Trophic Levels
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Producers (3)
Autotroph
produces their own food
use photosynthesis to transform light energy from the Sun to glucose
Primary producers Roles
regulating the hydrological cycle through transpiration
maintain the balance of gases in the atmosphere (CO2/oxygen
creating diverse habitats for animal species
prevent soil erosion

Photosynthesis
a system with inputs, flows, outputs, transfers and transformations
Consumers
heterotrophic organisms that feed on producers or other organisms to obtain their carbon compounds.
The number of consumers that an ecosystem can support is based on the number of producers in the community
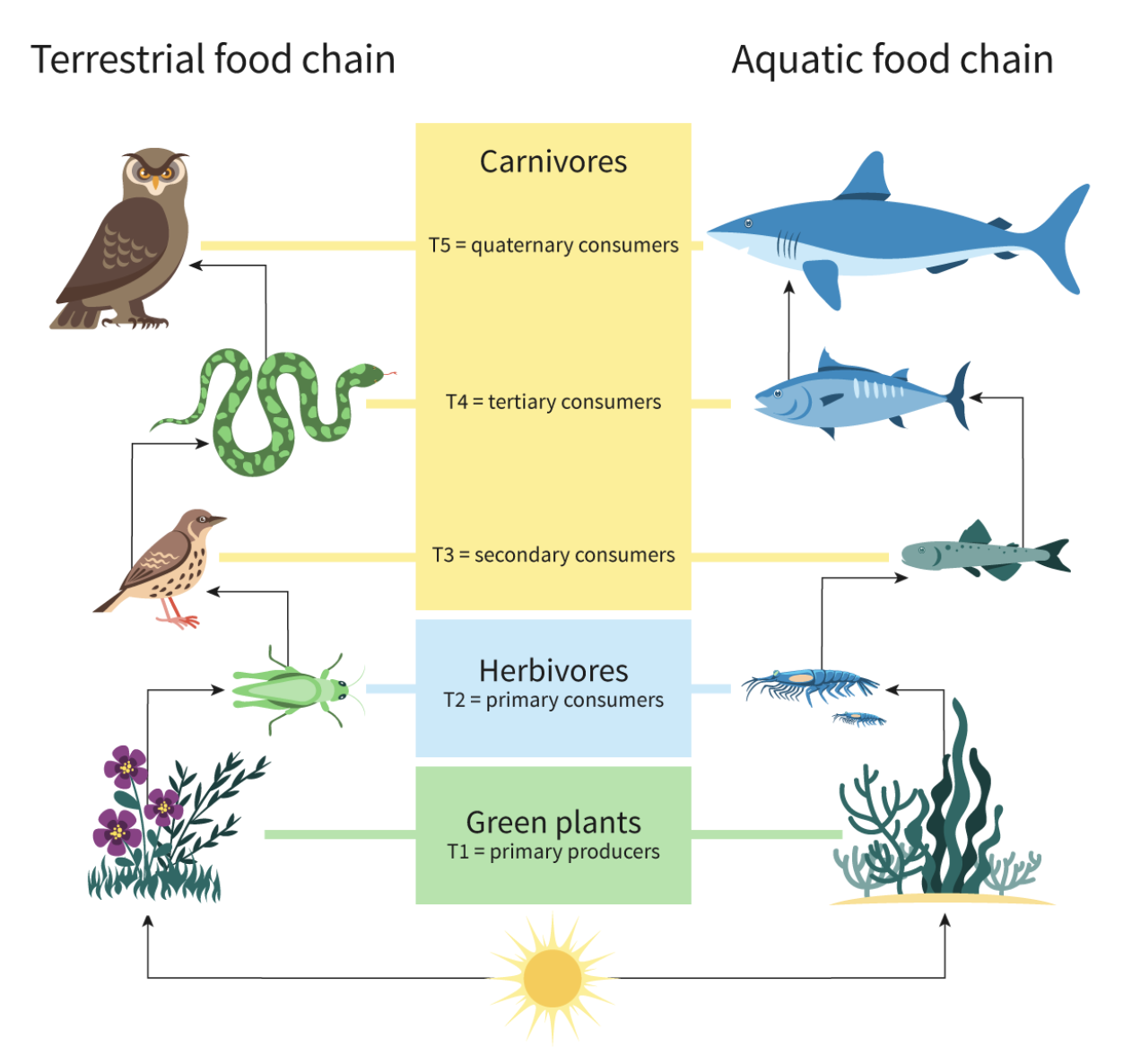
Trophic levels
show an organism's position in the energy transfer process.
Producers —> first trophic level,
primary consumers who eat the producers (second trophic level)
secondary consumers who eat the primary consumers (third trophic level)
Each trophic level represents a step in the transfer of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem.
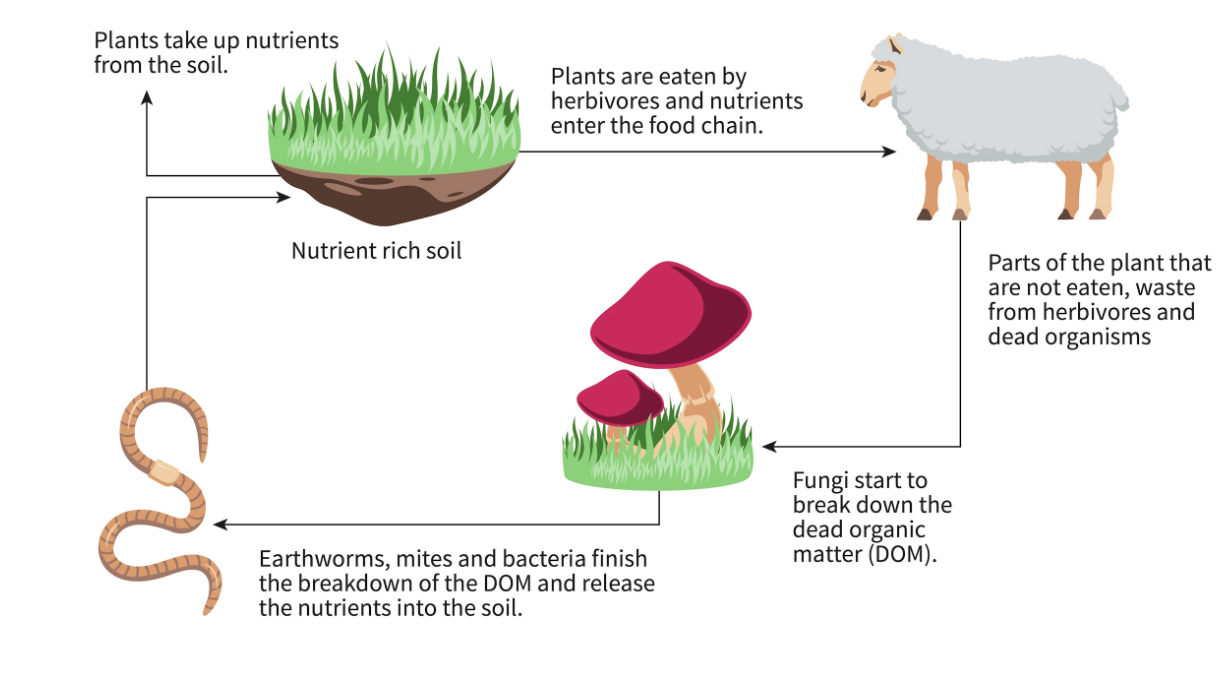
Humus
When decomposers break down any matter, some of this matter is left behind in small pieces in soils —> known as humus
Types of decomposers
saprophytes
detritivores
Saprophytes
They release chemicals into the surrounding soil to do external digestion on the dead matter before absorbing it. This means some of the matter that have not been absorbed remains good nutrients in the soil (bacteria, mushroom, moist)
detritivores
They eat the dead stuff (snail, crab, centipede)
Food chain
A linear model that shows the direct flow of matter and energy through trophic levels.
Scavenger
See entire glossary
An organism that feeds on dead or decaying animal matter rather than hunting for prey.