13 Energetics II
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is standard lattice energy?
The energy change when 1 mole of an ionic solid is formed from gaseous ions under standard conditions.
As strength of ionic bond increases, what happens to lattice energy?
Decreases
How do ionic charge and size affect lattice energy?
Higher charge = more energy released when an ionic lattice is formed due to the strong electrostatic forces between ions. More energy released means a more negative lattice energy.
The smaller the ions involved, the more exothermic the energy is as smaller ions have a larger charge density and the ions sit close in the lattice. Therefore attractions are stronger.
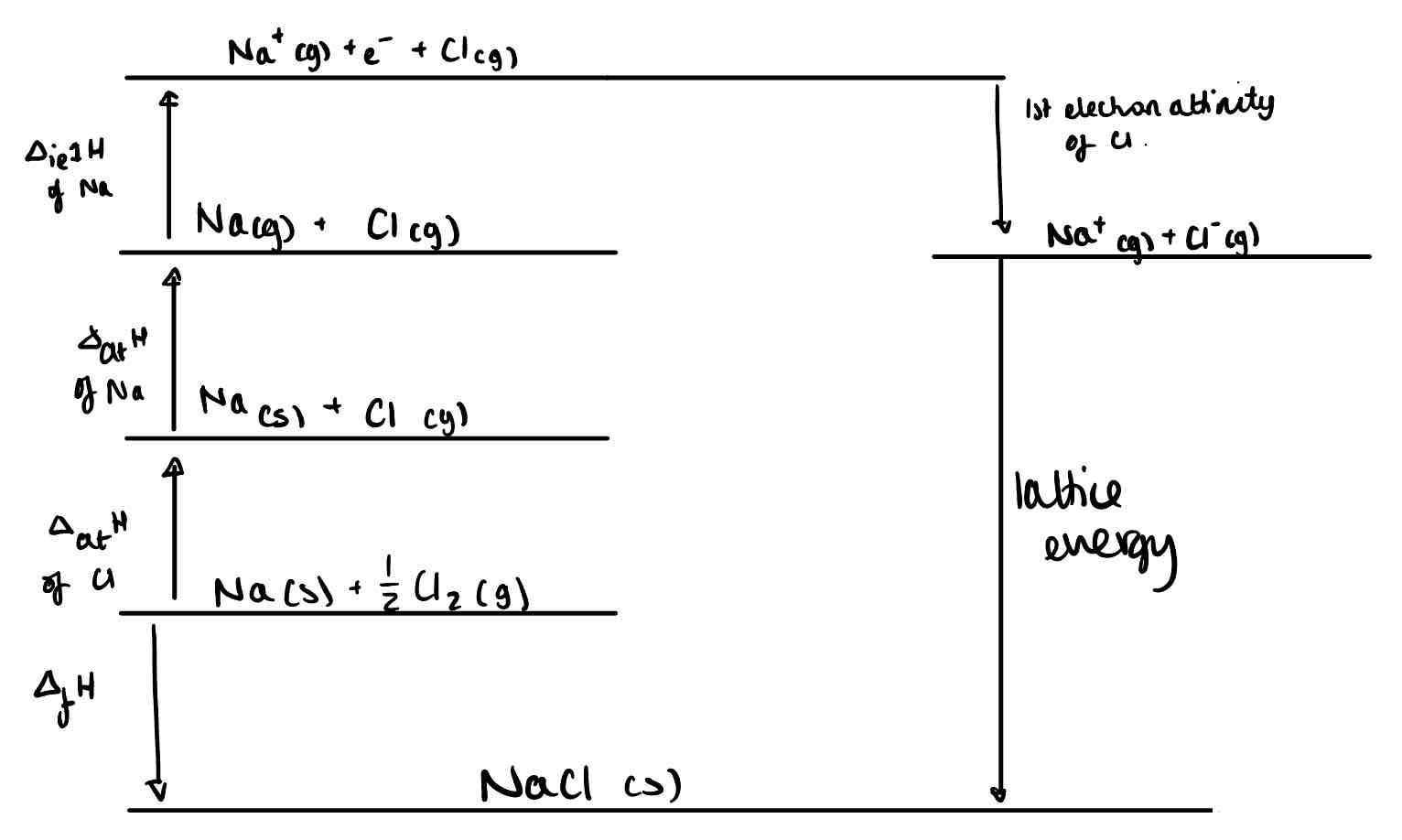
Create a Born-Haber Cycle for the lattice energy of NaCl.
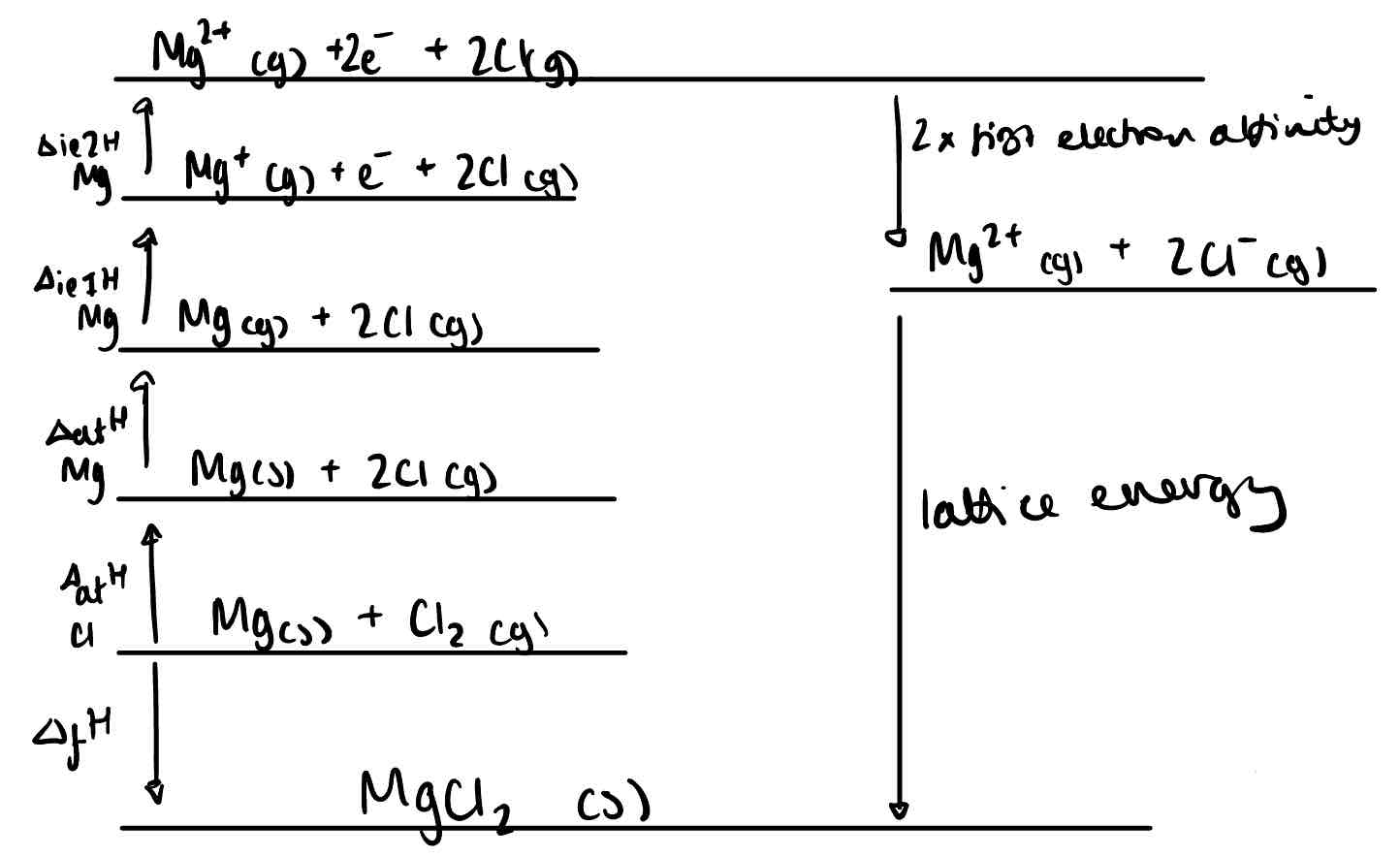
Create a Born-Haber Cycle for Magnesium Chloride.
What is the difference between theoretical and experimental enthalpy values in the context of ionic models?
Experimental enthalpy values are based on using values gained from experiments in a Born-Haber cycle to find the lattice energy.
Theoretical values are based on calculations based on the ionic model. This assumes that the ions are spherical and have charge evenly distributed through them.
If the experimental and theoretical values of an ionic substance are close, what does this tell you?
The compounds fit the purely ionic model well and therefore the structure is close to being purely ionic.
What does it tell you if the experimental and theoretical values of an ionic compound are very different?
The bonding is a different strength than the model predicts. The bonding isn’t close to purely ionic and must be more polarised, so the compound has some covalent character.
What impact does charge density of the cation tend to have on match between theoretical and experimental enthalpy values?
Greater the charge density of cation, the poorer the match will be between enthalpy values.
What is the enthalpy change of hydration?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions dissolves in water.
What is the enthalpy change of solution?
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of solute dissolves in water.
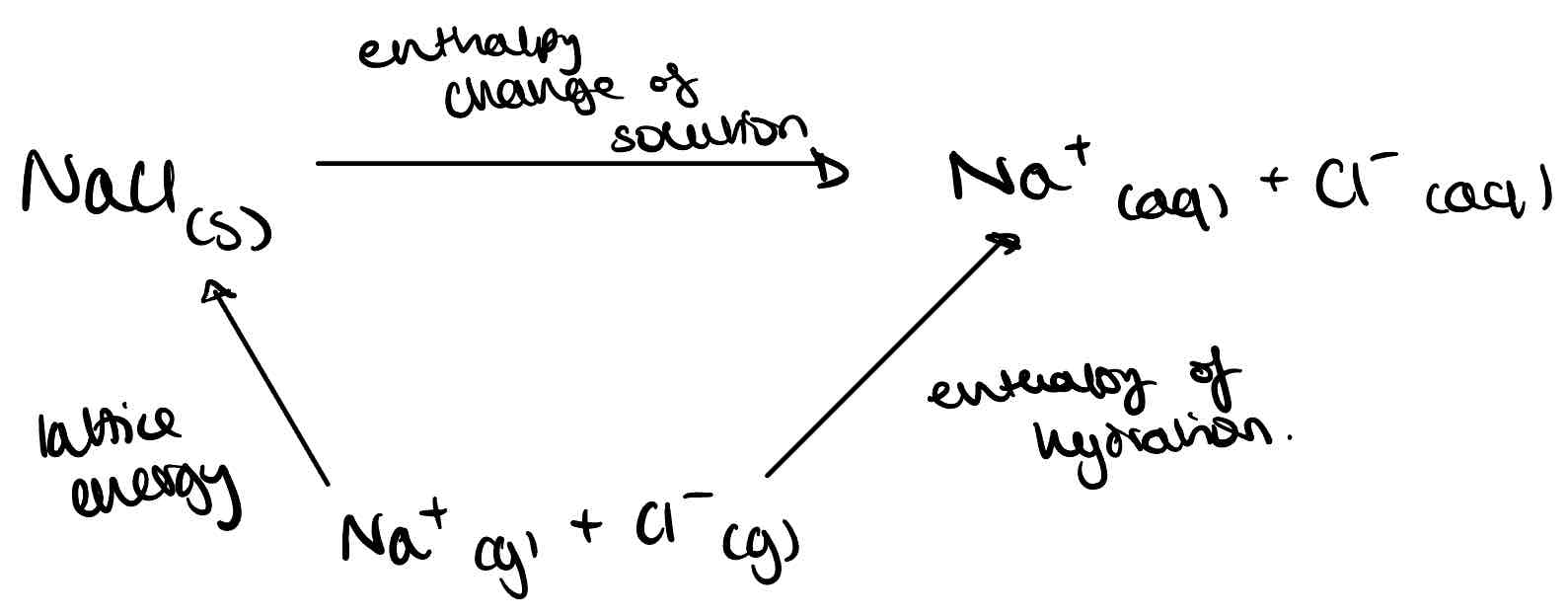
Draw the energy cycle for working out the enthalpy change of solution of NaCl.
Why do ions with a greater charge have a greater enthalpy of hydration?
Higher charge = better at attracting water molecules. More energy is released when the bonds are made so the formation is more exothermic.
Why do smaller ions have a greater enthalpy of hydration?
Smaller ions have a higher charge density, so attract water molecules better.
What is entropy?
A measure of the disorder of a system: the number of ways that particles can be arranged and energy can be shared out between them.
How does physical state affect entropy?
Solids have the lowest entropy as particles are not able to move. Gases have the highest entropy as particles do random movement.
How does dissolving affect entropy?
Dissolved particles are no longer held in one place and so move freely, increasing entropy.
How does more particles affect entropy?
More particles means more entropy, as there are more ways they can be arranged.
What is the equation for entropy change in a system?

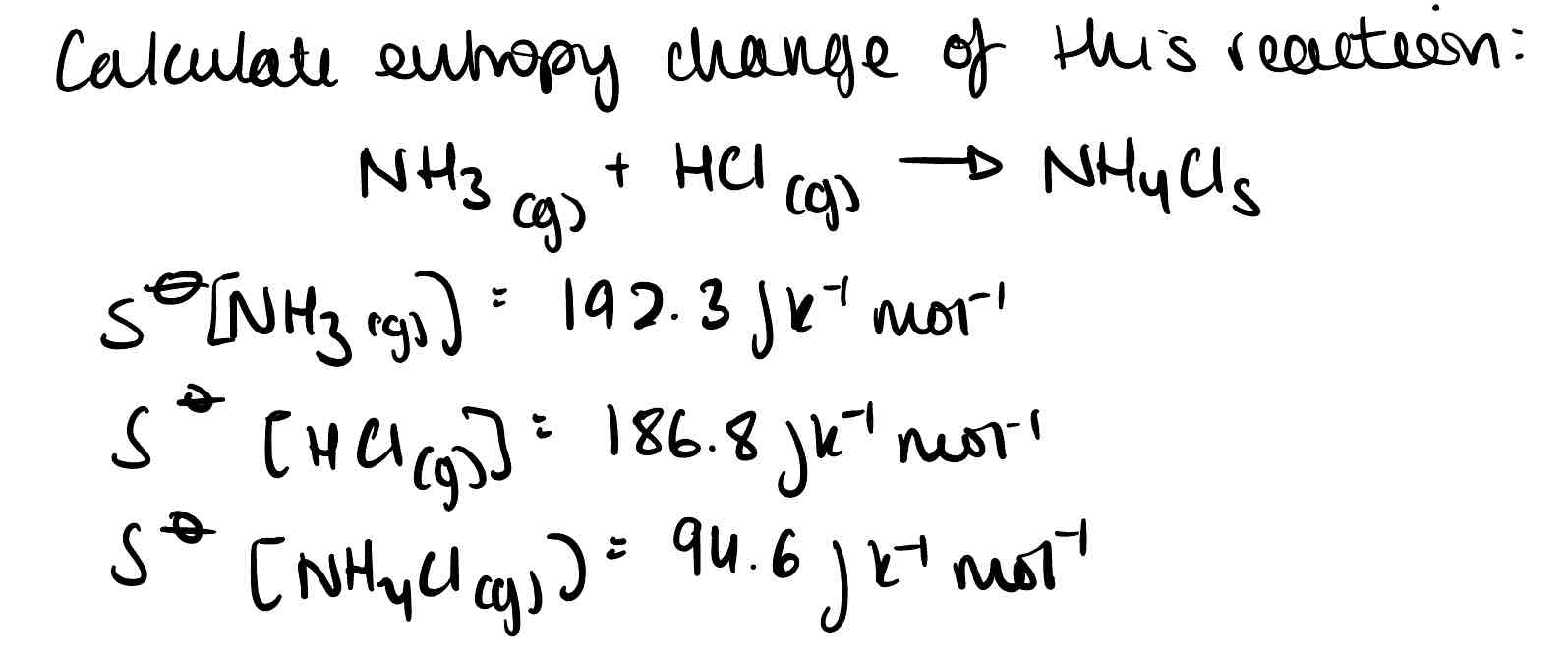
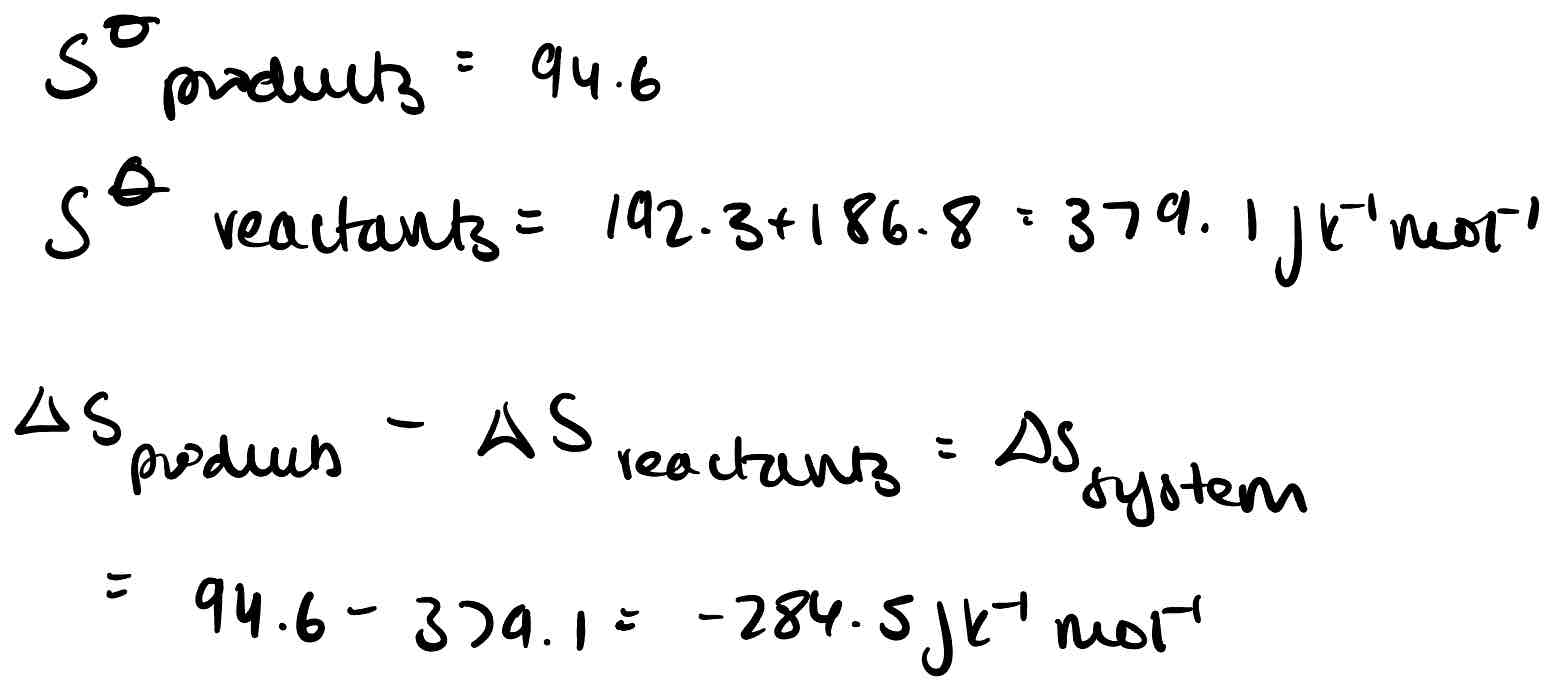
Why will particles move to try and increase their entropy?
Substances are more energetically stable with higher entropy.
What is the equation for total entropy change?

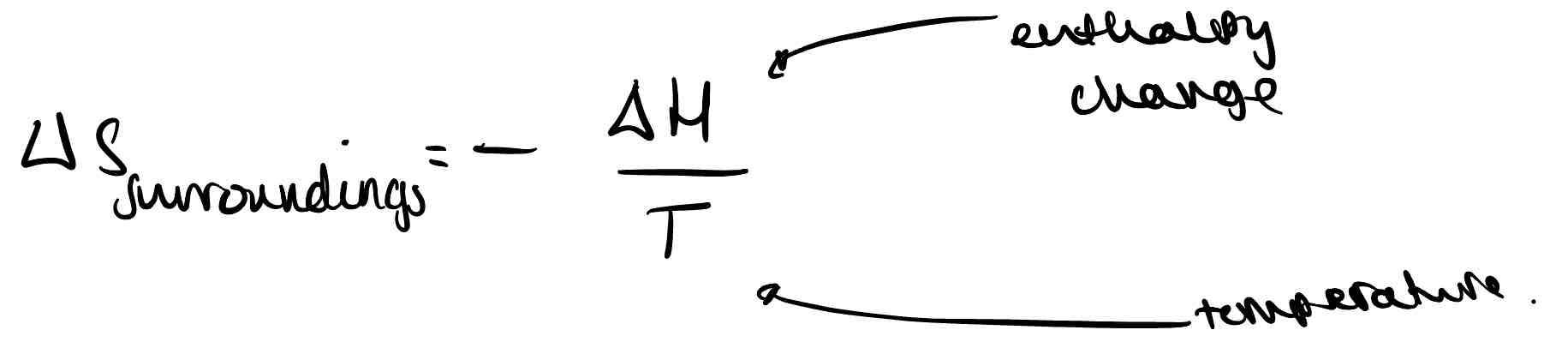
What is the equation for entropy of surroundings?
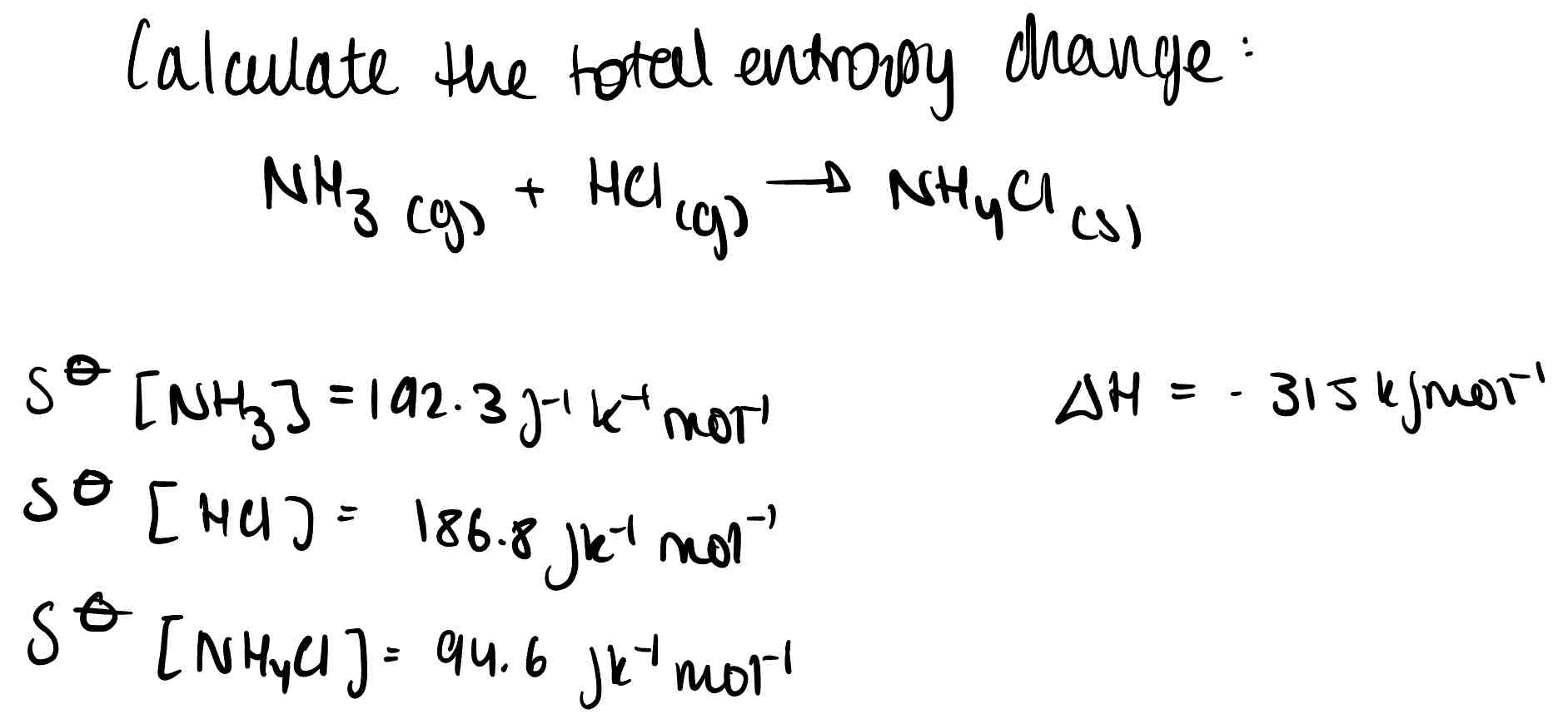
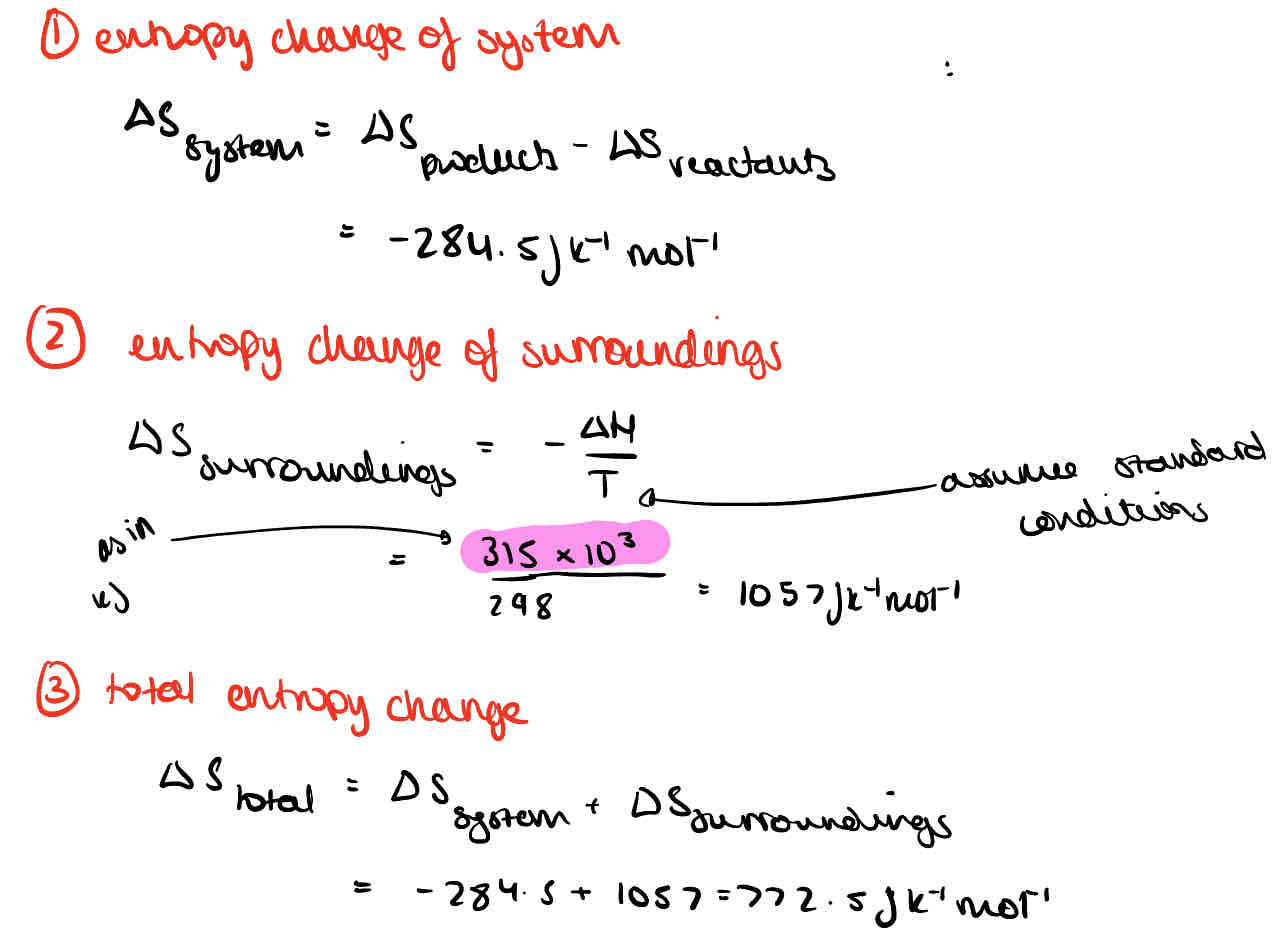
What is the free energy change?
Whether a reaction is feasible or not- the more negative the value, the more feasible.
What is the formula for free energy?
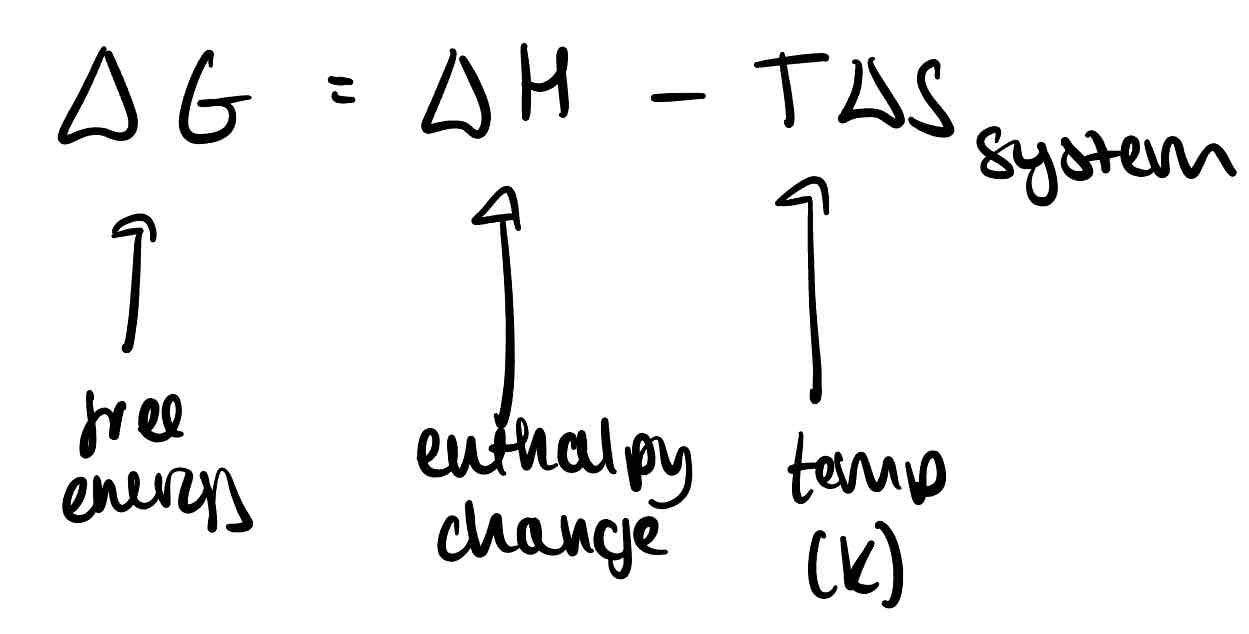
How can you calculate the temperature at which a reaction just becomes feasible?

What is the relationship between free energy and the equilibrium constant?
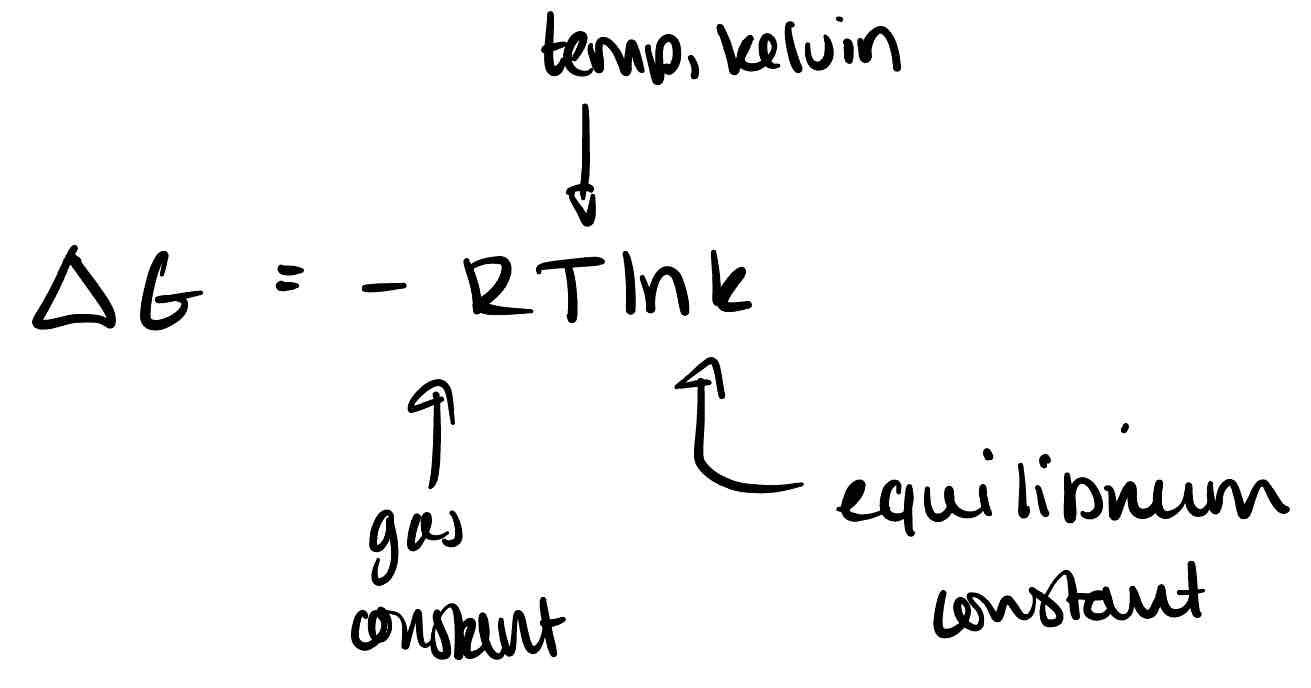
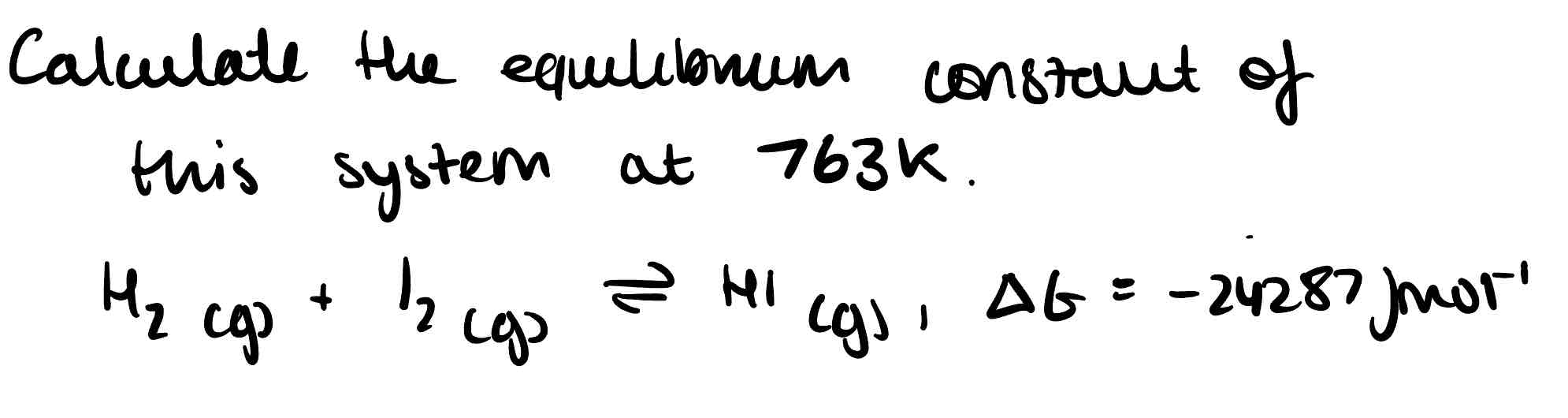
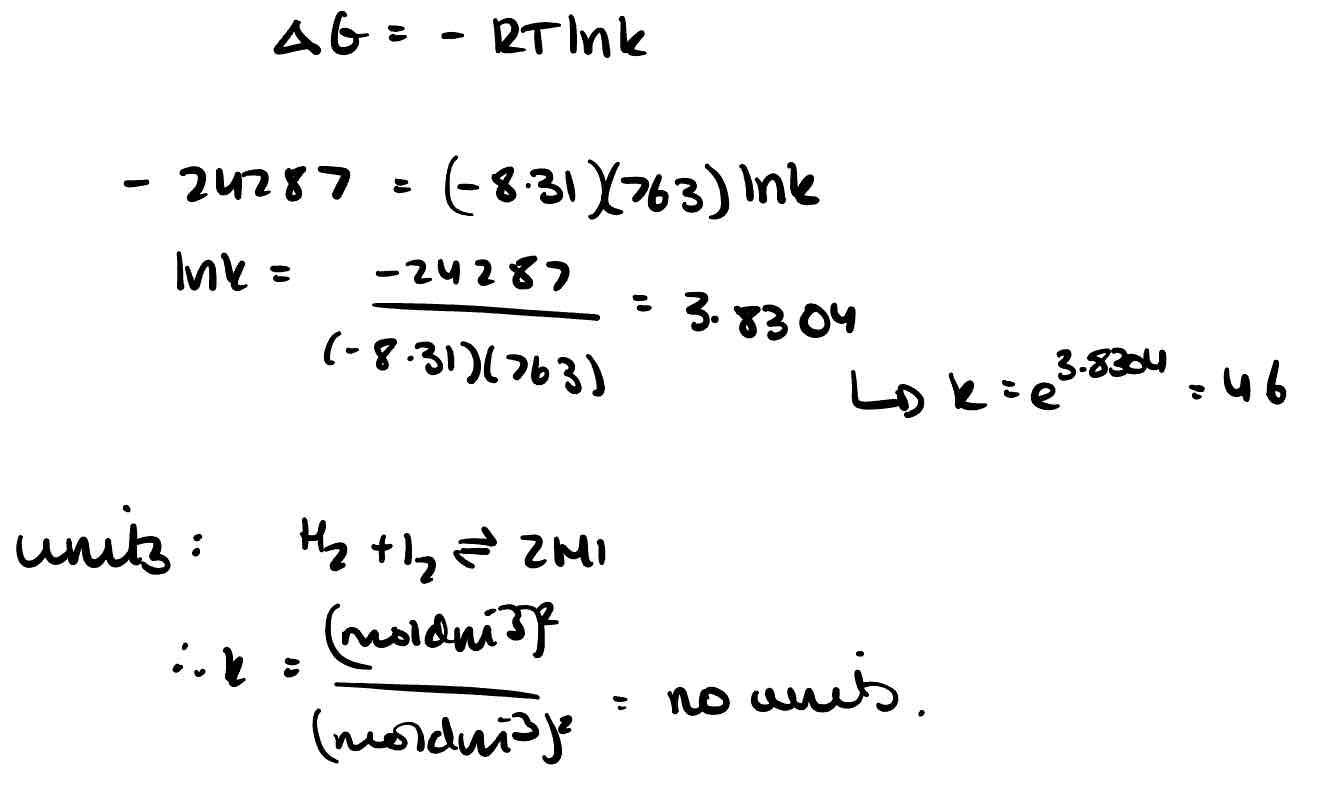
How doesn’t a negative free energy guarantee reaction?
The free energy may be 0 or negative, but this gives no information about rate. There may be a really high activation energy or happen so slowly that you don’t notice it.