DNA, Genetics, and Cell Division Study Guide
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, carries genetic information.
Nucleotide
The building block of DNA, made of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base.
Pentose sugars
5-carbon sugars: deoxyribose (in DNA), ribose (in RNA).
Nitrogen bases
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine (Uracil in RNA).
Complementary base pairing
A pairs with T (or U in RNA), G pairs with C.
Double helix
Shape of the DNA molecule.
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Holds DNA strands together.
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds between nitrogen bases.
Covalent bonds
Strong bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
DNA replication
Copying DNA before cell division.
Transcription
Making RNA from DNA.
Translation
Making proteins from RNA.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Technique to amplify DNA.
Gene mutation
A change in DNA sequence.
Gene expression
How a gene produces its product (protein).
Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, Watson & Crick
Scientists who contributed to discovering DNA's structure.
DNA subunits
Nucleotides (composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone with one nitrogen base).
Base pairing rule
A-T, G-C.
DNA vs RNA
DNA is double-stranded, has thymine, uses deoxyribose. RNA is single-stranded, has uracil, uses ribose.
DNA's functions
Stores genetic info, replicates, guides protein synthesis.
Gene mutations
Can change amino acid sequences, potentially altering protein structure and function.
Chromosome
DNA and protein structures that carry genes.
Chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome.
Centromere
Region connecting two chromatids.
Autosomes
Non-sex chromosomes (22 pairs in humans).
Sex chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes; determine biological sex (1 pair in humans).
Karyotyping
Visualising chromosomes to detect disorders.
Chromosomal disorder
Abnormal number/structure of chromosomes.
Trisomy
Three copies of a chromosome (e.g., Down syndrome = trisomy 21).
Monosomy
One copy of a chromosome (e.g., Turner syndrome = monosomy X).
Mitosis
Cell division producing identical cells for growth and repair.
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes (sperm/egg) with half the chromosome number.
Parent cell
Original cell before division.
Daughter cell
Resulting cells after division.
Gamete
Sex cell (sperm or egg), haploid.
Haploid
Half the number of chromosomes (23 in humans).
Diploid
Full set of chromosomes (46 in humans).
Fertilisation
Union of sperm and egg to form a zygote.
Zygote
First cell of a new organism after fertilisation.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
Stages of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis.
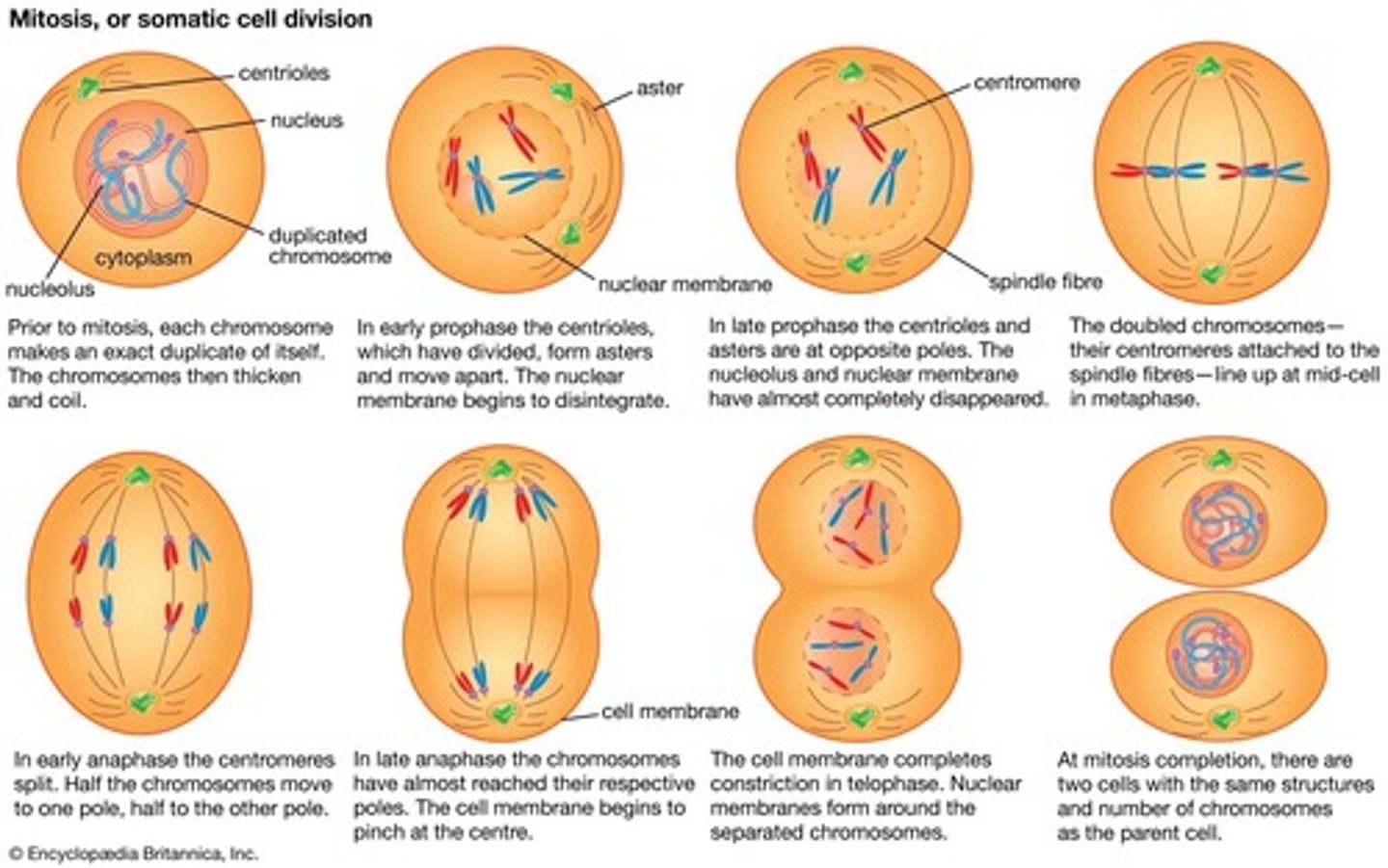
Mitosis produces
2 identical daughter cells; meiosis produces 4 genetically different daughter cells.
Mitosis: daughter cells
have 46 chromosomes; Meiosis: daughter cells have 23 chromosomes.
Mitosis is used for
growth and repair; meiosis is used for reproduction.
DNA
DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid, lives in the nucleus.
Genetic Blueprint
Instructions for how each cell behaves.
Proteins
Substances that give us our specific characteristics.
Genes
Sections of DNA that contain instructions to produce specific proteins.
Chromatin
A very long (3m) strand of DNA that can't be seen under a light microscope.
Chromosomes
Condensed, shortened, and thickened form of chromatin visible during cell division.
Humans Chromosomes
Humans have 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs, with one of each pair from each parent.
Autosomes
22 pairs of chromosomes that are numbered from 1 to 22 based on size.
Homologous pairs
Chromosomes from each parent that are identical in terms of size, shape, and type of genes they carry.
Karyotyping
A technique that allows us to look at chromosomes in utero and check for abnormalities.
Gametes
Sperm and ova that each have 23 chromosomes, allowing them to combine to make a full set.
Non-disjunction
A failure in meiosis where chromosomes do not separate properly, leading to gametes with too many or too few chromosomes.
Chromosomal mutation
A genetic alteration that occurs if gametes with abnormal chromosome numbers end up in the zygote.
Down syndrome
A chromosomal abnormality caused by having 3 copies of chromosome 21, characterized by distinct facial appearance and intellectual disability.
Turner's syndrome
A condition in females caused by missing an X chromosome, characterized by short stature and infertility.
Klinefelter's syndrome
A condition in males caused by an extra X chromosome, leading to characteristics such as delayed puberty and infertility.
Jacobs syndrome
A condition in males caused by an extra Y chromosome, characterized by tall stature and behavioral issues.
DNA monomers
Nucleotides, which are the repeating subunits of DNA.
DNA
A polymer made up of monomers called nucleotides.
Nucleotides
The building blocks of DNA, consisting of a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Nitrogenous bases
The four different components of nucleotides: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T).
Purines
Nitrogenous bases with two rings, specifically Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases with one ring, specifically Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T).
Protein synthesis
The process by which DNA tells the cell how to make proteins.
Transcription
The process of making a copy of DNA (template strand) and taking it into the cytoplasm via messenger RNA (mRNA).
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
The single-stranded copy of DNA that carries the genetic information to the cytoplasm.
Uracil
A nitrogenous base that replaces Thymine in RNA.
Covalent bonds
The type of bonds that join the phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar in nucleotides.
Hydrogen bonds
The type of bonds that join the nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Anti-parallel strands
The orientation of the two strands of DNA running in opposite directions.
Ribose
A sugar that is not deoxyribose.
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that unzips DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds and connects an RNA strand to one of the DNA strands.
Transcription
The process that begins when RNA polymerase unzips the section of DNA corresponding to the gene for a particular protein.
mRNA
Messenger RNA that adds free nucleotides to the exposed strand according to base pairing rules.
Codon
A sequence of three bases on the mRNA strand that represents an amino acid.
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins.
Stop codons
Three codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) that indicate the end of the gene.
tRNA
Transfer RNA that carries the amino acid corresponding to the mRNA codon to the ribosome.
Anti-codon
A three-base sequence on tRNA that binds with the mRNA codon.
Peptide bond
A strong bond formed when two amino acids are brought together.
Polypeptides
Long chains of amino acids.
Protein functions
Important purposes include providing structure, regulating body processes, transporting materials, helping with immunity, and providing energy.
DNA replication
The process of creating new DNA strands using existing strands as templates.
Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds.
DNA polymerase
Enzymes that attach to exposed strands and synthesize new strands of DNA.
Semi-conservative replication
A process where each of the two created DNA molecules contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Gene regulation
The process by which RNA polymerase copies only the wanted genes.
Stem cells
Unprogrammed cells that can differentiate into various cell types.
Epigenetics
An emerging field suggesting that life experiences can affect gene expression in offspring.
Nucleus
The cell organelle where DNA is stored and transcription occurs.
Cytoplasm
The part of the cell where tRNA retrieves amino acids.
25000 genes
The approximate number of genes present in every cell.
Locus
Position of gene on its specific chromosomes.
Linked genes
Genes on the same chromosome.
Cell division
The process by which cells grow, repair damaged tissue, or prepare for sexual reproduction.
Mitosis
Type of cell division for growth and repair.
Meiosis
Type of cell division for the production of gametes.