JJ's Study Guide WGU Patho
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What is used to treat prostate cancer?
Cryoablation
sporadic
ALS category
Osteo Arthritis (OA)
- joint cartilage is gradually lost
- unilateral
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
An autoimmune disease.
What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Swelling, stiffness, and pain in joints.
What causes rheumatoid arthritis?
Chronic soft tissue inflammation.
What can rheumatoid arthritis lead to?
Crippling deformities and degeneration of cartilage in joints.
endocarditis
-inflammation of the lining of the heart
-Vegetation shown on an echo
Type 2 MI
lack of oxygen
MI symptoms
-SOB
-Neck/Jaw pain
-Chest Pain
-Vomiting
Risk factor for Erectile Dysfunction
Heart Disease
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
-Ascites
-Jaundice
- Elevated AST & ALT
Symptoms of ESRD
-Decreased Urine output
-Anemia
-Fatigue
-Itchy Skin
What is a Chromosomal abnormality?
Turner's, missing X chromosome
What is a communicable disease causing muscle weakness/paralysis within 4-6 hours after onset?
A. Myelitis
B. Malaria
C. West Nile
D. Botulism
D. Botulism
What causes malaria?
Plasmodium
Ovarian Tumor/Cancer
HE4 Biomarkers
What solutions is ISOTONIC to RBC's ?
0.9 NaCl Solution (Normal Saline)
What causes peripheral neuropathy?
-Toxins
-Vitamin Deficiency
-Infections
What causes delayed puberty?
chronic illness
What symptom is associated with Dysmenorrhea (Painful Menstrual Cramps)?
-Lower Back Pain
-Nausea/Vomiting
-Diarrhea/Constipation
-Fatigue
-Headaches
Aplastic Anemia
failure of blood cell production in the bone marrow
Risk Factors for Cholecystitis (Gallbladder Inflammation)
"The 4 F's"
1. Female
2. Forty
3. Fat
4. Fertile
Symptoms of Stage One Lyme disease
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Spine Curvature
Lordosis
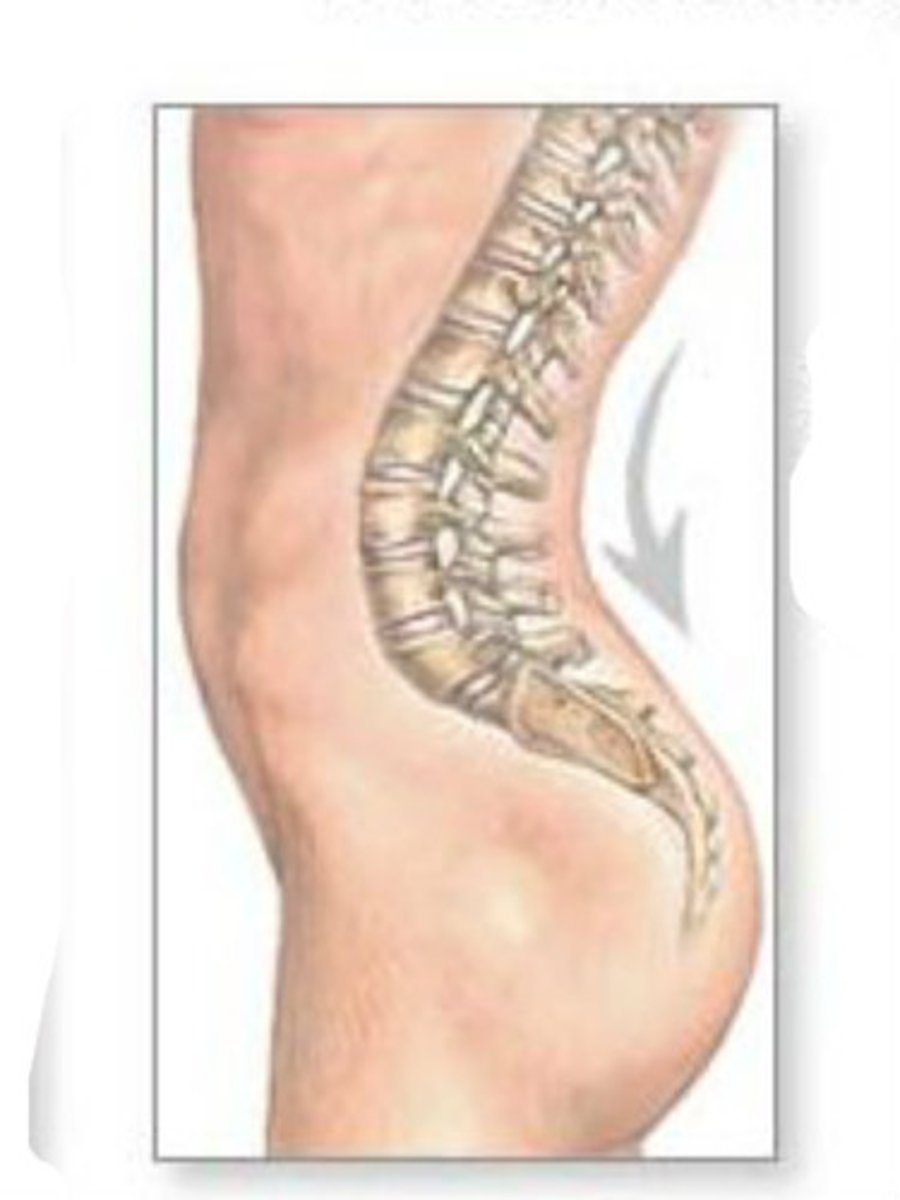
Symptoms of ALS
-Muscle weakness in one or more of the following: hands, arms, legs, or the muscles of speech, swallowing, or breathing
-Twitching (fasciculation) and cramping of muscles, especially those in the hands and feet
-Weakness
-The use of Prescribed Anti-glutamate
What causes secondary hypertension?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
What is Diffusion?
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
A Tympanic Membrane perforation can cause?
Middle Ear Infection
What triggers Vass occlusive Crisis in sickle-cell anemia?
Acidosis / Dehydration
RAAS (Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System) Steps
Step 1: Renin Release (Triggering the RAAS)
Step 2: Angiotensinogen Conversion
Step 3: Angiotensin 1 to Angiotensin 11
Step 4: Effects of Angiotensin 11
Step 5: Aldosterone and ADH Effects
RAAS: Step 1: Renin Release
- Stimuli for renin release:
Low blood pressure (hypotension)
Low sodium levels in the kidney
Sympathetic nervous system activation
- Renin, an enzyme, is released by the juxtaglomerular cells in the kidney.
RAAS: Step 3: Angiotensin 1 to Angiotensin 11
Angiotensin- converting enzyme (ACE), primarily found in the lungs, converts angiotensin 1 -> Angiotensin 11
RASS: Step 4: Effects of Angiotensin 11
Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor and has several key effects:
-Increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels.
-Stimulates aldosterone release from the adrenal glands.
-Increases ADH (vasopressin) secretion from the pituitary gland.
-Triggers thirst to encourage fluid intake.
RAAS: Step 2:Angotensinogen Conversion
Renin converts angiotensinogen (A protein made by the liver) into Angiotensin 1.
RAAS: Step 5: Aldosterone and ADH Effects
-Aldosterone (from the adrenal glands) promotes sodium and water retention in the kidneys, increasing blood volume and pressure.
-Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, also called vasopressin) increases water reabsorption in the kidneys, further raising blood pressure.
What is RAAS do?
A hormonal system that regulates blood pressure, fluid balance, and electrolyte homeostasis.
A pouchlike protrusion in the sigmoid?
diverticulosis
Fibromyalgia
-Muscle Weakness
-Emotional Distress symptoms
- Typically take antidepressants and use acupuncture
What do B cells do?
produce antibodies
What do T-cells do?
produce cytokines
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Stages
Chronic phase and accelerated phase or blast phase
What condition allows blood flow back into the left atrium from the left ventricle?
Mitral Insufficiency
Two tumors that are Benign?
-Adenoma
- Osteoma
A patient complains of mild discomfort and bulging submucosal veins, what would be the diagnosis?
Esophageal Varices
A pregnant lady with a non-healed wound and an HgA1C of 8, what is her suspected diagnosis?
Gestational Diabetes
A patients imaging shows a femur fracture and thickening of bone, what diagnosis could this be?
Paget's Disease
What are the treatments for Genital Warts?
-Cryotherapy
-Electrocautery
-Laser
What STI can cause conjunctivitis in a baby being delivered via vaginal birth?
1. Chlamydia Trachomatis
2. Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
Greenstick Fracture
bending and incomplete break of a bone; most often seen in children
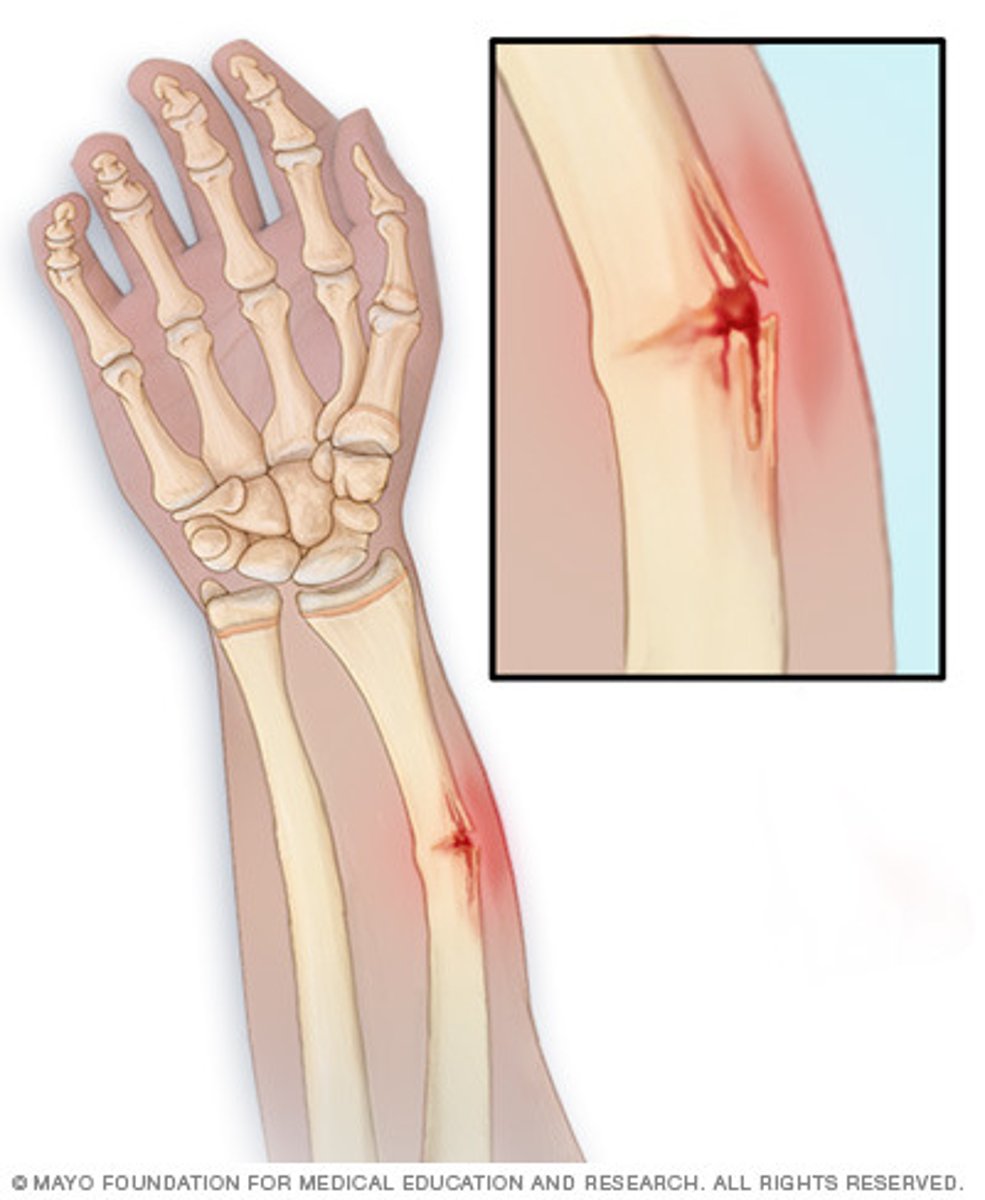
Compartment Syndrome
Increased pressure within one or more compartments, leading to decreased blood flow, tissue ischemia, and neurovascular impairment.
How long, if NOT treated, does neurovascular damage happen in compartment syndrome?
4-6 hours after onset
Sprain
stretching or tearing of ligaments
Stage 1 Sprain
Mild sprain with slight stretching or microscopic tearing of the ligament.
Symptoms: Mild Pain, Swelling, Tenderness, Bruising
Stage 2 Sprain
Moderate sprain with partial tearing of the ligaments.
Stage 3 Sprain
Severe Sprain with a complete tear of the ligament. Can lead to permanent instability.
basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
a surface epithelial tumor of the skin originating from basil or germinative cells. typically occur on the face and present as shiny, translucent, or pearly domes.
vitiligo
white patches on the skin caused by the destruction of melanocytes associated with autoimmune disorders
A patient presents with scaling and itching of the foot, the MD prescribes an antifungal, what disease could the patient have been diagnosed with?
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)
What are three things that can cause peripheral neuropathy?
1. Diabetes Mellitus
2. Chemotherapy treatments
3. Chronic Alcoholism
myasthenia gravis
autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by weakness of voluntary muscles
Signs and Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
-Droopy Eyelids
-Double Vision
-Difficulty making facial Expressions
-SOB
-Slurred Speech
-Weakness Arm/leg/Neck
What medication can help with Myasthenia Gravis?
Acetylcholine
Aneurysm
a localized weak spot or balloon-like enlargement of a vessel wall or cardiac chamber
thrombus
stationary blood clot
Embolus
moving blood clot
Cardiac dysrhythmias
-Deviations from normal cardiac rate or rhythm
Atherosclerosis
inflammatory process involving the accumulation of lipids, calcium, blood components, carbohydrates, and fibrous tissue on the intimal layer of a large or medium-sized artery
Hyperlipidemia (HLD)
high cholesterol
parnicious anemia
An autoimmune disorder; resulting in the inability to absorb vitamin B12
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is caused by HIV, which damages the cells (CD4 + T helper Cells) in the body's immune system so that the body is unable to fight infection or certain cancers.
Turner Syndrome (Monosomy X)
A genetic disorder that occurs when a female is born with one X chromosome instead of 2. (45,X instead of 46, XX)
Key Features of Turner Syndrome
-Short Stature
-Delayed Puberty
-Webbed Neck (Extra Skin folds)
-Heart Defects
-Learning difficulties
-Infertility issues
Introns
a noncoding DNA/RNA sequence within a gene that is removed before the RNA is translated into a protein.
Translation
Process where mRNA sequence is read by a ribosome to build a protein chain, essentially converting the genetic code into a functional code.
Neurobehavioral Disorder Associated with a Prenatal Alcohol Exposure (ND-PAE)
when alcohol is exposed prenatally; No SAFE level of consumption
Heberden's nodes and Bouchard's nodes
hard, bony enlargements characteristic of osteoarthritis that are caused by the formation of osteocytes
Where is Heberden's nodes found with osteoarthritis
Distal Interphalangeal Joint (Closest to the fingertip)
Where is Bouchard's nodes located?
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint (middle finger Joint)
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
a genetic disorder caused by a trisomy of the twenty-first chromosome
Signs/symptoms of Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
-Distinctive Facial Appearance
-Low nasal bridge
-Epicanthic folds
-Protruding tongue
-Flat, low set Ears
-CHF