NUFS 100 - Topic 2 Food Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Last updated 6:57 PM on 2/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
1
New cards
why are foods high in moisture
come from biological things like plants and animals
2
New cards
what is food a mixture of?
carbohydrates, fats, water, protein, and miscellaneous atoms (ash)
3
New cards
what are some complex organic molecules?
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
4
New cards
5 major chemical compounds in food
lipids, carbs, protein, water, minerals/ash
5
New cards
what does fat make when it oxidizes?
prefatty acids
6
New cards
What does proximation do?
implications for shelf life
foods must align with legal definition
directs processing parameters
determine energy in foods (caloric content)
always expressed in percentages
foods must align with legal definition
directs processing parameters
determine energy in foods (caloric content)
always expressed in percentages
7
New cards
True or false: you can not remove all the water in a food?
true. Molecules really like the water and can not let it go, so there will always be some water in a food no matter what
8
New cards
How to find Kcal
multiple by the macronutrients by proximation
9
New cards
What are the macronutrients in Carbs, Protein, Fat, and alcohol?
carbs - 4
protein - 4
fat - 9
alcohol - 7
protein - 4
fat - 9
alcohol - 7
10
New cards
What do carbohydrates do?
Hydrates carbon (Cn (h2o) n)
source of energy and fiber
source of energy and fiber
11
New cards
monosaccharides
pentoses (5 chain) and hexoses (6 chain)
glucose, fructose, galactose
glucose, fructose, galactose
12
New cards
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked.
13
New cards
sucrose
aka table sugar is glucose and fructose
14
New cards
lactose
glucose and galactose.
too power for isabelle
too power for isabelle
15
New cards
maltose
glucose and glucose
16
New cards
function of sugar in food
crystalizes
provide body and mouth feel
preservation effect
source of food for yeast
hygroscopic
browning reaction
provide body and mouth feel
preservation effect
source of food for yeast
hygroscopic
browning reaction
17
New cards
Millard reaction
reducing sugars and amino acids ie toast
18
New cards
caramelization
lose moisture, sugars decompose and create polymers
19
New cards
oligosaccharides
combination of 3 or more monosaccharides
20
New cards
polysaccharides
long chains of oligosaccharides: starch cellulose, pectin and some hydrocolloids
21
New cards
complex carbs are added to food to:
increase fibber
thicken foods
form gels
bind water
stabilize proteins
thicken foods
form gels
bind water
stabilize proteins
22
New cards
straches
long chains of glucose linked together (500-100,000)formed by two different molecules (amylose and amylopectin) , each different
\
\
23
New cards
amylose
linear chains, gel formation
24
New cards
amylopectin
branched chains, viscosity
25
New cards
cellulose
major component of cell walls
long chains of glucose linked together (1-4)
dietary fiber
long chains of glucose linked together (1-4)
dietary fiber
26
New cards
Pectin
functions as an intercellular cement in fruits and veggies
gelling agent in foods
dietary fiber
gelling agent in foods
dietary fiber
27
New cards
Gums
thicken and stabilize food products
xanthan, agar, guar gum etc
xanthan, agar, guar gum etc
28
New cards
dietary fibre
carbs not digested by humans
29
New cards
high fructose corn syrup HFCS
a development in the industry
derived from glucose and hydrolyzed by corn starch
developed in the 50s refined in the 70s, in food since 75
derived from glucose and hydrolyzed by corn starch
developed in the 50s refined in the 70s, in food since 75
30
New cards
true or false:
every component in complex carbs must do everything it is capable of
every component in complex carbs must do everything it is capable of
false
31
New cards
amino acids
builiding block of protein ( 20 amino acids)
\
\
32
New cards
The shape and function of the protein is determined by the..
amino acid
33
New cards
true or false:
a protein does not need to be broken down to be absorbed
a protein does not need to be broken down to be absorbed
false
34
New cards
4 types of protein structures
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
35
New cards
true or false:
denaturation affects the primary structure
denaturation affects the primary structure
false
36
New cards
denaturation
small changes have a big effect; cooking egg
37
New cards
primary structure
the sequence of a chain of amino acids
38
New cards
secondary structure
occurs when the sequence are linked by hydrogen bonds
include: alpha helix, beta-pleated sheet
include: alpha helix, beta-pleated sheet
39
New cards
tertiary structure
occurs when certain actions are present between the alpha helix and beta-pleated sheets
40
New cards
Quaternary structure
a protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain
involves noncovalent association of protein chains
protein chains may or may not be identical
involves noncovalent association of protein chains
protein chains may or may not be identical
41
New cards
Function of proteins in foods
emulsifiers
colours; through millard reaction
texture control - thickening, binding, gelling agents
flavour generation - savoury
colours; through millard reaction
texture control - thickening, binding, gelling agents
flavour generation - savoury
42
New cards
proteins precipitate at their _____ point
isoelectric
43
New cards
isoelectric
the ph where there is no net charge
44
New cards
what precipitates to make curd and whey
casein
45
New cards
fats appear solid at ____ temp
room temp
46
New cards
oils are ___ at room temp
liquid
47
New cards
lipids are mainly…
triglycerides
48
New cards
true or false:
lipids are not present in monoglycerides
lipids are not present in monoglycerides
false.
they are present in monoglycerides, diglycerides, and free fatty acids
they are present in monoglycerides, diglycerides, and free fatty acids
49
New cards
carotenoids
make food appear a yellow or orange colour
50
New cards
chlorophyll
make food appear green
51
New cards
structure of fatty acids esterified to _____ determines fat properties ie melting point
glycerol
52
New cards
determinates of faty acids
4-28 carbon atoms
saturated vs nonsaturated
cis vs trans orientation around double loom 67
saturated vs nonsaturated
cis vs trans orientation around double loom 67
53
New cards
function of lipids in foods
nutrients
texture and mouth feel
flavour
heat transfer
emulsifiers - bind immiscible food components
texture and mouth feel
flavour
heat transfer
emulsifiers - bind immiscible food components
54
New cards
hydrolytic rancidity
free faty acids are liberated when fat and water interact
55
New cards
oxidative rancidity
reaction across double bands of fats and oxygen.
long chains are degraded
shorter chains are released and odorous
\
long chains are degraded
shorter chains are released and odorous
\
56
New cards
what types of food are effected by rancidity most
food with high fat contents
57
New cards
water is a growth parameter for ___
microbes
58
New cards
lettuce is what % moisture
96
59
New cards
we remove water to:
inhibit microbial growth
prevent chemical reactions
prevent chemical reactions
60
New cards
how we remove water?
freezing - stopping water
drying - removing moisture
addition of salt or sugar
thermal processing
drying - removing moisture
addition of salt or sugar
thermal processing
61
New cards
Function of water in foods
flavors, minerals, and vitamins can be dissolved
lubricates as you chew and swallow
texture
facilitate heat transfer - in brine (canned)
facilitates microbial growth
facilitates freeze concentration
lubricates as you chew and swallow
texture
facilitate heat transfer - in brine (canned)
facilitates microbial growth
facilitates freeze concentration
62
New cards
true or false:
not all water is available for microbial growth
not all water is available for microbial growth
true
63
New cards
water activity
tells how much water id available for chemical reaction and microbial growth
64
New cards
water activity close to __ is low
0
65
New cards
water activity close to __ is high
1
66
New cards
Bacteria grows at a water activity of
0\.85
67
New cards
yeast grows at a water activity of
0\.68-0.80
68
New cards
mold grows at a water activity of
0\.65
69
New cards
measurement of water activity formula
\
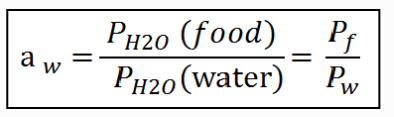
70
New cards
free water
can be extracted by a food easily by cutting or squeezing
71
New cards
bound water
can not be extracted easily
can not be used as a solvent for salt and sugar
can be frozen at temps lower than the water freezing point
molecules can not escape as vapour
can not be used as a solvent for salt and sugar
can be frozen at temps lower than the water freezing point
molecules can not escape as vapour
72
New cards
Pw is known because of the relationship between…
water and temperature
73
New cards
true or false:
vitamins and minerals do not contribute to energy
vitamins and minerals do not contribute to energy
true
74
New cards
why are vitamins and minerals called trace or ash
there is so little there is a trace amount
75
New cards
vitamins and minerals can be removed and added through..
fortification
76
New cards
thermal processing reduces vitamin _
C
77
New cards
true or false:
vitamin and mineral content can not be altered
vitamin and mineral content can not be altered
false
78
New cards
flour milling to reduce bran and germ reduces vitamin _
B