Neuroanatomy Study Guide - Midterm #1 (Written)
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
What are the two structural divisions of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (Brain & Spinal cord)
Peripheral Nervous System (Cranial & Spinal Nerves)
What are the two functional divisions of the nervous system?
Somatic Nervous System
Body wall (muscles, skin, and mucous membranes)
Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System
Portions of CNS and PNS
Smooth muscles and glands of internal organs, blood vessels
Returns sensory info from organs —> brain
What is considered to be the rostral portion of the brain?
Cerebrum / Forebrain
The rostral portion of the brain is the most ____________ advanced and has the most ________ functions
The rostral portion of the brain is the most phylogenetically advanced and has the most complex functions
What are the two sections of the cerebrum?
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
What comprises the telencephalon?
Cerebral cortex (gray matter)
Subcortical white matter
Basal ganglia (gray masses deep within hemispheres)
White matter has a high ______ content with no ________ or ________.
White matter has a high myelin content with no neuronal cell bodies or synapses
What comprises the diencephalon?
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
What are the different parts of the brainstem? What is their order from superior to inferior?
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
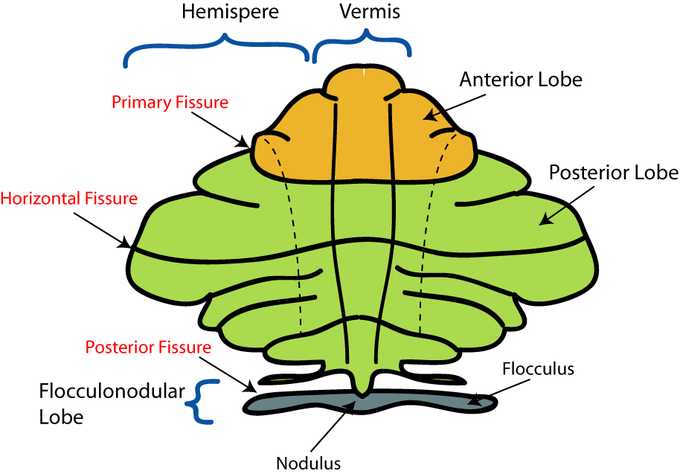
What comprises the cerebellum?
Vermis
Lateral Lobes/Hemispheres (2)
What is a ventricle?
Spaces within the hollow brain
Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
What is a neuron?
“Nerve cells”
Specialized cells that receive and send signals to other cells through extensions / axons
Encoded through electrical or chemical steps
Large cell bodies and long axons
What is an interneuron?
Small cell bodies and short axons
Transmits impulses locally
What is the definition of nuclei?
Nerve cells grouped together with common functions within the CNS
What is the definition of ganglia?
Nerve cells grouped together with common functions in the PNS
What is a tract (fasciculi)?
Pathways between groups of neurons in the CNS in the form of fiber bundles
Can descend or ascend
Pathways may cross (decussate)
What is a column (funiculi)?
Tracts in the spinal cord
What is a commisure?
Horizontal / Lateral Connections
Discuss the symmetry of the nervous system.
Bilateral symmetry is most apparent in cerebrum and cerebellum
Also present in brainstem and spinal cord
Some higher cortical functions (e.g., language) are more strong in one hemisphere than the other
What is decussation?
The crossing of fiber tracts from one side of the nervous system to the other (e.g., right side of the brain receives information from and controls motor function of the left side of the body)
What are the exceptions to decussation?
Sternocleidomastoid
Left SCM controlled by the left cerebral cortex
Cerebellar hemispheres control the ipsilateral side
(However, decussation still occurs in the cerebellum, it just crosses twice to control ipsilateral side)
What is a brain map?
Represents the outside world
Sensory map within the cerebral cortex (homunculus)
Maps within visual world in occipital, temporal, and parietal lobes
Retinotopic - preserve geometric shapes
What is the clinical importance of brain maps?
Helps clinicians localize lesions (focal lesions of the brain may only interfere with just part of the map)
What does it mean if something is afferent?
Information to the CNS
Convey sensory stimuli
What does it mean if something is efferent?
Information from CNS
Generally motor functions (muscle contraction or secretion from glands)
What are the different parts of a spinal nerve root? What is their function?
Dorsal → sensory
Ventral → motor
What would be the typical mechanism of injury of the peripheral nervous system?
Compression or physical trauma
Some systemic illnesses (diabetes, toxins / drug exposure)
What would be the effects of an injury of the peripheral nervous system?
Produces peripheral polyneuropathy (peripheral neuropathy)
Causes weakness, numbness, and pain
Typically feet are affected first (as well as the hands)
______ neurons are larger than ______ neurons.
Motor neurons are larger than sensory neurons
What is the dendritic zone?
Receptive part of the neuron
What is the synaptic terminal?
Downstream end of an axon
The cell body is the _______ and _______ center
The cell body is the metabolic and genetic center
T/F: The cell body makes up a large part of the neuron’s total volume
False (the cell body makes up a small part of the neuron’s total volume)
The receptive pole of the neuron includes the ________ and _________.
The receptive pole of the neuron includes the cell body and dendrites
What are dendrites? What is their function?
Branches of neurons that extend from the cell body (long and thin)
Branching pattern is complex and determines how a neuron integrates synaptic inputs
Receives incoming synaptic information
Acts as resistors, isolating electrical events
What is a dendritic spine? What is their function?
Small mushroom shaped projections that act as fine dendritic branches and receive synaptic inputs
Shape of the spine regulates strength of signal
e.g., thin neck = smaller influence
Dynamic and can change shape
Changes in shape can strengthen synaptic connections or alter function
What is an axon?
Long extension arising from a neuron
Cylindrical tube of cytoplasm covered by a membrane (axolemma)
What does the cytoskeleton consist of?
Neurofilaments
Microtubules
What is the function of a microtubule?
Provides framework for fast axonal transport
What is myelin?
Consists of multiple concentric layers of lipid rich membrane produced by Schwann cells (PNS) and oligodendrocytes (CNS)
What are the nodes of ranvier?
Small gaps in axon where myelin is absent
The smallest axons are ___________.
The smallest axons are unmyelinated
What is the function of myelin?
Acts as an insulator
Increases speed of impulse conduction
What are the different types of axonal transport?
Anterograde Transport
Retrograde Transport
What is anterograde transport?
The transport of materials from the cell body → synaptic terminals
Is anterograde transport fast or slow?
Both, may be fast or slow
What is retrograde transport?
The transport of materials from the synaptic terminals → cell body
T/F: Retrograde transport is similar to rapid anterograde transport?
True
After injury to an axon, the neuronal cell body responds by entering a phase called what?
Axon reaction or chromatolysis
How does regeneration differ between axons damaged in the PNS and CNS?
PNS: regenerate quickly
CNS: do not tend to regenerate
What occurs at a synapse?
Transmission of information between neurons (usually occurs between axon terminal to receptive region of receiving neuron)
What is a synaptic junction?
A specialized inter-neuronal complex
What is an axodendritic synapse?
A synapse located between an axon and dendrite
Is an axodendritic synapse considered to be excitatory or inhibitory?
Excitatory
What is an axosomatic synapse?
A synapse between an axon and nerve cell body
Is an axosomatic synapse considered to be excitatory or inhibitory?
Inhibitory
What is an axoaxonic synapse?
A synapse between an axon terminal and another axon
What is the function of an axoaxonic synapse?
Presynaptic inhibition (modulates transmitter release in postsynaptic axon)
What is an electrical synapse (gap junction)?
A specialized junction which involves the release of a chemical transmitter substance or electrical current pass directly from cell to cell
In what type of species are electrical synapses most common?
Most common in invertebrate nervous systems (but found in a small number of sites in mammalian CNS)
What are the three distinct characteristics of an electrical synapse?
Synaptic vesicles on pre-synaptic side
Synaptic cleft
Dense thickening of cell membrane on both sides
Synaptic vesicles contain ___________ and each vesicle contains a small packet (_____) of ____________.
Synaptic vesicles contain neurotransmitters and each vesicle contains a small packet (quanta) of transmitter
What is occurring during depolarization at a synaptic terminal?
Influx of calcium which leads to phosphorylation of class proteins called synapsins
Synaptic vesicles dock at the presynaptic membrane facing the synaptic cleft
Synaptic vesicle fuses with synaptic cleft
Synaptic vesicle releases transmitter
What is a transporter molecule?
Takes up transmitters from synaptic cleft (are not calcium dependent)
How are nerve cell bodies grouped?
Grouped characteristically (in many parts of the nervous system)
What is a projection neuron?
Has axons that carry impulses to other parts of the nervous system
Aggregates of tracts in the spinal corder are referred to as….
Columns (or funiculi)
Within the brain, certain axon tracts are referred to as…
Lemnisci
In some regions of the brain, axons are intermingled with dendrites and do not run in bundles so that pathways are difficulty to identify; these web-like networks are called the…
Neuropil
Glia _______ neurons in the brain and spinal cord and _______ form synapses
Glia outnumber neurons in the brain and spinal cord and do not form synapses
What are the important roles of glia?
Myelin formation
Guidance of developing neurons
Maintenance of extracellular K+ levels
Reuptake of transmitters after synaptic activity
What are the two classes of glia?
Macroglia
Microglia
Macroglia refers to…
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
What are the principle functions of oligodendrocytes?
Myelin formation in CNS
What are the principle functions of astrocytes?
Regulate ionic environment
Reuptake of neurotransmitters
Guidance of growing axons
Where is macroglia derived from?
Ectoderm
In contrast to neurons, macroglia have the capability to ________ (under some circumstances)
In contrast to neurons, macroglia have the capability to regenerate (under some circumstances).
What are the two classes of astrocytes?
Protoplasmic
Fibrous
What are the principle functions of microglial cells?
Immune surveillance of the CNS
What are the characteristics of the protoplasmic class of astrocytes?
More delicate
Processes are branched
Occurs in gray matter
What are the characteristics of the fibrous class of astrocytes?
More fibrous
Processes (containing glial fibrils) rarely branched
What are the functions of astrocytes?
Provide structural support to nervous tissue
Direct neuronal migration
Maintain appropriate concentrations of ions (K+) within brain and spinal cord
Synaptic transmission
Astrocytes surround endothelial cells within CNS
Contribute to blood-brain barrier
Where do oligodendrocytes predominate?
White matter
What are microglia?
Macrophage-like cells
What is the function of microglia?
Detect and destroy invaders (such as bacteria)
The extracellular matrix makes up about __% of the total volume of the brain and spinal cord
The extracellular matrix makes up about 20% of the total volume of the brain and spinal cord
What is ionic homeostasis?
Regulation of ion levels in extracellular space (performed by astrocytes)
What is cerebral edema?
Increase in bulk of the brain
Can be either vasogenic (extracellular) or cytotoxic (intracellular)
Must be treated emergently
What is wallerian degeneration?
If the axon is cut, the part distal to the cut degenerates
Occurs because materials for maintaining the axon are formed in the cell body and can no longer be transported down the axon (axoplasmic transport)
What is the function of the primary motor cortex?
Voluntary muscle activation
What is the function of the frontal eye field?
Eye movements
What is the function of Broca’s area?
Motor aspects of speech
What is the function of the primary sensory cortex?
Somatosensory
What is the function of the primary visual cortex?
Processing of visual stimuli
What is the function of the visual association cortex?
Processing of visual stimuli
What is the function of the primary auditory cortex?
Processing of auditory stimuli
What is the function of Wernicke’s Area?
Language comprehension
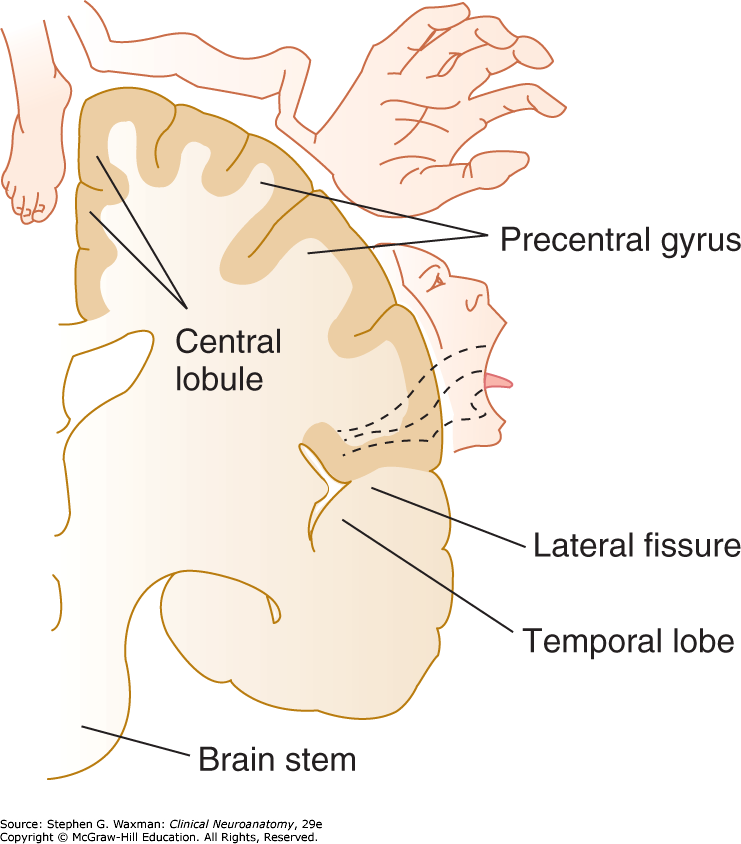
Describe the layout of the motor homunculus.
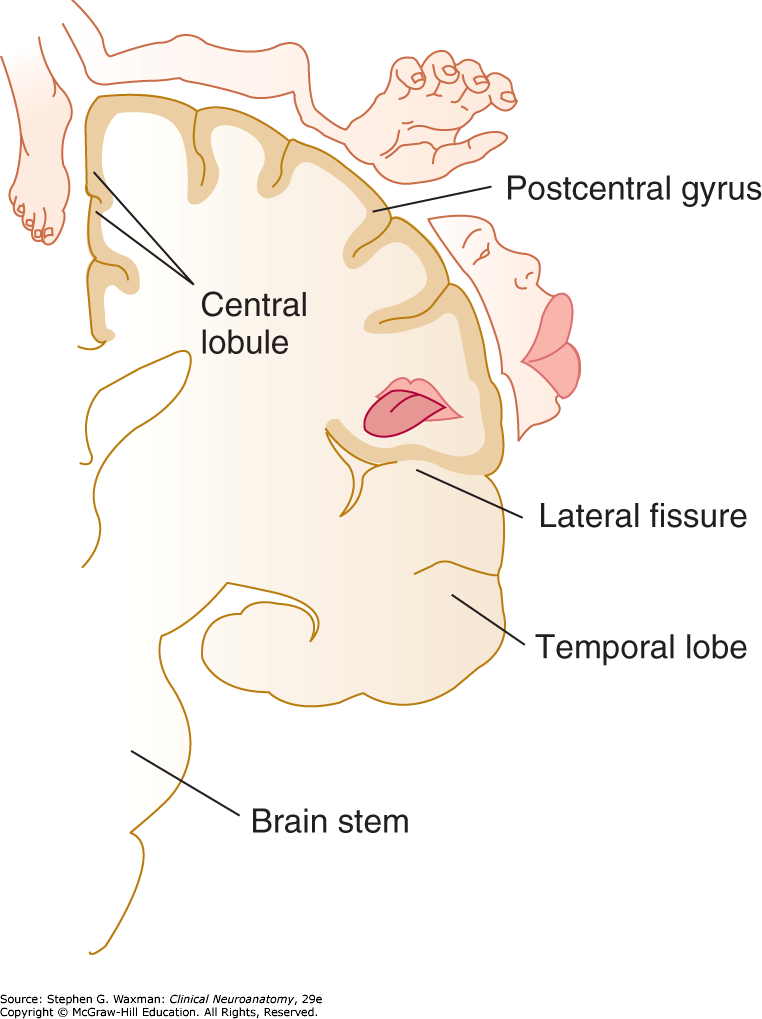
Describe the layout of the sensory homunculus.
What does the term basal ganglia refer to?
Refers to masses of gray matter deep within the cerebral hemisphere