4. BUILDING SELF- KNOWLEDGE
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Sasha recently ended a long-term relationship
and has embraced their newfound independence, feeling excited about their personal growth and new opportunities. According to research on self-concept clarity, how is Sasha most likely to feel about their self-
concept?
A. Sasha is likely experiencing self-concept confusion because a social role change always decreases one's self-concept clarity, at least temporarily
B. Sasha is unlikely to experience self-concept confusion because they feel positively about the change
C. Sasha is unlikely to experience self-concept confusion because their self-complexity is high
D. Sasha is unlikely to experience self-concept confusion because age is the most important factor in determining self-concept clarity
B. Sasha is unlikely to experience self-concept confusion because they feel positively about the change
intrapersonal
occurring within the individual mind or self
intrapersonal sources
self-perception and introspection
self-perception
we observe our overt behaviours and use these observations to infer what we're like (similar to how we infer what other people are like)

introspection
we direct our attention inwards to our internal states (thoughts and feelings) and use this self-awareness to draw conclusions about what we are like

What do we prioritize between self-perception(behaviour) or introspection(inside)
prioritization of internal states
Prioritization of introspection > behaviour(self-perception) to get to know one study
in general, internal states was more informative > friends/family or behaviour for several months
How does access to internal states vs. behaviour shape others' impressions? - prioritization of introspection>behaviour study (rating stranger's interviews of cognitive/affective, behavioural, control conditions) (interviewee's self rates)
Cognitive/affective interviews was the highest correlation between self-rating and stranger rating.
Lower for control (getting both cognitive/affective and behavioral)
Why do we prioritize thoughts and feelings (vs. behaviors) to construct self-knowledge
Behaviour can be influenced by external factors, and be ambiguous w different conclusions vs. thoughts and feelings are more revealing of inner self
When can self-perception be more useful for forming self-knowledge than internal states
When ppl are unclear about their internal states
RESULTS: accuracy of introspection/Are people aware of what impacts their mood study (daily diary report for 5 weeks, rltship of mood and predictor)
fairly accurate judgement of self predictors influencing mood (few errors) for both observer participants and are relying on shared theories of predictors not understanding
what are the implications of "accuracy of introspection/Are people aware of what impacts their mood study (daily diary report for 5 weeks, rltship of mood and predictor) "
people do not have a genuine understanding of why they think and feel the way they do
What is introspection not very useful at explaining
explaining why we feel these feelings in the first place (ex. why do i feel bored/excited/etc)
Interpersonal
relating to relationships or communication between people.
Symbolic interactionsim
the self-concept depends on our social interactions (no self without others)
Interpersonal sources of self-knowledge
social comparison
social comparison
comparing ourselves with others to form conclusions about our relative standing on attributes, abilities, opinions, etc
what does social comparison believe about self-perception and introspection
introspection and self-perception often rely on comparison
is social comparison automatic or manual
automatic
How does upward social comparison influence self-esteem
Decrease in self-esteem
What is upward social comparison?
comparing ourselves to people that are better than us resulting in a decrease in self-esteem
What is downward social comparison
comparing ourselves to people that are worse than us leads to an increase in self-esteem
How does downward social comparison influence self-esteem
increase in self-esteem
Looking-glass self (interpersonal source)
we construct our self-concept based on how others see us
What is going on during looking-glass self?
inferring how others see us using direct feedback, behaviours towards us
what does it mean if the looking-glass self theory is accurate
how we see ourselves is a direct internalization of how other people see us
Relating to the looking-glass self, what does people's self-reports have a strong positive relationship with
how they think they are perceived by others (may or may not be related to how this other person ACTUALLY sees me)
What relationships matter more when it comes to the looking-glass self
How people that are more important to us see us
Why is there the absence of correlation between how I see myself and how other ppl see me?
because we rarely get full honest feedback about what we are like (and gets interpreted by us) and feedbacks can be contradictory
we often dismiss or rationalize away negative feedback
Social Identity Theory (source of self-knowledge)
we place ourselves and others into social groups and this process shapes our shape concepts
Self-stereotyping
taking on and conforming to the shared identity of a social group in order to be accepted as part of that group by others
steps of social identity theory
1. what are the characteristics of the social group I value 2. self-stereotyping 3. validation by others that I'm a good member of the group
social identity theory evidence
when the group is important to sm, ppl adopt descriptions of themselves in line with that group
Social Identity Theory Evidence study (comparing performance on RT task to ratings of in-group)
Results: Faster RTs for traits on ppl see themselves matching ingroup (vs. traits w mismatch)
ppl are faster when there is a match between self-concept and their in-group/ faster when not descriptive of them and their ingroup (both for yes/yes and no/no)
What does the Social Identity Theory Evidence study (comparing performance on RT task to ratings of in-group) suggest about self and ingroup
perception of self is linked with perception of ingroup
What does the Social Identity Theory Evidence study (comparing performance on RT task to ratings of in-group) suggest about self and outgroup
ppl form some parts of their self-knowledge by trying to reject features they think are characteristics of an out-group
Does social identity theory mean everyone in that one group is similar
flexibility in social identity by uniqueness while conforming
where does the difference of self-description/behaviour in social identity determined by
expectations/standards for that identity & people's unique strengths and preference (ex. Griffyndor is being loyal and brave but ron is more stronger at being loyal and harry is more brave)
Including close others in the self (source of self-knowledge)
similiar to incorporating groups into our identity, also do this with people we are closest to
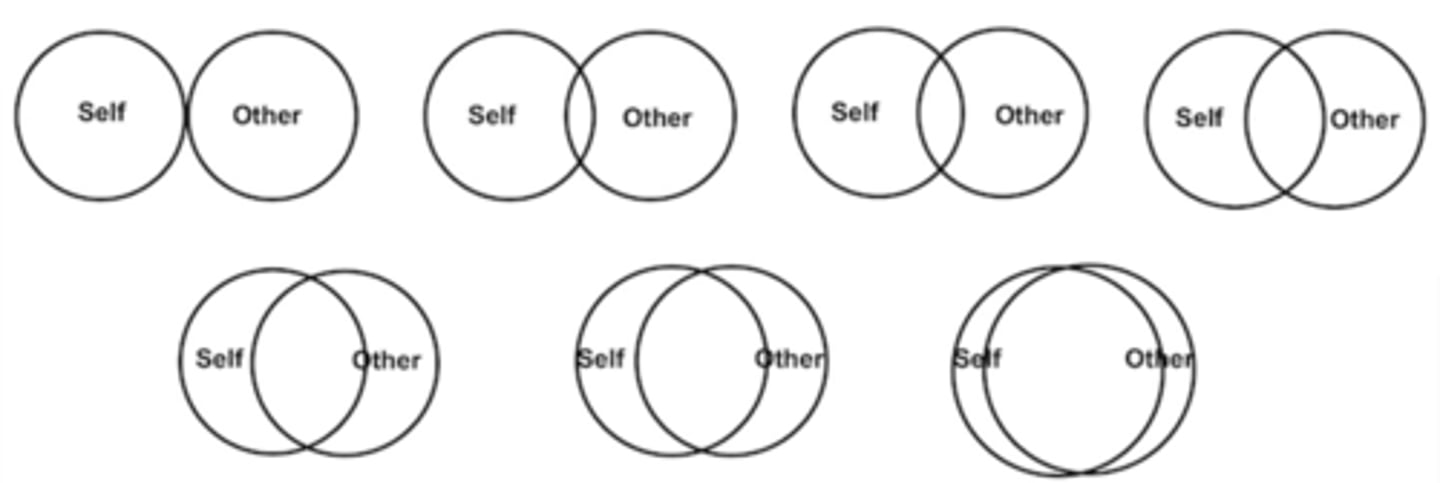
Do people confuse their partners' traits for their own - including others in the self study (same RT task with married graduate students) results
participants were slower and made more mistakes on traits that differed between self and spouse (for both me and not me judgements)
had slower RT for trait just for them and not spouse as they are confused who this trait belong to
Rachel has always though of herself as a hardworking person. However, recently she has begun to notice that her colleagues often work longer hours and take on more projects. Rachel now feels that she needs to push herself harder to match their level of commitment. Which source of self-knowledge is Rachel primarily relying on in this situation?
A. introspection
B. Self-perception
C. Social comparison
D. The looking-glass self
C. Social comparison
Sophia tends to feel anxious at parties because
she thinks that she doesn't make a great first
impression on others. Research into the looking-
glass self would suggest that she feels this way
because:
A. She is relying on her own internal evaluation of her social skills, which is independent of others' perceptions
B. She imagines the others view her negatively based on her past experiences, and this belief influences her feelings about herself
C. She is comparing herself to others and believes she is not as socially skilled as her peers
D> She has internalized feedback from others but does not adjust her self-concept based on those perceptions
B. She imagines the others view her negatively based on her past experiences, and this belief influences her feelings about herself