Diagnostic Evaluation
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is a voice disorder?
An individual’s quality, pitch, or loudness differs from voice characteristics typical of speakers of similar age, gender, cultural background, & geographic location
Etiologies vary…
Structural
Medical
Neurologic
Psychological
Predisposing, precipitating (inciting), & perpetuating factors
(Prevalence of Voice Disorders) What factors influence the prevalence of voice disorders?
Age
Gender
Occupation
(Prevalence of Voice Disorders) Largest epidemiology study of voice disorders undertaken…
7% of adults (aged 21-66 yrs) reported a “current” voice disorder
30% of adults reported a voice disorder at some point during their “lifetime”
(Prevalence of Voice Disorders) Who are chronic voice disorders more common among?
Women
Individuals 40-59 years of age
History of…
Heavy voice demands
Reflux symptoms
Chemical exposures
Frequent upper respiratory infections
What are the primary objectives of a voice evaluation?
Identify the causes
Etiologic, physiologic, or behavioral factors
Describe the present vocal components
Evaluate the effect of the disorder on respiration, phonation, and resonance
Develop the management plan
What are the secondary objectives of a voice evaluation?
Patient education
Patient motivation (educate on reasoning behind exercises like lip trills)
Establish credibility of voice pathologist
Who can serve as a referral source for voice disorders?
Otolaryngologists
Other medical specialists
SLP
Vocal coaches
Singing teachers
Former patients
Family
Friends
Pulmonologist
Cardiologist
GI
PCP
Allergy/asthma specialist
Professional Relationships:
Evolution of the voice team
Complementary relationships
Voice problems are describe as abnormalities in:
Quality
Pitch
Loudness
Resonance
What should a voice evaluation be comprised of?
Reason for the Referral
History of the Problem
– Medical and Surgical History
– Social history
Oral Mechanism Examination
Auditory-Perceptual Voice Assessment
– Respiration, Phonation, Resonance, Pitch, Loudness, Rate
Visualize the larynx!
Diagnostic Probes (Stimulability)
Patient Self-Assessment (PRO)
GRBAS
Evaluation Form:
Referral:
Establish referral source
Reason for Referral:
Establish exact reason for patient referral
Establish patient understanding for referral
Develop knowledge of the voice disorder
Establish credibility of examiner
History of the Problem:
Establish the chronology of the problem
Seek etiologic factors associated with the history
Determine patient motivation
Medical History:
Seek medically-related etiologic factors
Establish awareness of patient personality
What is an informal aerodynamic measure to look at respiratory support?
/s/ → voiceless
/z/ → voiced, if there’s laryngeal pathology, stiffness, or scarring → you will not be able to sustain phonation as long as you should be
Social History:
Identify work, home, recreational environments
Discover emotional, social, family, occupational activities, challenges, difficulties
Seek more etiologic factors
Oral-Peripheral Examination:
Determine physical condition of oral mechanism
Observe whole body tension
Observe laryngeal area tension
Check for swallowing difficulties
Check for laryngeal sensations
What should a perceptual evaluation include?
General Quality
Respiration
Phonation
Resonance
Pitch
Loudness
Rhythm & Rate
Non-speech Phonotrauma
General Quality:
Describe voice quality using descriptive terms (May use scale system, GRBAS, CAPE-V)
Examine inappropriate use of voice components
Respiration:
Describe type of breathing pattern (supportive/non-supportive)
s/z ratio
Maximum phonation time
Phonation:
Hard glottal attacks
Glottal fry
Breathiness
Diplophonia (2 pitches @ the same time)
Resonance:
Hypernasal
Hyponasal
Assimilative nasality
Cul de sac nasality
Inappropriate tone focus
Pitch:
Test present pitch range (how low vs. low)
Describe conversational inflection (monotone?)
Make subjective judgement of appropriateness
Loudness:
Too loud, soft, approrpiate (HEY!)
Check ability to shout/talk softly
Rhythm & Rate:
Too fast
Too slow
Interrupted (Spasm, Tremor)
Non-speech Phonotrauma:
Throat clearing
Coughing
Unusual laugh
What are perceptual signs of voice problems?
Quality → Roughness or Hoarseness
Pitch → F0 (fundamental frequency)
Loudness → Intensity
Other behaviors → stridor, excessive throat clearing
Aphonia → loss of voice
What should patient self-assessment incorporate?
Patient perspective related to the voice disorder
Describes the physical, functional, and emotional implications
What are some assessment tools for assessing the impact of a voice disorder on a patient’s daily life?
Voice Handicap Index (VHI)
Voice Handicap Index-10 (VHI-10)
Voice-Related Quality of Life (V-RQOL)
Voice Activity and Participation Profile (VAPP)
Voice Symptom Scale (VoiSS)
Aging Voice Index (AVI)
What should the voice pathology evaluation consist of?
Patient interview
Perceptual voice assessment
Instrumental assessment of vocal function
Laryngeal videostroboscopy
(The Voice Pathology Eval) What is crucial for accurate diagnosis of voice pathology?
visualization of the larynx! History can only give us clues into diagnosis
(The Voice Pathology Eval) When can indirect laryngoscopy be conducted?
In the clinic, while the patient is awake
Flexible fiberoptic endoscopy
Rigid endoscopy
High-speed imaging
(The Voice Pathology Eval) When can direct laryngoscopy be conducted?
while the patient is under anesthesia
What are the types of laryngeal imaging?
Flexible Fiberoptic Endoscopy
Rigid Endoscopy
Halogen or Stroboscopic Lighting
Flexible Fiberoptic Endoscopy:
Variety of sizes
Distal chip
Almost any patient can be visualized with this
technique
Rigid Endoscopy:
70-degree scope
90-degree scope
4mm, 10 mm
What are the advantages of rigid endoscopy?
increased clarity for assessing erythema, vascularity, tissue changes
Closer view
What are the disadvantages of rigid endoscopy?
Difficult to conduct w/ some patients
Gag reflex
Cannot assess other structures
What are the advantages of flexible endoscopy?
can assess velopharyngeal function, adenoid tissue, palatal structure
resting breathing & connected speech
can usually assess subglottis
What are the disadvantages of flexible endoscopy?
clarity is often diminished
numbing of nares
Stroboscopy:
Studying the motion of a body, especially during rapid revolution or vibration, by making the motion appear to slow down or stop
Intermittent flashes of light “frame” the action
Produces extremely short, brilliant bursts of light for synchronization with a camera having a high shutter speed in order to photograph a rapidly moving object
Videostroboscopy:
Video imaging of the larynx is standard and critical
Videostroboscopy provides information on both laryngeal function & structure
Allows recording of apparent vocal fold motion
Specialized equipment & training is necessary
Videostroboscopy scoring instruments are available
What is Talbot’s Law?
The eye cannot perceive more than 5 distinct
images per second
When a series of images are produced at more than 1/5 of a second, one image persists long enough to fuse with the subsequent image & an optical illusion occurs that is called apparent motion (Talbot’s Law)
What are laryngoscopic observations?
Supraglottic closure
VF movement
Tissue changes
VF edge
What are stroboscopic observations?
Degree of glottal closure
Periodicity
Phase symmetry
Mucosal wave
Amplitude of excursion
Phase closure
What may supraglottic activity indicate?
Muscle tension dysphonia
Poor respiratory support
Compensatory movements for pathology
Medio-lateral (side to side)
Antero-posterior (posterior squeezing)
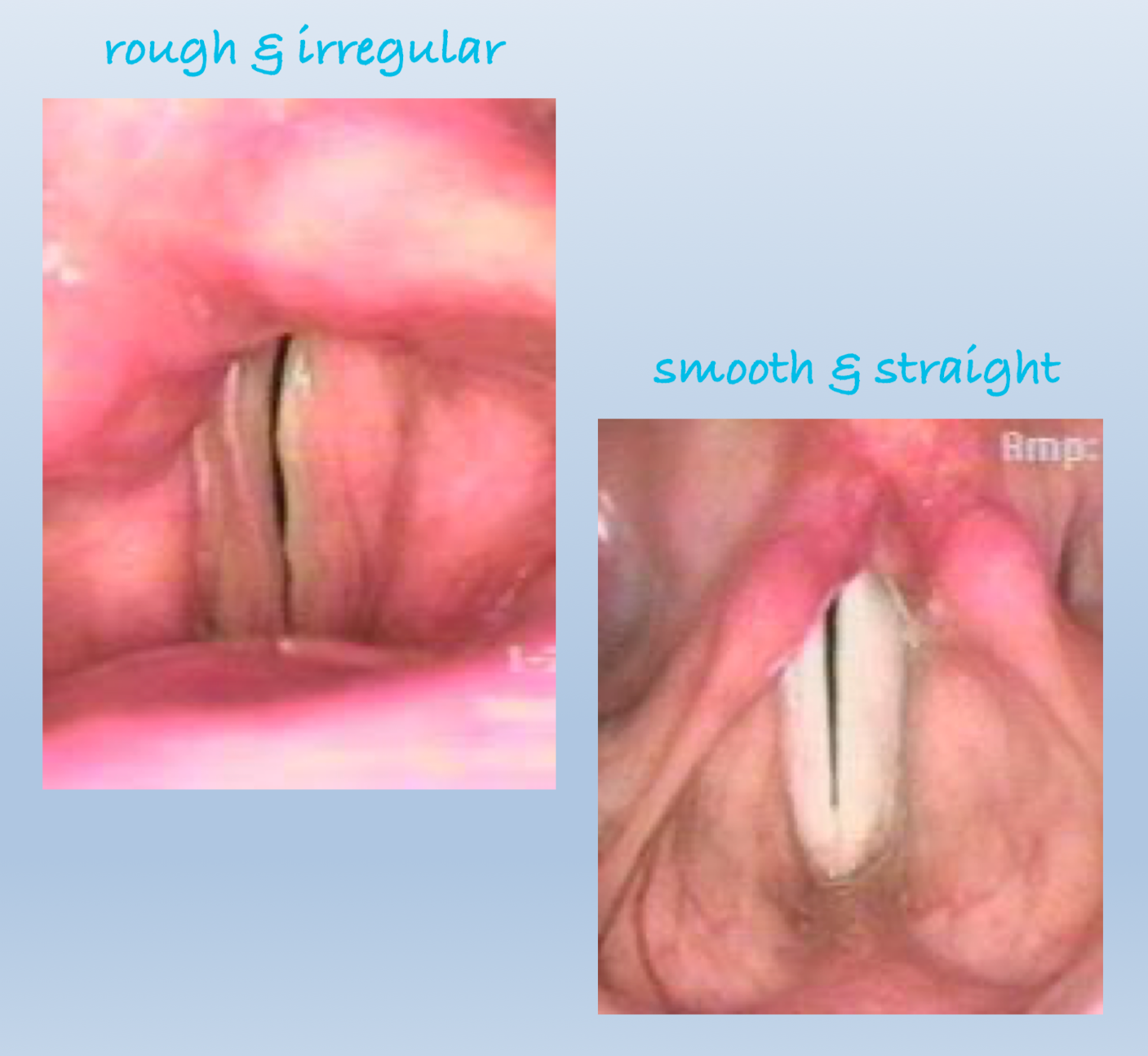
Vocal fold edge:
smooth & straight
rough & irregular
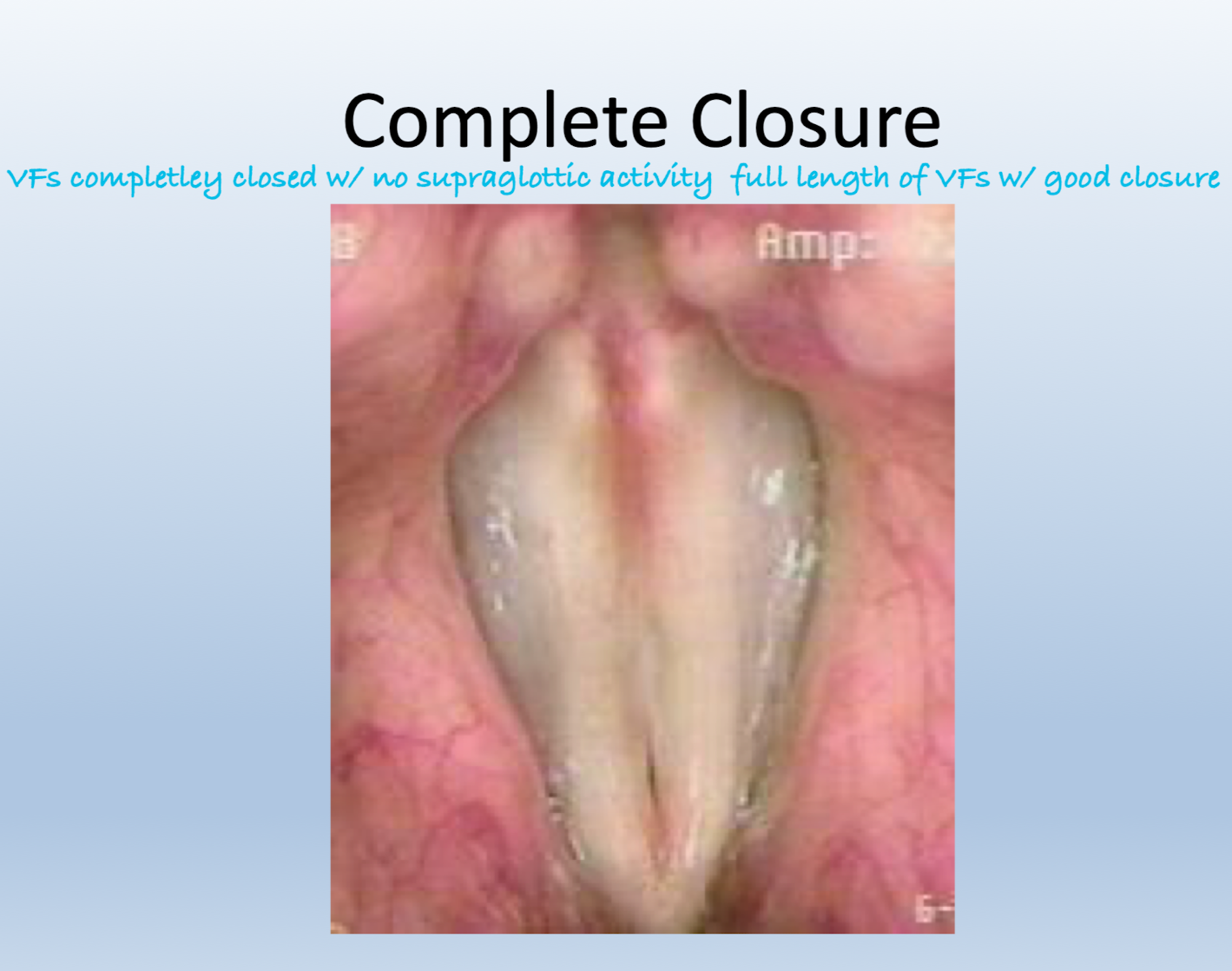
Glottal closure:
Complete closure
Spindle gap
Posterior gap
Irregular closure
Anterior gap
Hourglass
Incomplete closure
REFER TO IMAGES ON PDF!!!
Phase Symmetry:
Degree to which the VFs appear as mirror images of each other
Assessed during normal pitch & loudness
What is a mucosal wave?
Affected by disease processes that stiffen the mucosal cover of the vocal folds
Vertical movement of the mucosa over the body of the vocal fold during phonation
Fundamental frequency & intensity affect mucosal wave
Amplitude of Excursion:
Refers to how far the vocal folds move laterally during phonation
Assessment is made at normal pitch & loudness
Normally, the fold should travel approximately ½
(50%) of the visible width of the vocal fold
Phase Closure:
Assessed during normal pitch & loudness
Open Phase
Closed Phase
Should be equal
Hyperfunction = longer closing
Breathy = longer opening
Summary:
IMPRESSIONS: Summarize the etiologic factors associated
with the development and maintenance of the voice disorder
PROGNOSIS: Analyze the probability of improvement through voice therapy
RECOMMENDATIONS: Outline the management plan