Astro 105 Exam 2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Intersteller carbon monoxide gas emits radio-frequency spectra with a wavelength near:
2.6 mm
The daytime sky (on Earth) is blue because______.
blue light is a color that easily scatters.
A sufficiently cold and dense state of molecular hydrogen gas undergoes gravitational contraction from the inside toward the outside:
Jeans Instability
During the states of star formation, this object continues to accrete mass (mass is increasing) as it slowly produces glowing electromagnetic radiation (primarily infrared):
protostar
A teaspoon of white dwarf matter weighs about
5 tons
When the outer layers of a giant are blown away, high temperature cores comprised of crystalline carbon and oxygen are exposed. These objects are called:
White Dwarfs
THe maximum mass limit of a white dwarf (1.4 solar masses) is named after this physicist:
Chandrasekhar
These stars, because of their stable pulsation periods, are used to estimate distances:
Cepheids
From relativity, we realize that both space and time must be considered on an equal footing, we call this
spacetime
General Relativity predicts that matter (and/or energy) warps the surrounding space. The warping of the space is what we perceive as
the force of gravity
A neutron star and main-sequence star binary system in which matter from the main-sequence star falls onto the neutron star:
x-ray burster
A teaspoon of neutron star matter weighs about
1 billion tons
Through a process called Hawking Radiation, black holes...
will eventually evaporate
Only 3 physical quantities define all black holes:
no hair theorem
A black hole that is spoinning (has angular momentum), is what type of a black hole?
Kerr
When we fall into the black hole...
we get stretched like spaghetti
Interstellar Medium
a very cold, it does not give off visible light, therefore it is hard to detect. It also causes stars to redden.
Interstellar Reddening
Blue light is more easily scatters than red light.
Why are sun sets red and why the daytime sky is blue?
Interstellar Reddening
Protostar
is not yet massive enough for nuclear fusion to occur (early stages in star growing process) It does glow due to its increase in its internal temperature.
Pre-main Sequence
Star in the stage when it has not yet reached the main sequence.
This star will slowly contract until the core temperature reaches about 10 million Kelvin (to form a main sequence star.)
Main Sequence Star
a series of star types that typically fit on the H-R diagram
Brown Dwarf
for very small Pre-Main Sequence stars gravity is not sufficient to start nuclear fusion. They have large masses, heavier than our sun.
(Example: Jupitar)
Red Dwarf
main sequence stars having masses about 1/10 (10%) the mass of our sun
Giants
main sequence stars with masses greater than 40% mass of our sun will become______
Variable Stars
once helium fusion begins, the star is "post-Main Sequence" star leaves main sequence line and travels to the uppers right region (on the H-R diagram)
Recombination Photons
produces more photons
White Dwarf
As outer layers are blasted away, the hot interior region of the star is revealed
The star moves leftward and downward (on the H-R diagram)
Chandrasekhar limit
the maximum mass of a stable white dwarf star
Nova
in a binary containing a main-sequence and a white dwarf
Roche limit
the closest distance from the center of a planet that a satellite can approach without being pulled apart by the planet's gravitational field.
(gravity of the white dwarf is greater than the self-gravity of main-sequence)
Super Nova
Core bounces produce shock waves that travel away to the outer regions of the star.
Type Ia Super Nova
a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems (white dwarfs and giants)
Neutron Star
main sequence stars with masses greater than 8M sun, but less than 25M sun explode as a supernova. The leftover core is called________
Pulsars
Neutron stars, like our sun, have an intense magnetic field. The magnetic field has a very high spin rate. Electrically charged particles interact with the new magnetic field, producing a beamed radiation.
X-Ray Bursters
a binary system with a neutron star and a main sequence star. Hydrogen pulled off the main sequence. This builds up and its fusion begins, this releases a large blast of_______.
Special Theory
Laws of Physica are the same in every non-accelerating frame
The speed of light is the same in all non-accelerating frame
General Theory
this principle of relativity is extended to acceleration frames
Superstring
describing the inside of a black hole requires a Quantum theory of gravity. Currently ,this theory is only a framework in which this can be done.
Stephen Hawking
the first person to propose that during the big bang, very small black holes formed.
Schwarzchild
Created a method to measure the radius of a black hole as well as studied the concept of a no spin blackhole.
Roy Kerr
the first to calculate all the physics of a spinning black hole.
Wormholes
Eith's general relativity allows for ______ These are tunnel-like paths through hyperspace.
Also ____can be aligned along spatial dimensions or the time dimensions.
Galaxies
our solar system isolated in the milky way galaxy. There are about 10" galaxies in the visible universe.
Edwin Hubble
determined the absolute brightness, apparent brightness, and found the distance to M3I
Nuclear Bulge
(also known as Galactic Nucleus) a tightly packed group of stars within a larger formation, Star light in these areas create enough light to equal 200 full moons.
Globular Clusters
a large compact spherical star cluster, typically of old stars in the outer regions of a galaxy; used to locate the center due to the motion of ________________.
Synchrotron Radiation
strong field traps electrons into light spiral orbit produces____________
Dark Matter
made up of: Neutrinos, Black Holes, Brown Dawarfs, cold gas, something exotic/unkown
our galaxy is made up of 90% of __________
No-hair theorem
The ___________ postulates that all black hole solutions of the Einstein-Maxwell equations of gravitation and electromagnetism in general relativity can be completely characterized by only three externally observable classical parameters: mass, electric charge, and angular momentum.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
The ___________________ is the quantum mechanical principle that states that two or more identical fermions (particles with half-integer spin) cannot occupy the same quantum state within a quantum system simultaneously.
Keplerian rotation curves
in our solar system, when planet rotate around the sun, it obeys ___________ 3rd law.
as you get further away the velocity decreases.
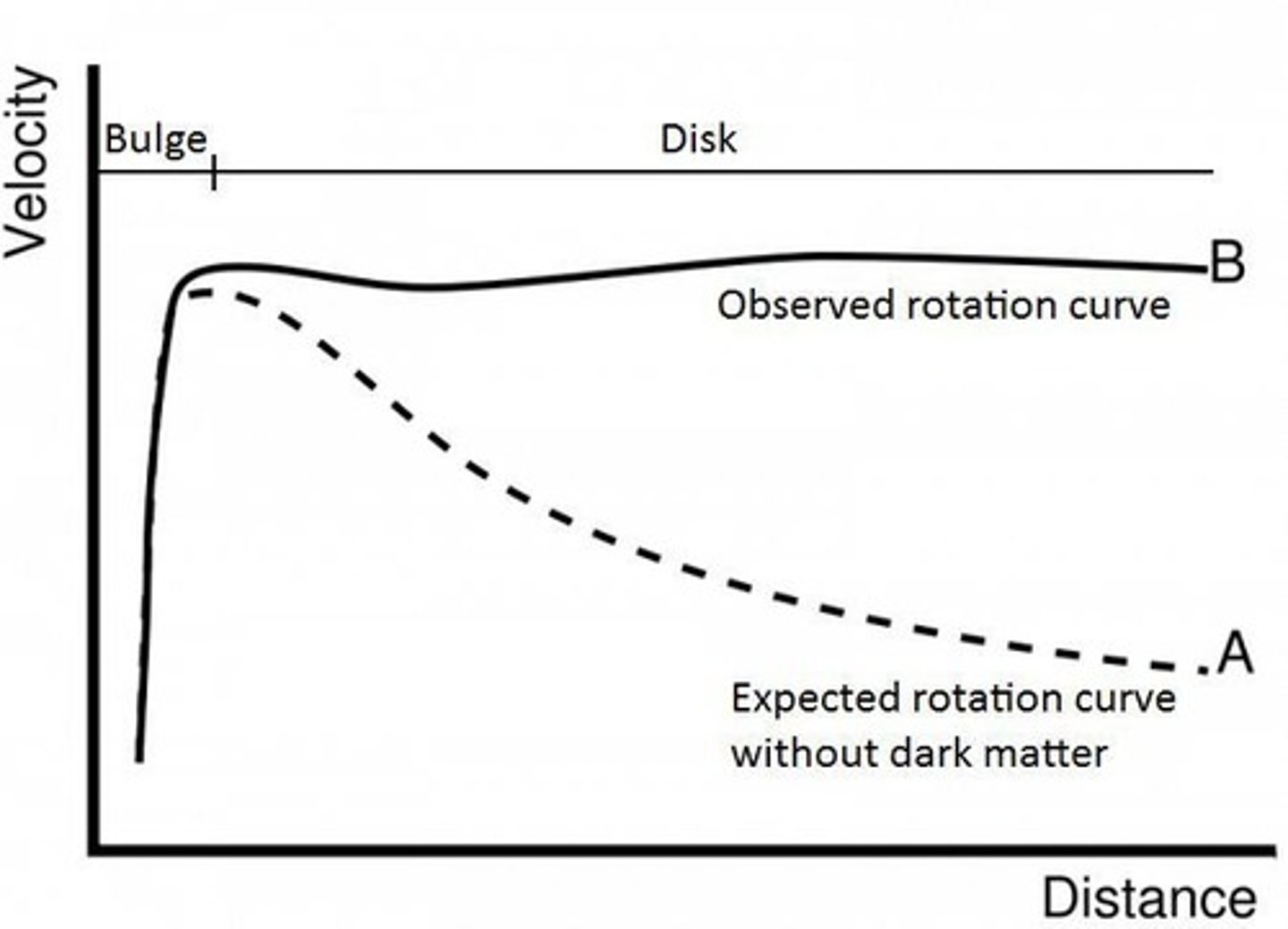
Solid body rotation curves
smaller the rotation/closer to the radius means there will be less/smaller velocity
Milky Way has _____ stars
100 billion
Masses of an average galaxy range between __________
10^9 to 10^13 M
Spiral Galaxy
has a nuclear bulge and spiral arms. The larger the bulge, the tighter the spiral arms.
Barred Spiral Galaxies
this is a spiral galaxy with a bar of stars in the center
Shell fusion
Stars such as our Sun move off the main sequence and up the red giant branch (RGB), fusing hydrogen into helium in hydrogen shell burning.
flashes
Stars such as our Sun move off the main sequence and up the red giant branch (RGB), fusing hydrogen into helium in hydrogen shell burning. A very short helium ________ sees the start of helium core fusion and the star moves along the horizontal branch (HB).
realitivity
a theory, formulated essentially by Albert Einstein, that all motion must be defined relative to a frame of reference and that space and time are_______.
made up of special theory and general theory.
spin flip radiation of hydrogen
observations of the___________ reaveal the exact nature of the rotation velocity of the milky way galazy.
stellar lifetimes
______________is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can vary.
variable star
a star whose brightness changes, either irregularly or regularly