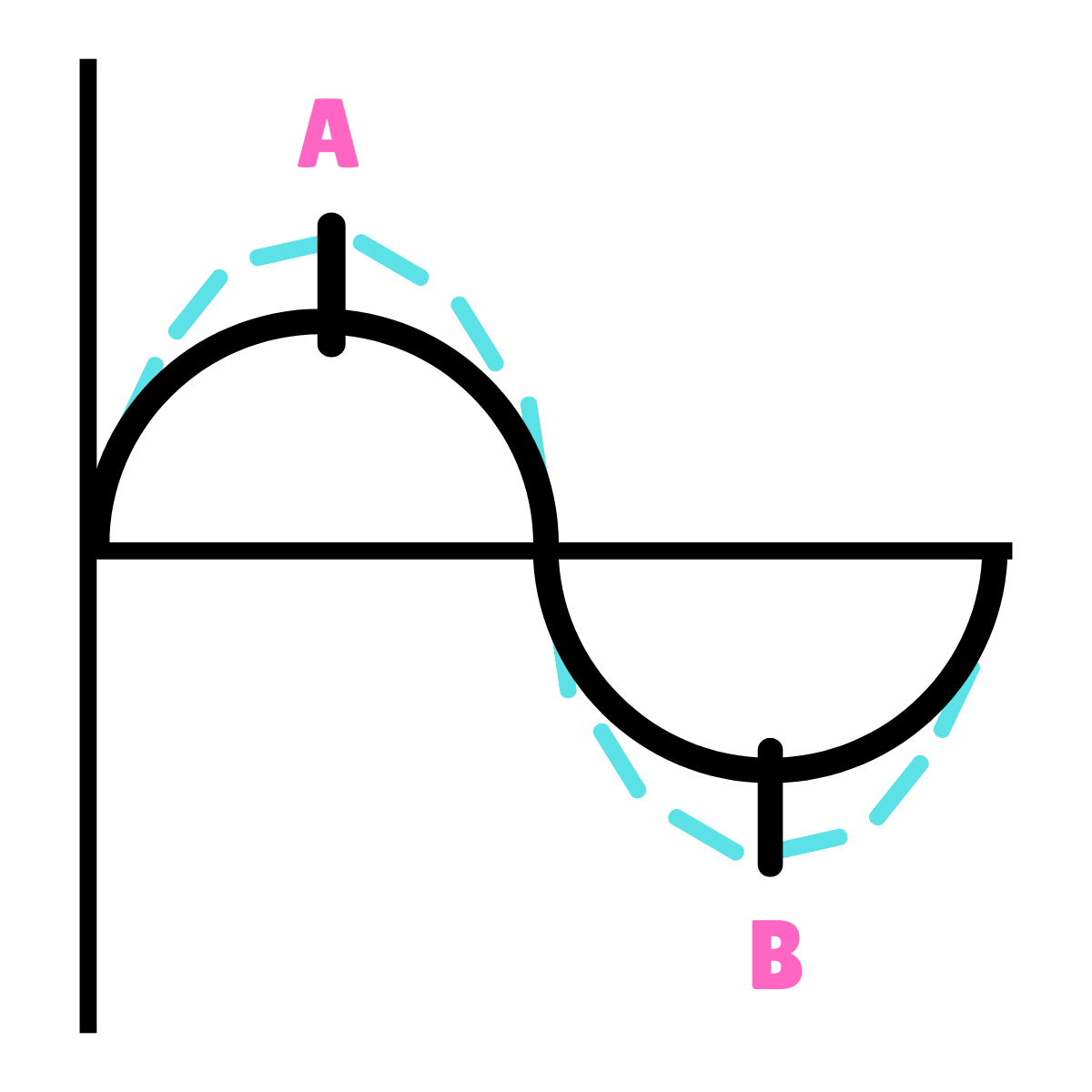
What type of phase relationship is this drawing representing?
In-Phase
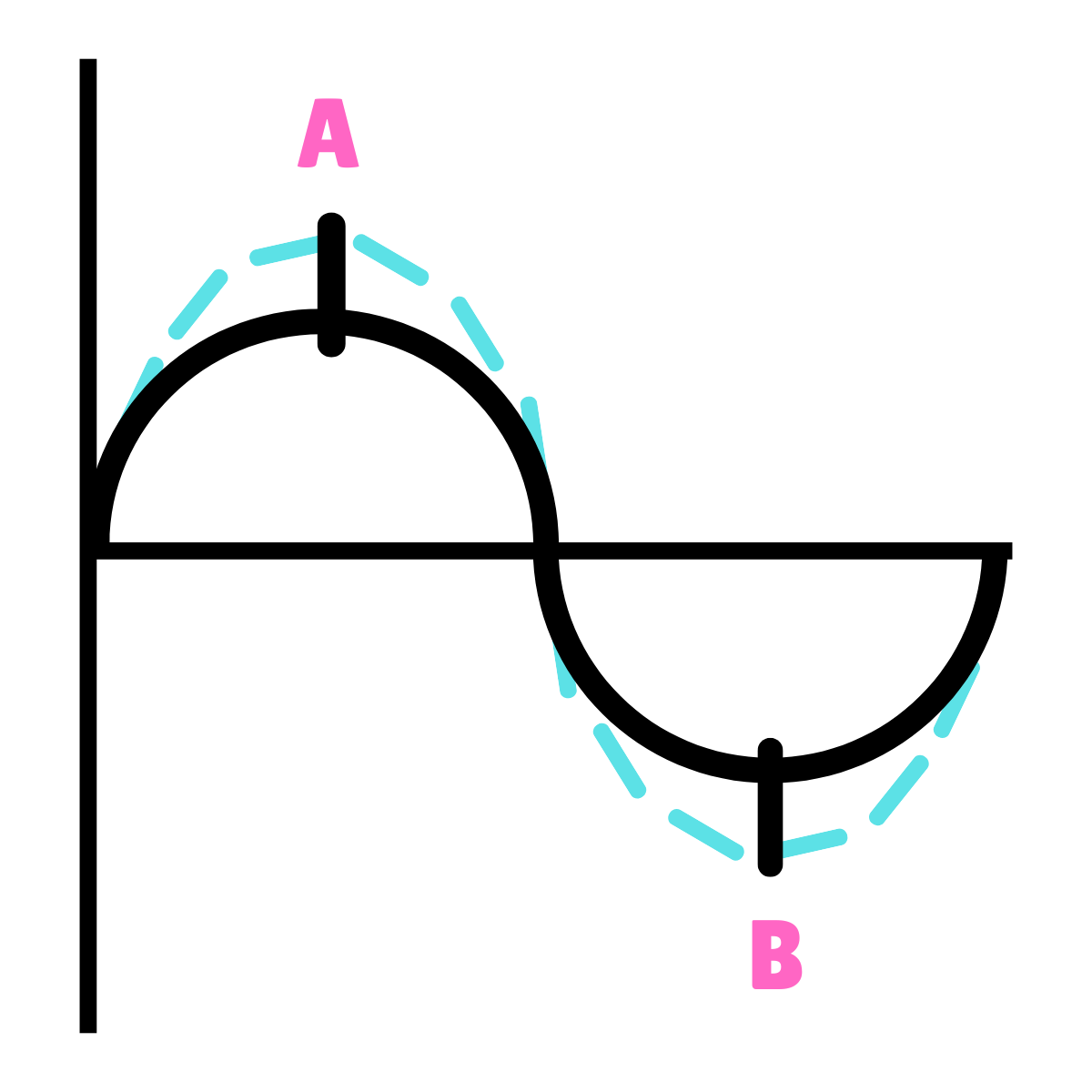
On this drawing, what does point A represent?
90*
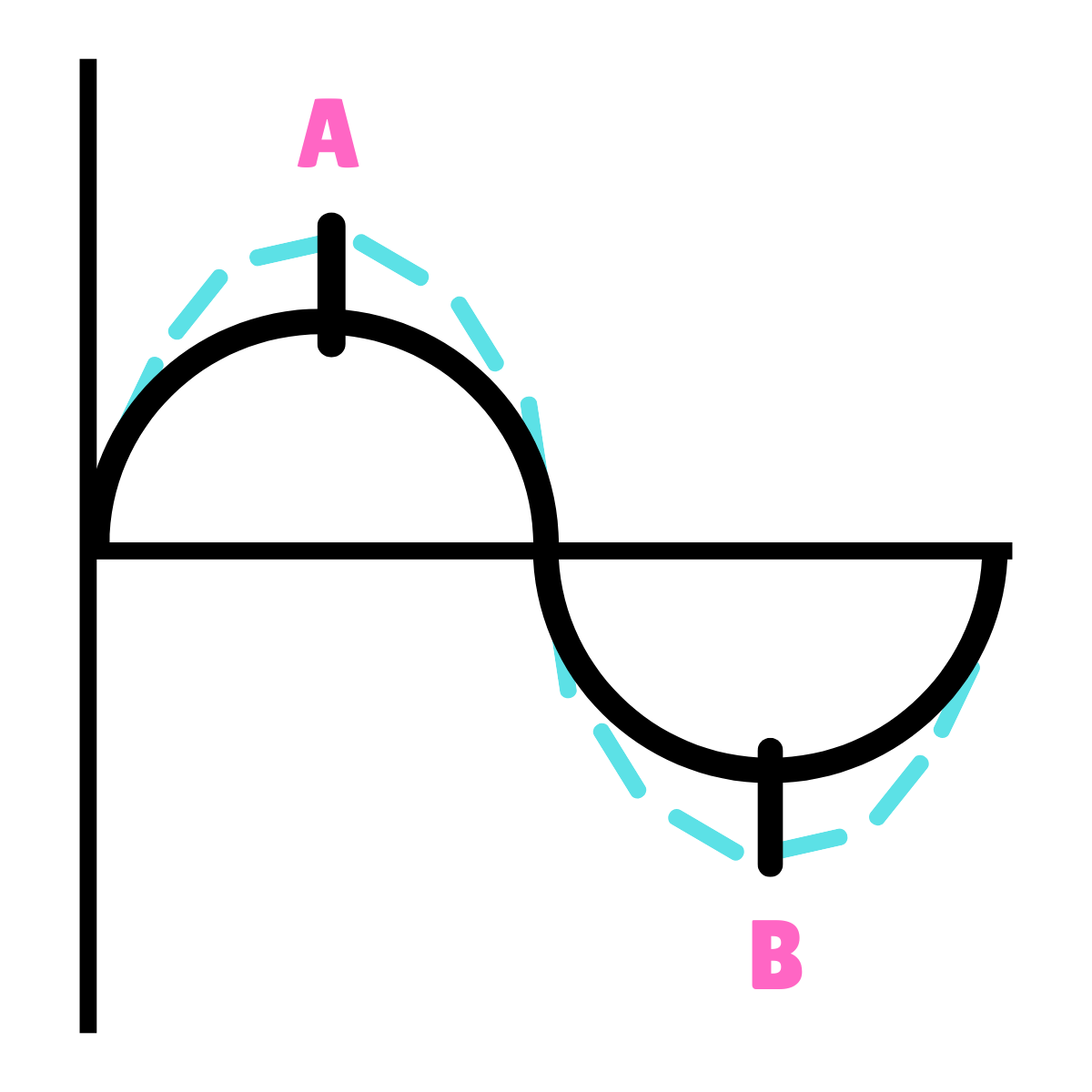
On this drawing, what does point B represent?
270*
Define Amplitude:
Maximum magnitude; using the y-axis to tell us how much.
“how loud”
Force + Power increases the intensity.
Define Peak-To-Peak Amplitude:
Range magnitude changes within one period.
What is the average magnitude for simple harmonic motion?
ALWAYS zero
Adding the peak and trough max displacements will always add to zero; one is positive (peak) and one is negative (trough).
How is amplitude measured?
From equilibrium to the next max displacement.
What does the mass and spring model represent?
The same sinusoidal motion as the pendulum.
What two forces interact to keep the mass and string vibrating once it’s displaced?
Elasticity and Inertia
The spring itself keeps the object in motion, not gravity; it also dictates how far the spring can compress or stretch.
Why does the mass and spring model eventually stop?
Internal Friction
The more _____ applied to the system, the more my ____ is displaced from equilibrium, thus bigger vibration and a larger _________.
Force ; Mass ; Amplitude
This is the same as turning up the volume on a radio.
Force influences the amplitude of vibration, NOT _________ of vibration.
Frequency.
If the mass and stiffness is constant, but the force is changed, what happens?
The amplitude changes.
If force is increased, the amplitude increases.
If force is decreased, the amplitude decreases.
If the force and stiffness is constant, but the mass is changed, what happens?
The frequency changes.
If mass is increased, the frequency decreases.
If mass is decreased, the frequency increases.
Why does the frequency change if the mass changes but everything else remains the same?
Heavier mass can take more time, and it can stretch further to achieve equilibrium; (and vis versa) smaller masses can take less time and can stretch less distance to achieve equilibrium.
If the mass and force is constant, but the stiffness is changed, what happens?
The frequency changes.
If stiffness is increased, the frequency increases.
If stiffness is decreased, the frequency decreases.
Why does the frequency change if the stiffness changes but everything else remains the same?
The more stiff of a spring, the more resistant it is to changing it’s equilibrium.
The stretchier it is, the further from ___________ it can travel.
Equilibrium
What is the only thing that changes amplitude?
The amount of force applied.
Describe why three different sine waves can have the same frequency.
Although the different sign waves are amplified differently, they still hit all phase angles on each peak, trough, and equilibrium at the same time, i.e. 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, and 360º.