AP U.S. History Study Guide Overview and Key Concepts
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
Period 1
1491-1607
Key Concept 1.1
As native populations migrated and settled across the vast expanse of North America over time, they developed distinct and increasingly complex societies by adapting to and transforming their diverse environments.
Key Concept 1.2
The legacy of Christopher Columbus is still being debated. Some see him as a noble explorer, while others blame him for the wrongs inflicted on the American Indian population.
Columbian Exchange
Contact among Europeans, Native Americans, and Africans resulted in the Columbian Exchange and significant social, cultural, and political changes on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean.

1491
Christopher Columbus claims the islands of Hispaniola and Cuba for Spain.
Encomienda System
A forced labor system developed by the Spanish that required American Indians to work for Spanish colonists.
1512
Hernan Cortes invades Mexico.
1519
Previous to European contact, American Indian tribes across both North and South America had complex societies with distinctive social structures, political organizations, and religious beliefs.
Maize
This was the main crop cultivated by American Indians.
Christopher Columbus
An Italian explorer who stumbled upon the New World after convincing the Spanish monarchs that he could sail across the Atlantic to India.
God, Gold, Glory
Early European explorers were motivated by a desire to spread Christianity, enrich themselves and their monarch, and gain glory for discovering new lands.
American Indian tribes
Across both North and South America, these tribes had complex societies with distinctive social structures, political organizations, and religious beliefs.
Sedentary lifestyle
A lifestyle developed by tribes in the American Southwest and modern-day Mexico due to the cultivation of maize.
Hunter-gatherer lifestyle
A lifestyle followed by American Indians in the American northwest, characterized by a combination of permanent settlements and nomadic practices.
Diseases
The American Indian population was decimated by diseases brought over by Europeans.
Cash crops
Crops that were farmed in the New World, often requiring slave labor to cultivate.
Columbian Exchange
A trade system that moved crops, animals, and diseases from the Old World to the New World and vice versa.
Potatoes, tomatoes, corn
American crops introduced to Europe through the Columbian Exchange.
Wheat, rice, grapes
European crops introduced to the Americas through the Columbian Exchange.
Slavery
The practice of bringing slaves to the New World to farm cash crops and mine for precious metals.
Timeline
A chronological account of significant events from 1491 to 1754.
1607-1754
The time period that counts for 10% of recommended instructional content for an AP® class.
Mercantilism
An economic system where countries tried to increase their wealth through government control of all aspects of trade.
Encomienda system
A forced labor system developed by the Spanish that required American Indians to live on plantations and convert to Christianity.
Cash crops
Crops that could be grown in large quantities, harvested, and sold for a profit.
First Great Awakening
A religious movement that promoted emotional, evangelical Protestantism often through 'fire and brimstone' sermons and camp meetings.
Jamestown
The first English colony in the New World, founded in 1607.
French and Indian War
A conflict between Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763, part of the larger Seven Years' War.
Political exchanges
Interactions between the British colonies and Great Britain that influenced governance and policy.
Cultural exchanges
The sharing of cultural practices and ideas between the British colonies and Great Britain.
Economic exchanges
Trade and economic interactions between the British colonies and Great Britain.
Spanish control
The Spanish held the largest amount of territory in the New World, primarily seeking precious metals.
Pilgrims
A group of English settlers who signed the Mayflower Compact before settling at Plymouth Colony in 1620.
Wampanoag
A Native American tribe that engaged in conflict with New England colonists during King Philip's War.
Salem Witch Trials
A series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts in 1692.
Colonial diversity
The varying characteristics and economies of different English colonies, particularly between New England and the southern colonies.
Plantations
Large agricultural estates that relied on the labor of enslaved people or indentured servants.
Religious persecution
The mistreatment of individuals based on their religious beliefs, prompting some colonists to seek refuge in America.
Trade networks
Systems of trade established between colonists and Native Americans.
British control
The dominance of British governance over American colonies, particularly following the decline of French and Dutch influence.
Cohesive unit
The British government's aim to unify its colonies to strengthen economic and political ties.
Evangelical religiosity
A heightened sense of religious fervor and commitment among colonists during the First Great Awakening.
Colonial economies
The various economic systems that developed in the colonies, influenced by geography and resources.
Religious meetings
Gatherings for worship and discussion, which were sometimes restricted by colonial authorities.
Cultural unity
The shared cultural practices and beliefs that developed among colonists, influenced by various movements and events.
Economic regulations
Policies implemented by the British government to control colonial trade and economic practices.
Proclamation of 1763
Ordered colonists to stop migrating west of the Appalachian Mountains.
Declaration of Independence
Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776.
No Taxation without Representation
A rallying cry for colonists who were unhappy with British rule, arguing against taxes imposed by a government in which they had no representation.
Articles of Confederation
The first constitution of the United States, adopted in 1780.
British control of American colonies
The British government tried to make its colonies into a cohesive unit to help boost the economy of Great Britain.
American Revolution
A movement for independence from British rule that led to the Revolutionary War.
Colonial independence movement
A response to British attempts to assert tighter control over North American colonies.
Democratic and republican ideals
Ideas that inspired new experiments with different forms of government during the American Revolution.
Migration within North America
Movement of people that intensified conflicts over resources, boundaries, and trade.
French and Indian War
A conflict between Britain and France in North America that contributed to British attempts to control the colonies.
Boston
The location where British troops arrived in 1768.
Lexington and Concord
The sites of the first battles of the American Revolution in 1775.
The Stamp Act
A tax imposed by the British government that led to protests from the colonists.
The Townshend Acts
A series of laws passed by the British government that taxed goods imported to the American colonies.
The Tea Acts
A law that granted the British East India Company the right to sell tea to the colonies free of competition.
Colonial resolve
The determination of the colonies to pursue self-government despite British control.
Cohesive unit
A term describing the British government's goal for its colonies to function together effectively.
Evangelical religiosity
A sense of religious fervor that emerged among colonists during the First Great Awakening.
Economic regulations
Policies applied by the British government to control colonial economies in a haphazard fashion.
Colonial unity
The increasing collaboration and solidarity among the colonies in response to British policies.
Articles of Confederation
The first constitution of the United States, established a very weak federal government.
U.S. Constitution
The foundation of the U.S. federal government.
Federalist Papers
A series of papers written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison that advocated for a strong federal government.
Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution that guarantee individual rights.
French and Indian War
A conflict between the French and the English over control of the Ohio River Valley.
Preamble to the U.S. Constitution
The introductory statement that outlines the purpose of the Constitution.
Key Concept 4.1
The United States began to develop a modern democracy and celebrated a new national culture.
Key Concept 4.2
Innovations in technology, agriculture, and commerce powerfully accelerated the American economy.
Key Concept 4.3
The Hudson River School was one of the first truly American artistic movements focused on American landscapes.
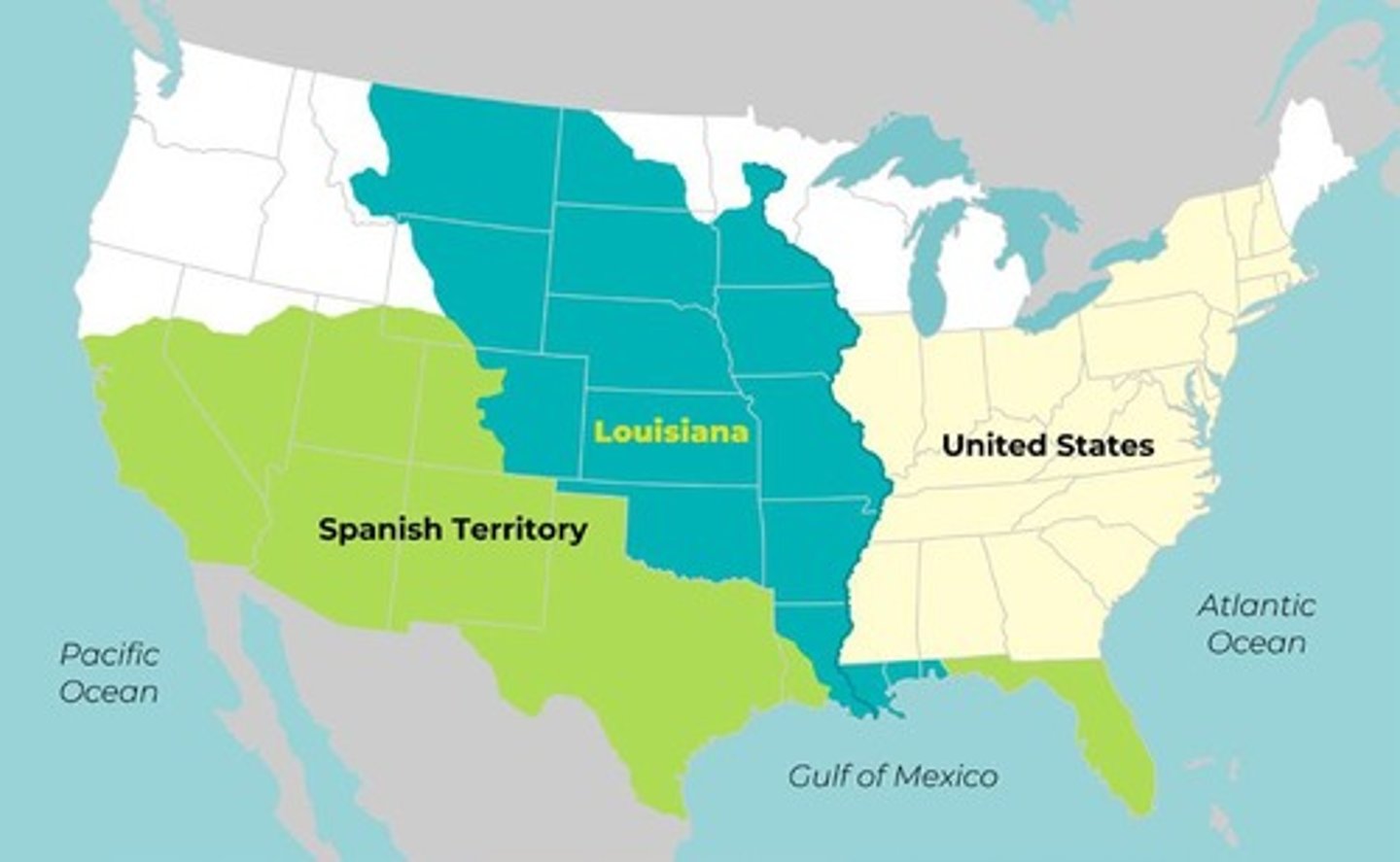
1803 Louisiana Purchase
The federal government finalized the acquisition of the Louisiana Territory.
1807 End of International Slave Trade
Congress votes to end the international slave trade.
1812 War against Britain
The U.S. declares war against Britain.
Period 4: 1800-1848
This time period extends from 1800 to 1848 and counts for 10% of recommended instructional content for an AP® class.
American Democracy
The evolving political system in the U.S. that began to take shape in the early 19th century.
National Culture
The shared cultural identity that began to emerge in the United States during the early 1800s.
Economic Changes
Profound changes to U.S. society and to national and regional identities due to economic innovations.
Gradual Change
A period characterized by slow and steady transformation in U.S. society and governance.
Mexican-American War
A conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848.
Constitutional Limits
The need for the new country to define and limit the powers of the Constitution.
Judicial Review
The ability of the Supreme Court to determine whether a law is constitutional
Second Great Awakening
A series of religious revivals in the early 1800s that focused on personal religious experience
American System
A plan proposed by Henry Clay that was intended to strengthen the economy of the U.S. through a combination of tariffs, national banks, and infrastructure
Louisiana Territory
A large portion of land that was purchased from France by the U.S. Federal government in 1803 for $15 million
Manifest Destiny
The belief in the 19th century that the expansion of the U.S. across the American continents was both justified and inevitable
Indian Removal Act
A law signed by Andrew Jackson to relocate American Indians west of the Mississippi River
Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
An autobiography published in 1845 by Frederick Douglass detailing his experiences as a slave and his journey to freedom
Seneca Falls Convention
The first women's rights convention held in 1848 in Seneca Falls, New York
Economic Changes in the U.S.
The transition from an agricultural economy to a manufacturing economy during the early 19th century
Telegraph
An invention that revolutionized communication by allowing messages to be sent over long distances almost instantly
Textile Machinery
Machines used in the textile industry that contributed to the manufacturing economy
Cultural Identities
Distinct cultural identities that developed in the North and South due to economic differences
Expansionist Foreign Policy
A policy pursued by the U.S. to expand its territory and influence, particularly in the Western Hemisphere
Civil War
A conflict in the United States from 1861 to 1865 primarily over issues of slavery and states' rights
Reconstruction
The period following the Civil War during which the Southern states were reorganized and reintegrated into the Union