Cell structures and functions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
epithelial cells
fibroblasts
erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Cells that connect body parts, form linings, or transport gases
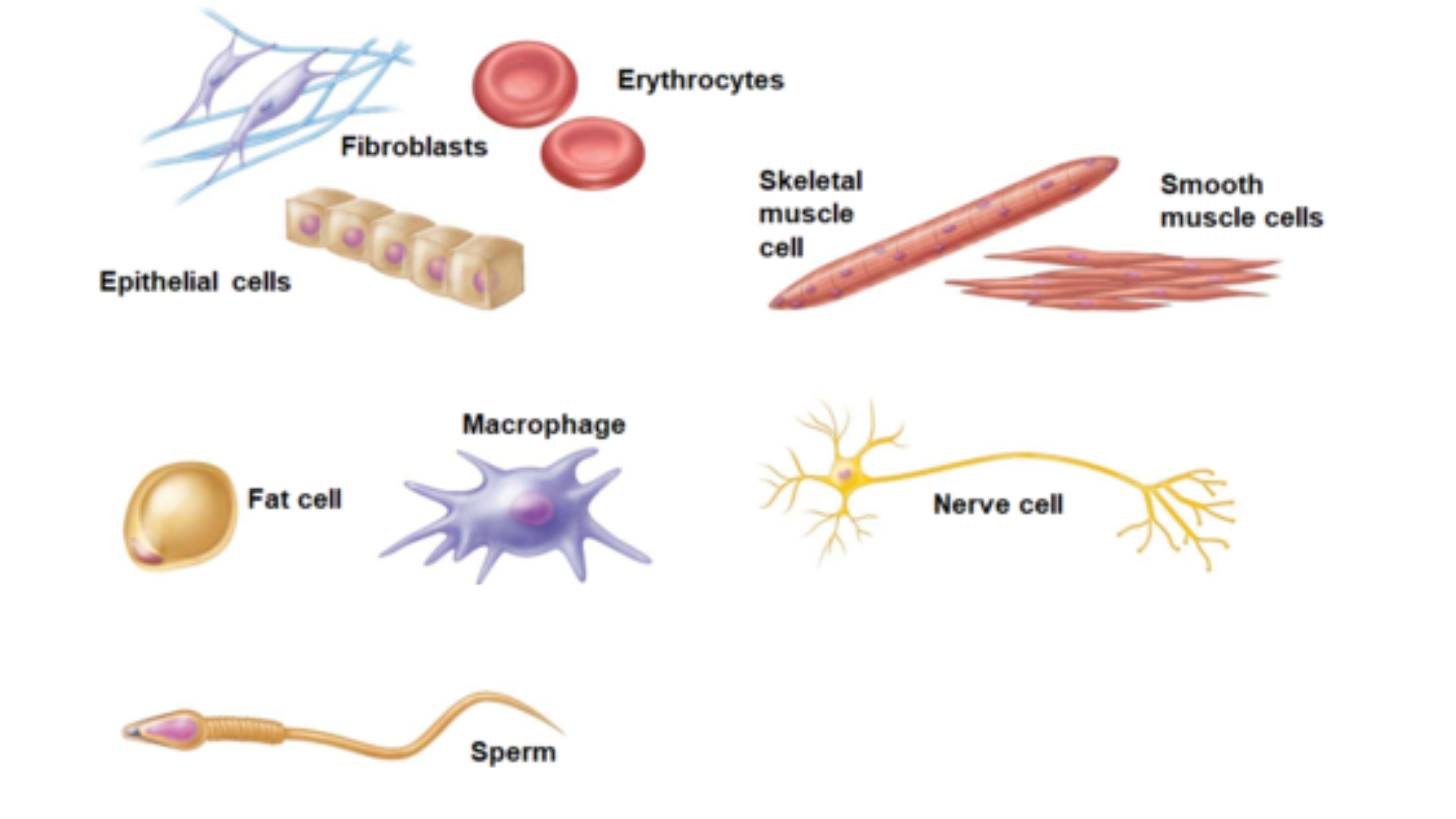
Epithelial cells
Form linings and protective barriers.

Fibroblasts
Connect body parts by forming connective tissue.

Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
Transport gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide).
skeletal muscles cells
smooth muscle cells

Cells that move organs and body parts

Skeletal muscle cells
Responsible for voluntary movements of the body.

Smooth muscle cells
Involved in involuntary movements in organs.

fat cells
Cell that stores nutrients

fat cells
Stores energy in the form of fat.

Macrophage
Cell that fights disease

Macrophage
Engulfs and digests harmful substances and microbes.

nerve cells
Transmits signals in the nervous system.

sperm
Reproductive cell involved in fertilization.
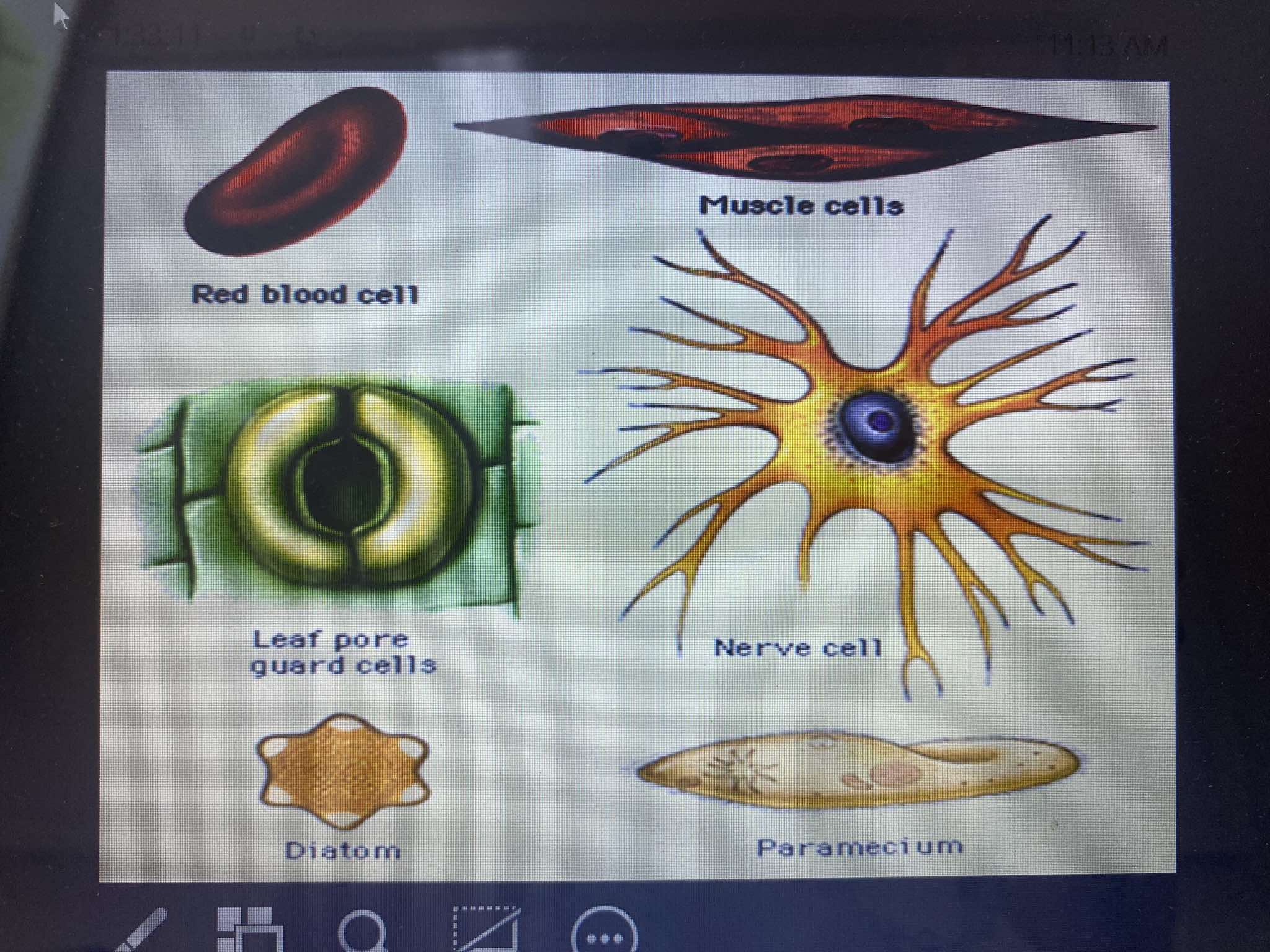
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
Function: Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream.
Structure: Biconcave, disc-shaped, allowing for flexibility and increased surface area for gas exchange.
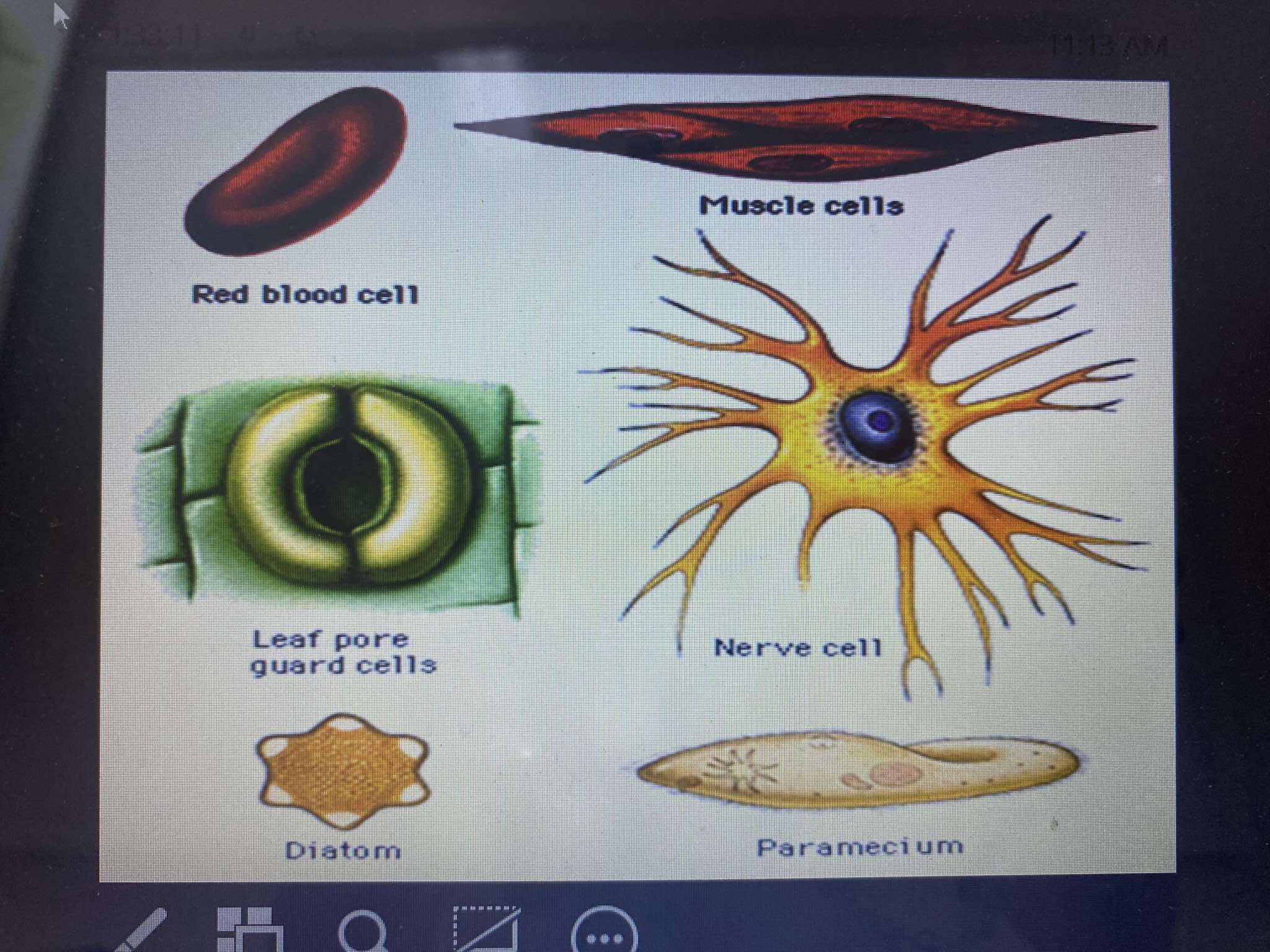
Muscle Cells
Function: Responsible for contraction, which enables movement of the body and organs.
Structure: Long, spindle-shaped, and designed for contraction through specialized proteins like actin and myosin

Nerve Cell (Neuron)
Function: Transmits electrical signals throughout the nervous system, facilitating communication between the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body.
Structure: Characterized by branching projections (dendrites and axons) that enable signal transmission.
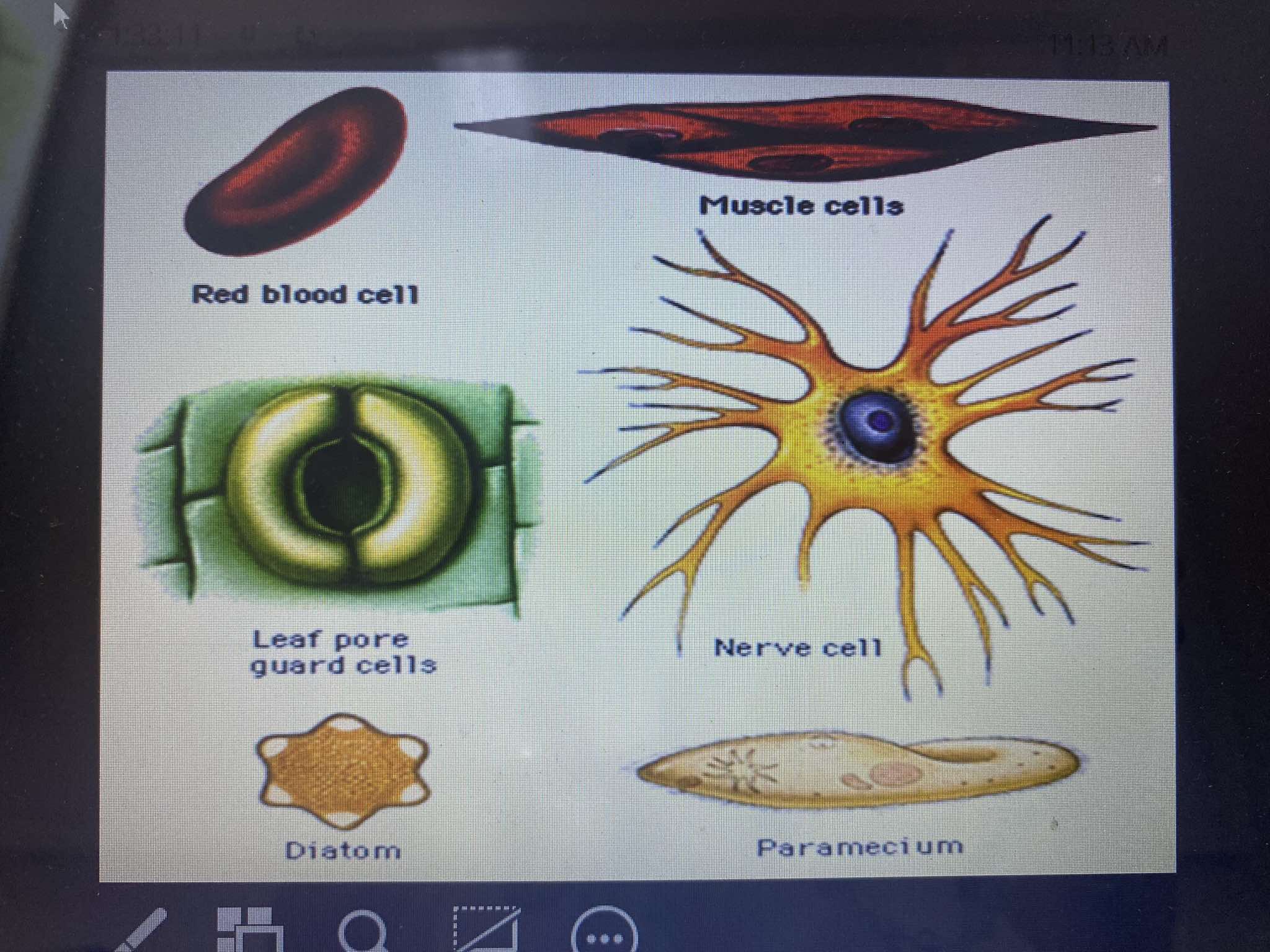
Leaf Pore Guard Cells
Function: Regulate the opening and closing of stomata (pores) in plant leaves, controlling gas exchange (oxygen, carbon dioxide) and water loss.
Structure: Two kidney-shaped cells that swell or shrink to open or close the stomatal pore.

Diatom
Function: Single-celled algae that perform photosynthesis. They contribute to oxygen production and are a key component of the marine ecosystem.
Structure: Enclosed in a silica-based cell wall, known as a frustule, with a unique and intricate pattern.
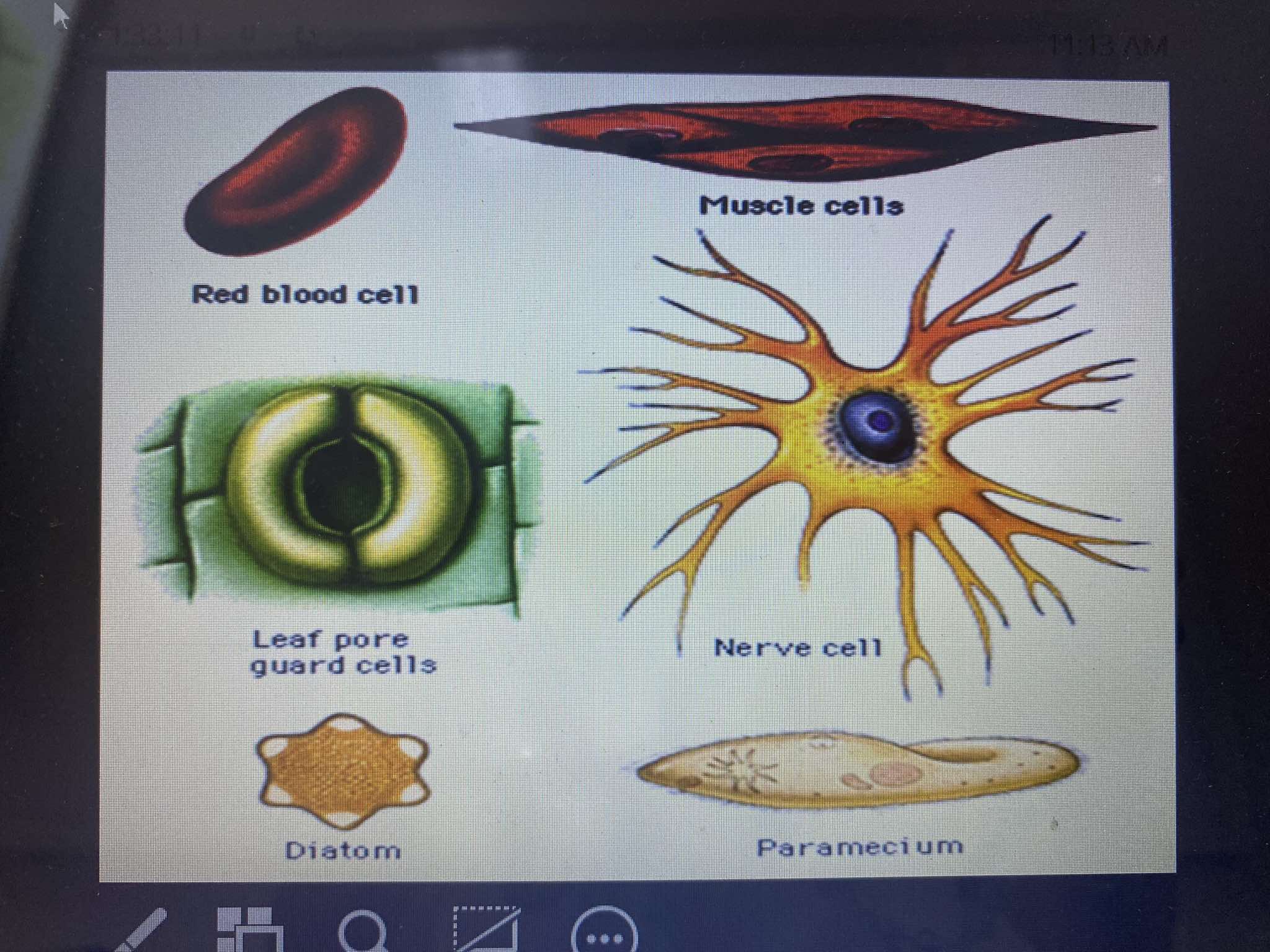
Paramecium
Function: A single-celled organism (protist) that moves through water using hair-like structures called cilia. It feeds on smaller microorganisms like bacteria.
Structure: Oval-shaped and covered with cilia that help in locomotion and feeding.
bacteria
archaea
what are prokaryotic cells?