Lectures
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
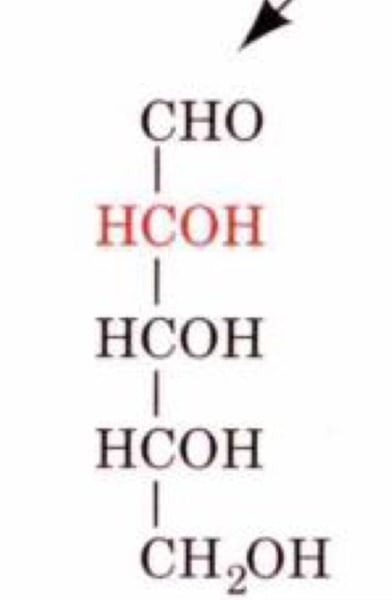
The following figure is the structure of:
a. D-Arabinose
b. D-Lyxose
c. D-Ribose
d. D-Xylose
D-Ribose
Which enzyme does not function with a large negative delta G?
a. hexokinase
b. enolase
c. phosphofructokinase
d. pyruvate kinase
enolase
2 NADH molecules is equivalent to approximately ___ ATP molecules
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 6
6
Valine can enter the citric acid cycle as converted to ____ via enzymatic reaction
a. fumarate
b. malate
c. oxaloacetate
d. succinyl-coa
succinyl-coa
the function of oligosaccharides is to:
a. influence the way a protein folds
b. help define protein structure
c. mediate recognition events
d. all of the above
all of above
which disaccharide is made up of 2 glucose monosaccharides?
a. fructose
b. lactose
c. maltose
d. sucrose
maltose
pyruvate gets converted ___ via alcoholic fermentation
a. ethanol
b. lactate
c. NADH
d. Isopropanol
ethanol
which molecule must be regenerated for glycolysis to continue occurring?
a. ADP
b. ATP
c. NAD+
d. FADH2
NAD+
Lactate from muscle goes to which organ for gluconeogenesis?
a. brain
b. heart
c. liver
d. muscle
liver
A glucose molecule, after pyruvate goes through the citric acid cycle and the conversion of GTP, FADH2, and NADH molecules to ATP produces a total of how many ATP?
a. 30
b. 32
c. 36
d. 38
32
the net amount of ATP from glycolysis is:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 8
2
Consider a reaction with Delta H= 1.5 kL and Delta S= 10 J*K-1. is the reaction spontaneous at -173 C?
a. spontaneous only at temperatures below -173 C
b. spontaneous
c. non-spontaneous
d. not enough information
non-spontaneous
which is not a coenzyme or prosthetic group of pyruvate dehydrogenase:
a. coenzyme A
b. FAD
c. Mg2+
d. NADH
Mg2+
A red blood cell has an internal salt concentration of ~350mM. The cell s placed in a beaker of 100 mM salt. Assuming the cell membrane is permeable to water, but not to ions, describe what will happen to the cell in terms of osmosis.
a. the salt ions will move from inside the cell to the outside the cell
b. the salt ions will move from outside the cell to inside the cell
c. water will move from inside the cell to outside the cell
d. water will move from outside the cell to inside the cell
water will move from outside the cell to inside the cell
*water moves from lower concentrations to higher concentrations
*its asking about what will happen to the cell. if there's high salt inside, it needs water to dilute it so it will swell
**DOUBLE CHECK
the first irreversible step of glycolysis is:
a. phosphate addition to glucose
b. addition of phosphate to form fructose 1,6 bisphosphate
c. removal of phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate
d. the formation of pyruvate
Phosphate addition to glucose
which has lower entropy, liquid water at 0 C or ice at 0 C?
a. liquid water
b. ice
c. the entropies are the same
d. not enough information
ice
Calculate how much solid reagent you would need to make a 10 mL of a 50 mg/mL solution of Ampicillin
a. 0.5g
b. 1.0g
c. 1.5g
d. 2.0g
0.5 g
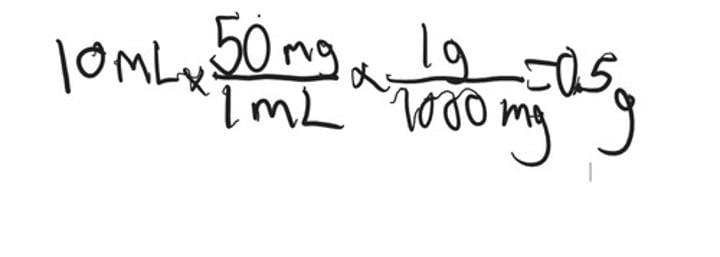
ATP binding to myosin is immediately proceeded by:
a. myosin power stroke
b. actin power stroke
c. the actin head releasing myosin
d. the myosin head releasing actin
the myosin head releasing actin
General acid and general base catalysis can be defined as:
a. proton extraction for general acid catalysis and proton transfer from the base for general base catalysis
b. proton extraction for general acid catalysis and covalent bond formation for general catalysis
c. proton transfer from the acid for general acid catalysis and proton extraction for general base catalysis
d. covalent bond formation for general acid catalysis and proton transfer from the base general base catalysis
proton transfer from the acid for general acid catalysis and proton extraction for general base catalysis
*CHEGG
which AA is most likely to be found in a middle of an alpha helix?
a. P
b. L
c. G
d. Y
P
On the molecular level, what is the role of myoglobin in O2 transport in rapidly respiring muscle tissue?
a. myoglobin decreases the solubility of O2 in the cell
b. myoglobin directly induces hemoglobin conformational change to deliver O2 in the cell
c. myoglobin increases the solubility of O2 in the cell
d. myoglobin conformational change is directly induced by hemoglobin to deliver O2 in the cell
myoglobin increases the solubility of O2 in the cell
Arginine enters the citric acid cycle through which substrate?
a. fumarate
b. alpha- ketoglutarate
c. pyruvate
d. succinate
alpha- ketoglutarate
determine the net charge of the predominant form of the Lys at pH=5. Lys has a pK1 of 2.16, a pK2 of 9.06, and a pKa of 10.54.
a. +2
b. +1
c. 0
d. -1
+1
in a multistep reaction, does the transition state with the highest free energy always correspond to the rate-determining step?
a. yes, the transition state with the highest free energy will always correspond to the rate determining step
b. no, the transition state with the highest free energy will not always correspond to the rate determining step
c. yes, the transition state with the highest free energy will always correspond to the rate determining step, and the rxn will always be spontaneous
d. not enough information
no, the transition state with the highest free energy will not always correspond to the rate determining step
a certain metabolic pathway can be diagrammed as: X Y Z
A-> B -> C -> D
Where A,B,C, and D are the intermediates and X,Y, and Z are the enzymes that catalyze the reactions. The physiological free energy changes for the reactions are:
X -0.5kJ * mol-1
Y -2.3 kJ * mol-1
Z -13.2 kJ * mol-1
Which rxn is likely to be a major regulatory point for the pathway?
a. the step catalyzed by X
b. the step catalyzed by Y
c. the step catalyzed by Z
d. The combined free energy changes of the rxns determine the major regulatory point
the step catalyzed by Z
The major regulatory point in the pathway is likely to be the conversion of B to C by Y. This is due to the large negative free energy change associated with this step, indicating its largely, irreversible nature. Irreversible reactions are major sites of regulatory control in metabolic pathways.
*CHEGG
Which AA is more likely to be on a protein's surface?
a. W
b. I
c. V
d. N
N
The starting compound for glucogenesis is
a. lactate
b. malate
c. oxaloacetate
d. pyruvate
oxaloacetate
Inhibitor X competitively binds to protein Y. How much inhibitor X affect the apparent Km and Vmax of a sample of protein Y?
a. apparent Km changes and Vmax stays the same
b. both apparent Km and Vmax change
c. both apparent Km and Vmax stay the same
d, Apparent Km stays the same and apparent Vmax changes
apparent Km changes and Vmax stays the same
How does Calcium regulate muscle contraction?
a. a conformational change in tropomyosin occurs causing a movement of troponin, which opens the myosin binding sites
b. a conformational change in troponin occurs causing a movement of tropomyosin which opens the actin binding site
c. a conformational change in tropomyosin occurs causing a movement of troponin, which opens the actin binding sites
d. a conformational change in troponin occurs causing a movement of tropomyosin which opens the myosin binding sites
a conformational change in troponin occurs causing a movement of tropomyosin which opens the actin binding site
In what order would Asp, Arg, and Phe be eluted from a diethylaminoethyl (DEAE) column at pH 8?
a. Arg, Asp, Phe
b. Arg, Phe, Asp
c. Asp, Phe, Arg
d. Asp, Arg, Phe
Arg, Phe, Asp
In what order would Arg, Asp, Cys, and Ser be eluted from a diethylaminoethyl column at pH 8.5?
a. Asp, Cys, Ser, Arg
b. Arg, Ser, Cys, Asp
c. Asp, Ser, Cys, Arg
d. Arg, Cys, Ser, Asp
Arg, Ser, Cys, Asp
or
Arg, Cys, Asp
Which enzyme is a major flux controlling enzyme in glycolysis
phosphofructokinase
which compound would not serve as an inhibitor in the citric acid (TCA) cycle?
compounds that will serve as inhibitors
1. Pyruvate
2. ADP
3. Ca2+ (high Mg2+)
4. K+
Why is 1,3-biphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG) considered a high-energy intermediate?
The two phosphates in the tiny 1,3BPG molecule repel each other and give the molecule high energy. It uses this energy to phosphorylate ADP to make ATP.
Which accompanies the formation of fumarate?
a. ATP
b. GTP
c. NADH
d. FADH2
FADH2
*CHEGG
For the reaction:
NADH + FAD + H+ --> NAD+ + FADH2
Which reactant serves as an electron acceptor?
Reactant FAD+ serves as the electron acceptor & product FADH2 act as a the electron acceptor.
*CHEGG
The reaction catalyzed by which enzyme in the TCA cycle forms one GTP molecule?
Succinyl-CoA Synthetase
In eukaryotes, where go glycolysis and the TCA cycle take place?
glycolysis: cytoplasm
TCA: mitochondria
Where do gluconeogenesis occur:
liver and kidneys
How many carbons are in a ring of glucose?
5
Protein glycosylation typically occurs through which amino acid?
asparagine
What is the sugar used in DNA or RNA
Ribose
Which is a ketose?
fructose
a certain metabolic pathway can be diagrammed as: X Y Z
A-> B -> C -> D
Where A,B,C, and D are the intermediates and X,Y, and Z are the enzymes that catalyze the reactions. The physiological free energy changes for the reactions are:
X -0.5kJ * mol-1
Y -2.3 kJ * mol-1
Z -13.2 kJ * mol-1
How would the concentrations of B and C be affected if an inhibitor that inhibits enzyme Z was added to the reaction?
A. B & C will stay the same
b. B would stay the same and C would accumulate
c. B and C would accumulate
d. B would accumulate and C would stay the same
If Z is blocked, conversion of C to D would stall. Therefore, concentration of D would decrease and that of C would increase. Acuumulation of C would also make the upstream reactions unvafourable, leading to increase of B, and A, respectively. Thus, A*, B, and C would increase, whereas D would decrease.
*CHEGG
While ___ is always involved in reactions that require the transfer of 2 electrons, ___ can participate in reactions that transfer either 1 or 2 electrons.
a. O2; NAD+
b. NAD+, FAD
c. Flavin, Niacin
d. FAD, NAD+
NAD+, FAD
*Quizlet
Which of the following is NOT a direct product of pyruvate metabolism?
a. acetyl coa
b. lactate
c. oxaloacetate
d. phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
*Quizlet
Phosphofructokinase is allosterically ___ by high concentrations of ___
a. activated, ATP
b. inhibited, ATP
c. inhibited, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
d. activated, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
B & d
*quizlet
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the conversion of glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate?
a. glucose-1-isomerase
b. glucokinase
c. glycose 1-phosphatase
d. phosphoglucomutase
e. glycogen phosphorylase
phosphoglucomutase
*Socratic; Google
Which statement is true regarding the activation of pyruvate carboxylase by acetyl CoA?
a. feedback activation enhances flux through glycolysis
b. feed-forward activation enhances the entry of pyruvate through the TCA cycle as Acetyl-CoA
c. Ensures that gluconeogenesis occurs rather than pyruvate conversion to acetyl-CoA
d. Ensures that ATP is not wasted in the production of oxaloacetate
e. feedback inhibition ensures that excess glucose-6-phosphate is not produced
Ensures that gluconeogenesis occurs rather than pyruvate conversion to acetyl-CoA.
*Quizlet
Which of the following best describes the importance of the citric acid cycle as a central pathway of metabolism?
It allows the recovery/ Capture of energy from several metabolic fuels that are broken down by acetyl-CoA
Which of the following would decrease activity of the citric acid cycle overall?
a. high concentration of NADH
b. high concentration of Ca2+
c. high concentration of ATP
d. high concentration of citrate
a, c, d
How is flux throughout the citric acid cycle controlled?
a. control of isocitrate dehydrogenase
b. control of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
c. control of citrate synthase
d. at many points, including all of the above
at many points, including all of the above
*Quizlet
Which of the following are products of the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase?
a. CO2
b. NADH
c. acetyl-CoA
d. phosphoenolpyruvate
a, b, c