Diseases of White Blood Cells, Lymph Nodes, Spleen, and Thymus - Scarpa
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
what is the hematopoietic system?
system of organs and tissues involved in the production of blood
what hematopoietic tissues include the bone marrow, red blood cells, platelets, granulocytes, and monocytes?
myeloid tissues
what hematopoietic tissues include lymph nodes, the thymus, and the spleen?
lymphoid tissues
what are the pluripotent, self-renewing progenitor cells that form all the formed elements of blood?
hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
what is the chief site of hematopoiesis in until shortly after birth?
liver; hematopoietic stem cells migrate to the liver during the third month of embryogenesis
(t/f) hematopoietic stem cells can reside in fetal placenta and can be harvested to be used for hematopoietic stem cell transplants
true
during the fourth month of embryogenesis, the hematopoietic stem cells will migrate to the _________ __________
bone marrow
(t/f) at birth, hepatic hematopoietic activity increases and hematopoiesis in the marrow dwindles down
false; at birth, hepatic hematopoietic activity decreases and hematopoiesis in the marrow becomes more active
after puberty, hematopoiesis is restricted to the (appendicular/axial) skeleton
axial
(t/f) after puberty, only a quarter of the total marrow space is hematopoietically active
false; after puberty, half of the total marrow space is hematopoietically active
(t/f) committed progenitors self-stimulate their own proliferation and differentiation
false; hematopoietic growth factors, like erythropoietin and thrombopoietin, act on the committed progenitors for proliferation and differentiation
hematopoietic growth factors are the basis for (short/long) term physiological needs. __________ _________ fine tune the marrow output.
short, feedback loops
infectious and inflammatory condition results in a(n) (decrease/increase) in granulocyte output by the bone marrow
increase
tumors of hematopoietic origin either result from a progenitor cell maturation ____________ or ___________
blockage, dysregulation (independent growth factors)
which white blood cell disease category refers to a deficiency of leukocytes?
leukopenia
which white blood cell disease category refers to an increase of white blood cells in the blood (typically from reacting to an infection)?
leukocytosis
what term refers to the reduction in circulating neutrophils with a count below 1500 neutrophils per microliter?
neutropenia
what is the most common cause of leukopenia? why?
neutropenia; neutrophils are the most prevalent circulating leukocytes
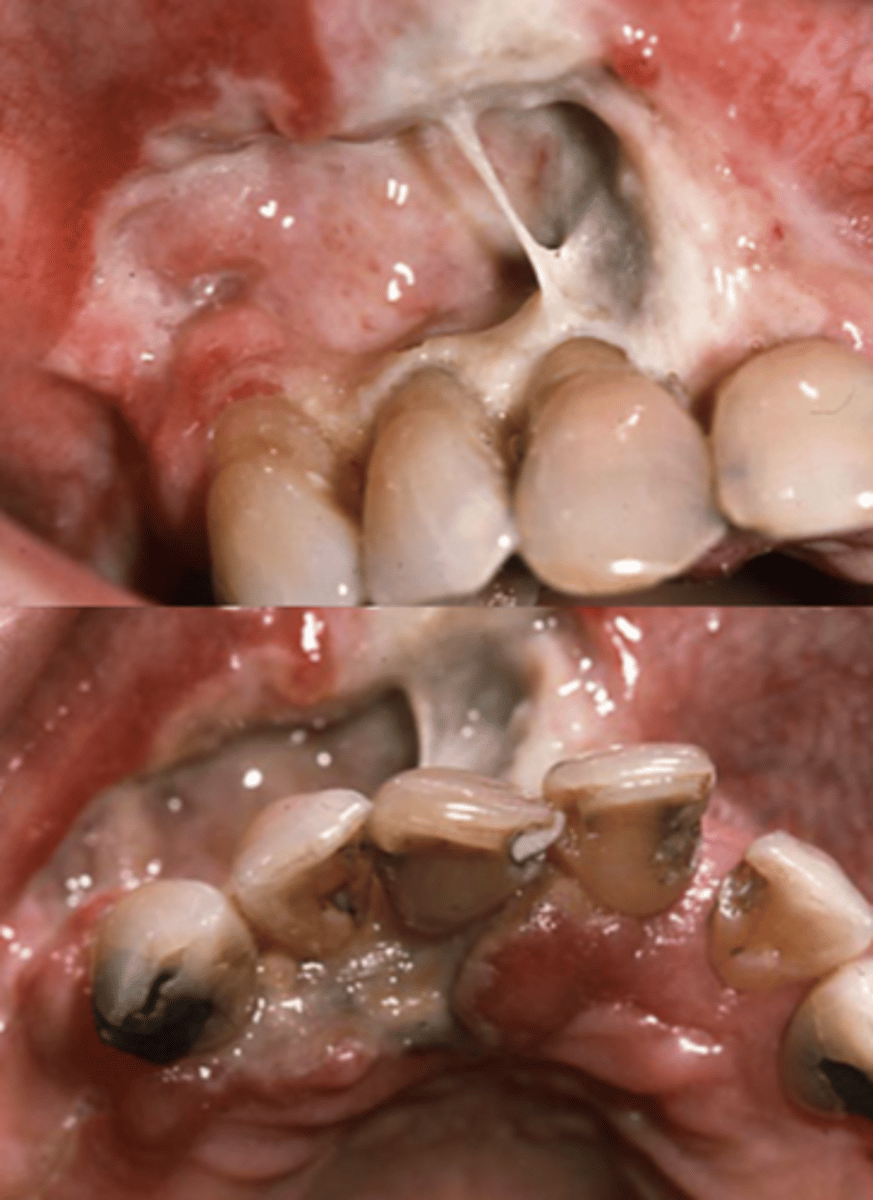
what condition is susceptible to bacterial and fungal infections, especially in the oral cavity, causing ulcerating and necrotizing lesions in the oral cavity or pharynx, as well as malaise, chills, fever, and weakness?
neutropenia
(t/f) serious infections with neutropenia are most common when the absolute neutrophil count is below 1500 neutrophils per microliter
false; serious infections with neutropenia are most common when the absolute neutrophil count is below 500 neutrophils per microliter
what is benign ethnic neutropenia?
a non-pathologic condition in which individuals have chronically low neutrophil counts without increased risk of infection or evidence of disease; 25% of healthy individuals of African ethnicity have ANC levels of 1000-1500/microliter
what are the 4 major causes of neutropenia?
1. drug/toxin induced
2. nutritional deficiencies
3. hematologic conditions
4. infections
what type of neutropenia is a rare disorder attributed to mutations in ELANE, characterized by recurrent neutropenia everyday 21 days?
cyclic neutropenia
what type of neutropenia is recurrent and has recurrent symptoms such as fever, pharyngitis, gingivitis, stomatitis, oral ulcerations, periodontal disease, and bacterial infections?
cyclic neutropenia
cyclic neutropenia is a measure twice a week for 6-8 weeks and shows ANC levels to be less than ________ neutrophils per microliter for 3-5 consecutive days per cycle
200
along with dental care and antibacterial therapy, what is another way of effectively treating cyclic neutropenia?
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)
(t/f) symptoms of cyclic neutropenia usually worsen as the individual grows
false; symptoms usually improve as individuals grow older
what condition is described as a significant neutrophil reduction with an ANC below 100 neutrophils per microliter making individuals markedly susceptible to infection (and may cause death within hours to days)?
agranulocytosis
(t/f) narrow spectrum antibiotics are indicated for individuals with agranulocytosis
false; broad spectrum antibiotics are indicated for individuals with agranulocytosis
(t/f) significant infection is the most common cause of agranulocytosis
false; the most common cause is drug toxicity like from chemotherapy cause generalized hematopoietic suppression and other agents like aminopyrine and sulfonamides
what drug can be used to combat potential agranulocytosis from chemotherapy?
granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)
what lymphoid structures are discrete encapsulated structure with B-cell and T-cell zones?
lymph node
what lymphoid structures are richly vested with phagocytes and antigen-presenting cells and are important for the activation of resident immune cells leading to morphologic changes and enlargement?
lymph node
what term refers to the inflammation of the lymph node?
lympadenitis
which lymph node region is often inflamed due to the drainage of infected teeth or tonsils?
cervical region
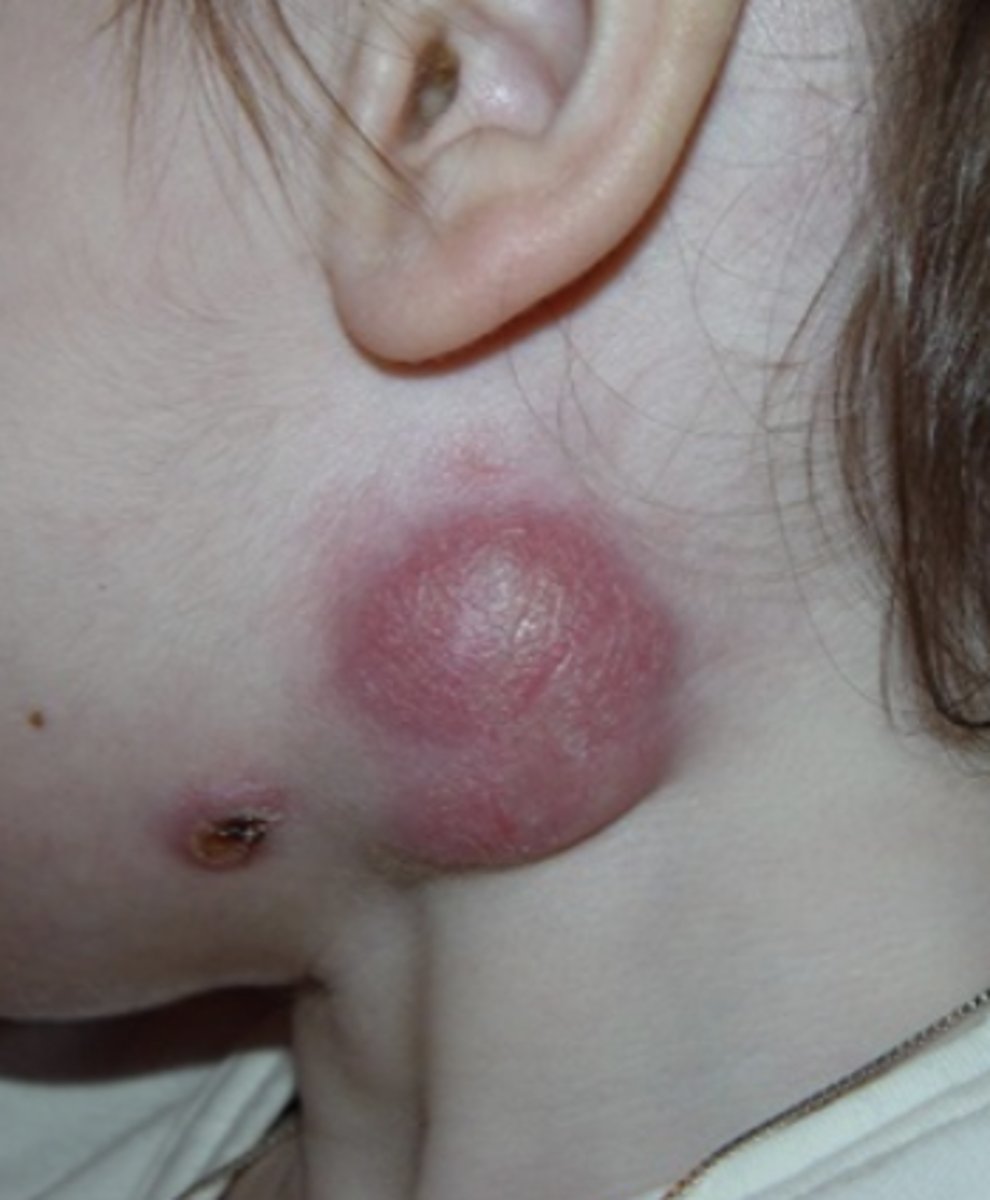
which lymph node region is often inflamed due to infections in the extremities/limbs?
axillary (for the arms) or inguinal (for the legs) regions
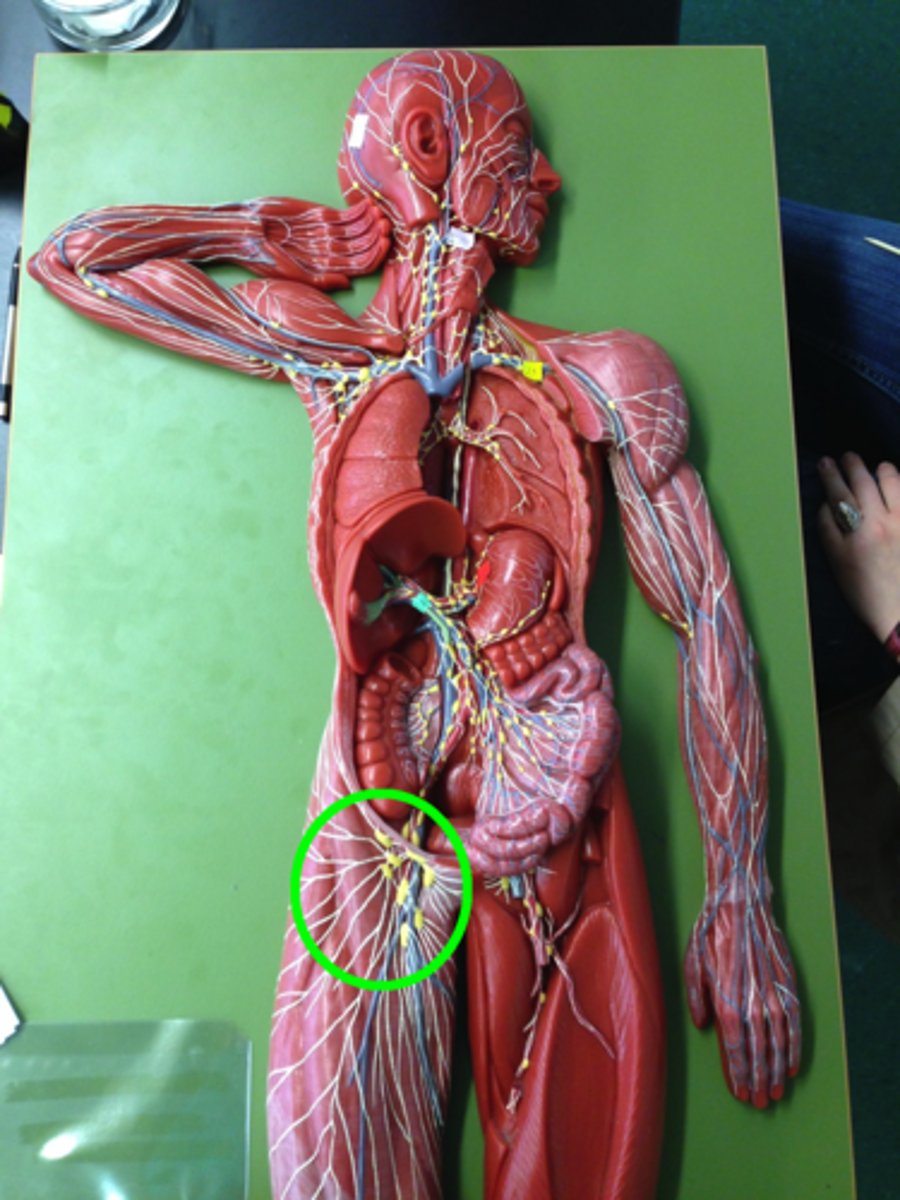
which lymph nodes are often inflamed due to appendicitis?
mesenteric lymph nodes
what term refers to the enlargement of lymph nodes?
lymphadenopathy
(t/f) systemic infections may cause acute generalized lymphadenopathy
true
acute vs chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis: lymph nodes enlarged and painful
acute
acute vs chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis: may be fluctuant, with red overlying skin, and sinus tract may be present
acute
acute vs chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis: nodes usually heal with scarring and are mildly hyperplastic
acute
acute vs chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis: lymph nodes are enlarged and non-tender
chronic
how can you tell whether a lymph node is inflamed from a past infection or a present infection on palpation?
non-tender lymph nodes indicate a past infection, while tender/painful lymph nodes indicate a present infection
what are the 3 broad categories of neoplastic proliferations of white blood cells?
1. lymphoid neoplasms
2. myeloid neoplasms
3. histiocytes
what are neoplastic proliferations of white blood cells?
abnormal, clonal expansions of white blood cells due to uncontrolled growth of a mutated cell
somatic hypermutations of white blood cells normally occur in the geminal centers of lymph nodes. how does this lead to neoplasm?
high affinity antibodies are generated which predisposes cells to acquire critical immortalizing and cancer-promoting mutations
what are 5 predisposing factors to the neoplasm of white blood cells?
1. genetic mutations
2. inherited genetic factors
3. viruses
4. chronic inflammation
5. iatrogenic factors (radiation and chemotherapy)
lymphoid neoplasms are primarily of (b/nk/t) cell origin, followed by (b/nk/t) cell origin, and rarely from (b/nk/t) cell origin
b, t, nk
(t/f) neoplastic cells do not resemble normal lymphocytes. instead they have their own unique structures.
false; neoplastic cells frequently resemble that of a particular stage of normal lymphocyte maturation
leukemia and lymphoma are common clinical presentations of (histiocytes/lymphoid neoplasms/myeloid neoplasms)
lymphoid neoplasms
what condition refers to a neoplasm of hematopoietic origin with widespread involvement of the bone marrow and peripheral blood (also known as liquid cancer)?
leukemia
what condition refers to a neoplasm of hematopoietic origin presenting a discrete mass?
lymphoma
(t/f) lymphomas and leukemia cannot mix. these are 2 distinct conditions.
false; the divisions can blur. lymphomas may have leukemic presentations and leukemias may present as soft tissue masses without bone marrow disease
what are the 2 ways lymphomas present?
1. enlarged, non-tender lymph nodes (two-thirds of presentations)
2. extranodal location with symptoms related to organ and site involved (one-third of presentations)
what 3 regions are the most common extranodal areas of lymphomas?
1. head
2. neck
3. gastrointestinal tract
(leukemias/lymphomas) often present with signs/symptoms related to suppression of normal hematopoiesis like anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia
leukemias
what lymphoid neoplastic condition refers to the bony destruction of the skeleton and is associated with pain and pathological fracture?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
what category of white blood cell neoplasm is associated with B symptoms (fever, night sweats, and weightloss)?
lymphoid neoplasms
what category of white blood cell neoplasm is associated with the neoplastic cells circulating through the lymphatics and peripheral blood?
lymphoid neoplasms
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is the most common cancer of children?
acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ALL)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is associated with rapidly appearing symptoms related to the suppression of bone marrow function, CNS manifestations from meningeal spread, bone pain, generalized lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly?
acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ALL)
(t/f) most children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ALL) achieve remission with aggressive chemotherapy and up to 85% of children are cured
true
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is the most common leukemia of adults in the western world?
chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is a B-cell lymphoid neoplasm with a well-recognized capacity to more typically present as leukemia, but also as lymphoma?
chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
(t/f) patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) are typically asymptomatic
true
what lymphoid neoplastic condition may disrupt immune function through uncertain mechanisms which increase infection susceptibility and may develop hemolytic anemia or thrombocytopenia through an autoimmune origin?
chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is an indolent neoplasm with no known cure, but may extend life 5-10 years with chemotherapy or hematopoietic stem cell transplants?
chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
what chemotherapy drug is a monoclonal antibody that targets CD20 proteins present on the surface of many lymphoid neoplasms of B cell origin?
rituximab
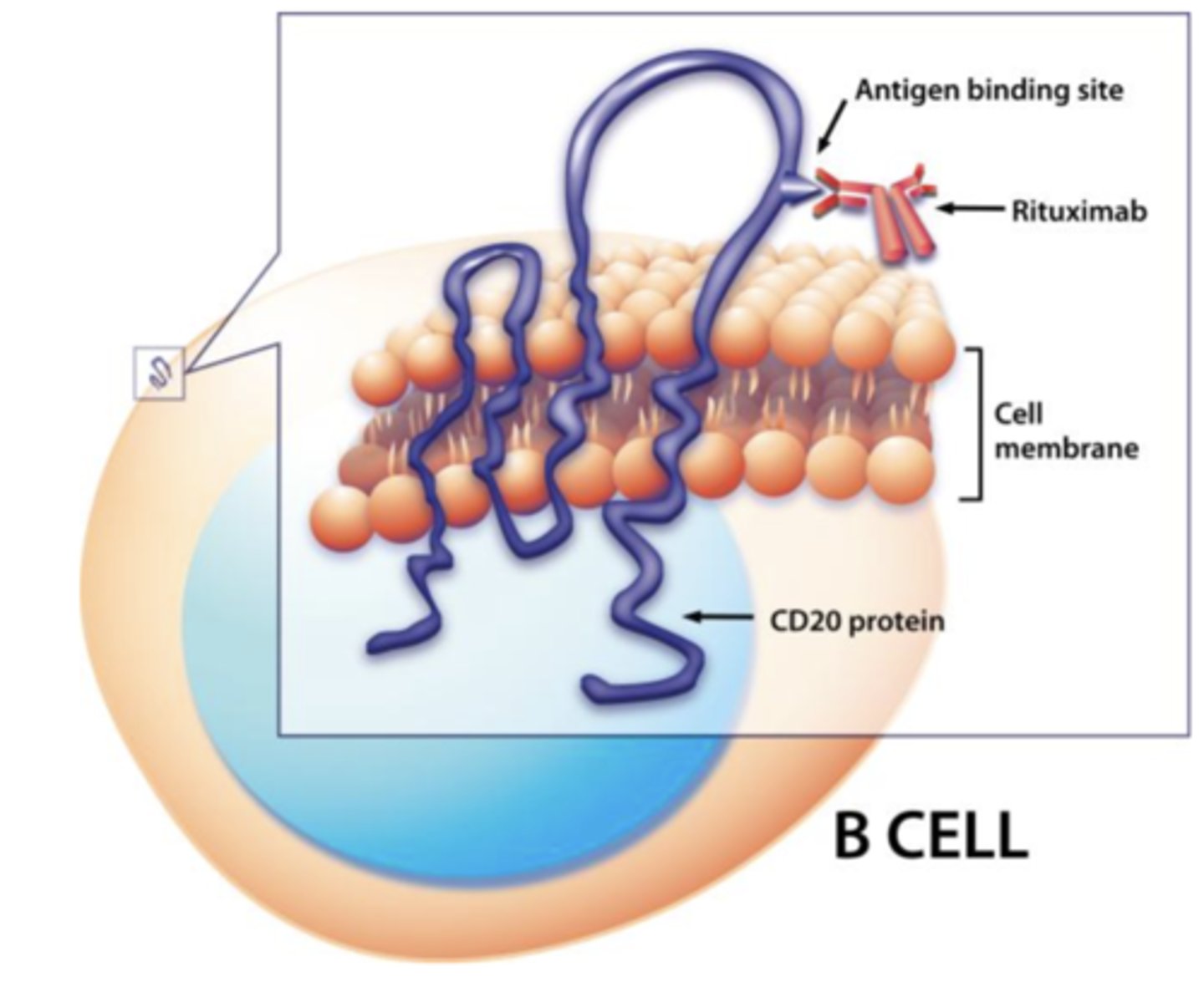
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is a common indolent B-cell lymphoma that frequently presents as painless with generalized lymphadenopathy?
follicular lymphoma
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is incurable with a 7-9 year median survival with chemotherapy and has a high-grade transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)?
follicular lymphoma
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is the most common form of lymphoma?
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition typically presents as a rapidly enlarging mass at nodal and extranodal sites (such as the Waldeyer ring) and is the most common intraoral lymphoma?
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is aggressive and rapidly fatal without treatment, but can be treated with aggressive chemotherapy?
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is a highly aggressive lymphoma typically seen in the context of HIV/AIDS and is associated with the Epstein-Barr virus?
plasmablastic lymphoma
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is considered a variant of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and is most commonly seen in the oral cavity and mandible with 75% of patient dying of the disease within 6-7 months?
plasmablastic lymphoma
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is a highly aggressive B-cell lymphoma usually arising at the extranodal sites and is the fastest growing human cancer?
burkitt lymphoma
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is endemic in Africa, highly associated with the Epstein-Barr virus and HIV, but responds well to aggressive chemotherapy with most patients cured?
burkitt lymphoma
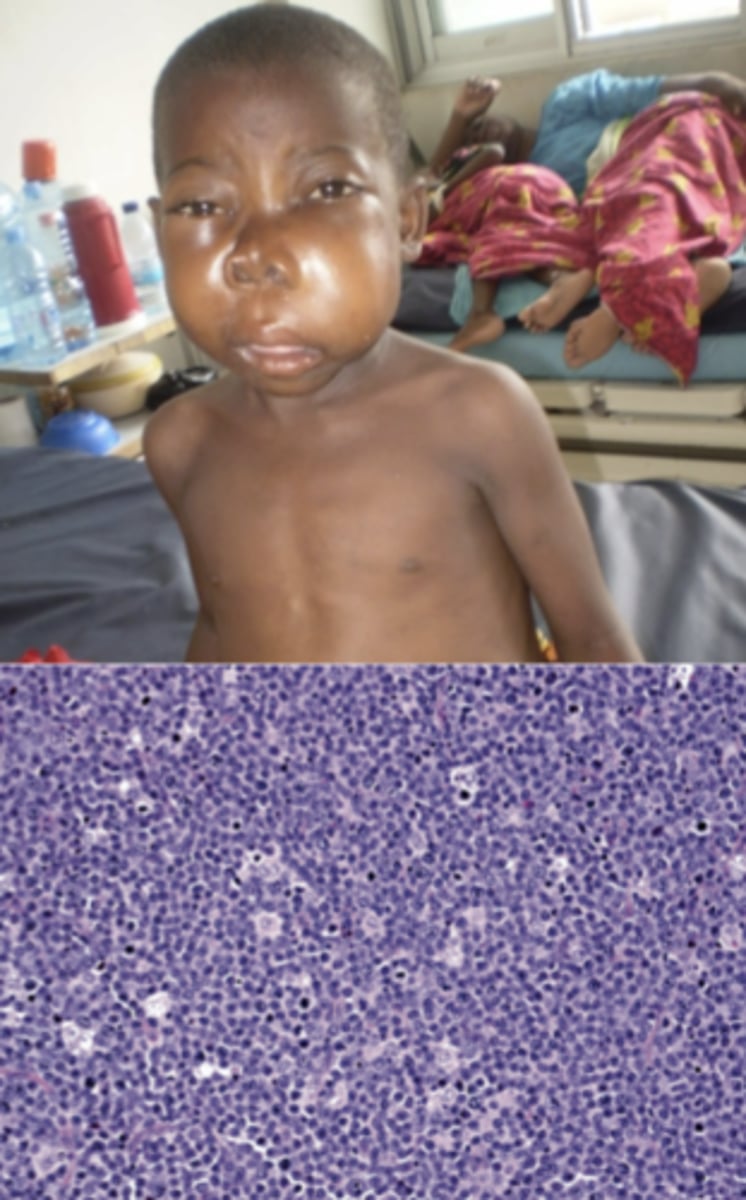
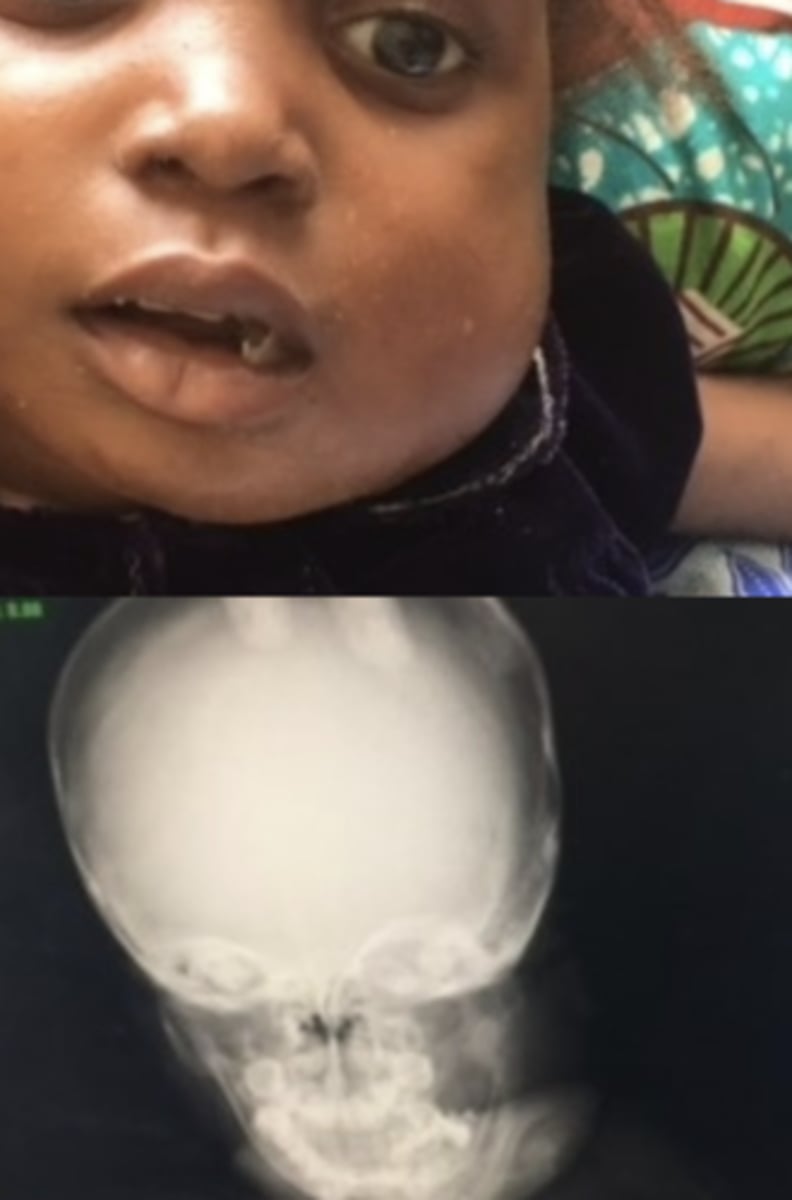
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is associated with progressive jaw swelling?
burkitt lymphoma
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is a category of B-cell lymphomas arising within lymph nodes, the spleen, or extranodal tissues initially recognized at mucosal sites and referred to as mucosa associated lymphoma?
marginal zone lymphoma (MALT lymphoma)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition often arises within tissues involved with chronic inflammation like the salivary gland in Sjögren syndrome, the thyroid in Hashimoto thyroiditis, and the stomach with H. pylori gastritis?
marginal zone lymphoma (MALT lymphoma)
other than chemotherapy, how can marginal zone lymphoma (MALT lymphoma) be treated?
removal of the underlying inflammation
what are plasma cell neoplasms?
a subset of B-cell lymphoid neoplasms that contain neoplastic plasma cells which secrete immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin fragments that serve as a diagnostic marker
(t/f) neoplastic plasma cells vary greatly and secrete different type of immunoglobulins
false; neoplastic plasma cells are clonal and secrete identical (monoclonal) immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin components
monoclonal immunoglobulins secreted by neoplastic plasma cells can be identified in (blood/urine) and referred to as _____ proteins
blood, M
immunoglobulin light chains secreted by neoplastic plasma cells can be identified and detected in (blood/urine) and referred to as __________-__________ proteins
urine, Bence-Jones
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is the most deadly plasma cell neoplasm with the highest incidence in men, African Americans, and the elderly?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition usually presents as tumorous masses scattered throughout the skeletal system and shows features stemming from the effects of neoplastic plasma cell growth in bones, and the suppression of humoral immunity?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition causes lytic bone lesions throughout the skeleton, bone pain, hypercalcemia, renal dysfunction, neurologic conditions, and the suppression of normal hematopoiesis?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition causes the production of excessive immunoglobulins potentially forming immunoglobulin aggregates and deposits in soft tissues as amyloids and causes the suppression of normal immunoglobulins leading to recurrent bacterial infections?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
(M/Bence-Jones) proteins, found in multiple myeloma, are toxic to renal tubular cells and cause renal damage
Bence-Jones
what lymphoid neoplastic condition causes death mainly by infections and renal failure and is preferably managed with high-dose chemotherapy with a bone marrow transplant?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition may preveiously present with a solitary lesion (solitary plasmacytoma of the bone or extraosseous plasmacytoma) for 10 years before progressing into this condition?
multiple myeloma (plasma cell myeloma)
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is the most common plasma cell neoplasm, is asymptomatic by definition due to the absence of CRAB (hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, anemia, bone lesions) features, and serum M proteins less than 3 grams per deciliter?
monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS)
what term refers to a proteinaceous substance characterized by aggregates of proteins in a characteristic cross-beta pleated sheet conformation?
amyloid
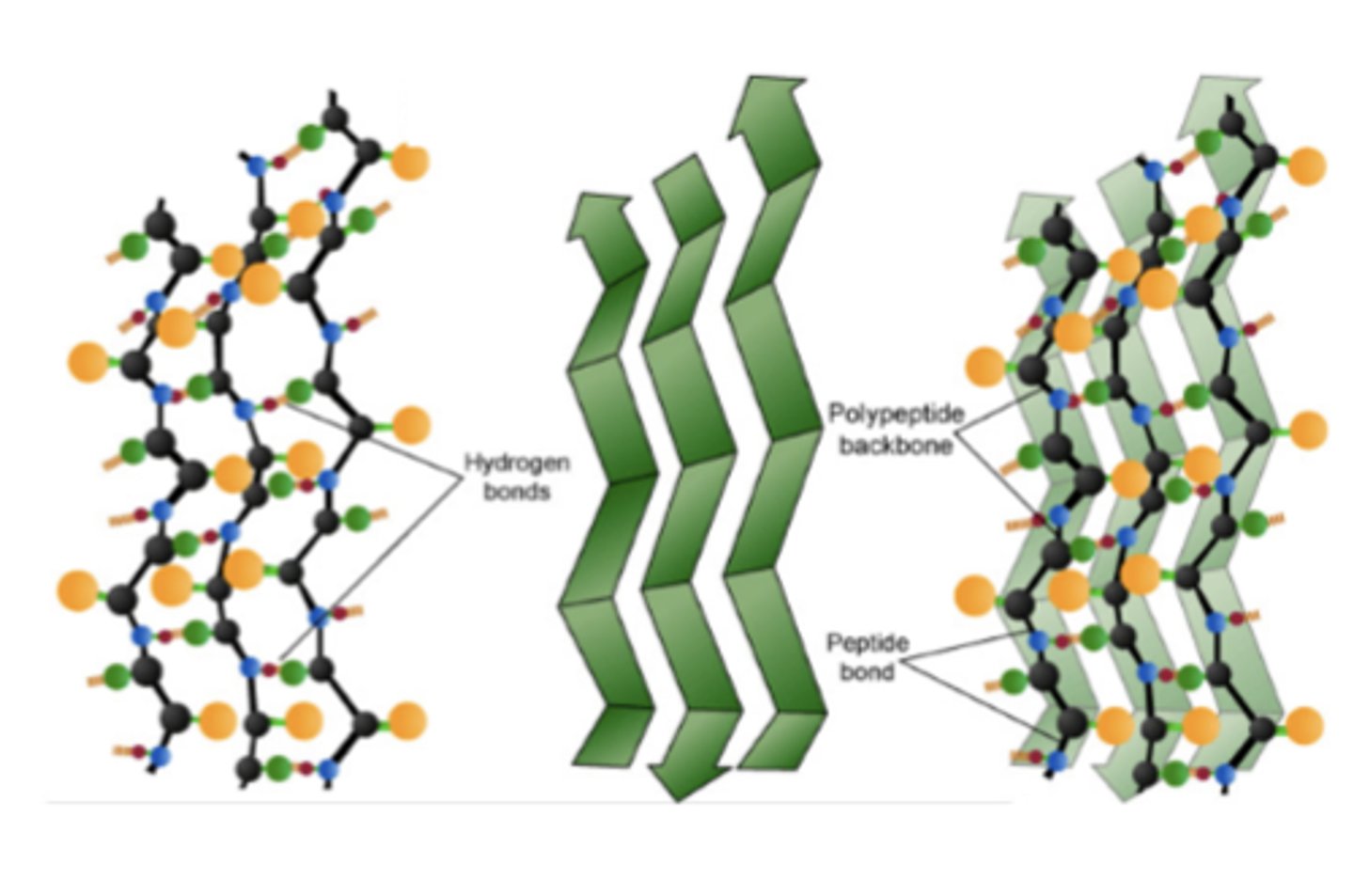
what term refers to over 20 identified degradation-resistant proteins that can aggregate and deposit in tissues?
amyloid
(primary/secondary/hemodialysis-associated) amyloidosis is associated with plasma cell disorder
primary
(primary/secondary/hemodialysis-associated) amyloidosis is a complication of an underlying inflammatory disorder
secondary
(systemic/localized/hereditary) amyloidosis is described as deposition in a single organ like the heart, tongue, or brain (Alzheimer disease)
localized
what lymphoid neoplastic condition is a highly aggressive neoplasm of NK or T cell lineage universally associated with Epstein-Barr virus and most often presents as a destructive nasopharyngeal mass?
extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma