Unit 10: Humanbody + Homeostasis
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Homeostasis
body keeps internal conditions stable, in balance
Negative feedback
Body responds to reverse changes
Positive Feedback
Body increases change, moving it further away from normal
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas that reduces blood sugar, turning glucose into glycogen
Glucagon
A hormone produced by the pancreas that raises blood sugar levels, by breaking glycogen back into sugar, and releasing it into the bloodstream.
Respiratory System
To supply 02 and remove CO2 from the body
Respiratory Structures
Lungs, alveoli, diaphragm, trachea, nose/moth
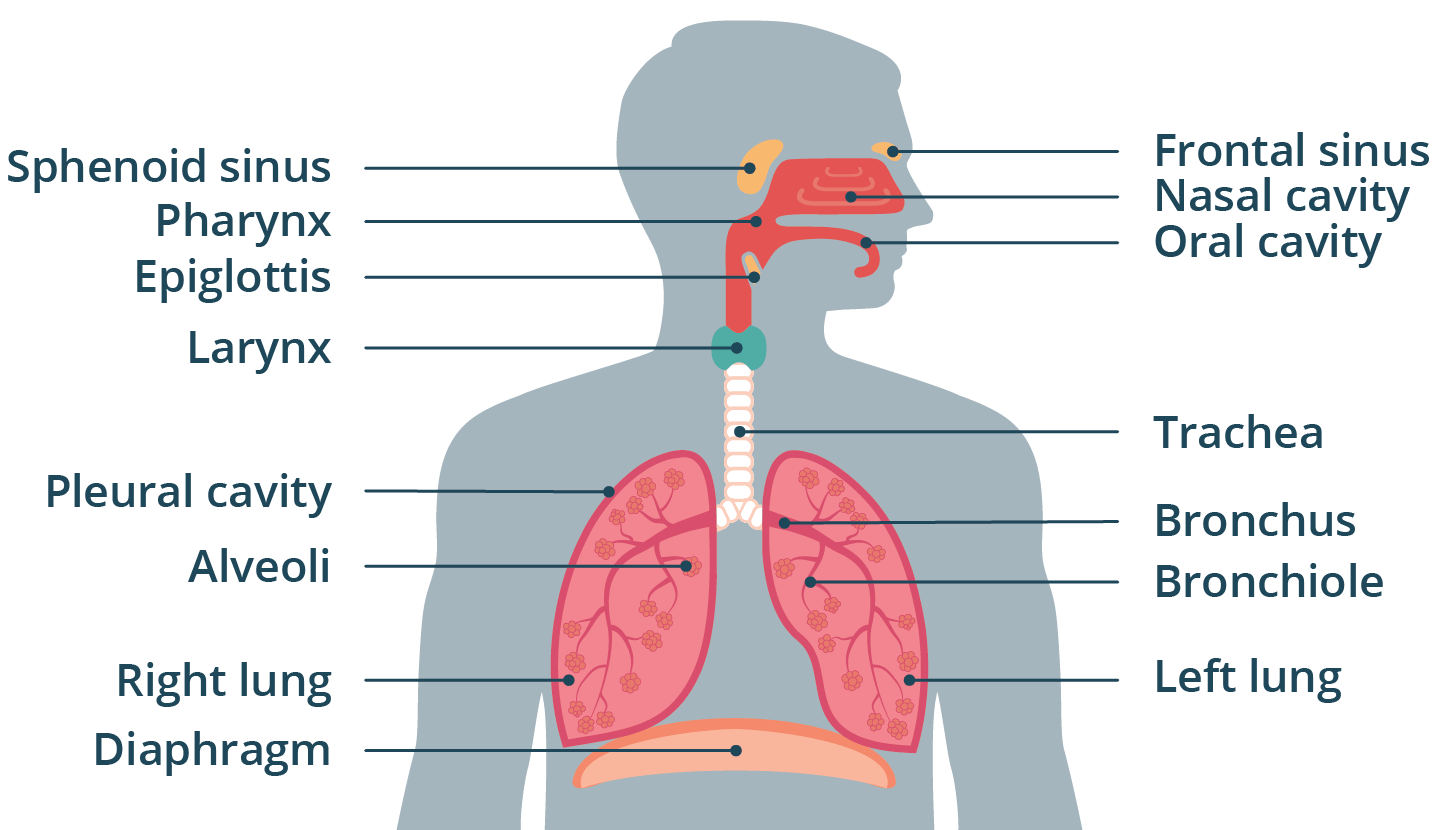
Alveoli
Cluster of air sacs where gas exchange occurs. Is 1 cell thick which allows diffusion of gas, as 02 enters and CO2 leaves
Capillaries
Thinnest blood vessel in the body and 1 cell thick, that connect arteries to veins and are main sites of exchange.
Circulatory System
To transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste throughout the body via blood
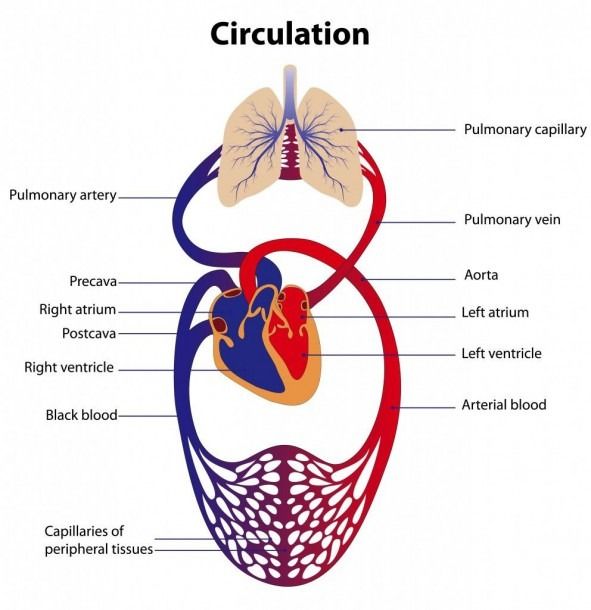
Pulmonary vein → only vein to carry oxygen rich blood
Aorta (artery) →Largest blood vessel in human body
Vena cava
Interior v.c →enters heart from below
Superior v.c →enters heart from above
Pulmonary Artery → only artery that carries 02 poor blood
Hemoglobin
A protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying 02 and CO2 throughout the body by binding to them
Arteries
Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart, are 1 cell thick
Veins
Blood vessel that carries blood towards the heart, are thick and with valves to prevent back flow.
Blood pressure
The force of blood pushing against walls of blood vessels
Systolic pressure
the pressure of arteries when the heart contracts and pushes blood into body (higher number: 80-120)
Diastolic pressure
The pressure in your arteries when your heart is at rest between beats (Lower number: 60-80)
Causes for high blood pressure
Narrow veins, thick blood, high blood amount in system
Human Nervous System
To send, receive, and process messages between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body - allowing you to sense, move and react.
Central Nervous System(CNS)
Made of brain and spinal cord to process info and make decisions
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Motor and sensor nerves outside the brain
Motor neurons: muscle movement and gland activity
Sensory neurons: sensation (touch, pain, temp, ect)
Neurons
A specialized cell that carries electrical signals (tiny burst of electricity from external factors) to help the body sense, move, and respond.
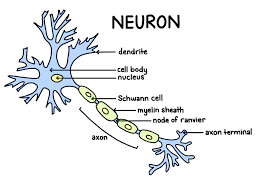
Dendrites→receives signals
Nucleus → contains DNA
Myelin Sheath →Insulates axon and speeds up signals
Axon →Action potential travels down
Axon terminal →Releases neurotransmitters to transmit signals at the synapse, onto the next cell.
Stimulus→Dendrites→Cell body→Axon→ Axon terminal→Synapse→Next neuron
Neurotransmitters
A chemical substance that is released at the axon terminal by the arrival of action potential, and diffuse across into the synapse, causing the transfer of action potential onto the next neuron.
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Chemical messenger that makes the next neuron more likely to send down electrical signal
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger that makes the next neuron less likely to send an electrical signal
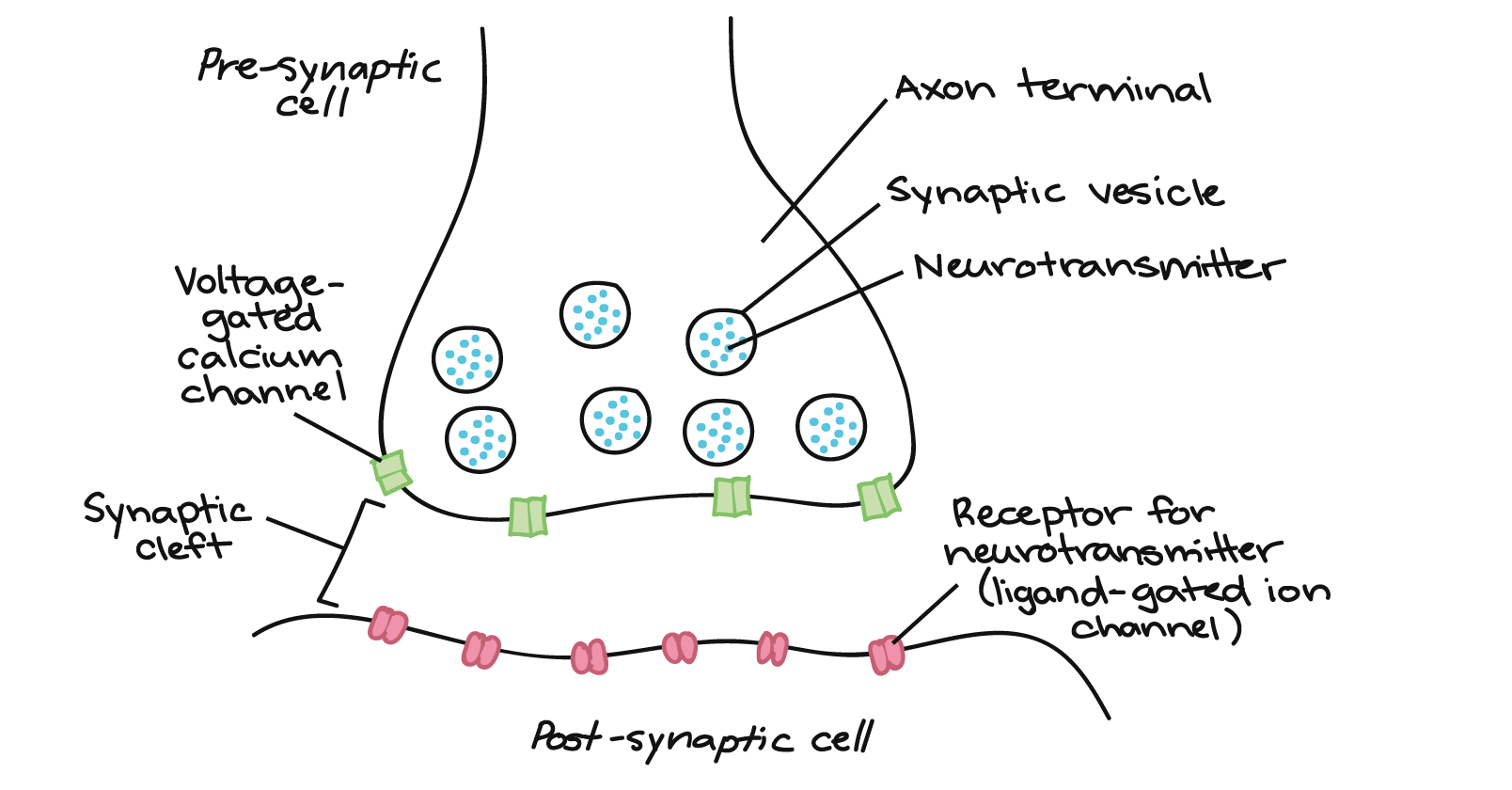
How do neurons communicate?
Action potential reaches axon terminal
Action potential causes vesicles to move towards the membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synapse
Neurotransmitters travel onto the other neurons dendrites, binding to receptor proteins
New electrical signal(action potential) is sent down the post-synaptic neuron
Afterwards, unused neurotransmitters are broken down or reabsorbed.
Cocaine
Blocks dopamine(type of transmitter) from being reabsorbed
Meth
Blocks dopamine re-absorption and release large amounts of dopamine
Nicotine
Binds to receptors of neurons and causes dopamine release
→also binds to cell body receptors, increasing speed of action potential, meaning more dopamine releases
How a brain develops
Dendrite connections grow between neurons
The more often certain neurons communicate, the stronger their communications become
New protein receptors will form on dendrite to increase signaling
Myelin
A fatty coating that wraps around the axon
→When learning, myelin recognizes the repeated signals, making signals travel faster down the axon.
→Weak connections between neurons are pruned as axons and dendrites die and decay