Biochem: Fatty Acids
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Lipids (Overview)
-can be extracted from cells via nonpolar solvents
-associate with each other when put in water => decreases entropy
-stored as triglycerides as energy
-used in lipid membranes
-used to modify proteins
-can be signaling molecules
-two major classes = Isoprenoids & Fatty Acids
> isoprenoids--> bile acids/salts, membranes, hormones, cofactors, fat soluble vitamins
> fatty acids --> carboxyl group + unbranched hydrocarbon chains
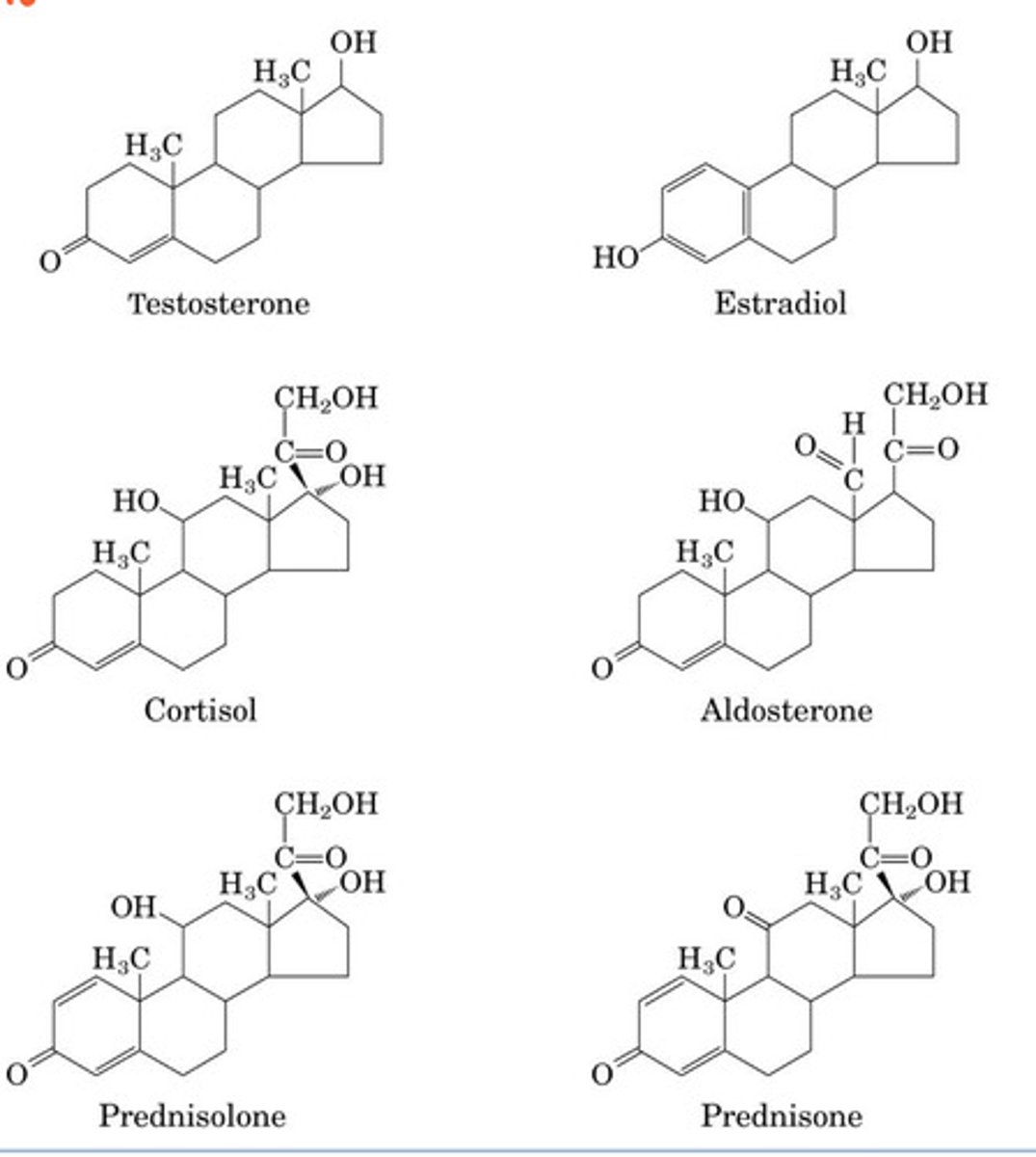
Isoprenoids
Major class of lipids that are made out of isoprene unit
-Bile acids/salts
-membranes
-hormones --> testosterone, estradiol, cortisol, aldosterone, prednisolone, prednisone
-cofactors
-fat soluble vitamins
Fatty Acids
major class of lipids that have a carboxyl group + hydrocarbon chain
-alpha carbon = the carbon next to the carboxyl group (C2)
*alpha nomenclature --> count carboxyl C as #1
-omega carbon = the last carbon in the chain
*omega nomenclature --> count the omega C as #1
-amphipathic due to carboxyl group @ neutral pH
>forms micelles in water
>soaps
-fat deposits for energy storage, cushion organs, & insulate against heat loss
-electrical insulation of nerves
-signaling molecules
-in membranes (phospholipids & sphinolipids)
Long Chain Fatty Acids
FA w/ more than 12 C
-absorbed in small intestine
-enter circulation via subclavian vein
Medium Chain Fatty Acids
FA w/ 6-12 C
-enter circulation via the portal vein (like carbohydrates) = a readier fuel source
-broken down by lipase easier
-produced in the mammary gland
-used to Tx waldmann disease, epilepsy, chronic pancreatitis
Short Chain Fatty Acids
FA w/ less than 6 C
-produced by microbiome in colon ==> coloncytes use for energy (make up 80% of all the energy sources colon cells use)
-small enough to cross BBB
-make up 6-10% of the total energy sources used
True or False: At acidic pH fatty acids act as soaps
False ===> FA are soaps at neutral pH
FA Symbol (Alpha Nomenclature)
#C : # double bonds
-# before colon = carbon chain length
-# after the colon = # of double bonds in chain
-superscript = list of double bond positions
ex: 18:0 = octadecanoic acid
Omega Number
number of carbons from the terminal methyl carbon to the nearest double bond
= (# of C) - (C # of the last double bond)
*can get the answer by either counting back from omega carbon or from the equation above
Linoleic & Linolenic Deficiency
Linoleic & Linolenic are essential fatty acids b/c they are a precursor to a lot of important signaling molecules
* deficiency =
-scaly dermatitis
-alopecia (hair loss)
-thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
- low cognitive development in children
Melting Point of Fatty Acids (Overview)
- mp of uncharged FA increases with increasing chain length
> increased stability due to increased van der waals interactions
- saturated FA mp > trans FA mp > cis FA mp
Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC)
concentration at which FA begin to form micelles in water.
*FA are solube at very very low conc., this is the point where they stop being soluble
lysophospholipid
lipids that form spherical detergents (phospholipids with only 1 FA chain)
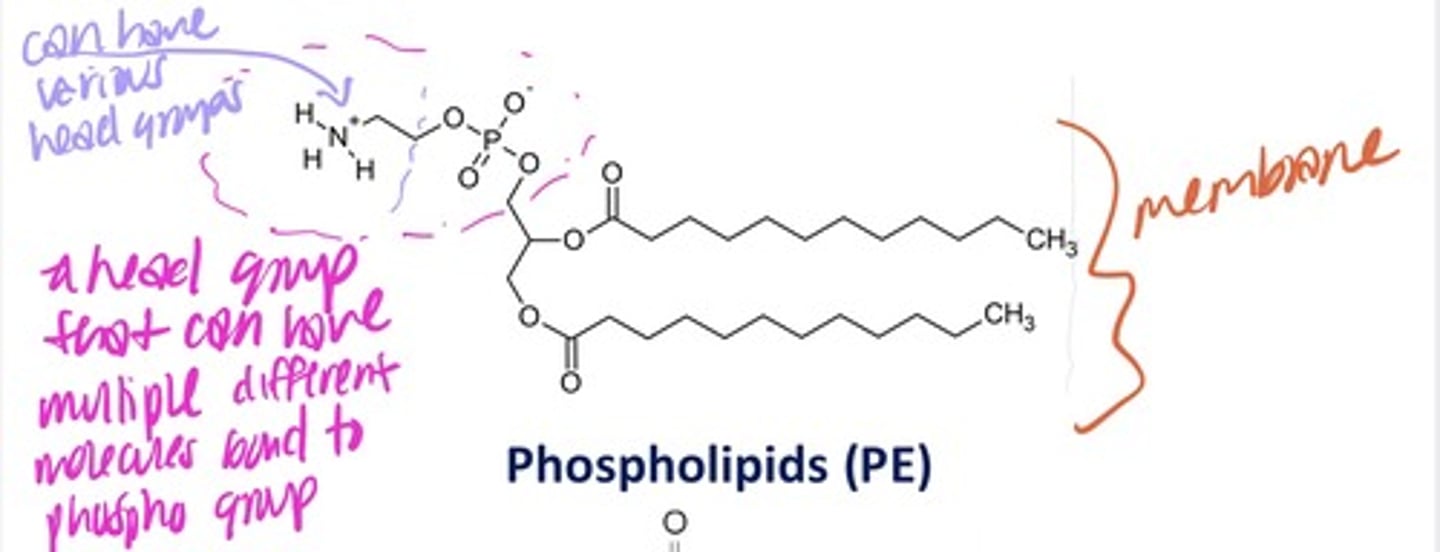
Phospholipids
-geometry made to create sheets (phospholipid bilayer)
-based on glycerol
-can have different head groups by having different molecules bond to phospho group
Triglycerides
(Triacylglycerols TAG)
3 fatty acids esterified to glycerol
* storage form of FA
monoacyl glycerol (MAG)
1 FA chain esterified to glycerol
diacyl glycerol (DAG)
2 FA chains esterified to glycerol
True or False: Lipid concentration on one side of membrane bilayer must equal the lipid concentration on the other side
False ==> lipid conc on one sidfe doesn't have to equal the conc other side (& doesn't usually)
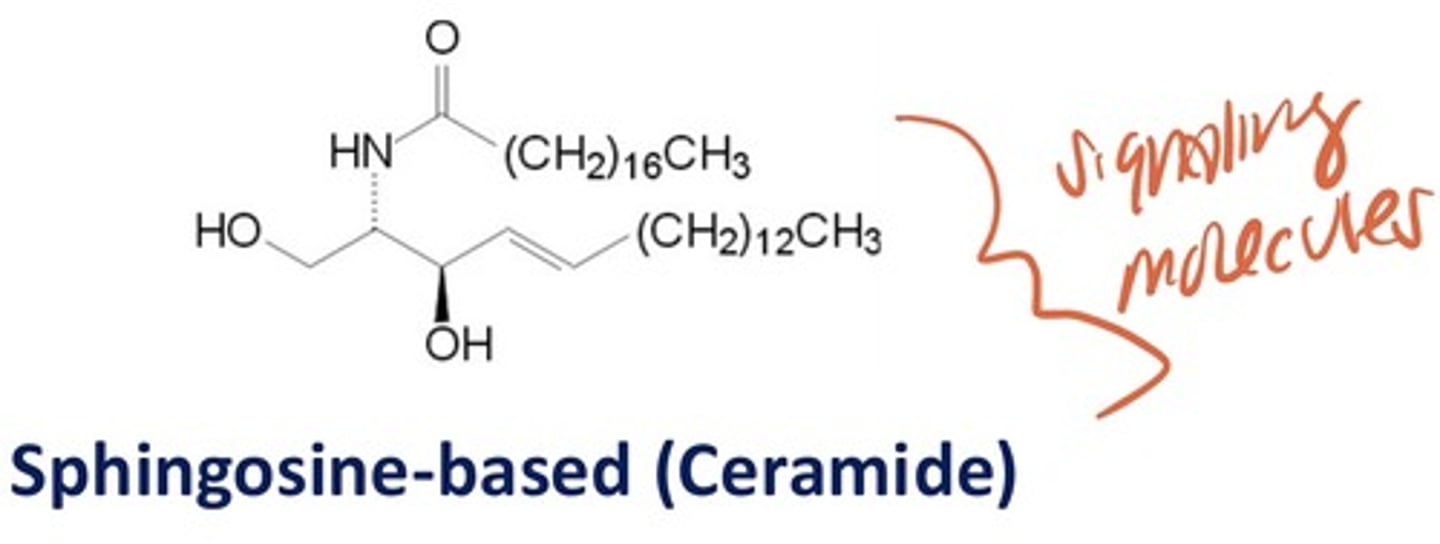
Sphingosine-based (Ceramide)
signaling molecules with esterfied FA
Triglyceride Digestion
lingual lipase in mouth --> gastric lipase in stomach --> gastric emptying into small intestine makes I cells secrete CCK --> stimulates release of bile salts from gallbladder & pancreatic lipase (& cofactor colipase) + phospholipase
*pancreatic lipase hydrolyzes TAG --> DAG --> MAG
**don't need to hydrolyze the last FA off b/c 2-MAG is pretty soluble in water
True or False: Pancreatic lipase doesn't recognize olestra
True ==> can't recognize FAs in ester linkages to hydroxyl groups on sucrose
True or False: Lingual Lipase is the best at digesting long chain fatty acids
False ==> lingual lipase is the best at digesting medium chain fatty acids
emulsification of fats
bile salts and phospholipids released from the gall bladder bind fat droplets of TAG and allows droplets to be broken up during peristalsis ==> makes TAG more accessible for pancreatic lipase
Bile Acid Synthesis
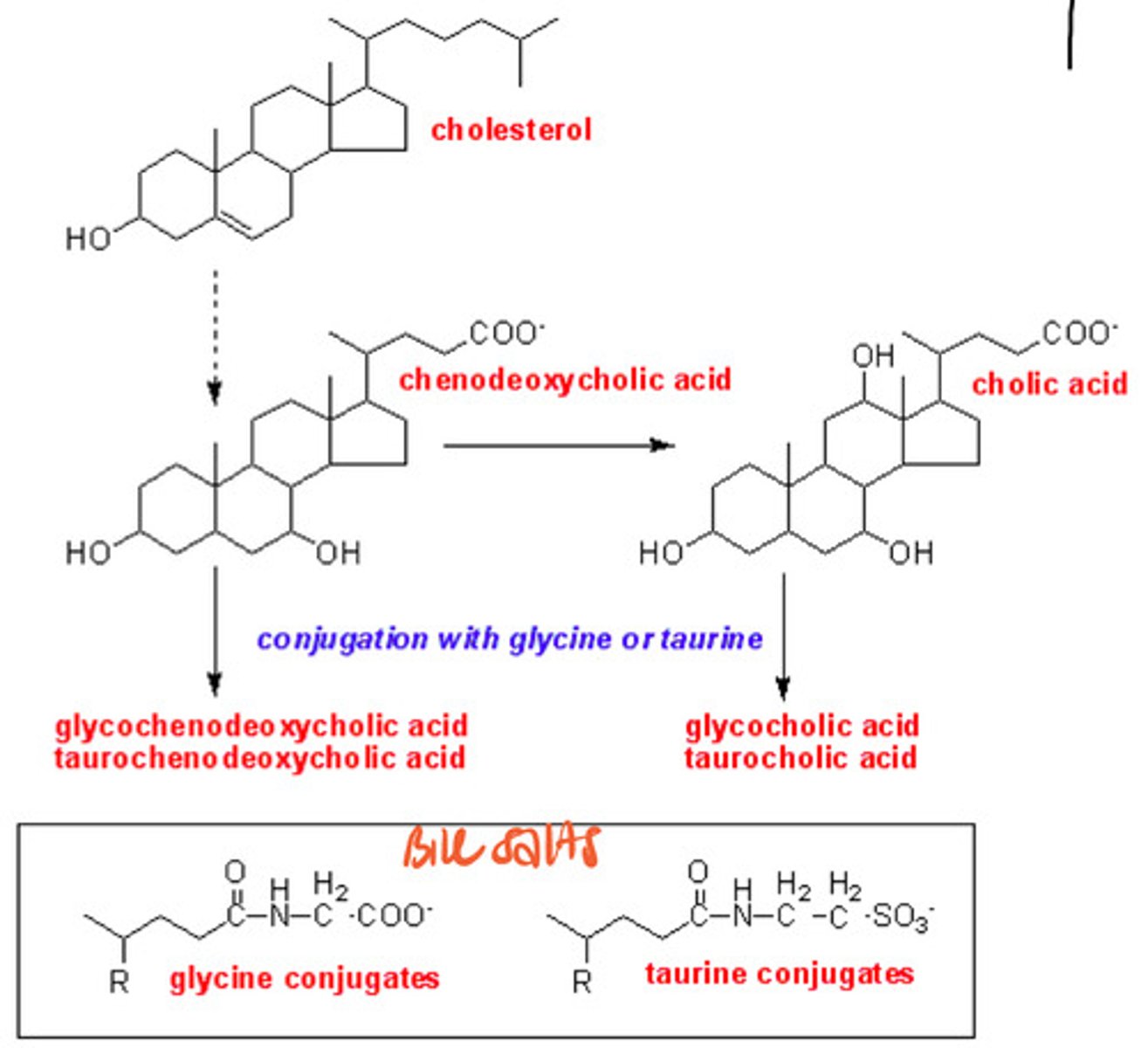
cholestyramine
cholesterol lower drug that works by preventing the recycling of bile salts in enterohepatic circulation (makes bile salts be excreted w/ poop) --> makes liver uptake cholesterol from blood to make more bile salts = decreased cholesterol in blood
True or False: If bile salts leave enterohepatic circulation and end up in lower intestine it can lead to malabsorption of fats
True ==> if bile salts are excreted then they aren't available to emulsify TAG droplets & then pancreatic lipase can't break it down to make 2 MAG . . .
Biliary Obstruction
gallstones can form when imbalance of cholesterol, bile salt, & phospholipid --> blocks bile secretion --> no emulsification of fat droplets
* = intestinal discomfort, loss of essential fatty acids, & fat -soluble vitamins
pancreatitis/pancreatic disease
pancreatic inflammation/disease that causes steatorrhea (malabsorption of lipids b/c TAG couldn't be broken down)
-severe abdominal, back, or epigastric pain
-nausea or vomiting
-sign = increase in serum lipase & amylase
*causes loss of essential fatty acids & fat-soluble vitamins
Effect of Celiac Disease on Lipid Digestion
celiac disease decreases surface area for absorption ==> malabsorption of fat
* = intestinal discomfort, loss of essential fatty acids, loss of fat-soluble vitamins
Lipid Digestion Disorders that lead to Fat Malabsorption
-biliary obstruction
-pancreatic disease
-celiac disease
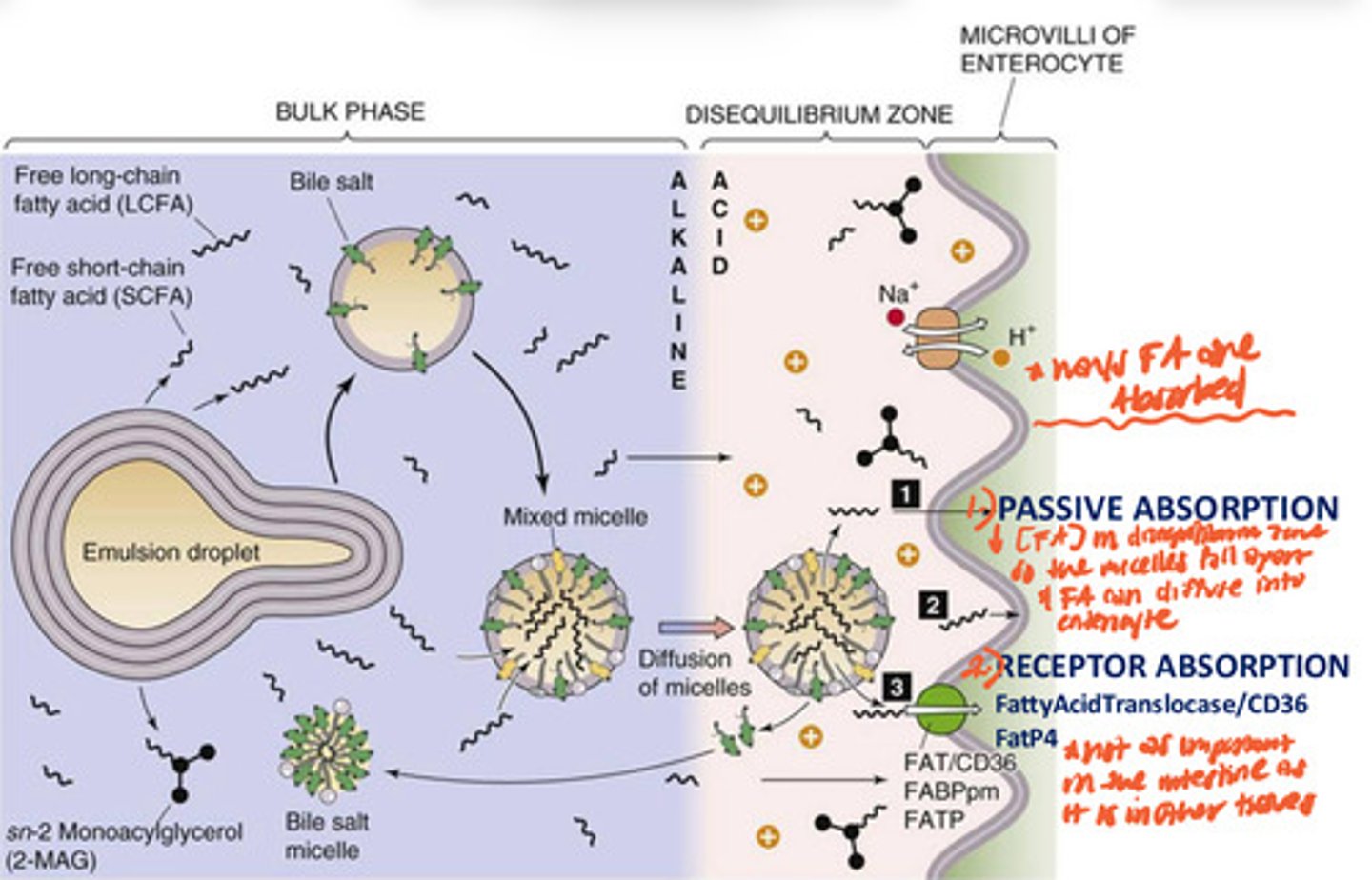
Absorption of Long Chain Fatty Acids (& MAG) in Enterocytes
emulsification of fat droplet in bulk zone of intestinal lumen (alkaline environment) -->broken into smaller mixed micelles--> diffuse into the disequilibrium zone (acidic environment) near enterocyte membrane --> low conc. of FA in disequilibrium zone so micelles disassemble --> FA passively diffuse into enterocytes or do receptor mediated absorption via FattyAcidTranslocase/CD36 FatP4
NPC1L1 transporter
transporter in intestines for absorption of cholesterol
*inhibited by ezetimibe (Tx for high cholesterol)
Why is ezetimibe a treatment for high cholesterol?
inhibits cholesterol absorption by blocking NPC1L1 transporter in intestine
Re-esterification of fatty acids w/in enterocytes
fatty acyl-CoA synthetase puts CoA on the free fatty acids (requires ATP for energy) --> triacylglycerol synthase takes FA off CoA & places them on. 2-MAG --> TAG re-made
* done w/in enterocytes after absorption of free FA so that they can get ready for body transport (make another micelle = chylomicrons )
cellular acyl-cholesterol acyl transferase (ACAT)
enzyme that re-esterifies cholesterol inside enterocytes
Why are most fatty acids in the body long chain fatty acids?
cuz the primary product of FA synthesis is palmate (long chain)
* can be converted to serate
Chylomicrons (overview)
-transport long chain FA, cholesterol, & fat soluble vitamins
-the biggesr micelle but the least dense
-makes serum have milky appearance (after eating)
Chylomicron Life Cycle
long chain FAs & cholesterol re-esterified in membrane of ER of enterocytes --> re-estered lipids form a droplet that buds off into the ER lumen --> ApoB48 added = Nascent Chylomicron --> Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Proteins (MTP or MTTP) add more lipids to chylomicrons in ER lumen --> chylomicrons transported to golgi apparatus --> released from golgi in vesicles --> vesicles fuse w/ enterocyte membrane --> chylomicron released --> go into lacteals of lymphatic system -->> drain into subclavian vein --> HDL in blood places ApoCII & ApoE on chylomicron = mature chylomicron --> mature chylomicron interacts w/ LPL-GPIHP1 complex on endothelial cells--> ApoCII binds LPL (lipoprotein lipase)--> activates LPL--> breaks triglycerides down into FA & 2-MAG again--> FAs get passively absorbed by cells --> chylomicron remanent travels to the liver --> ApoE & ApoB48 bind LDL-receptor related protein (LRP) on liver cell --> chylomicron remanent endocytosis --> cholesterol esterase breaks cholesterol esters into free cholesterol
Abetalipoproteinemia
(Bassen-Kornzweig Disease)
An MTP deficiency characterized by very low blood triglyceride, low total cholesterol levels, & weird looking RBCs
* no MTP --> no lipids added to nascent chylomicrons in ER lumen -->>> not enough triglycerides taken to tissues for use
Familial Chylomicron Syndrome
disease characterized by severe hypertriglyceridlipidemia, pancreatitis, & xanthoma (fat + cholesterol skin leisons) that's mostly due to LPL receptor defects
**less FA getting into tissues = more blood [fat]
Tx = Olezarsen --> blocks LPL's inhibitor (ApoCIII) so they defective LPL receptors can work to the best of their ability & less Chylomicrons accumulate in the blood
Olezarsen
Drug that inhibits ApoCIII
-ApoCIII is a LPL inhibitor ==> blocking it will make LPL be more readily active
*Tx for Familial Chylomicron Syndrome where LPL receptors are defective