HIBE MIDTERM
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:35 PM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Scanning Microscope
a microscope that produces an enlarged, three-dimensional image of an object by using a beam of electrons rather than light
1. **Cannot have live specimen**
2. Requires vacuum
3. Uses electron detector to detect electrons and form an image
1. **Cannot have live specimen**
2. Requires vacuum
3. Uses electron detector to detect electrons and form an image
2
New cards
Atomic Force Microscope
A device for mapping surface atomic structure by measuring the force acting on the tip of a sharply pointed wire or other object that is moved over the surface; damages specimen & can only be used once
1. Samples used do not need any special preparation, does not require a vacuum, can image biological samples
1. Samples used do not need any special preparation, does not require a vacuum, can image biological samples
3
New cards
Virus Vaccine
* Contain a weakened or inactivated virus
* Will create immune response without having to fight virus at full strength
* Sure-fire response, may have symptoms
* Will create immune response without having to fight virus at full strength
* Sure-fire response, may have symptoms
4
New cards
Protein-based vaccine
* Contain synthetic viral proteins and adjuvants
* Will trigger immune response without having to fight virus (proteins only, contains nothing that could replicate)
* Will trigger immune response without having to fight virus (proteins only, contains nothing that could replicate)
5
New cards
Nucleic Acid Vaccine
* Contain DNA or mRNA fragments to produce surface proteins
* DNA encoding for surface proteins will be transcribed into mRNA, proteins will be built and expressed, and will trigger immune responses
* DNA encoding for surface proteins will be transcribed into mRNA, proteins will be built and expressed, and will trigger immune responses
6
New cards
Functions of Vaccine
* A preventative treatment or tool in order to prevent infectious disease
* Is not necessary in an individual that already has immunity
* Is not necessary in an individual that already has immunity
7
New cards
Benefits to Vaccines
* Individuals: will receive protection
* Next time they are infected, the secondary response will trigger, which is faster and stronger
* Herd Immunity: the level at which enough of a population is immune to the disease
* Means that people who are unable to get a vaccine will still be protected.
* Fewer people who can host the virus means less chance of spreading and less mutations
* Next time they are infected, the secondary response will trigger, which is faster and stronger
* Herd Immunity: the level at which enough of a population is immune to the disease
* Means that people who are unable to get a vaccine will still be protected.
* Fewer people who can host the virus means less chance of spreading and less mutations
8
New cards
Muscular System Basics
* Facilitate movement, maintain posture, stabilize joints, produce heat, or maintain a constant body temperature
* Locomotion
* Posture maintenance
* Stabilize joints
* Produce heat when contracted
1. keeps constant body temp
* (muscles can:
1. contract
2. extend
3. return to original shape)
* Locomotion
* Posture maintenance
* Stabilize joints
* Produce heat when contracted
1. keeps constant body temp
* (muscles can:
1. contract
2. extend
3. return to original shape)
9
New cards
3 types of muscles
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal (or striated muscle)
10
New cards
Smooth
involuntary, found in walls of hollow organs (blood vessels, intestines), help blood and food move
1. characteristics:
1. no striations
2. spindle-shaped cells
3. SINGLE nucleus
4. involuntary
1. characteristics:
1. no striations
2. spindle-shaped cells
3. SINGLE nucleus
4. involuntary
11
New cards
Cardiac muscle
found only in the heart, involuntary, what makes the heart beat
1. Characteristics:
1. striations
2. SINGLE nucleus
3. involuntary
4. cells join to each other at intercalated disc
1. Characteristics:
1. striations
2. SINGLE nucleus
3. involuntary
4. cells join to each other at intercalated disc
12
New cards
Skeletal muscle
voluntary, what moves bones, found in nervous tissue, blood vessels, connective tissue, uterus, eye
1. Characteristics:
1. ==mostly attached to tendons and bones==
2. MULTIPLE nuclei
3. striated
4. voluntary
5. cells are surrounded and bundled by connective tissue
1. Characteristics:
1. ==mostly attached to tendons and bones==
2. MULTIPLE nuclei
3. striated
4. voluntary
5. cells are surrounded and bundled by connective tissue
13
New cards
What happens when muscles contract?
They get shorter… by the thick filament (myosin) using ATP to pull the thin filaments (actin) closer to each other. The more contracted muscle causes the angle between the joint to lessen.
The intersection, which is where the muscle end is attached across to the joint, moves toward the origin end of the muscle. **DIstance between origin and intersection decreases**.
The intersection, which is where the muscle end is attached across to the joint, moves toward the origin end of the muscle. **DIstance between origin and intersection decreases**.
14
New cards
What is each muscle covered with?
Each muscle is covered by **fascia**, a type of connective tissue, can also be called **epimysium**
15
New cards
What is each muscle attached to?
Each muscle attaches to bone at the **origin** point (a fixed point), and the other end attaches across a joint to the **insertion** point
16
New cards
What happens when a muscle contracts
When a muscle contracts, the insertion point moves **towards the origin point,** the origin point is unable to move, and as the muscle shortens, the points it attaches to must come closer together, and so the insertion point has to move closer to the origin point.
17
New cards
Relationship between primer movers, antagonists, fixators and synergist muscles:
The **prime mover produces the motion,** this muscle is assisted by other muscles, called **synergist muscles.** In order for one muscle to contract, another must relax, this muscle is usually on the opposite side of the muscle that is contacting, called the **protagonist**. The muscle that does the relaxing is the **antagonist,** the **fixator muscle** stabilizes the motion of the prime mover
18
New cards
primary movers
Large muscles meant to create a large amount of force
19
New cards
antagonist muscle
* Muscles which relax to allow another muscle to contract
* Help ensure that the prime movers are not over extending
* Help ensure that the prime movers are not over extending
20
New cards
fixators
* A muscle which stabilizes the origin of a prime mover.
* Allows the agonist (main actor) to function properly
* Allows the agonist (main actor) to function properly
21
New cards
sygernist
Muscles that aides a prime mover and helps prevent rotation
22
New cards
Latin terms (and what they do)
* *myo= muscle*
* *mys= muscle*
* *sacro= flesh*
* Latin names of muscles allow one to identify different characteristics of muscles, direction of muscle fibers, size, location, and number of origins
* *rectus= straight muscle fiber*
* *maximus= largest muscle of a group*
* *temporalis= location on a bone*
* *triceps= three origins*
* *mys= muscle*
* *sacro= flesh*
* Latin names of muscles allow one to identify different characteristics of muscles, direction of muscle fibers, size, location, and number of origins
* *rectus= straight muscle fiber*
* *maximus= largest muscle of a group*
* *temporalis= location on a bone*
* *triceps= three origins*
23
New cards
Flexion
decreasing the angle between two adjacent body parts
24
New cards
Extension
increasing the angle between two adjacent body parts
25
New cards
Rotation
The bone distal to the joint is moved towards or away from the midline
26
New cards
Abduction
the movement of a body part away from the midline
27
New cards
Adduction
the movement of a body part back toward the midline
28
New cards
Circumduction
a combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction (windmilling the arms)
29
New cards
Skeletal system functions
Support and protection of the body, movement of the body, blood cell formation (hematopoiesis), storage of inorganic materials, regulation of homeostasis
30
New cards
2 divisions of skeletal system
Axial skeleton (trunk), and the appendicular skeleton (limbs)
31
New cards
synthrotic joints
non-movable joints (skull)
32
New cards
fibrouos
articulating parts of joints are separated by collagen fibers
* synthrotic sub-joint
* synthrotic sub-joint
33
New cards
symphasis
joint in the body where one bone meets another
* synthrotic sub-joint
* synthrotic sub-joint
34
New cards
cartiligiounous
unossified masses between bones or parts of bones which have a cartilaginous stage
* synthrotic sub-joint
* synthrotic sub-joint
35
New cards
amphiarthrotic
Slightly moveable joints (vertebrates)
36
New cards
***Syndesmosis***
joint with complete fibrous connective tissue
* amphiarthrotic sub-joint
* amphiarthrotic sub-joint
37
New cards
Symphysis
joint with broad, flat fibrocartilage plate which cushions joints and allows for some movement
* amphiarthrotic sub-joint
* amphiarthrotic sub-joint
38
New cards
diarthrotic
moveable joint (knees, elbows, wrist, shoulder)
39
New cards
Synovial
joint found between bones which move against each other
* Ball and socket joint (shoulder and hip)
* Hinge (elbow or knee)
* Pivot (lower arm)
* Saddle (thumb)
\
* diarthrotic sub-joint
* Ball and socket joint (shoulder and hip)
* Hinge (elbow or knee)
* Pivot (lower arm)
* Saddle (thumb)
\
* diarthrotic sub-joint
40
New cards
3 fracture patterns (fracture puzzle)
Transverse, Spiral, Comminuted
41
New cards
Transverse pattern:
straight across fracture caused by bending force
42
New cards
Spiral pattern:
caused by twisting force
43
New cards
Comminuted pattern:
caused by impact force
44
New cards
3 Categories of (Type 1) Bone Fractures
greenstick fracture, fissured fracture, comminuted fracture
45
New cards
greenstick fracture
* incomplete- break occurs on the convex surface of the bend
46
New cards
fissured fracture
* incomplete- longitudinal break
47
New cards
comminuted fracture
complete- fragments the bond
48
New cards
Categories of (Type 2) Bone Fractures
transverse, oblique, spiral
49
New cards
transverse
* complete- occurs at right angle to axis of bone
50
New cards
oblique
* complete- occurs at angle other than right angle
51
New cards
spiral
* complete- caused by twisting bone
52
New cards
Cobbs Angle
Used to measure the severity of a scoliotic curve from the x-ray
53
New cards
How to measure cobbs angle
1. Extend lines from the most tilted vertebrae above apex and most tilted vertebrae below apex until they cross
2. Draw a line perpendicular to the top line and a line perpendicular to the bottom line, they should cross and make an X
3. The vertical angle in the X is the Cobb angle:
**Top vertebrate is the atlas (C1); The second is the axis (C2)**
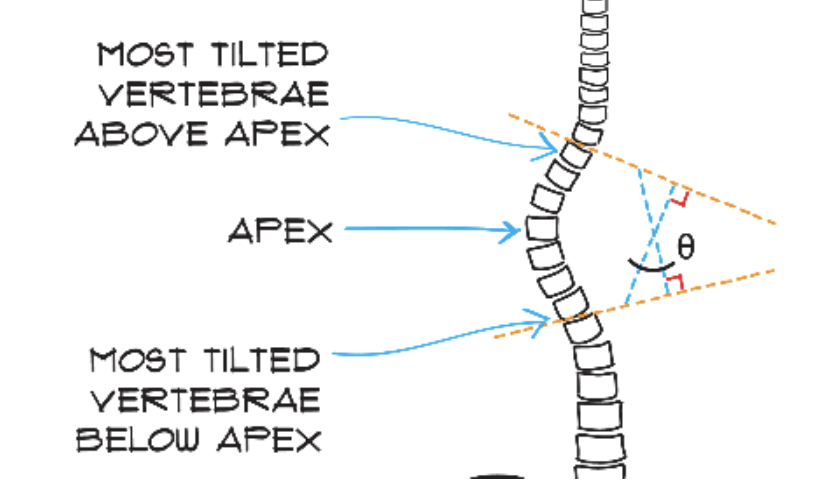
54
New cards
when does a scoliosis patient need bracing?
25deg≤θ≤45 deg
55
New cards
when does a scoliosis patient need surgery
θ≥45 deg
56
New cards
Spine Anatomy( Vertebrae and regions - basic)
Spine has 24 vertebrate sorted into 3 functional regions
57
New cards
Cervical region
has the top 7 vertebrae
58
New cards
Thoracic region
has middle 12 vertebrae
59
New cards
Lumbar region
has bottom 5 vertebrae
60
New cards
Sacrum
area with pelvis and tailbone (coccyx)
61
New cards
Difference between normal and abnormal spine:
* normal spine: has S-shaped curve when viewed from the side, appear straight vertical when viewed from front or back on x-rays
* Abnormal spine: has an abnormal curve to the side, front, or back
* Kyphosis
* Hunchback curve
* Lordosis
* Swayback in the lower region
* Abnormal spine: has an abnormal curve to the side, front, or back
* Kyphosis
* Hunchback curve
* Lordosis
* Swayback in the lower region
62
New cards
human hand anatomy
14 phalanges in the fingers
5 metacarpals in the palm
8 carpals in the wrist
5 metacarpals in the palm
8 carpals in the wrist
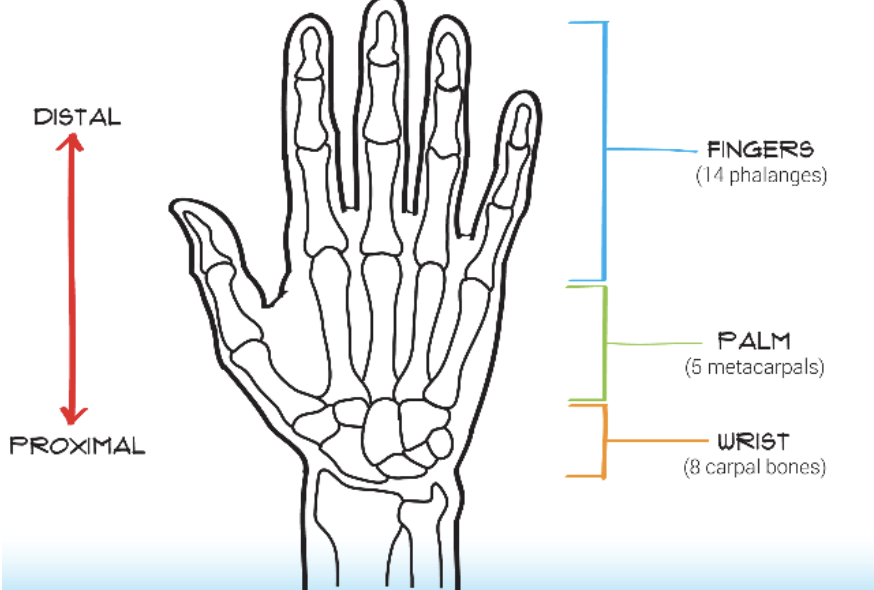
63
New cards
hand joints
* **Distal interphalangeal joint** between the distal and middle phalanges
* **Proximal interphalangeal joint** between the middle and proximal phalanges
* **Metacarpal phalangeal joint** between the proximal phalanx and metacarpal of the wrist
* **Proximal interphalangeal joint** between the middle and proximal phalanges
* **Metacarpal phalangeal joint** between the proximal phalanx and metacarpal of the wrist
64
New cards
Hand tendons
connect bones of each finger to muscles in forearm and allow the fingers to curl into a grip
* Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon ends at the distal phalanx
* Required for deep grip
* Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) tendon ends at middle phalanx
* Required for shallow grip
* Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon ends at the distal phalanx
* Required for deep grip
* Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) tendon ends at middle phalanx
* Required for shallow grip
65
New cards
what affects grip strength
Whether or not both tendons are used in the grip, grip with both FDS and FDP will be stronger than just FDS alone
66
New cards
Knee anatomy
* Four bones: femur, tibia, fibula (small one), patella
* Four ligaments: anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
* Four ligaments: anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
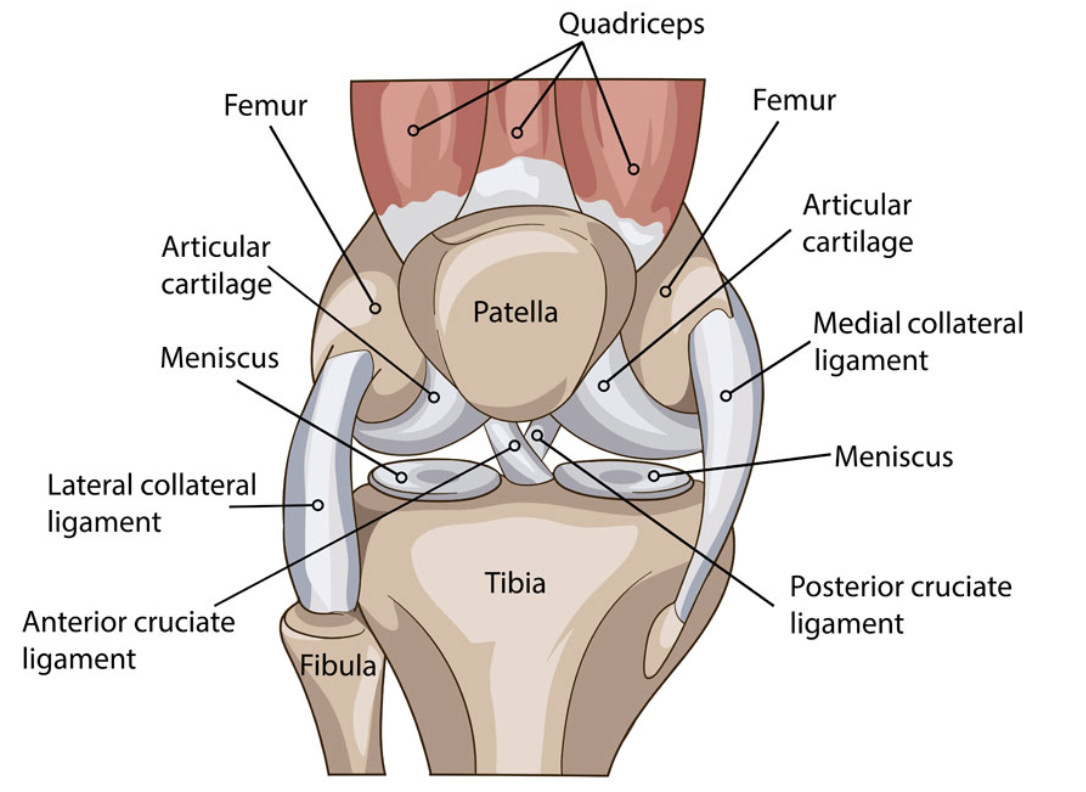
67
New cards
anterior vs lateral view
Anterior shows front view, lateral shows side view
68
New cards
Motions of knee
Flexion, Extension, Varus, Valgus
69
New cards
flexion of knee
knee bending backwards, shin coming closer to body
70
New cards
extension of knee
knee moving forwards, shin moving away from body
71
New cards
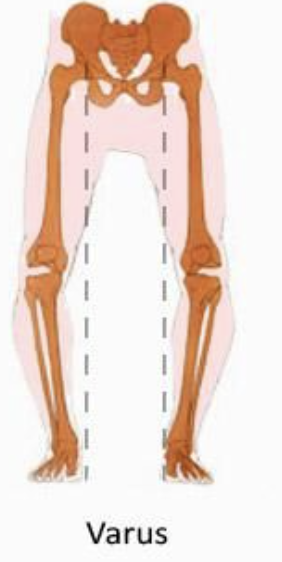
varus of knee
movement inside (towards the midline)
72
New cards
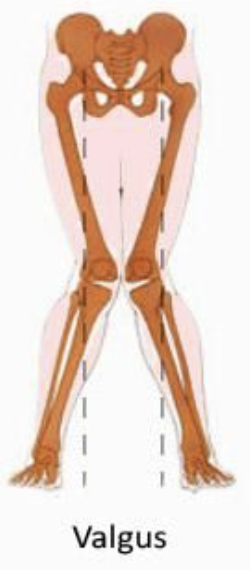
valgus of knee
movement outside (away from midline)
73
New cards
4 Principle Ligaments of knee
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
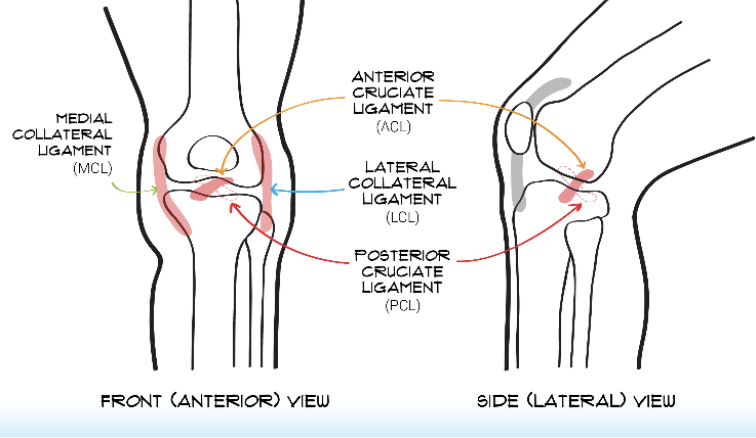
74
New cards
Clinical Tests to Test Injury
* Anterior drawer test, pulling shin out away from midline
* Posterior drawer test, pushing shin in towards midline
* Varus stress test: pulling shin in sideways, towards midline
* Valgus stress test: pulling shin out sideways, away from midline
* Posterior drawer test, pushing shin in towards midline
* Varus stress test: pulling shin in sideways, towards midline
* Valgus stress test: pulling shin out sideways, away from midline
75
New cards
transverse patter force
bending force
76
New cards
spiral fracture patter force
twisting force
77
New cards
comminuted fracture pattern force
impact force
78
New cards
Anatomical Directions
* **Proximal**: nearer to the center of the body or point of attachment
* **Distal**: farther away from the center of the body or point of attachment
* **Medial**: nearer to the midline of the body
* **Lateral**: outside/ in the region farther from the midline of the body
* **Distal**: farther away from the center of the body or point of attachment
* **Medial**: nearer to the midline of the body
* **Lateral**: outside/ in the region farther from the midline of the body
79
New cards
Femur Features
* Femoral head at top of bone (proximal) near hip joint
* Femoral neck
* Trochanteric region
* Shaft
* Condyles by knee joint
* Femoral neck
* Trochanteric region
* Shaft
* Condyles by knee joint
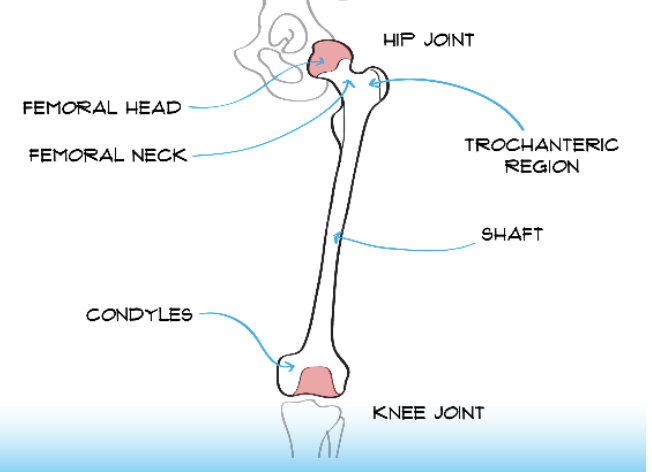
80
New cards
proximal fractures (femur)
Occur near the femoral head, neck, or trochanteric region
81
New cards
distal fractures (femur)
* Entra-articular fractures are outside the cartridge area of condyles
* Intra-articular fractures are inside the cartilage area of condyles
* Intra-articular fractures are inside the cartilage area of condyles
82
New cards
this is just an image of femur breaks
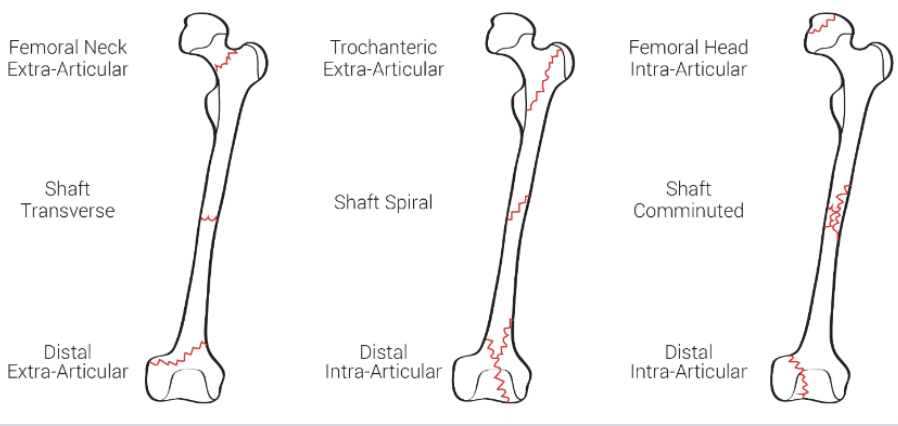
83
New cards
Nanoscale
The scale at which an object can be considered nano, 1-100 nm
84
New cards
nanotechnology
Application of property modifications that happen at the nanoscale to some beneficial endeavor
85
New cards
kilo
10^3, 1000 g/m/s
86
New cards
Base unit
BU: 10^1, 1 g/m/s
87
New cards
mili
10^-3, 0.001 g/m/s
88
New cards
micro
10^-6, 0.000001 g/m/s
89
New cards
nano
10^-9 0.000000001 g/m/s
90
New cards
pico
10^-12, 0.000000000001 g/m/s
91
New cards
astronomical
needs to be seen with a telescope (10^11 and larger)
92
New cards
macro
can be seen with the human eye (10^3 - 10^-3)
93
New cards
micro
must be seen with a microscope (10^-4 - 10^-6)
94
New cards
nano
use electron microscope to see, must be 1-100 nm to be considered nano (10^-7 to 10^-9)
95
New cards
atomic
size of atoms and molecules ( 10^-10)
96
New cards
subatomic
size of subatomic particles (10^-15)
97
New cards
color at nanoscale
* Result of interaction of light with the composition and atomic structure of the sample
* Optical properties change
* Optical properties change
98
New cards
size at nanoscale
Between 1 and 100 nm
* Will have greater surface area to volume ratio than larger particles
* Will have greater surface area to volume ratio than larger particles
99
New cards
nanoparticle
nano in all 3 directions
100
New cards
nanofilm
nano in 1 dimension but unlimited in the other 2, physical properties still change to what they are in nano, but size can be unlimited