Bio mid term 1 :(
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
249 Terms
1
New cards
Two types of Science
Induction and Hypothesis based science
2
New cards
Induction Based Science
A predictive generalization
Ex. Cell theory - generalizations about cells
Ex. Cell theory - generalizations about cells
3
New cards
Hypothesis Based Science
Deductive Reasoning
Hypothesis - explanation for an observations
Hypothesis - explanation for an observations
4
New cards
Occam's Razor
If several explanation work with your evidence, then go for the simplest one. The razor shaves off unnecessary details.
5
New cards
What happens if there is no control in an experiment
No support for hypothesis
6
New cards
Negative Control
Did nothing
7
New cards
Positive Control
A known characterized treatment.
It will give a well known effect that is no surprise
It will give a well known effect that is no surprise
8
New cards
Progress in Science
Explanatory power
New ideas are formed, and the old rejected
New ideas are formed, and the old rejected
9
New cards
Theories
Need a huge amount of evidence
Ex. Theory of natural selection
Theories are excepted only because of the evidence behind them.
Ex. Theory of natural selection
Theories are excepted only because of the evidence behind them.
10
New cards
Replication
Sample size does not equal 1
Has a greater chance of convincing results with replicates
Did all results do the same thing ?
Has a greater chance of convincing results with replicates
Did all results do the same thing ?
11
New cards
Reproducibility
Can others do your experiment?
The same results should be from the same experiment, regardless of where and when.
The same results should be from the same experiment, regardless of where and when.
12
New cards
Composition of an Atom
Nucleus has protons (1+) and neutrons (0)
Electrons (1-) are in orbitals around nucleus
Electrons (1-) are in orbitals around nucleus
13
New cards
What defines an atom
The number of protons and the number of neutrons
14
New cards
Isotopes
Have the same atomic number, but a different number of neutrons
15
New cards
What are bonds based on
Electrons
16
New cards
How many bonds does Carbon have
4
17
New cards
How many bonds does Hydrogen have
1
18
New cards
How many bonds does Oxygen have
2
19
New cards
Hydrogen
Smallest atom
H+ are important for cellular metabolism
H+ are important for cellular metabolism
20
New cards
What is left over if Hydrogen loses an electron
Only a proton
21
New cards
Cations
positively charged ion
22
New cards
Anion
a negatively charged ion
23
New cards
Helium
Second smallest atom
Two protons
atom is mostly empty space
Noble gas
Two protons
atom is mostly empty space
Noble gas
24
New cards
What does a chemical bond require
one pair of electrons each atom providing one electron
25
New cards
What type of bond is N
3
26
New cards
Non polar
no partial charge on atoms
Share equal
Share equal
27
New cards
Covalent
Bonds are shared
28
New cards
Electronegativity (EN)
The ability of some atoms to attract electrons to itself
29
New cards
Polar Covalent Bonds
Shared unequally in a covalent bonds - if moderate difference
30
New cards
Polar
Refers to the fact that partial charges due to unequal sharing
31
New cards
What is water held together by
two polar bonds - example of a polar molecule
32
New cards
Examples of Non polar covalent bonds
O-H, N-H, 0-C, N-C
33
New cards
Ionic Bonds
No sharing
Taking electrons (higher EN)
Ex. Salts
Form between between atoms with different EN
Taking electrons (higher EN)
Ex. Salts
Form between between atoms with different EN
34
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
Constantly breaking and reforming (transient)
Consequence of polar covalent bonds containing hydrogen
Water molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonds
Consequence of polar covalent bonds containing hydrogen
Water molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonds
35
New cards
Water
Cells are 80% water
Water is the solvent of life
Water is the solvent of life
36
New cards
Universal Solvent
Does not exist
37
New cards
What does water exhibit
Cohesion
38
New cards
Hydrophilic
Water liking
Polar/Charged
Polar/Charged
39
New cards
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Non polar covalent bonds
not soluble in water
Non polar covalent bonds
not soluble in water
40
New cards
What is water attracted to
Large polar/ charged molecules
Ex. Sugars
Ex. Sugars
41
New cards
What is more soluble
Small hydrophilic molecules
42
New cards
Large polar molecule solubility
They are also hydrophilic
But can be too big to be soluble
But can be too big to be soluble
43
New cards
What are Hydrophobic molecules composed of
Non polar covalent bonds
Ex. C-C, C-H Fats are hydrophobic
Ex. C-C, C-H Fats are hydrophobic
44
New cards
What can water do
Reverse disassociate
45
New cards
Strong acid
Complete dissociation unlike equilibrium for water dissociation
HCl-->H+ +Cl-
HCl-->H+ +Cl-
46
New cards
Acidity
protons (H+)
More than High acidity
More than High acidity
47
New cards
pH
Measure of acidity
-log[H+]
-log[H+]
48
New cards
What is pH 7
Neutral/water
49
New cards
Higher than 7 pH
Acidic
50
New cards
Lower than 7 pH
Basic
51
New cards
What makes water pH lower
The atmosphere
52
New cards
What is carbon based
Life ;)
53
New cards
What roles do Carbon molecules play
1) Structural Role
2) Metabolic Role
2) Metabolic Role
54
New cards
Why is carbon a Lego block
Will form non polar covalent bonds with C+H
Form polar covalent bonds with O or N
Form polar covalent bonds with O or N
55
New cards
How many types of isomerism
3
56
New cards
Double Bonds (Planar)
cannot rotate
57
New cards
Structural Isomerism
Same molecular formula, but differ in how carbons are arranged
Different covalent arrangements of atoms
Different covalent arrangements of atoms
58
New cards
Cis/Trans isomerism
Different molecules have the same formula, but different on how parts of molecules are based around carbon
59
New cards
Enantiomer Isomerism
Called asymmetrical
Same 4 things attached but in different ways
Mirror images not equivalent
Same 4 things attached but in different ways
Mirror images not equivalent
60
New cards
How to read organic Chemistry
C and H are implied
Every angle has Carbon unless differently shown
Carbon has 4 bonds if not Hydrogen is attached
Every angle has Carbon unless differently shown
Carbon has 4 bonds if not Hydrogen is attached
61
New cards
Macromolecules
Very large
Polymer
Many monomer subunits
Ex. Carbon molecules
Condensation synthesis
Polymer
Many monomer subunits
Ex. Carbon molecules
Condensation synthesis
62
New cards
Large Biological Molecules
Not a big as macromolecules
Ex. Lipids
Still big tho
Ex. Lipids
Still big tho
63
New cards
Monomers
Can exist on their own
Also building blocks
Ex. Glucose
Also building blocks
Ex. Glucose
64
New cards
Polymer
Linked monomers from covalent bonds
Ex. Polytrene
Ex. Polytrene
65
New cards
Condensation Reaction/ Dehydration
Formation of covalent bond
Loss of water molecules
H20 is product
Loss of water molecules
H20 is product
66
New cards
Condensation Synthesis
Several to many rounds of condensation reaction
Leading to large biological macro molecules
Leading to large biological macro molecules
67
New cards
Hydrolysis
Break apart using water
Opposite of condensation
release monomer
Water is reactant
Opposite of condensation
release monomer
Water is reactant
68
New cards
Hydrolysis of macromolecules
Remove damaged macro molecules
Monomer subunits can be recycled
Monomer subunits can be recycled
69
New cards
Carbs
Monomer/small polymer
Carbs that are larger than monomers are monosaccharide
Simple sugars or polymer of sugar unit
May contain 3-7 carbon atoms
Carbs that are larger than monomers are monosaccharide
Simple sugars or polymer of sugar unit
May contain 3-7 carbon atoms
70
New cards
Proteins
polymers of amino acids
(Amino acids are monomer sub units
(Amino acids are monomer sub units
71
New cards
Lipids
Large biological molecule
(not a macro molecule)
Have C-C/C-H (non polar covalent)
(not a macro molecule)
Have C-C/C-H (non polar covalent)
72
New cards
Nucleic Acid
DNA and RNA
Nucleic acid are polymers of nucleotides
Nucleic acid are polymers of nucleotides
73
New cards
Two Major Roles of Monosaccharides
1) Form parts of other molecules
2) Energy metabolism Ex. glucose is blood sugar
2) Energy metabolism Ex. glucose is blood sugar
74
New cards
Oligosaccharides
Short Chain 2 or more sugar monomer (not macro or large)
Chain is formed by condensation synthesis
Chain is formed by condensation synthesis
75
New cards
Disaccharides
2 subunits
76
New cards
Trisaccharides
3 subunits
77
New cards
Polysaccharide
True macromolecule
Many rounds of condensation synthesis
Cannot dissolve well
100-1000 monomer subunits
Ex. starch, glycogen, cellulose
Many rounds of condensation synthesis
Cannot dissolve well
100-1000 monomer subunits
Ex. starch, glycogen, cellulose
78
New cards
Cellulose
Glucose polymer
Cellulose is not a good energy for humans
(dietary fiber in human diets)
Cant access glucose in digestive system
Cellulose is not a good energy for humans
(dietary fiber in human diets)
Cant access glucose in digestive system
79
New cards
Sub Groups of Lipids
Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
Phospholipids
Steroids
80
New cards
Fats
Don't dissolve in water
Can dissolve in less polar solvent (acetone)
Fats have greater density than terms
Can dissolve in less polar solvent (acetone)
Fats have greater density than terms
81
New cards
How to Build a Fat
Glycerol and three fatty acid join H and OH and palmitic acid
3 condensation reactions
3 H20 are released in the process
3 condensation reactions
3 H20 are released in the process
82
New cards
Saturated Fatty Acid
C-C single bond, straight
83
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
C=C double bond, causes kink in chain
Trans (H on different side) or Cis (H on same side)
Trans (H on different side) or Cis (H on same side)
84
New cards
What is Saturated Fat at room temp?
Solid
85
New cards
What is Poly Saturated Fat at room temp
Liquid
86
New cards
Phospholipids
3 carbon back bone
2 fatty acids and a head group
Structural molecules
2 fatty acids and a head group
Structural molecules
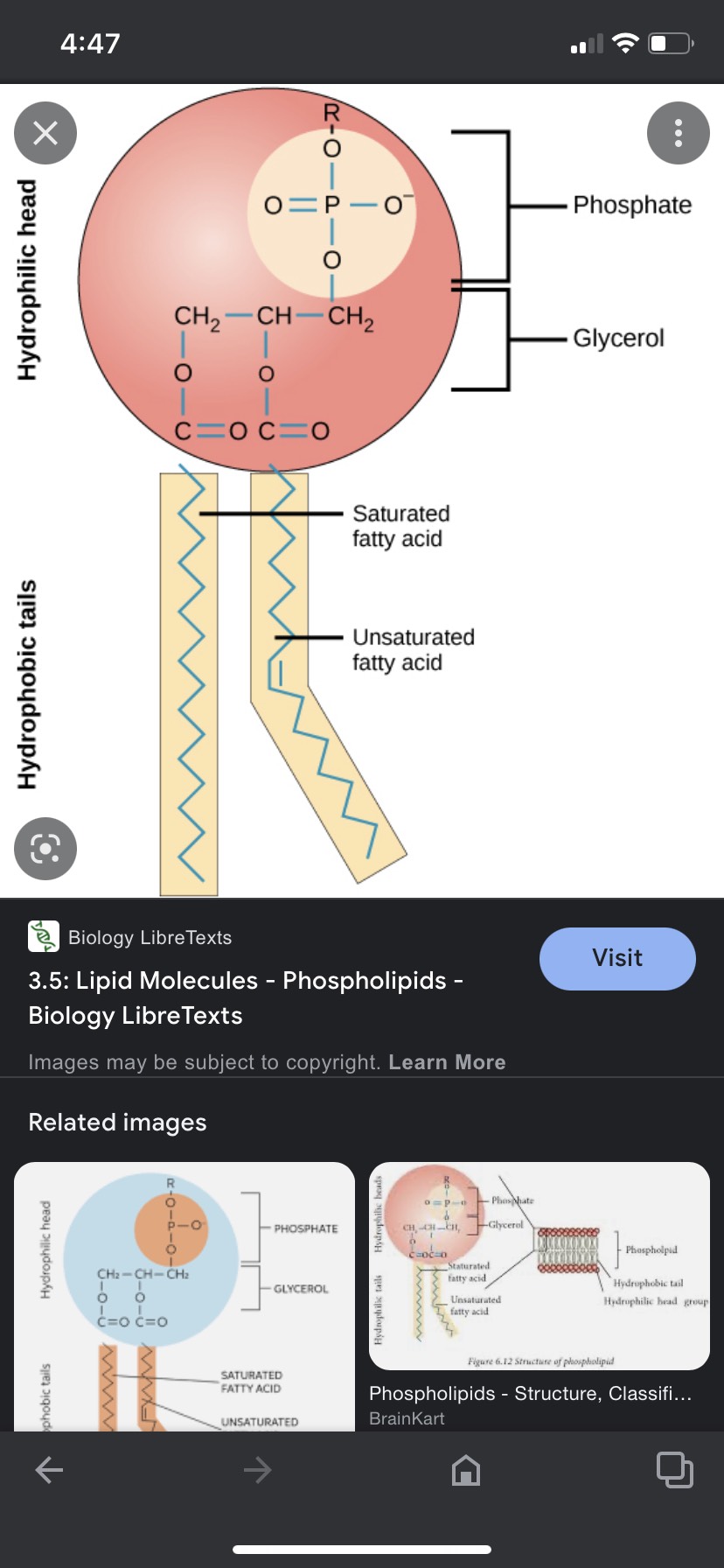
87
New cards
Is a head group hydrophilic or hydrophobic
Both ! It is Amphipathic (has polar and non polar regions)
88
New cards
Steroids
Hydrophobic, non fatty acid lipids
All have four C- based rings
All have four C- based rings
89
New cards
What Two Major Roles do Steroids Play?
1) Hormones Ex. estrogen, testosterone
2) Structural - components of bio membrane (influence fluidity of membrane)
2) Structural - components of bio membrane (influence fluidity of membrane)
90
New cards
Basic Steroid Structure
Steroids are like cholesterol
They are made from 4 fused hydrogen rings
They are made from 4 fused hydrogen rings
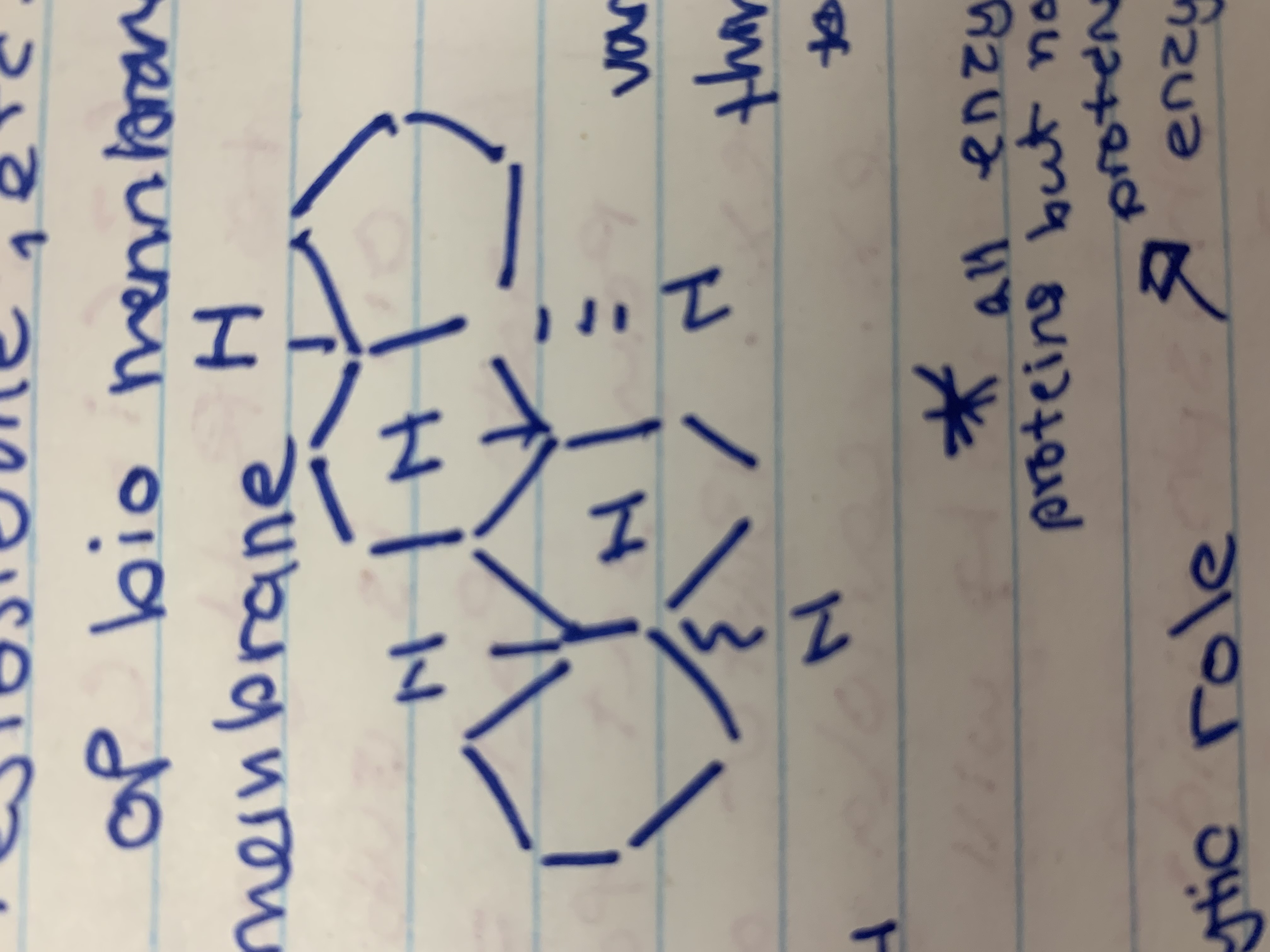
91
New cards
Proteins are Macromolecules
Amino acids are the monomer subunits
They are a linear sequence they don't branch
They are a linear sequence they don't branch
92
New cards
Protein Amino Acids
There are 20
Plants have the ability to produce/synthesize all of them
Humans cant synthesize all of them
Essential amino acids must be provided in the diet
Plants have the ability to produce/synthesize all of them
Humans cant synthesize all of them
Essential amino acids must be provided in the diet
93
New cards
Amino acids have a central asymmetric (chiral carbon)
An amino group
Carboxyl group
Hydrogen atom
and a side chain
Carboxyl group
Hydrogen atom
and a side chain
94
New cards
What are proteins held together by
Peptide bonds
95
New cards
What are Peptide bonds
Condensation /Dehydration synthesis reaction
96
New cards
What are the Levels of Protein Structure?
All have primary, secondary, and tertiary
Some have quaternary
Some have quaternary
97
New cards
Primary Structure
Linear sequences of amino acids
98
New cards
Secondary Structure
Alpha helices, and Beta pleaded sheets
Due to H between H-O in amino acids
Due to H between H-O in amino acids
99
New cards
Tertiary Structure
4 chemical bonds between R groups
Vanity of chemical interactions determine the proteins tertiary structure
Includes hydrophobic, ionic bond, H bond
Vanity of chemical interactions determine the proteins tertiary structure
Includes hydrophobic, ionic bond, H bond
100
New cards
Quaternary Structure
From 2+ polypeptide units - string of amino acids
Also has 1,2,3 in it as well as 4
Also has 1,2,3 in it as well as 4