AP BIO: EXAM REVIEW
1/271
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
272 Terms
Monomers
Building blocks of polymers
Dehydration synthesis
One monomer forms a covalent bond to another monomer and releases a water molecule
Hydrolysis
Bond between polymers is broken by addition of water molecule
Carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars, 3-7 carbon atoms
Disaccharide
Form when two monosaccharides bond via dehydration synthesis
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds
Primary protein structure
Sequence of amino acids
Secondary protein structure
Interaction of peptide backbone (hydrogen bonds)
Tertiary protein structure
Side chain interaction
Quaternary protein structure
Arrangement of multiple chains together
Fatty acids
Carbon chains and an acidic carboxyl group
Saturated fat
Saturated by hydrogen (solid @room temp)
Unsaturated fat
Less hydrogens (liquid at room temp)
Lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sometimes phosphorus
Nucleic Acid
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
Chromosomes
DNA broken into long, linear pieces
Monomer of nucleic acid
Nucleotides
Polynucleotide
Chain resulting from combination of nucleotides
Purine
(Adenine, guanine) 2 rings
Pyramidine
(Thymine, uracil, cytosine) single ring
DNA sugar
Deoxyribose (2nd carbon has hydrogen)
RNA sugar
Ribose (2nd carbon has hydroxyl group)
DNA written
5’—> 3’
m-RNA
Between protein coding gene and it’s protein product
r-RNA
helps accelerate chemical reactions (helps RNA bind to the right spot)
t-RNA
Brings amino acids to the ribosome
Element
Pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reaction
Compound
Substance consisting of two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio
CHON
90% of living matter
Subatomic particles
Proton, neutron, electron
Electron arrangement
2 in the first shell and 8 in the outer shell
Covalent bonds
Strongest chemical attraction, sharing valence electrons
Ionic bonds
Formed due to the result of two ions of opposite charge
Ion
Atom or molecule with a positive or negative charge due to the amount of electrons
Cation
Positive ion
Anion
Negative ion
Hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge that allows it to be attracted to a different electronegative atom nearby
Van Der Waals
Occur only when atoms and molecules are very close together
Chemical reaction
Making and breaking of bonds
Bonds involved in water
Polar bond, hydrogen bond
Water’s Cohesive Behavior
Hydrogen bonds hold the substance together. (Hydrogen bonds adhere water to different molecules. High surface tension)
Water’s Moderation of temperature
Absorbs and releases heat (high heat capacity)
Water’s Heat vaporization
As a liquid evaporates, the surface that remains behind cools down. (moderates climate and prevents organisms from overheating)
Water’s density
Less dense in its solid state (inversely proportional to temperature and volume). Sustains life underneath frozen bodies of water (ice works as an insulator).
Water’s Solubility
Due to its polarity, water can dissolve ionic and nonionic
Acids
Release H+ to the solution when dissolved in water
Bases
Release OH- to solution when dissolved in water
Types of carbon skeletons
Hydrocarbons, isomers
Isomers
Structural, cis-trans, enantiomers
Carbon skeletons
Vary in length, may be on branch or branch, may have double bonds or rings
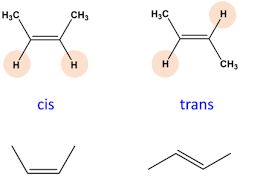
Cis-isomer
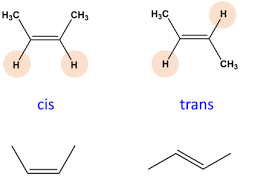
Trans-isomer
Enantiomers
Mirror each other
Functional groups
Atoms attached to organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions
ATP
Important source of energy for cellular processes
Dehydration reaction
Removes water, forms a new bond between monomers
Hydrolysis reaction
Add a molecule of water, break down polymers
Carbohydrates (CHO)
Main source of energy, fuel molecules, energy storage, structural function
Proteins (CHON(S))
made of amino acids, chemical catalyst, messengers
Nucleic acids (CHONP)
DNA and RNA, Genes and proteins, nucleotides(sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base)
LIPIDS (CHO(P))
Hydrophobic, fats
Carbohydrates
Sugars (monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharide)
Lipids
Fats, steroids, and phospholipids
Proteins
Polymer made of amino acids, joined by a peptide bond (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary structural)
Types of nitrogen bases
Pyrimidines, purines
Nitrogen bases in DNA
thymine, cytosine, adenine, guanine
Nitrogen bases in RNA
Uracil, Guanine, adenine, cytosine
Adhesion
2 different substances sticking to each other
Cohesion
Same substance sticking to another molecule of the same substance
Water’s surface tension
Water has no force from above so they become more tightly packed =surface tension
Solute
Being dissolved
Elements
Pure substances
Atom
Smallest form of an element
Number of Protons
Defines an element
Ionic bond
Bond between ions (a negative and positive atom hanging out together) (stealing electrons)
Covalent bond
2 atoms sharing electrons to add up to 8
Lysosomes
Have an acidic pH in order to dispose of cellular waste
Peroxisomes
Carry out oxidation reactions and produce hydrogen peroxide
Compartmentalization in cells
Maintain different environments inside a single cell allows eukaryotic cells to carry out complex metabolic reactions
Eukaryotic cells have
Membrane-bound nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, linear chromosomes
Endomembrane system
Group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins
What organelles does the endomembeane system not include
Mitochondria, chloroplasts, peroxisomes
Endoplasmic reticulum
Plays an important role in the modification of proteins and the synthesis of lipids
Rough ER
Has ribosomes that make proteins and feed the newly forming protein chains into the cumen
Smooth ER
Synthesize carbs, lipids, and steroid horomones
Golgi apparatus
Storing, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins
Lysosome
Organelle that contains digestive enzymes and acts as an organelle recycling facility
Central vacuole
Stores water and waste, isolates hazardous material, and has enzymes to break down macromolecules and cellular components
Mitochondria
Break down fuel molecules and capture energy in cellular respiration
Stacked thylakoids
Grana
Inter membrane space
Space between membranes
Mitochondrial matrix
Compartment enclosed by the inner membrane
Endosymbiosis
Symbiosis where one organism lives inside the other
Plasma membrane
Components that move freely and fluidly in the plane of the membrane
Glycoprotein
Protein with carbohydrates attached
Glycolipid
Lipid with carbs attached
Phospholipid
Lipid made with glycerol
Phospholipid bilayer
2 layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inwards
Transmembrane proteins
Extend all the way across the membrane