Diagnostic Imaging Exam 3
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 9 +
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
roots, pulp chamber, and alveolar bone
what is the primary imaging goal in dental radiograph
exposure time
what is the only changing factor on dental x-ray machines
buccal
towards the cheek
labial
towards the lips
lingual
towards the tongue (bottom)
palatal
towards the palate (top)
mesial
towards the midline
distal
away from midline
400s
what numbers classify the lower right teeth
300s
what numbers classify the lower left teeth
200s
what numbers classify the upper left teeth
100s
what numbers classify the upper right teeth
4
what ended number is always canines
kVp and mA
what is constant in dental radiography
dental formula * 2
what is the formula to determin total number of teeth
on the up side
for positioning dental radiographs, the area of interest should be ____
mandibular PM4 and caudal
what to use the parallel technique with dental radiographs
bisecting angle technique
most common technique used in dental radiography
dental prophylaxis, mobile tooth, post extraction, FORL
4 reasons for dental radiography
foreshortening
what occurs when xray beam is perpendicular to film (not bisecting angle)
elongation
what occurs when xray beam is perpendicular to long axis of tooth (not bisecting angle)
dorsal recumbency, rotate along z-axis
position for mandibular canines and incisors for dental radiography
lateral recumbency, side of interest up, parallel technique
position for mandibular PM4 and molars for dental radiographs
sternal recumbency, towel under jaw, tube head over nose
position for maxillary incisors for dental radiography.
sternal or lateral position, include incisory and PM
position for maxillary canines and incisors
mesiolateral oblique and distolateral oblique views
what views are required for maxilarry PM 4
carnassial tooth
another name for the maxillary PM 4 tooth
high contrast
what type of contrast do you want for skull radiograph
low kVp
how to achieve high-contrast radiographs
nasal cavity, frontal sinuses, calvarium
what does lateral view of skull evaluate
nasal septum parallel, rami of mandible and tympanic bullae superimposed
perfect positioning for lateral skull view
superimposed transverse processes, and rib heads, equal intervertebral foramina
perfect positioning for lateral view of vertebral column
symmetric transverse processes, ilial wings, sternum and thoracic spine superimposed, and spinous processes centered over vertebral bodies
perfect positioning for VDview of vertebral column
tarsus
equine calcaneus is associated with what joint
cassette tunnel
what device allows equine patients to stand on the cassette for radiographs
remove shoe, trim overgrowth, pick/scrub sole, pack sole with radiolucent material
hoof prep in equine radiography patient
play-doh, soften soap, vaseline
radiolucent material that can be used for equine radiography
metatarsal 2
what metatarsal bone is on the medial side
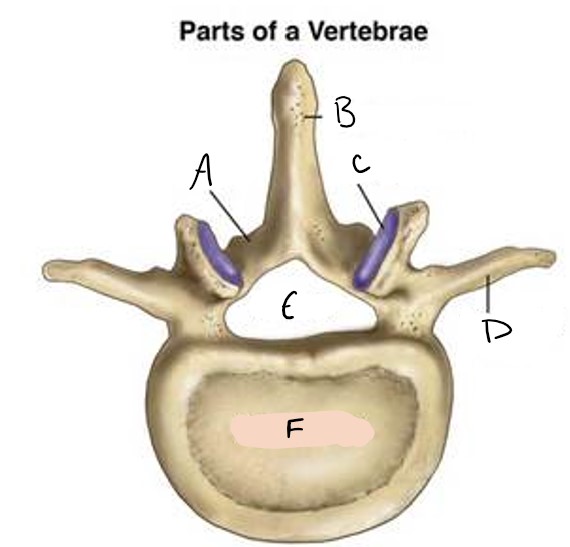
lamina
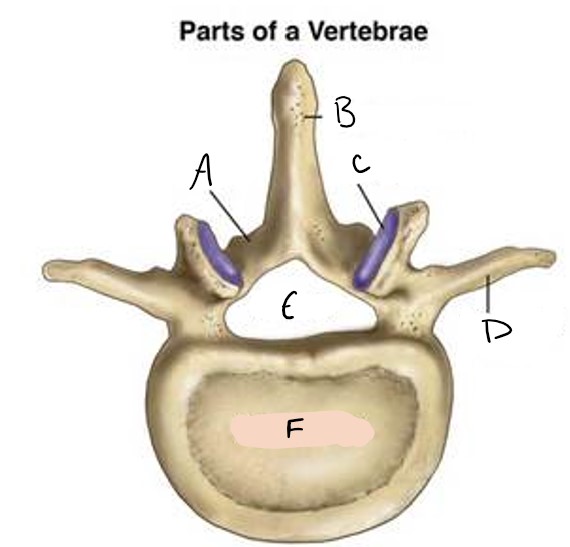
A
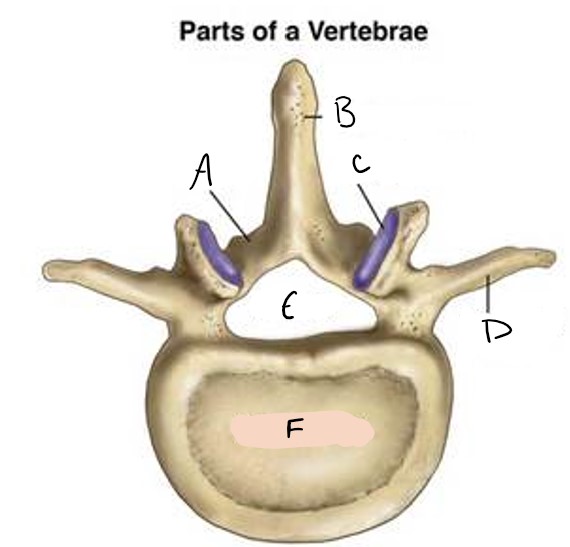
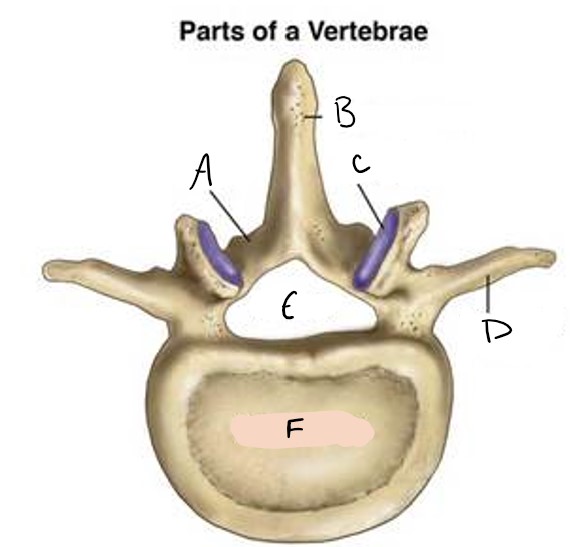
spinous process
B
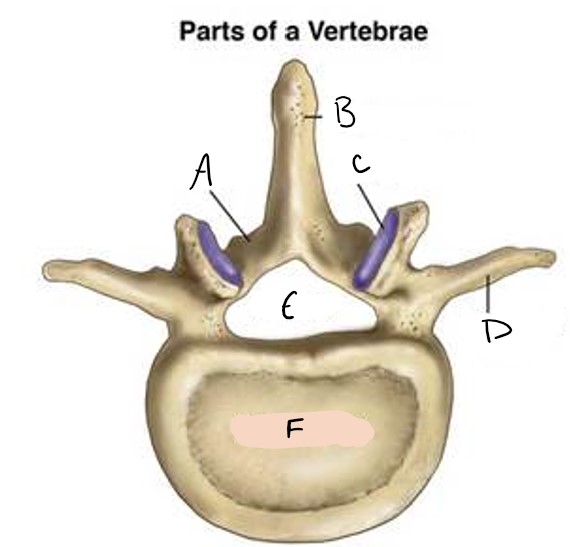
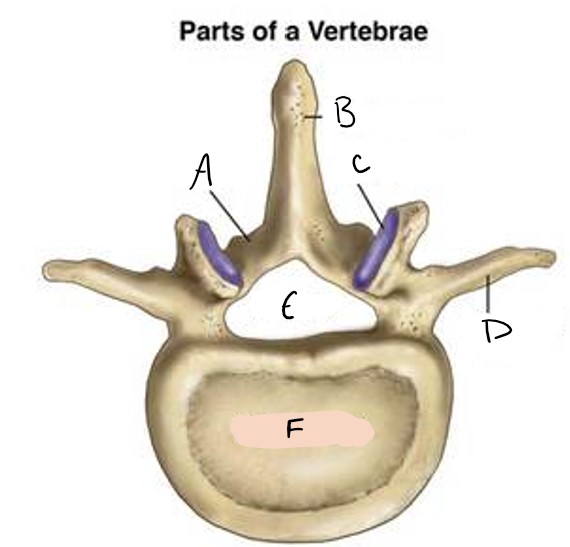
facet
C
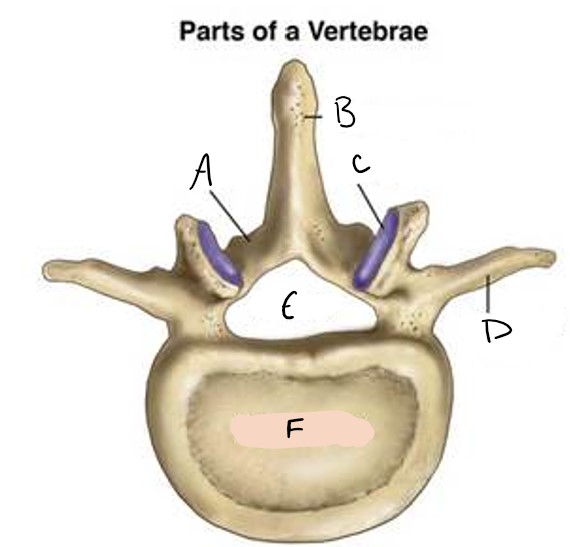
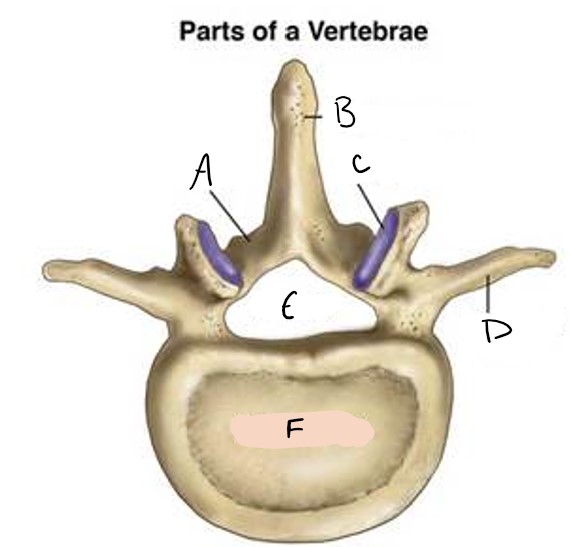
transverse process
D
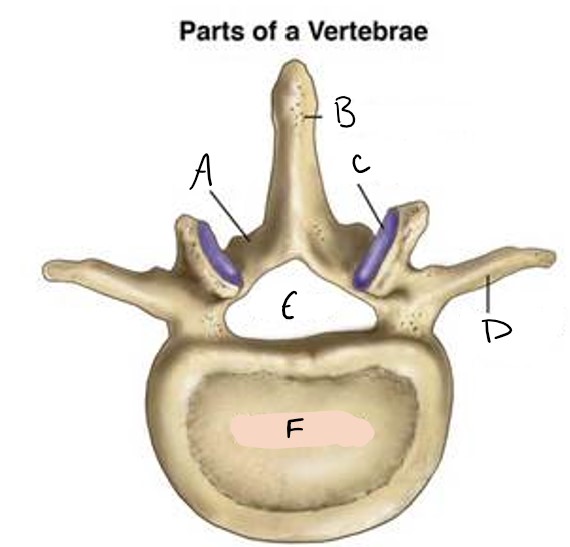
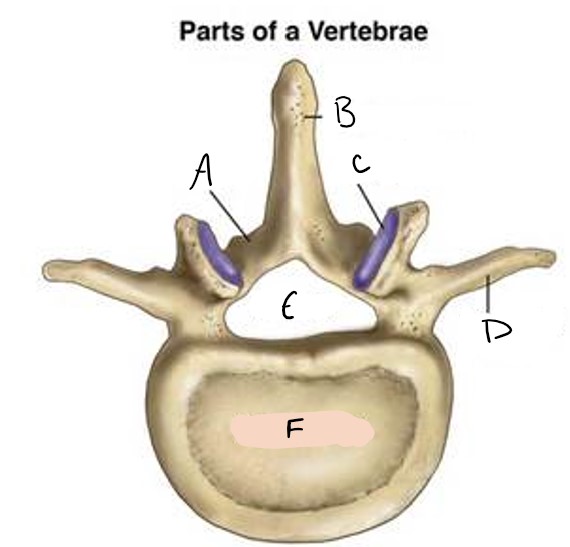
foramen
E
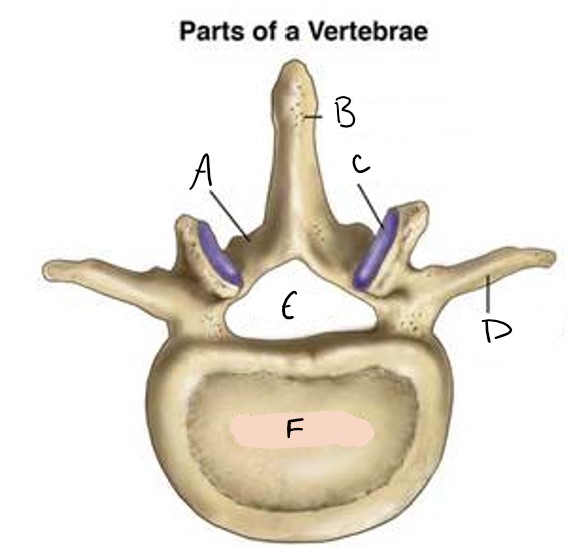
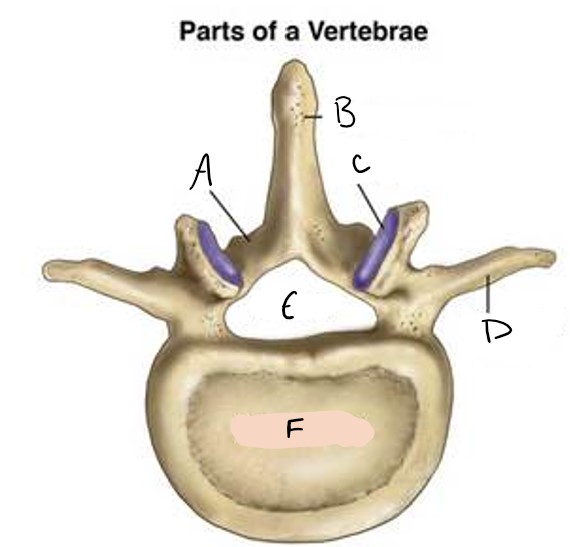
vertebral body
F
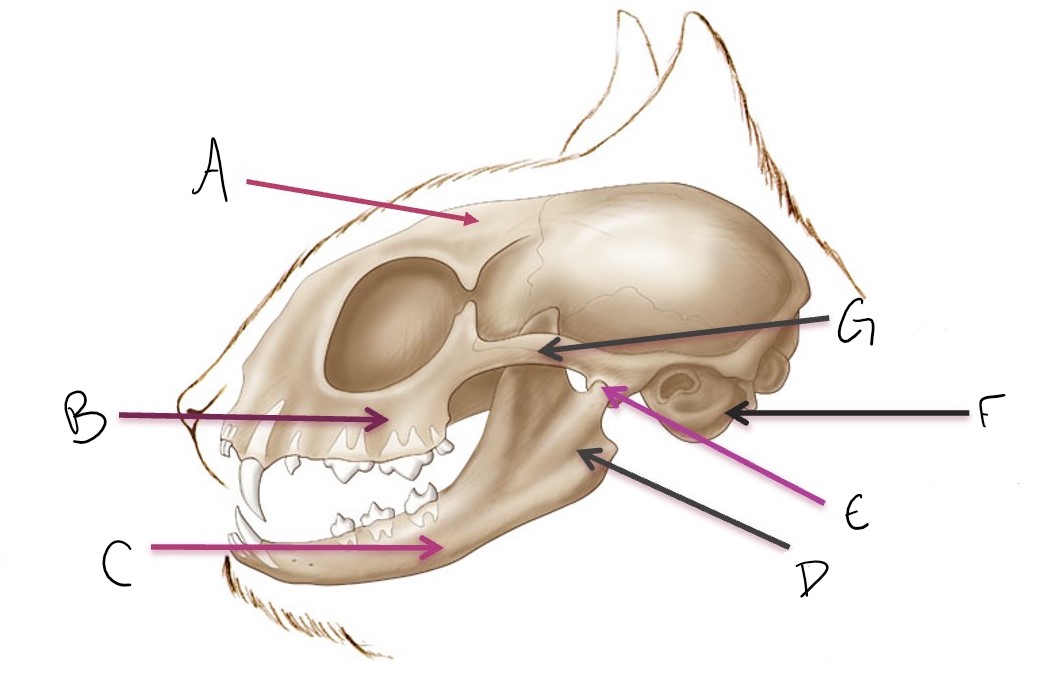
calvarium
A
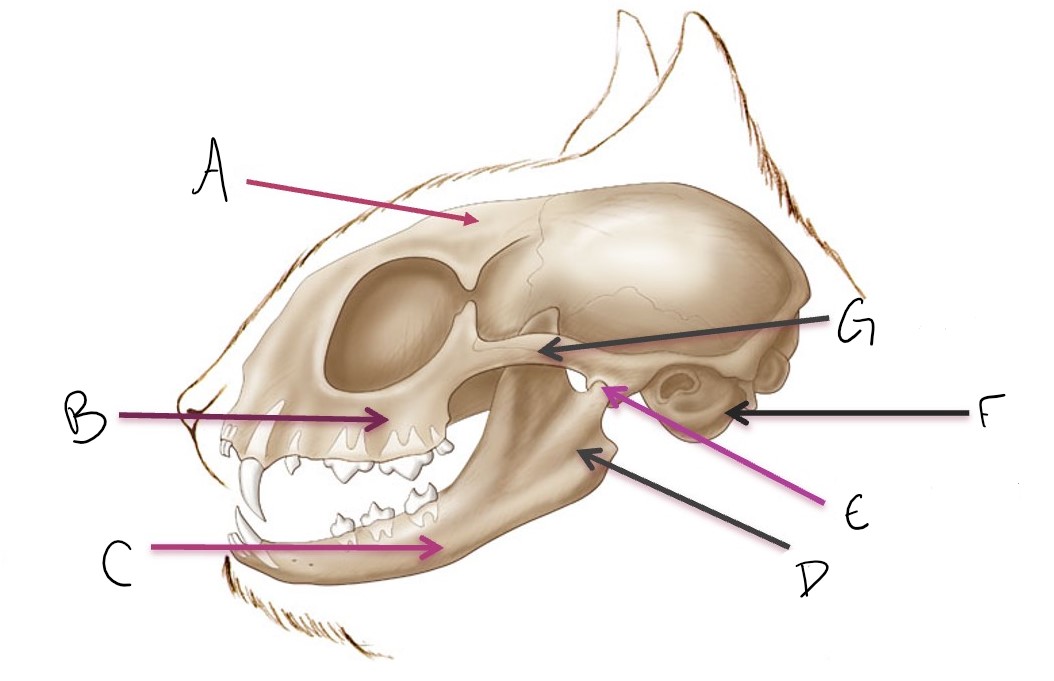
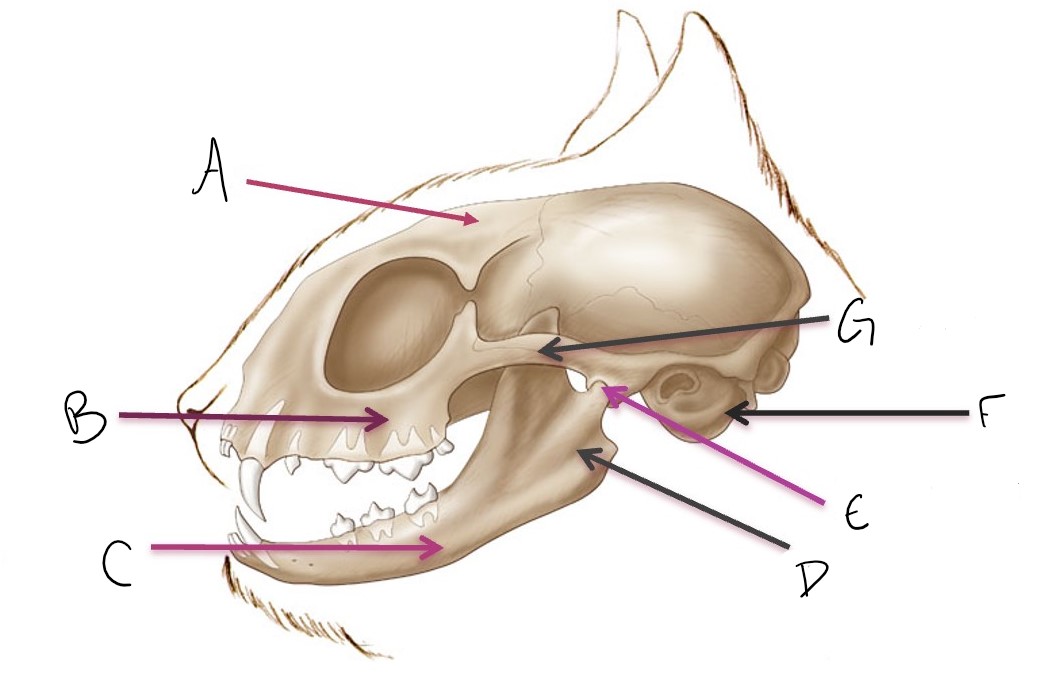
maxilla
B
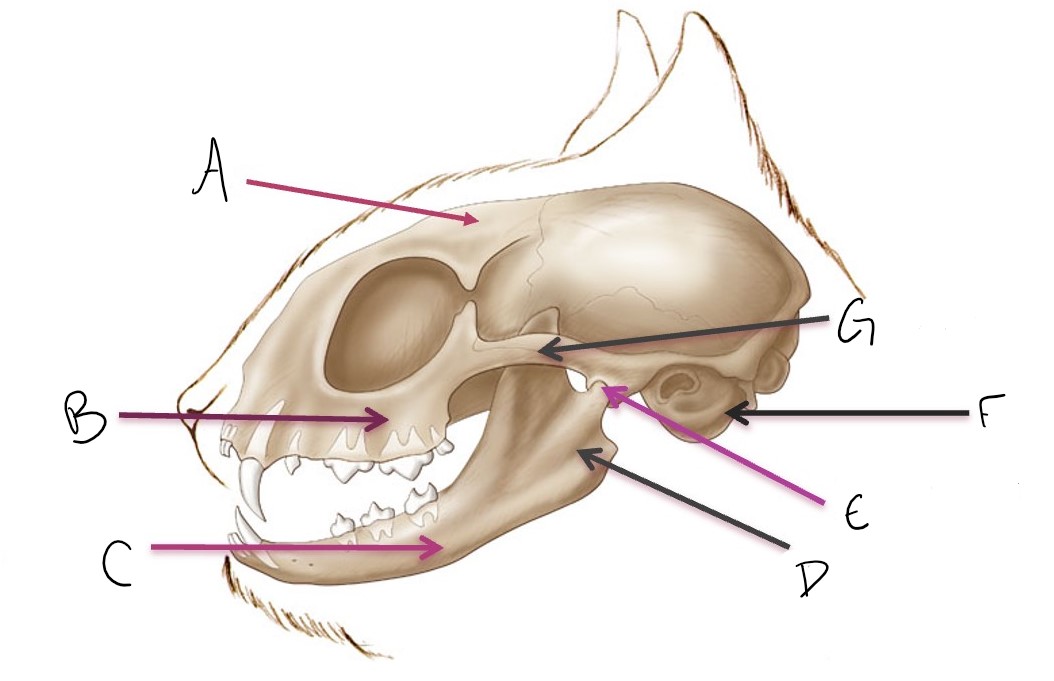
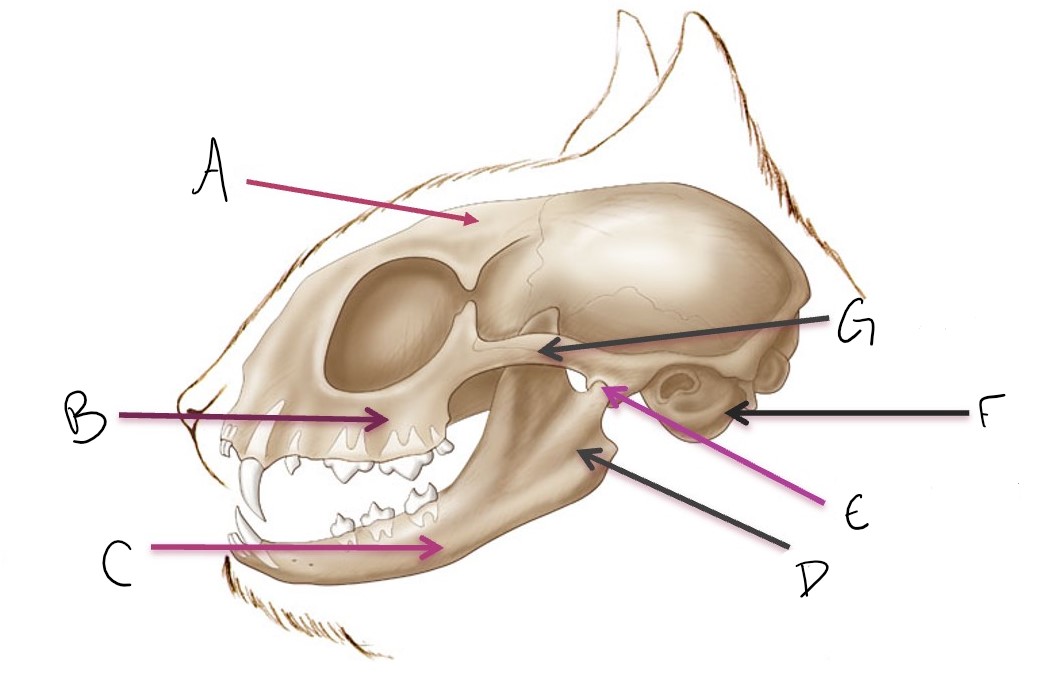
mandible
C
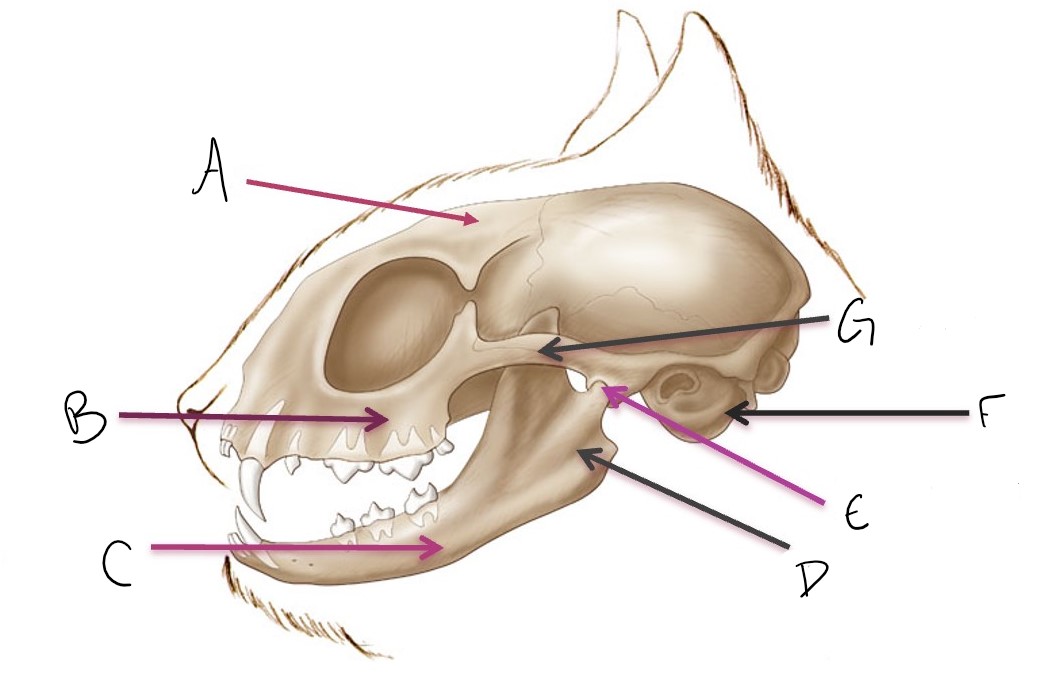
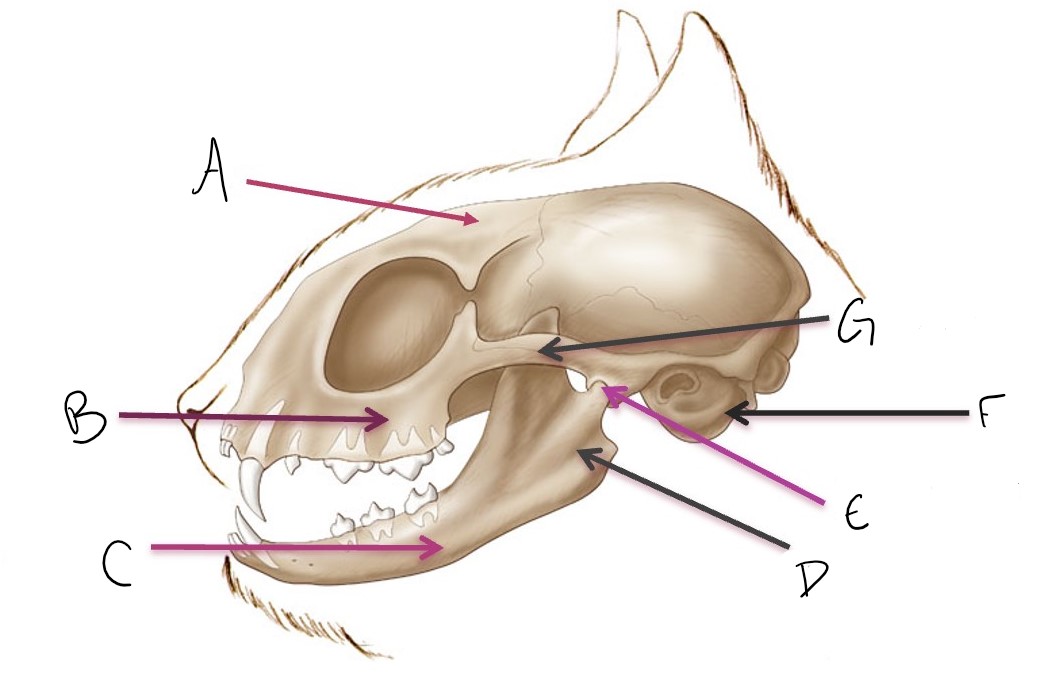
ramus of mandible
D
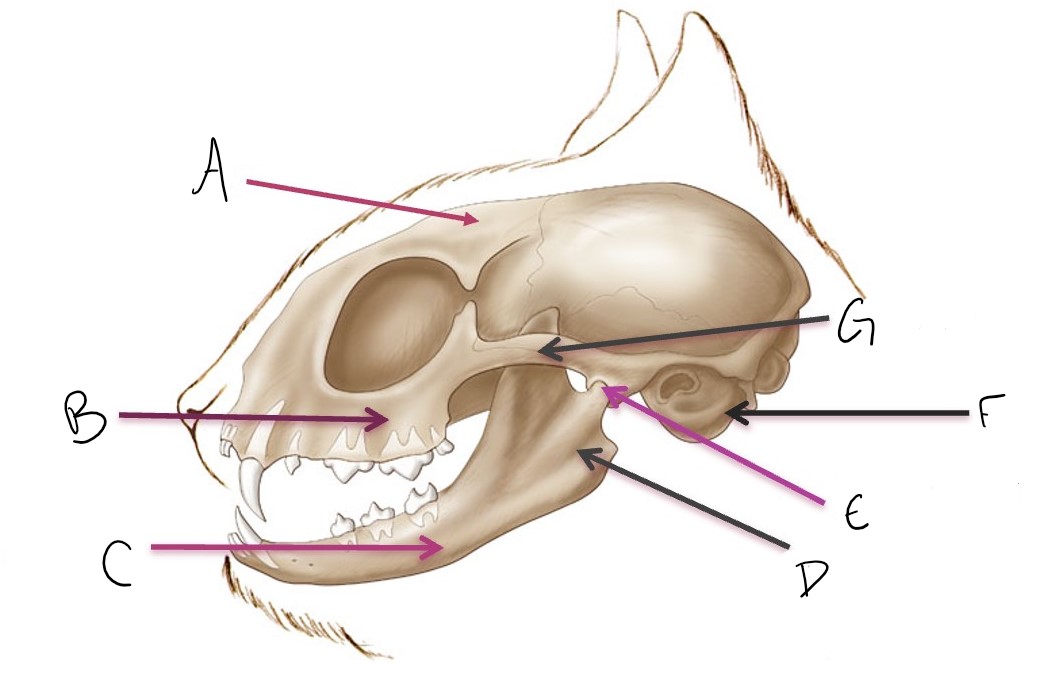
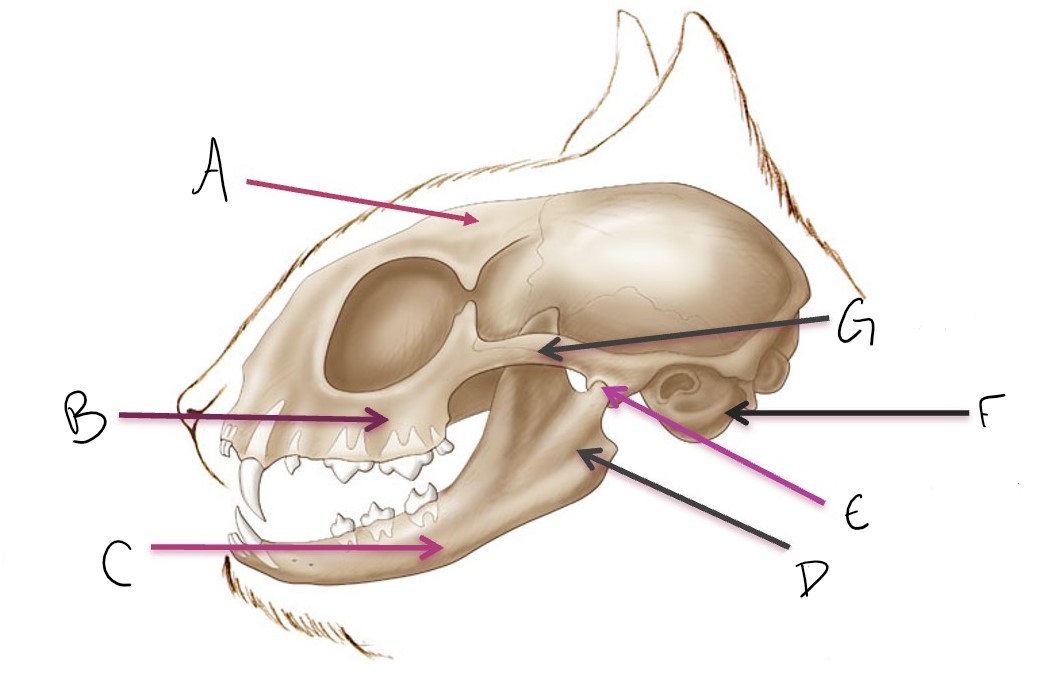
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
E
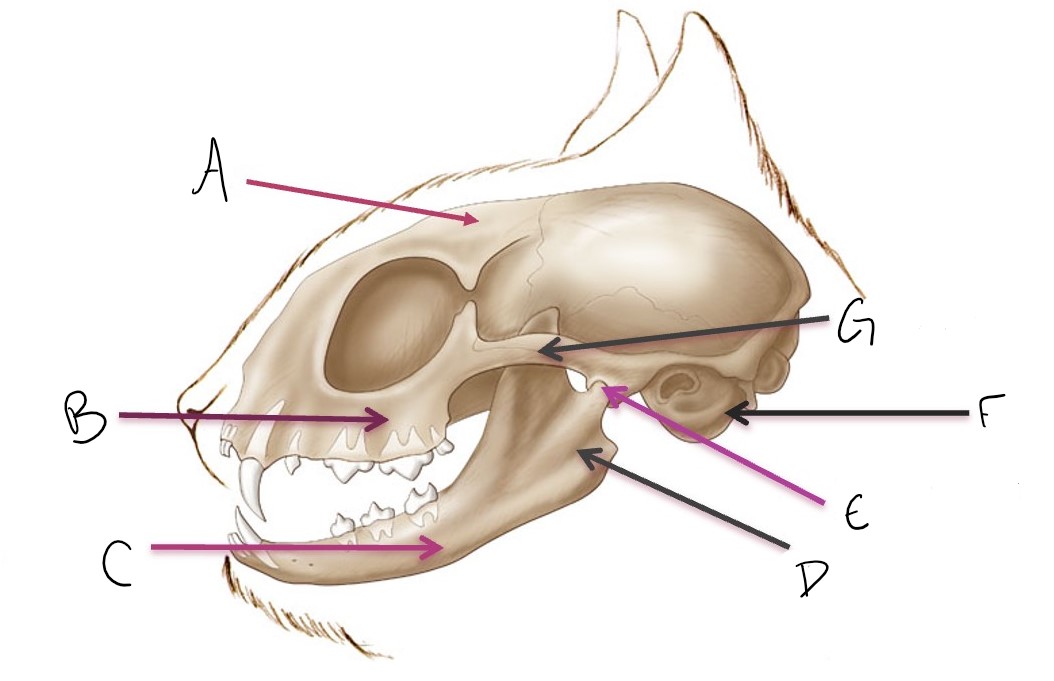
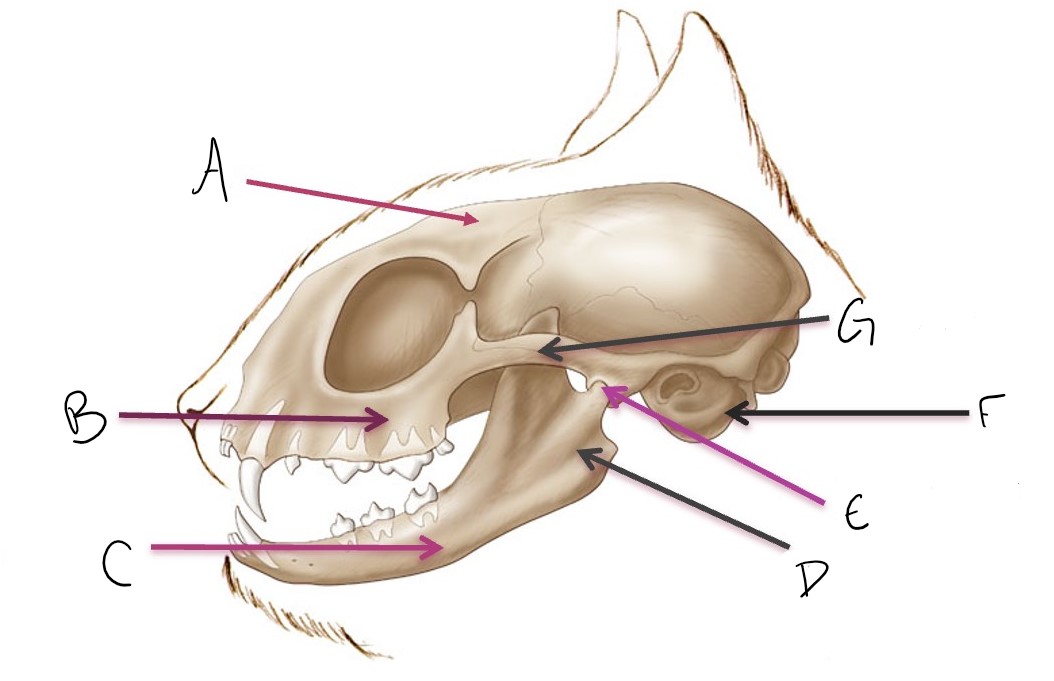
tympanic bulla
F
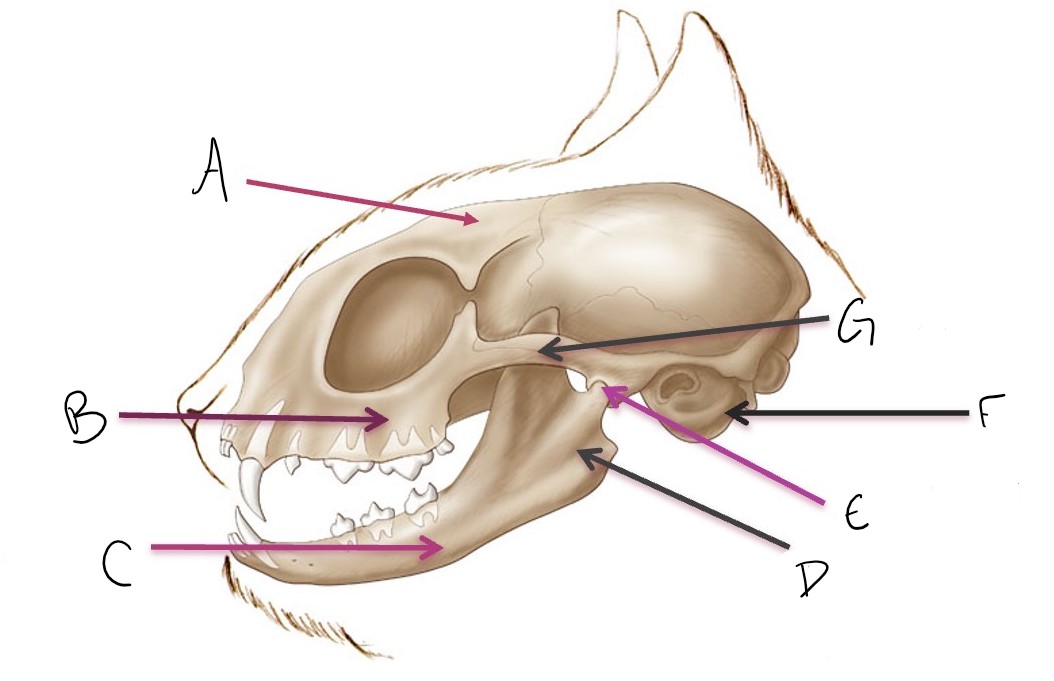
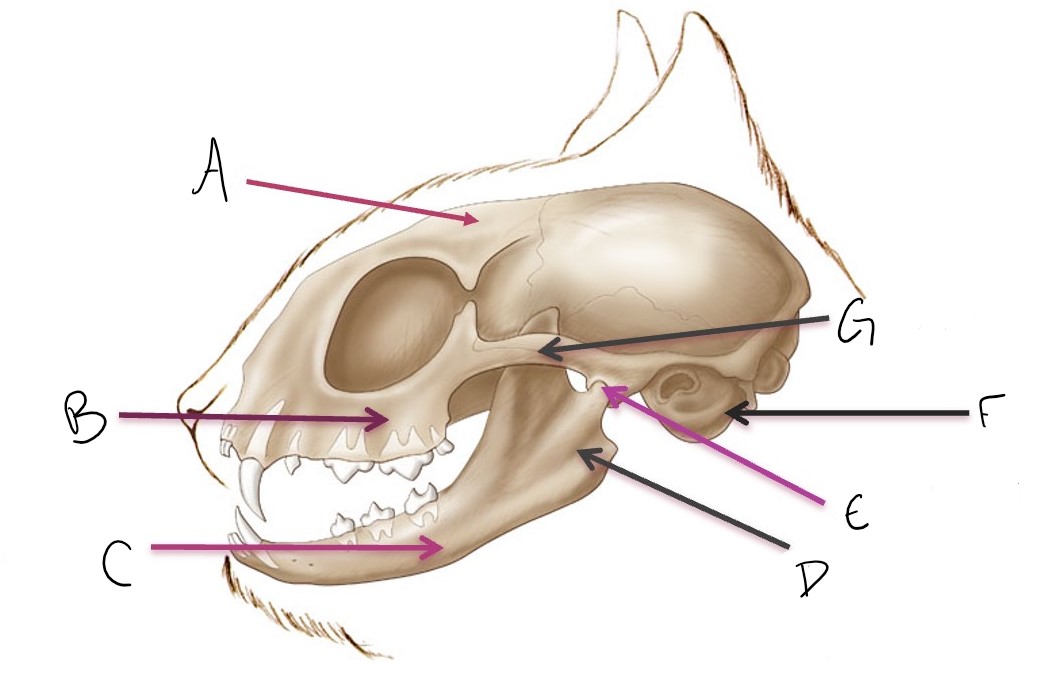
zygomatic arch
G
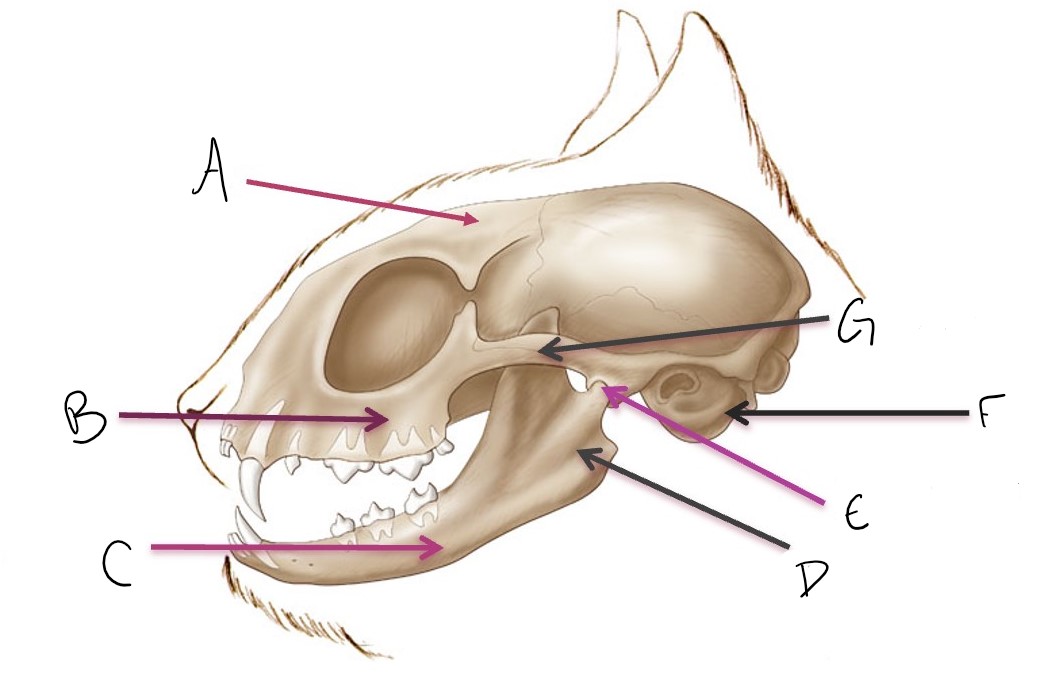
metacarpal 4
what metacarpal is found on lateral side
metacarpal 2
what splint bone is visualized in a DMPaLO view
metacarpal 4 and calcaneus
what splint bone (and other bone) is visualized in a DLPlMO view
lateral structure visualized on the palmar aspect of radiograph
what is the general cheat to what is visualized (and on what surface) in oblique views use example of a DLPaMO view
first 2 letter are xrays entering, second 2 letters are xrays exiting, O is saying not standard view
how to read full oblique views (enter & exit & type of view)
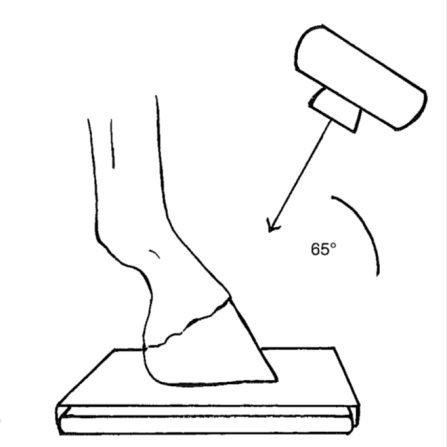
degree angle from ground to xray beam
when adding specific angle to oblique views what does the numbered angle tell you
D65Pr PaDiO
name this view
low kVp technique
what technique to use for high contrast
carpus and below
when to change from cranial/caudal to dorsal/palmar
superimposed femoral condyles and sesamoid bone of the stifle
perfect positioning of lateral femur view
limb parallel and patella center between femoral condyles
perfect positioning of CrCd view of the femur