FINAL - Lecture 13 - Flowers, Fruit, and Seeds
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Do both Angio and Gymnosperm have pollen and seeds
yes
Do both Angio and Gymnosperm have Fruit
only angiosperm
Do both Angio and Gymnosperm have Ovules
Yes
Do both Angio and Gymnosperm have Ovaries
ONLY ANGIOSPERM
Gymnosperm do not make fruit because they lack _________
OVARIES
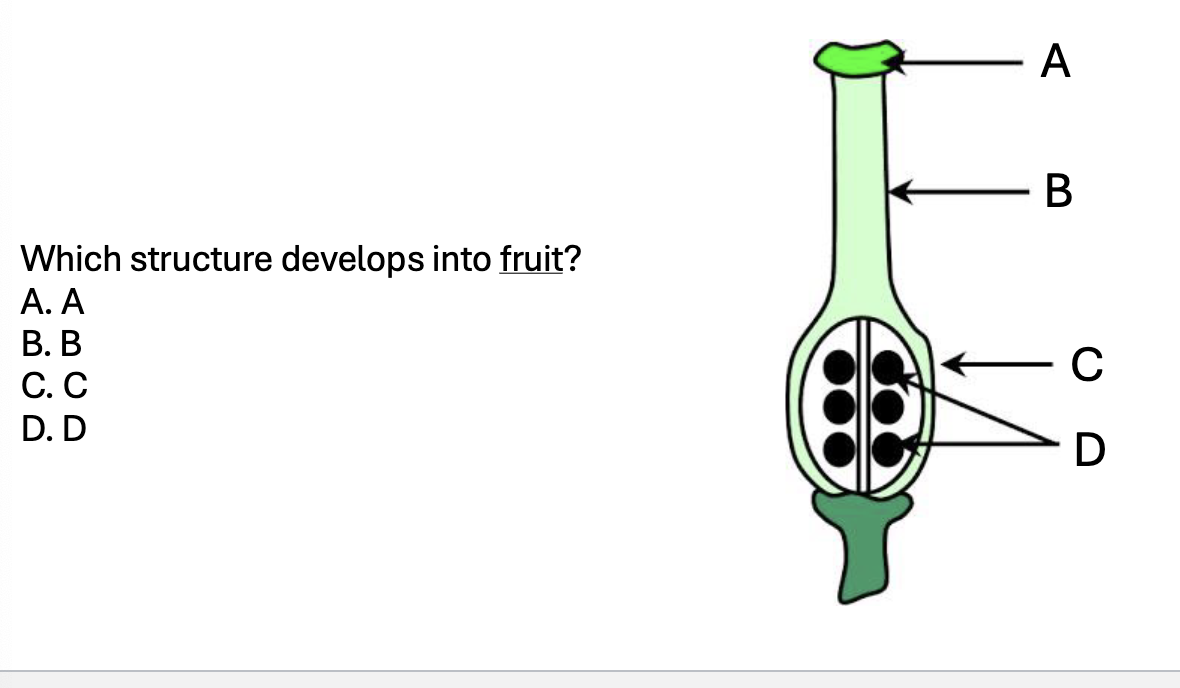
C
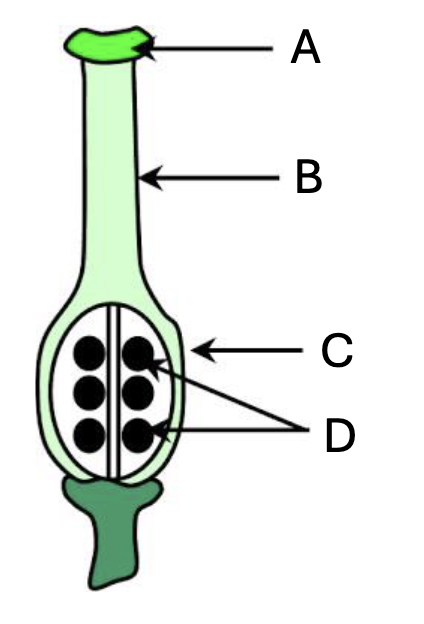
Where are seeds
D
What part of the plant is popcorn
endosperm
T/F - Endosperm is only produced by angiosperms
TRUE
Endosperm is produced by the process of ___________
Double Fertilization
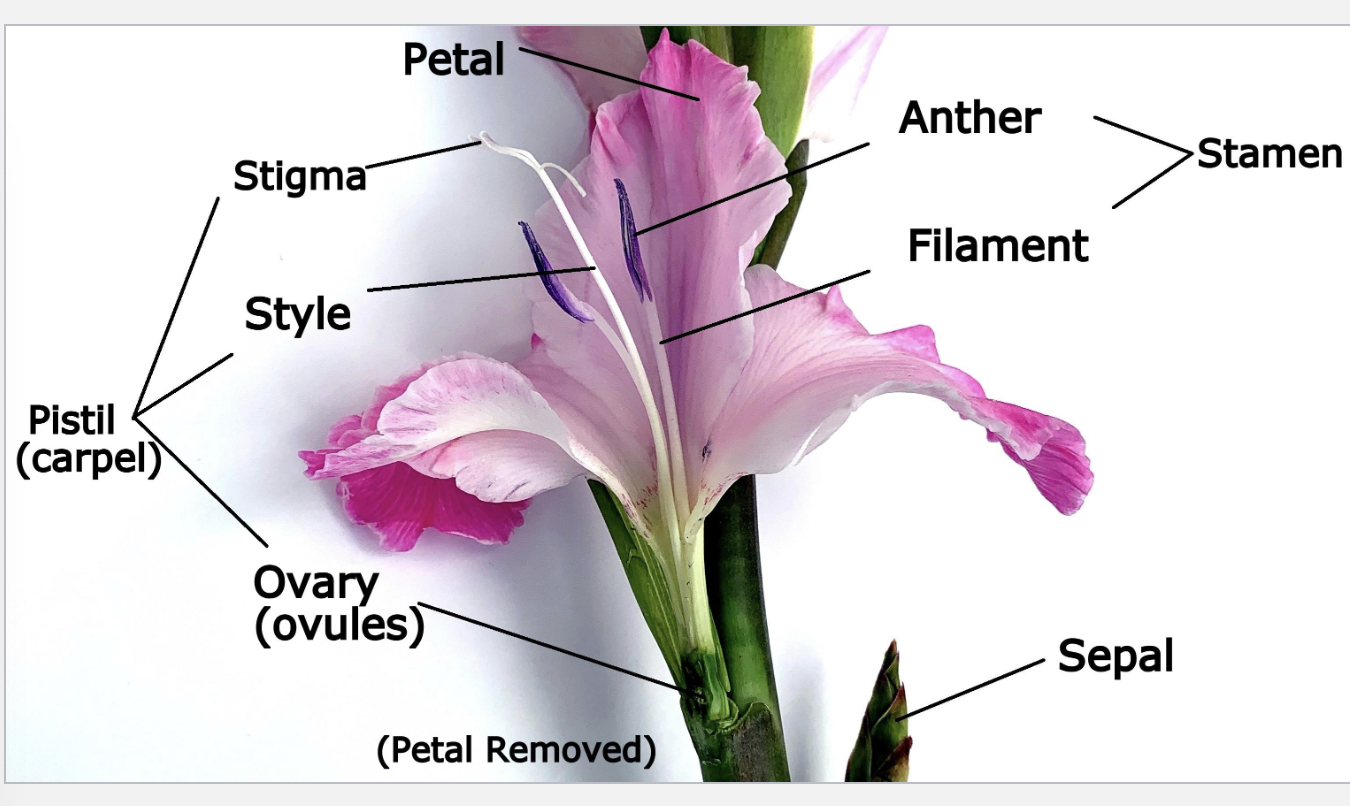
Label
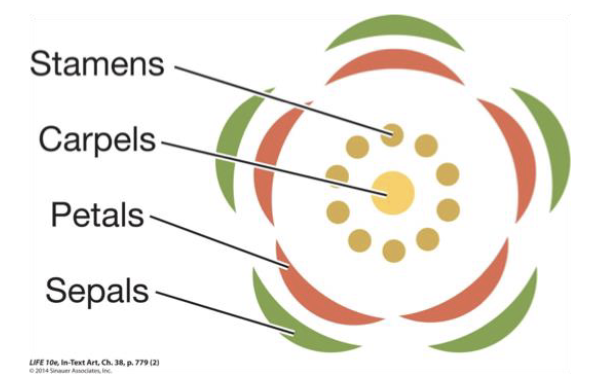
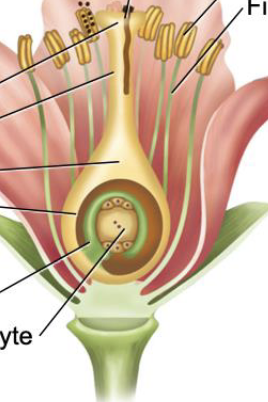
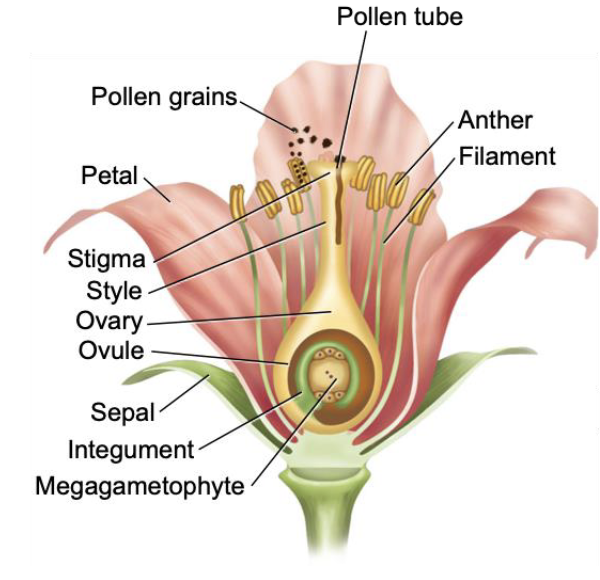
Perianth
calyx + corolla
(sepal and petals)
Receptacle
part of flower stalk where parts are attached
Flowers have a combination of __________ and _________whorls
non-reproductive
Reproductive
Flowers are arranged in ______
whorls
non-reproductive whorls
calyx and corolla (( PERIANTH ))
(sepal and petals)
Reproductive Whorls
Stamen and Carpels (aka pistol)
Whorls are in a ___________ order
specific order
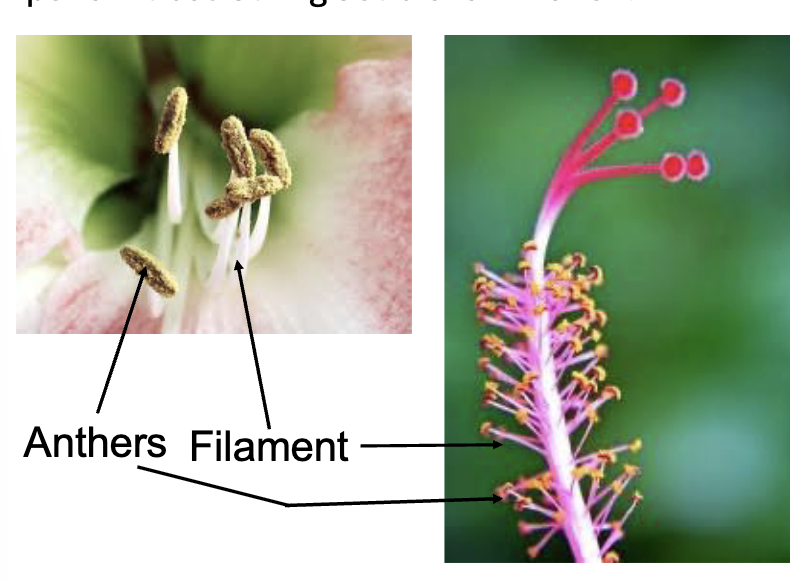
androecium
all the stamens of a flower
gynoecium
ALL the carpels // pistol of a flower
gynoecium types
apocarpous
syncarpous
Monocarpous
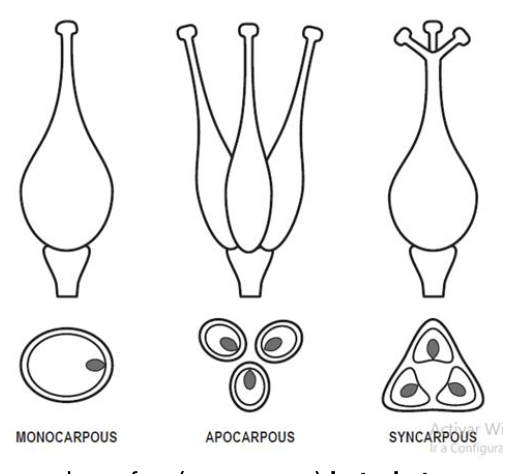
apocarpous gynoecium
Free standing carpels
syncarpous gynoecium
fused carpels
Monocarpous gynoecium
singular carpels
Blackberry carpels are _______
apocarpous



Pollen is comprised of ________ cells
2
Parts of pollen and what they do
The tube cell → elongates to produce the pollen tube
The generative nucleus → undergoes mitosis to produce sperm cells.
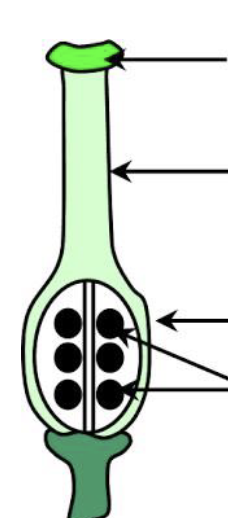

Pistils can be _________ or ___________
simple
compound
Simple Pistil
ONE CARPEL
TWO or MORE CARPEL
compund
differences between gymno and angiosperm
REVIEW
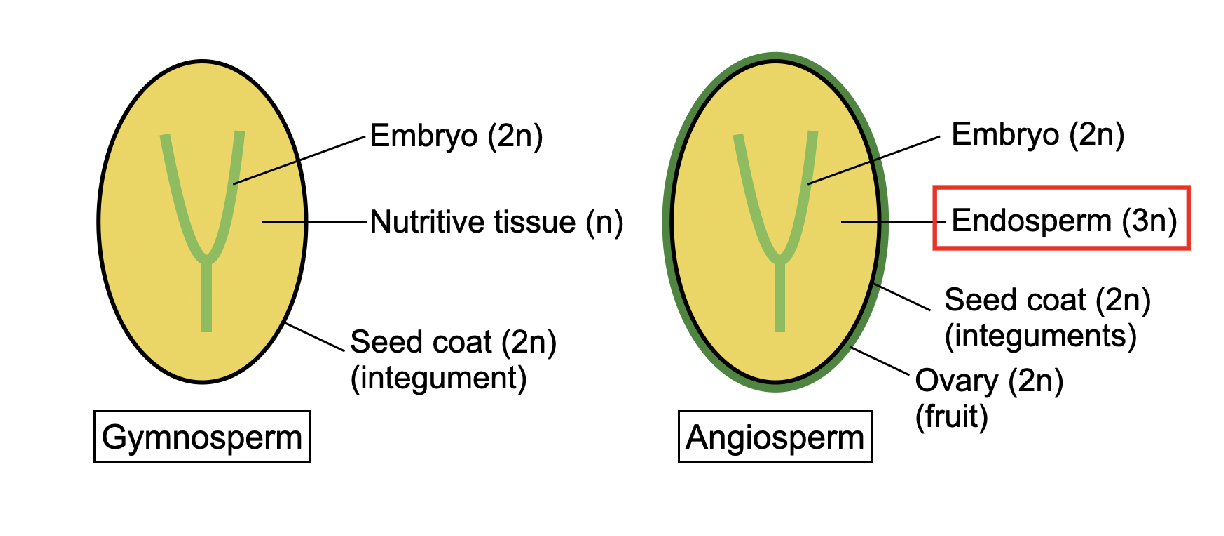
Angiosperm undergo _________- fertilization
double fert
Explain double fertilization
each pollen grain delivers two sperm cells,
one of which fertilizes the egg to form the zygote,
while the other fuses with the central cell to produce the endosperm
Embryo sac
megagametophyte
Ovule
embryo sac + integuments (+ nucellus)
Placenta
part of the ovary wall where the ovules attach
Flowers can be __________ or __________
perfect or imperfect
perfect flowers
pistils and stamens on same flower
imperfect flower
plant has either pistils/carpel OR stamens on a single flower
Types of IMPERFECT FLOWER plants
Monoecious
Dioecious
Monoecious
male and female on the same plant
Dioecious
male flowers and female flowers on different plants
T/F - It is possible to have a monoecious plant
with imperfect flowers
TRUE
Which are monoecious which are dioecious
A is MONO
B is DIOE
A flower develops from a _________ meristem in one set of reproductive, ______, organs
floral
Determinant
what is an inflorescense
An inflorescence develops from an inflorescence meristem that
produces multiple floral meristems, resulting in many flowers on a shoot
Flowers vs. Inflorescences
ADD
Individual flowers are considered determinate organs because their growth stops once they reach a certain size and form.
However, the way flowers are arranged on the plant's main stem (the inflorescence) can be either determinate or indeterminate
Flowers are regulated by _________- and _______ cues,
like …
External (temp / photoperiod)
Internal
Steps of flower transition
1. The SAM changes shape (becomes flatter and broader),
2. Floral organs are initiated
3. flower parts mature
4. The flower opens
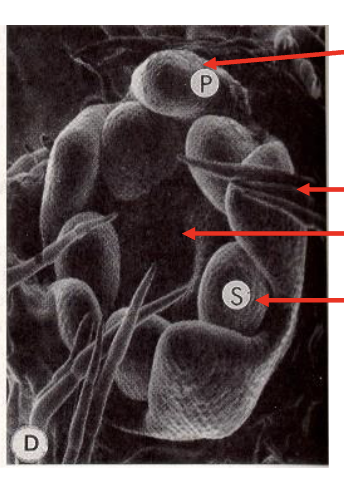
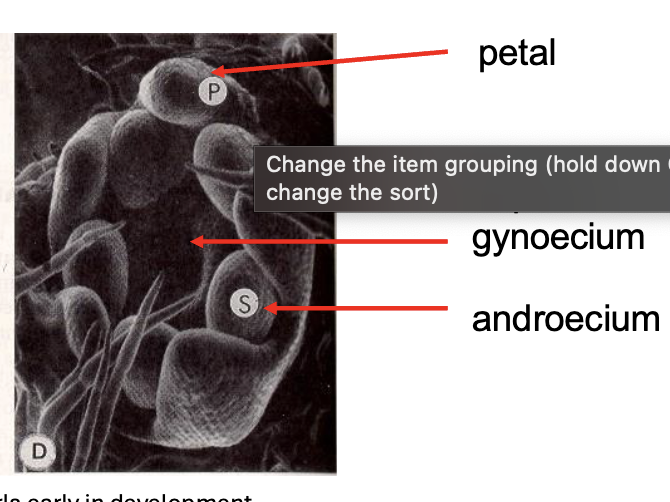
How do flowers arange in the correct order of whorls?
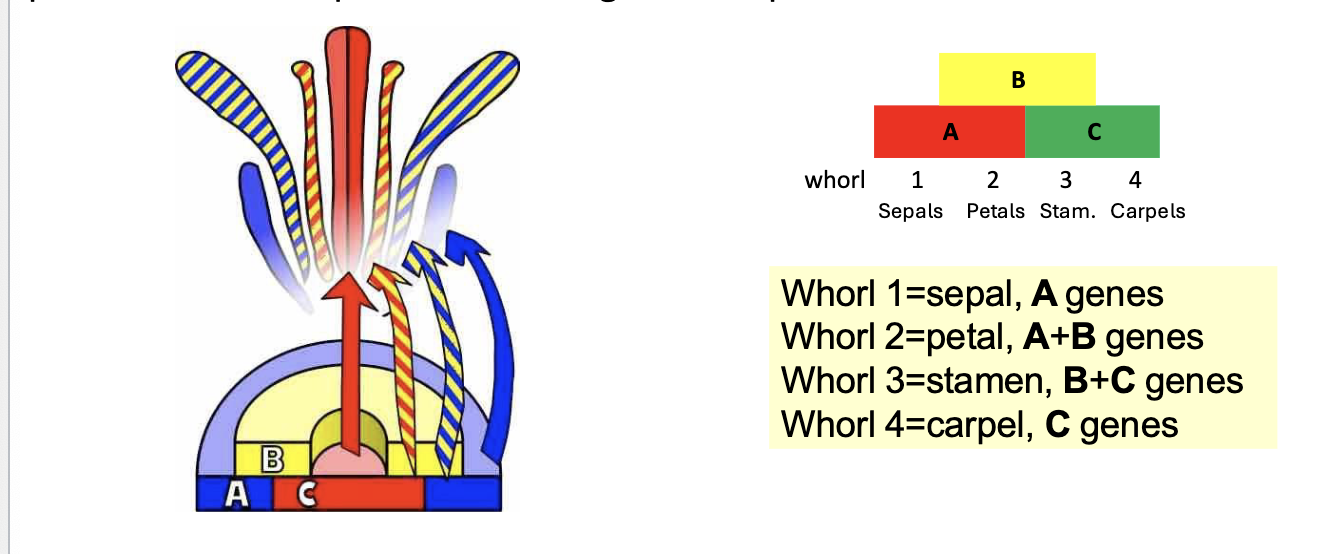
MADS-box genes // ABC model
Whorl 1
forms sepal
A genes
Whorl 2
forms petal
A and B
Whorl 3
forms stamen
B and C genes
Whorl 4
Forms carpel
C Genes
describe whorl arrangement
DONUT ESC
Homeotic genes
genes whose mutation causes homeosis—
the transformation of one body structure or organ into another
Homeobox
conserved DNA sequence found in many eukaryotic genes
found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists
Hox genes
subgroup of homeobox genes found only in animals
act as master regulators that pattern major parts of the
animal body
MADS-box genes
MADS-box genes are a different, conserved family
of transcription factors that do not have a homeobox
in plants, many MADS-box genes are _________; including many floral organ identity genes.
homeotic
C
ABC genes are regulate each other, with A and C using ________
mutual inhibition
Arrangememtn of ABC
B on top middle
A and C on bottom
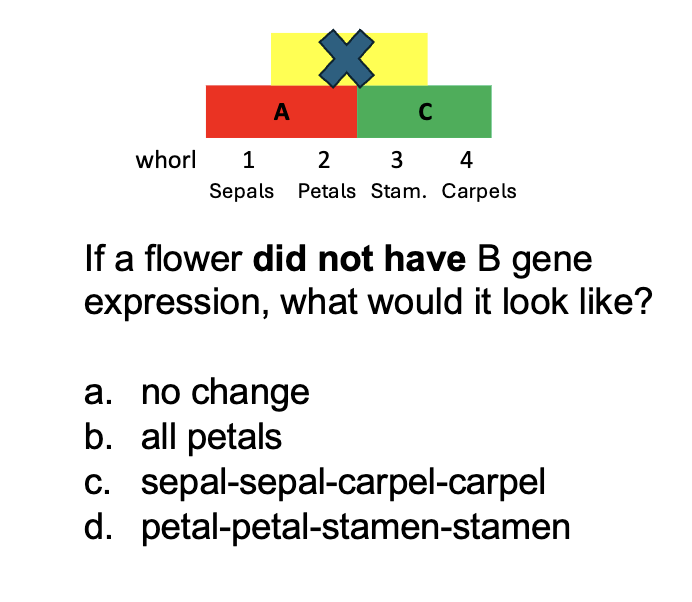
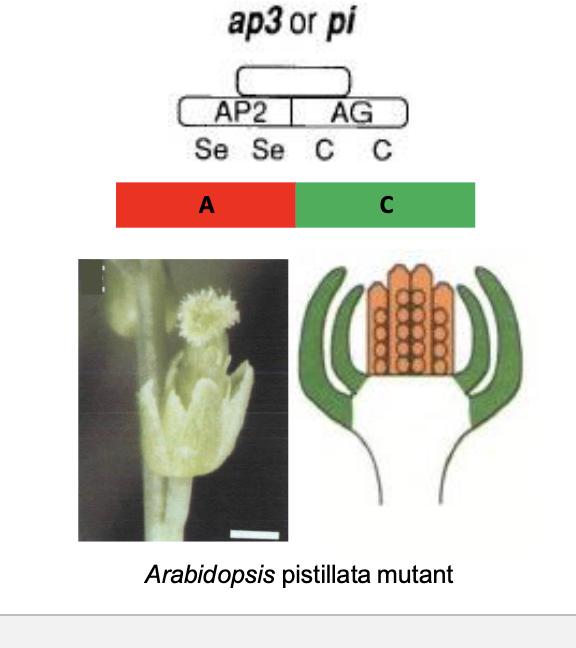
If A gene expression is missing or reduced…..
C gene expression expands, resulting in more whorls with
overlap of C with B and thus stamens replace petals
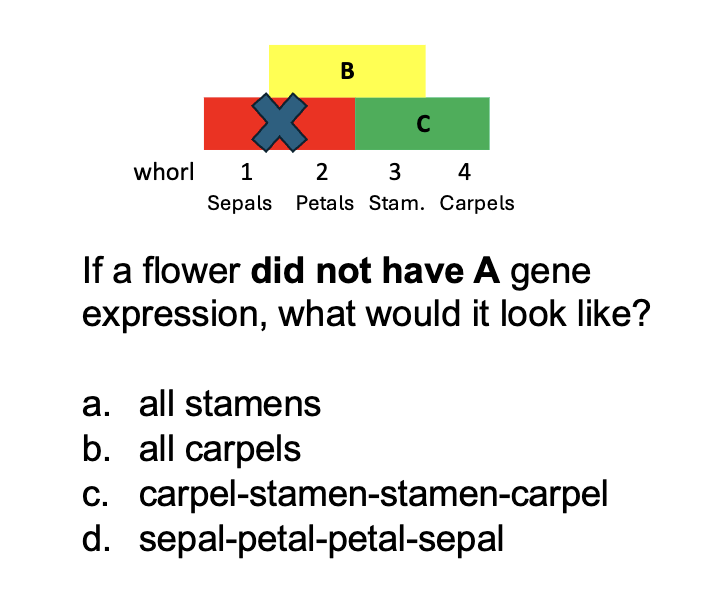
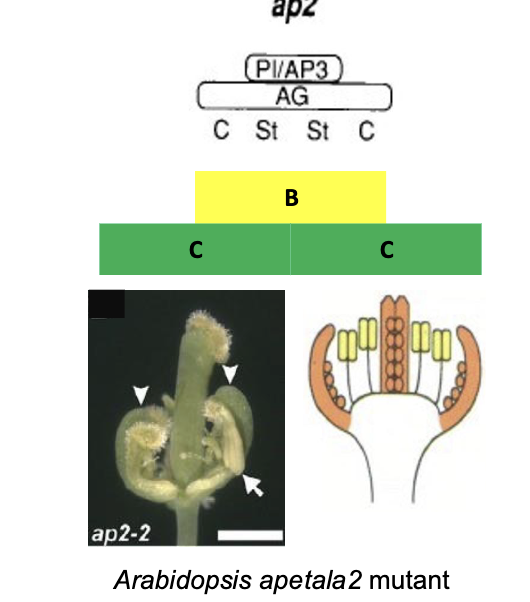
If C gene expression is missing or reduced…
A gene expression can expand, resulting in more whorls with
overlap of A and B and thus petals replace stamens.
C
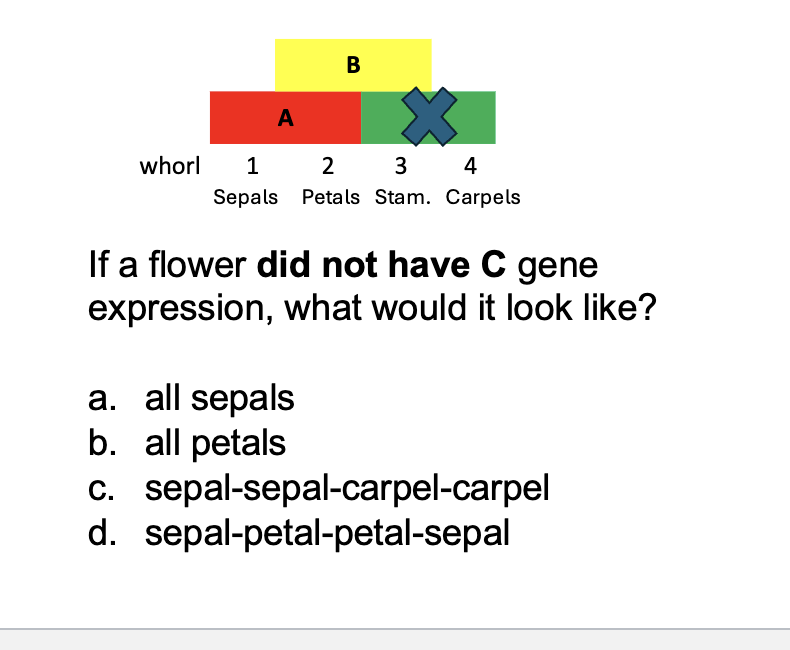
D

C gene can impacts…
whorls and determinency
Just a bunch of whorls of leaves

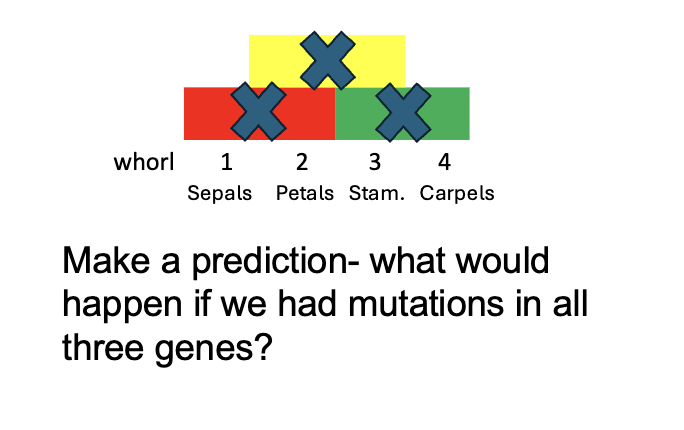
What happens when all three are mutated, but then you insert ABC into the leaves
Do you get flowers
No
more leaf whorls (CHECK)
Transcription factors (TFs)
regulatory proteins that control gene expression
by binding specific DNA sequences, usually within the promoter or enhancer regions of target genes
Their binding either activates or represses transcription
regulate ABC gene
ABC genes are regulated by
Transcription Factors
Are there more genes that impact flowers besides ABC
Yes
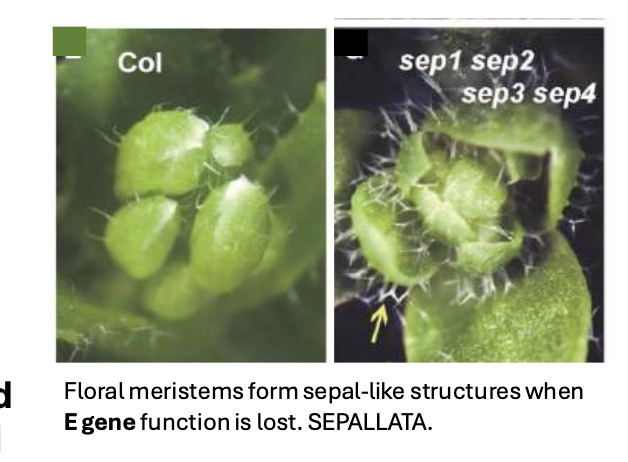
D and E
D class proteins
promote ovule identity
E class proteins
key MADS-box transcription factors that act as the "glue" in the floral quartet model
CONNECT ABCD
Can ABCD genes be in different arrangements, but still do their typical organs
yes
Homologs exist
What are Tepals
floral organs that do not show a distinction between sepals and petals
AKA → Sepals and petals look very similar
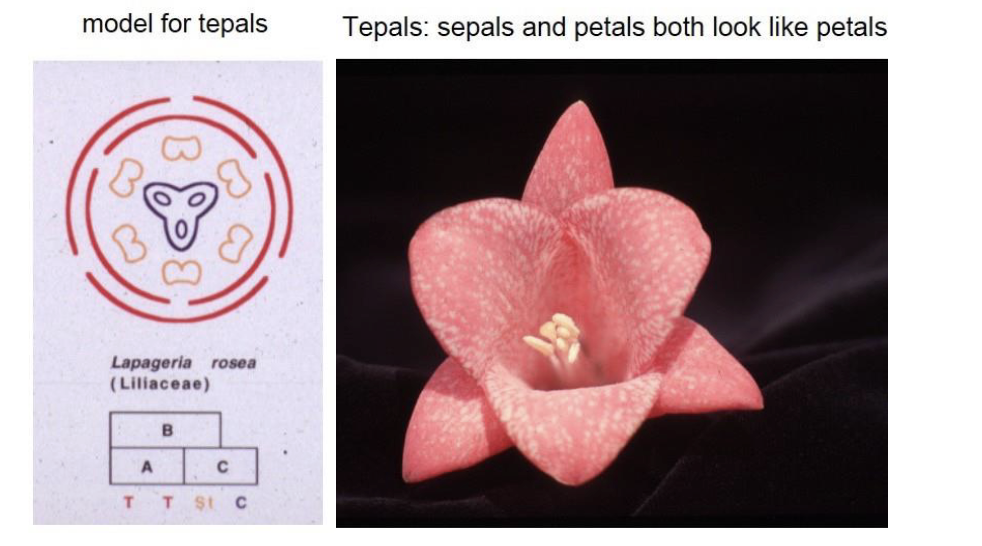
What causes tepals
A and B full overlap
Expansion expression of B genes affects
morphology
B extends over A causes
tepals
Tepals are common in …
TULIPS
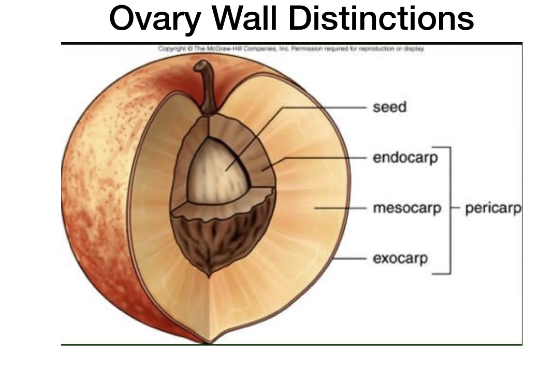
ovary wall typically develops into the fruit wall, AKA ________
pericarp
Parts of the pericarp
Endocarp
mesocarp
Exocarp
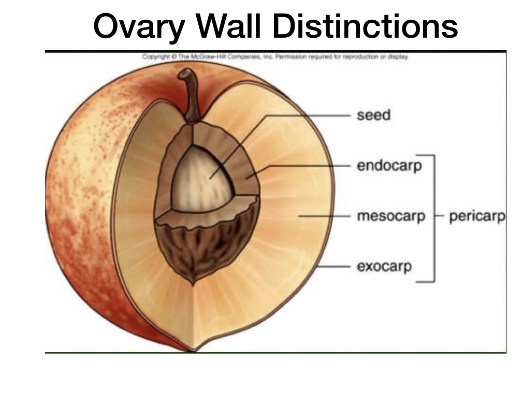
pericarp
ovary wall
(usually the term is used with no morphologically distinct
differentiated layers)
Exocarp
outer differentiated layer of the ovary
Usually the skin
Mesocarp
middle differentiated layer of the ovary wall.
Usually the flesh
endocarp
inner differentiated layer of the ovary wall
Usually the area surrounding the seed
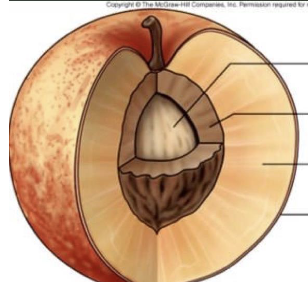
label parts of pericarp and locate the seed
hypogynous // superior
flower has the ovary above the receptacle,

epigynous (inferior).
The flower has an ovary covered by the
receptacle and sitting below the floral organs
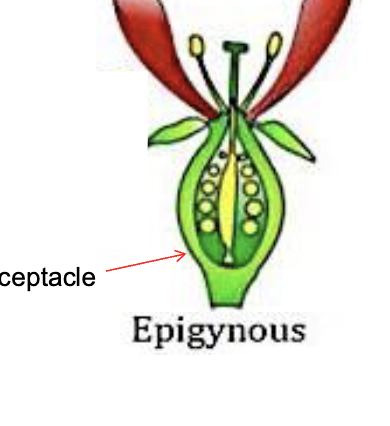
Are apples superior or inferior
INFERIOR
the lower portion on the base with brown bits are dead leaves
What are the simple fruits
Drupe
Nut
Berry
Hesperidium
Pome
Samara
Legume
Achene