1.1: Sequential Models
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Syntax
Programming constructs, what we write
Semantics
State machines, the behaviour we produce
Synchronous Reactive Components Properties
Inputs
Internal State
Outputs
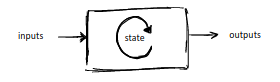
Reactive Component Syntax
Finite set of input variables defining a set of inputs
Finite set of output variables defining a set of outputs
Set of state variables defining a set of states
Initialisation defining the set of initial states
Reaction defining a set of reactions from s → t (i/o), where s and t are states, i is an input and o is an output.
Reactive Component Semantics
A set of inputs (Qi = {0, 1} or Qi ={(0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1)})
A set of outputs (QO= {0, 1})
A set of states (Qs = {0, 1})
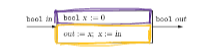
Reactions Properties
Assignments (x := e)
Sequential statements
Conditional statements
Local variables
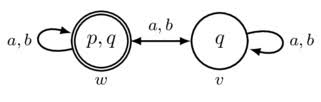
Input-Enabled Component
A component where every input is enabled in every state.
An input i is said to be enabled in a state s if there exists and output and state t such that s → t (i/o).
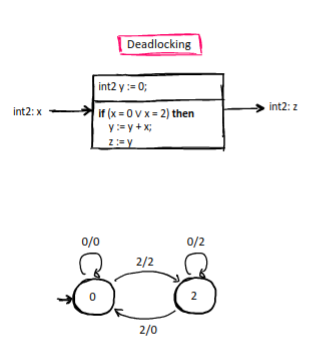
Deadlock
When a program crashes/returns an undefined error.
Finite-State Component
A synchronous reactive component where the type of each of its input, output and state variables are finite.
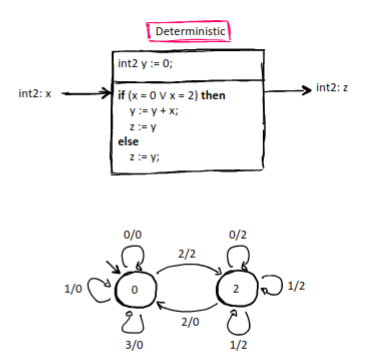
Deterministic Component
A synchronous reactive component where:
C has a single initial state
For each state and every input, there is precisely one output and state such that s → t (i/o) is a reaction of C.
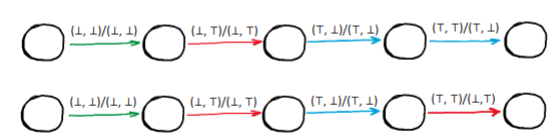
Non-Deterministic Compontents
Responds with different output sequences for the same input sequence.
Combinational Component
A synchronous reactive component where the set of its state variables is empty.
Atomic Propositions
Statements on a variable - often used to label states.
Kripke Model
Set of states
Set of initial states
Transition relation R is a subset of Qs x Qs.
No inputs and outputs
Set of atomic propositions AP over variables S.