Plate Tectonics: Boundaries, Stresses, and Earth's Layers
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Theory of Plate Tectonics
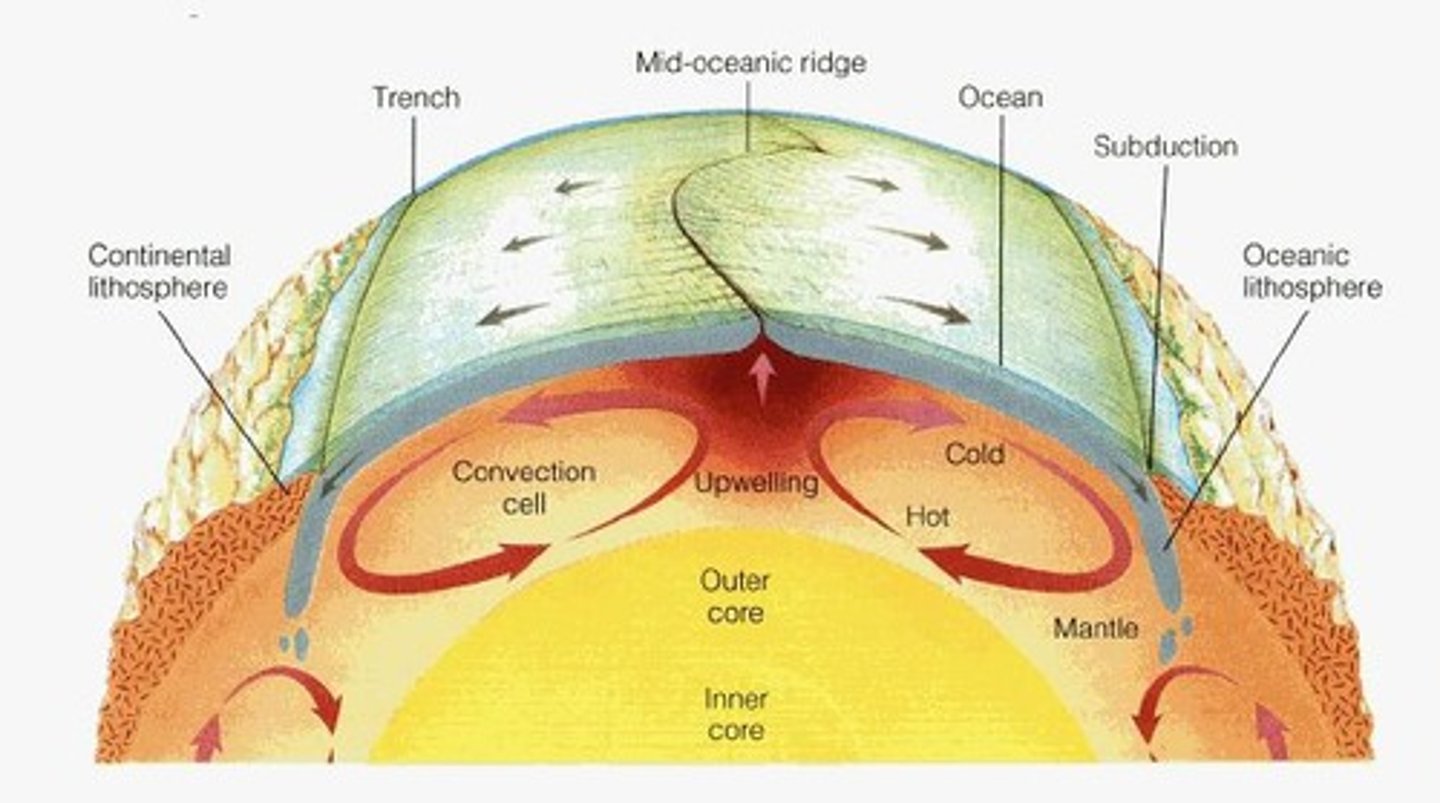
The theory which states that pieces of Earth's lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle.
Plates
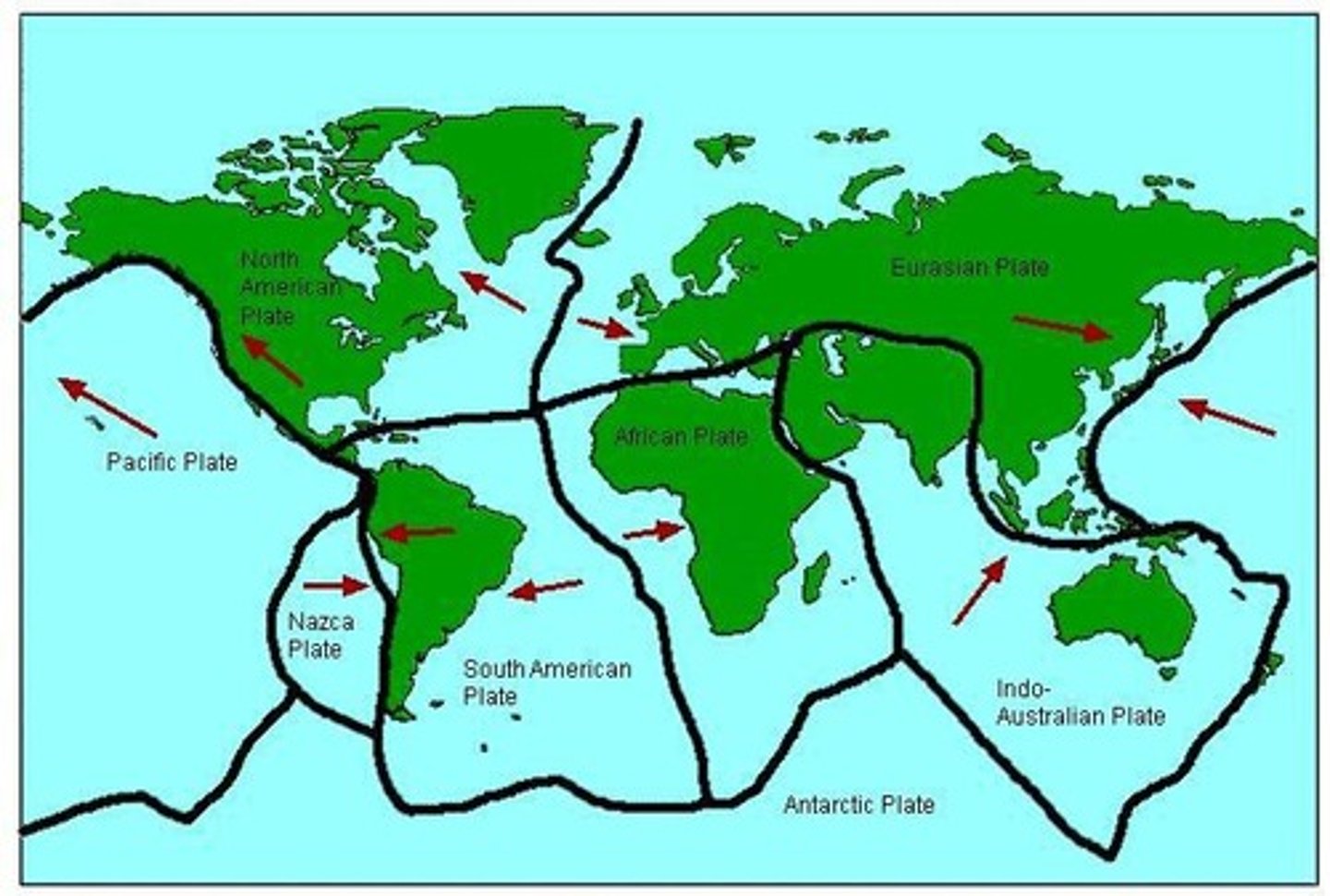
The Earth's crust and upper mantle (Lithosphere) are broken into sections called plates.
Convection Currents
Currents in the mantle that move the plates as the core heats the slowly-flowing asthenosphere.
Plate Boundaries
The edges of Earth's plates meet at plate boundaries, which extend deep into the lithosphere.
Fault
Breaks in Earth's crust where rocks have slipped past each other.
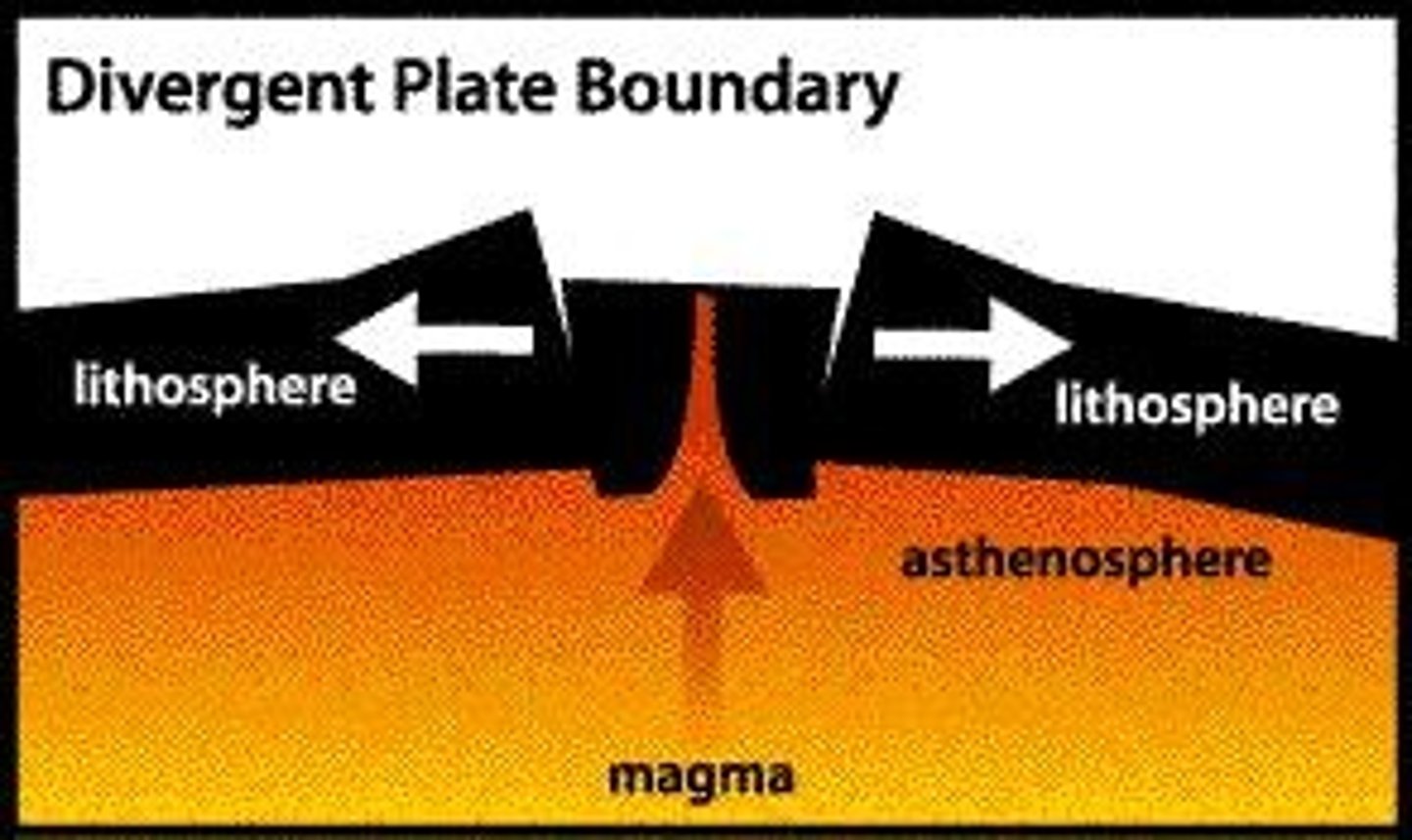
Divergent Boundaries
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
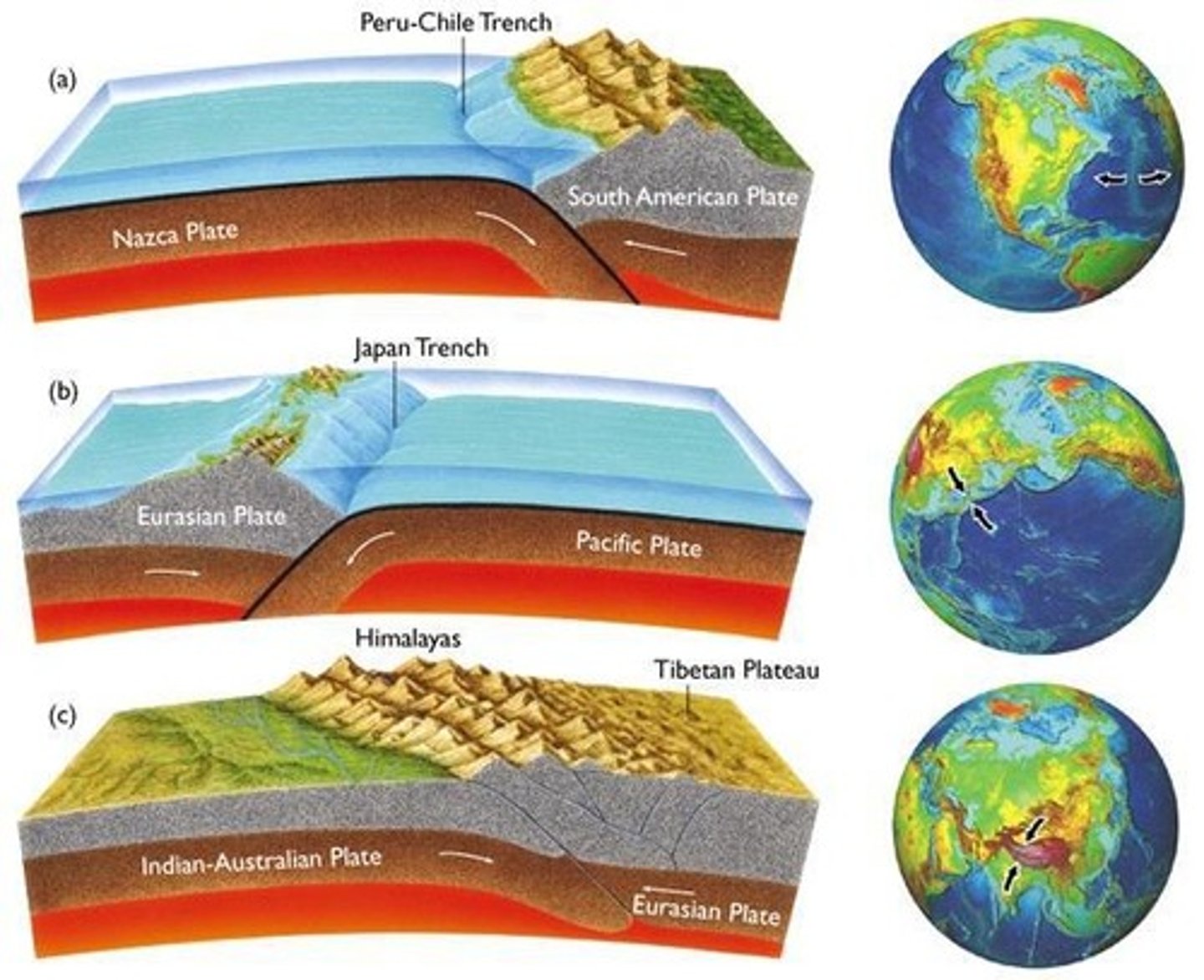
Convergent Boundaries
A type of plate boundary where two plates move towards each other.
Transform Boundaries
A type of plate boundary where two plates slide past each other.
Seafloor Spreading
The process that occurs at divergent boundaries where new oceanic crust is formed as plates move apart.
Normal Fault
A fault that occurs when rock drops down as it breaks due to tension stress.
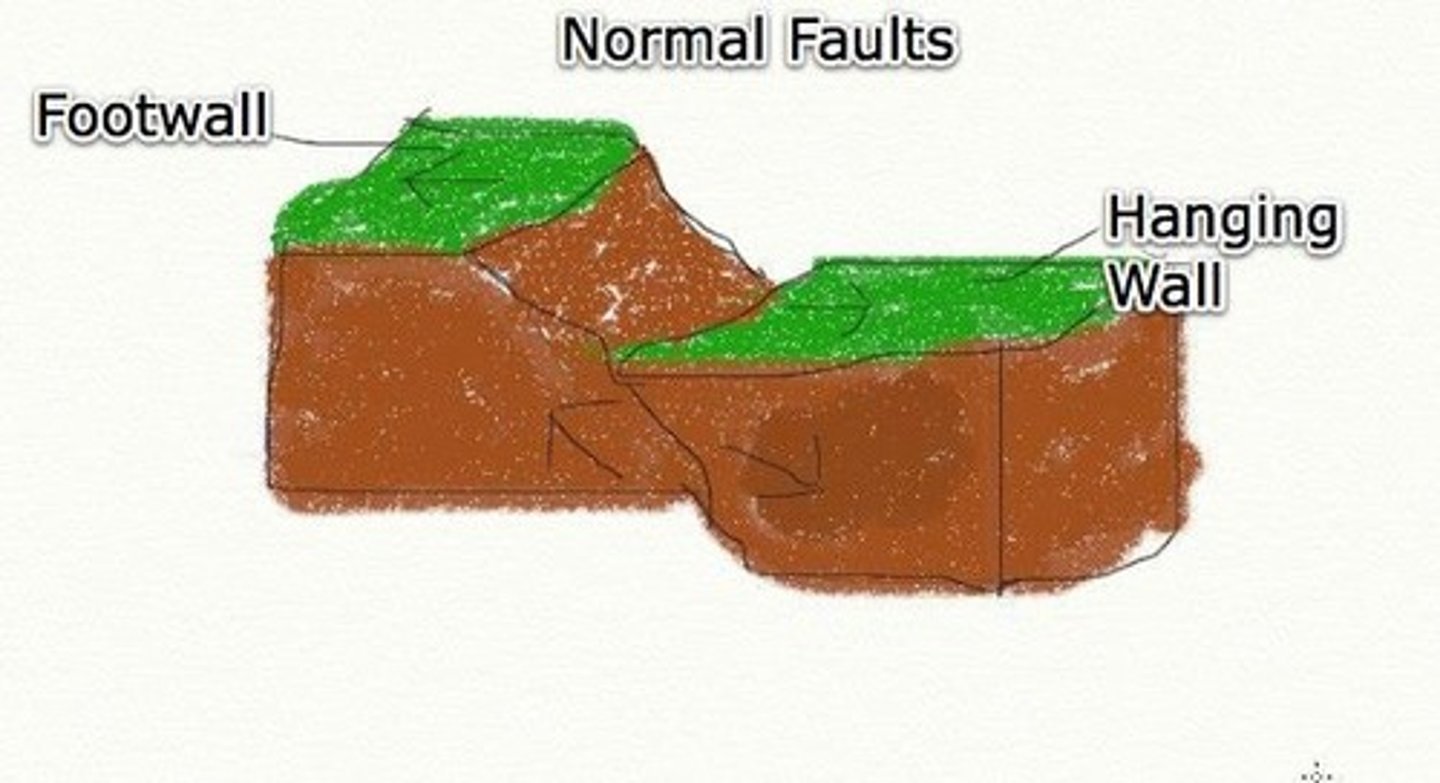
Rift Valleys
Geologic features that may form on continents at divergent boundaries.
Mid-ocean ridges
Underwater mountain ranges formed by seafloor spreading at divergent boundaries.
Fissure volcanoes
Volcanoes that may form at divergent boundaries due to the movement of plates.
Stress of Tension
The stress that occurs when rock is pulled apart at divergent boundaries.
Asthenosphere
The elastic/plastic-like part of the mantle over which the lithosphere moves.
Lithosphere
The rigid outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
Rock thinning
The process that occurs in the middle of divergent boundaries as rock is pulled apart.
Rifting
The process of the lithosphere being pulled apart at divergent boundaries.
Divergent
A term describing the movement of plates away from each other.
Geologic features
Structures that form as a result of tectonic activity, such as rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges.
Compression
The stress that occurs at convergent boundaries when two plates collide.
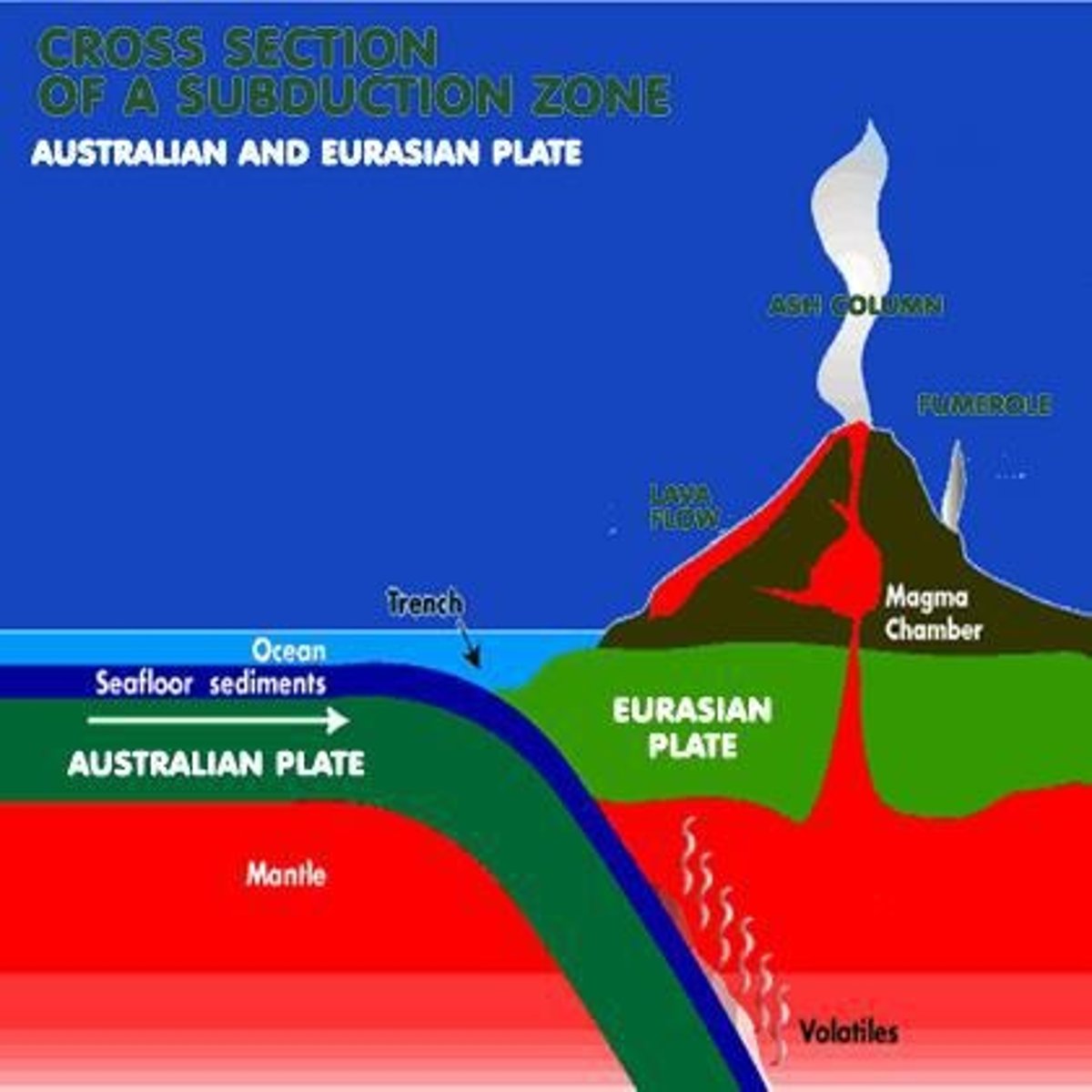
Subduction Zone
The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary.
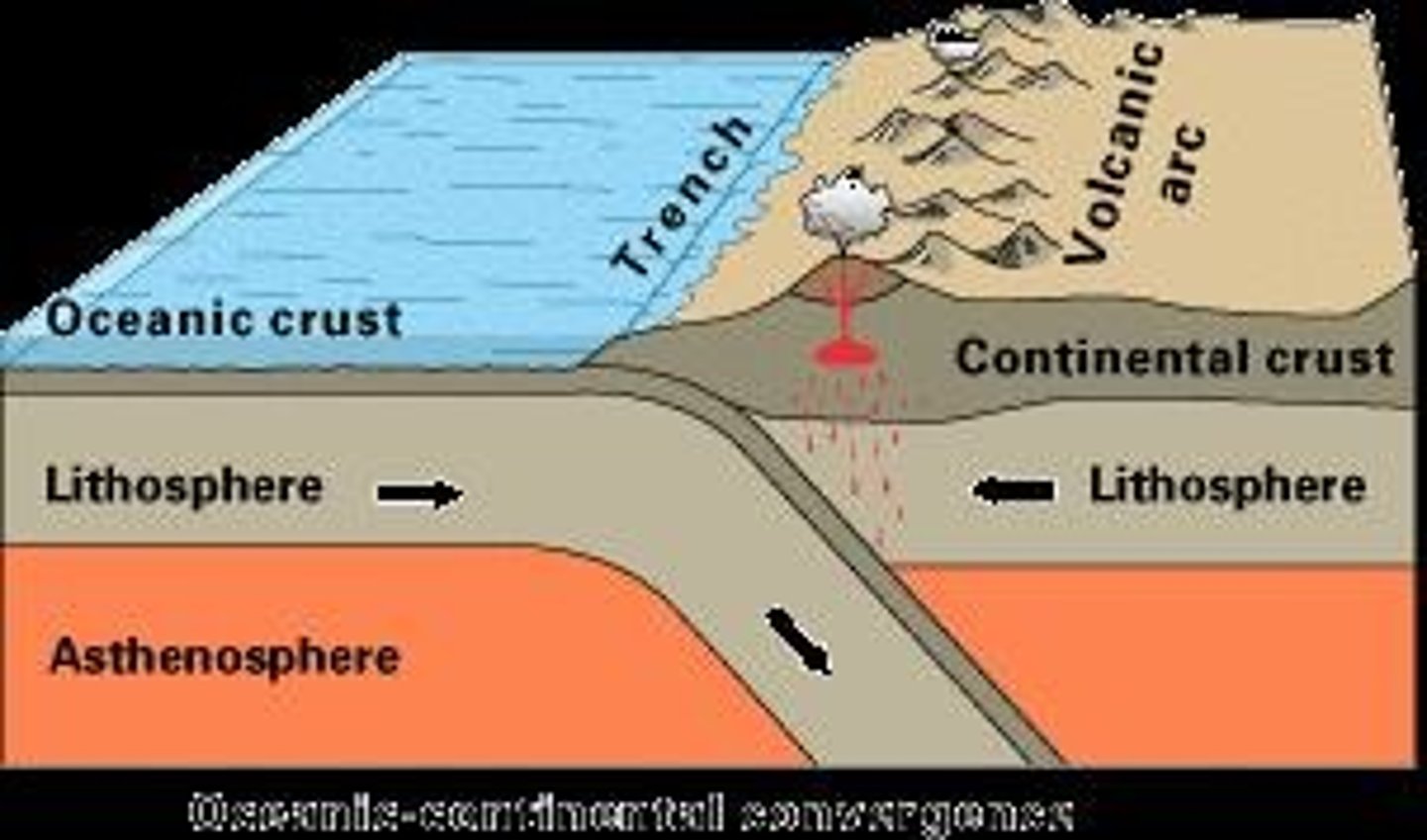
Volcanoes
Formed at subduction zones where one plate sinks under another.
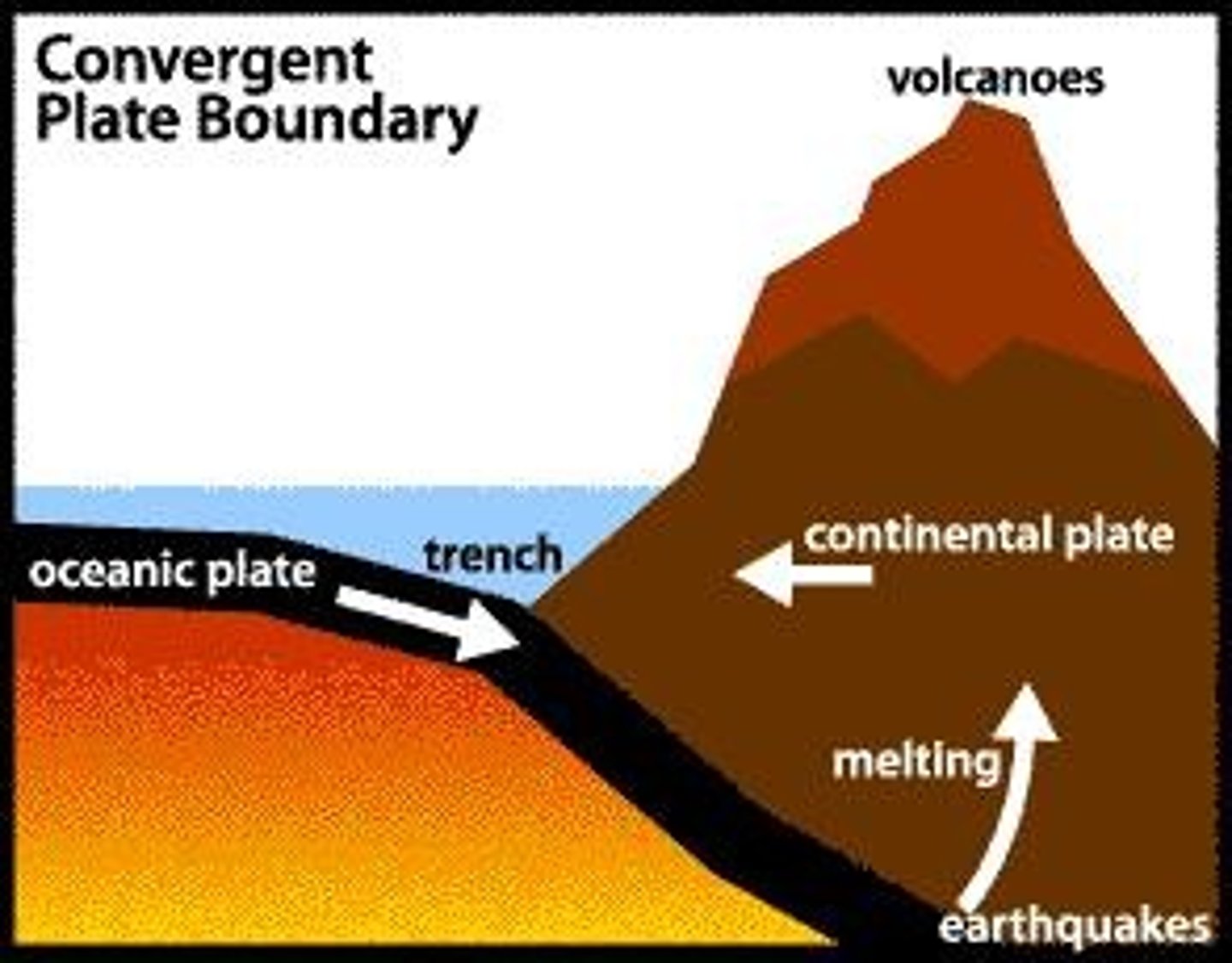
Trench
A subduction zone created when an ocean plate collides with a more dense ocean plate.
Collision Zones
Areas formed when a continental plate collides with another continental plate, leading to folded and thrust faulted mountains.
Folded Mountains
Mountains that may form at collision zones, such as the Himalayas or the Rockies.

Reverse Fault
A fault that occurs when rock is forced upward due to compression.
Shearing
The stress that occurs at transform boundaries when rock is pushed in two opposite directions.
Earthquakes
May occur at transform boundaries when rock snaps from pressure.
San Andreas Fault
A famous fault located at a transform boundary in California.
Strike-Slip Fault
A fault that occurs when rocks on each side slip past each other due to shearing.
Ocean Plate vs. Continental Plate
A type of convergent boundary where an ocean plate collides with a less dense continental plate.
Ocean Plate vs. Ocean Plate
A type of convergent boundary where an ocean plate collides with another ocean plate.
Continental Plate vs. Continental Plate
A type of convergent boundary where two continental plates collide.
Mountain Ranges
Formed from the collision of continental plates at convergent boundaries.
Shearing
means cutting
Crust
Outermost shell of a terrestrial planet, divided into older, thicker continental crust and younger, thinner oceanic crust.
Continental crust
About 50 - 100-km thick, composed of granitic rocks with a density of about 2.7 g/cm³, referred to as 'sial'.
Oceanic crust
About 5-10 km thick beneath the ocean floor, composed of basaltic rocks with a density of about 3.0 g/cm³, referred to as 'sima'.
Mantle
About 2,885 km thick, subdivided into the upper and lower mantle.
Core
Inner part of the Earth, consisting mostly of iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni), subdivided into the liquid outer core and the solid inner core.
Outer core
About 2,210-km thick, the only layer that is liquid, made up of molten nickel and iron.
Inner core
About 1,216-km thick, composed mostly of solid iron.
Crust temperature
Continental crust - 20 ºC to 600 ºC; Oceanic crust - 20 ºC to 1,200 ºC.
Mantle temperature
Upper mantle - 900 ºC; Lower mantle - 1,000 ºC to 3,700 ºC.
Outer core - 3,700 ºC to 4,300 ºC;
Inner core - about 6,000 ºC.
Core temperature
Heat source of Earth's interior
Heat accumulated from the radioactive decay of uranium, thorium, and other radioactive isotopes.
Mohorovicic discontinuity
Boundary between the crust and mantle.
Gutenberg discontinuity
Boundary between the mantle and outer core.
Lehmann discontinuity
Boundary between the liquid outer core and solid inner core.
100-km deep crust
1% of the Earth's mass.
Crust Mass
made of solid rocks and minerals.
Crust composition
2.7 g/cm³.
Density of continental crust
3.0 g/cm³.
Density of oceanic crust
900 ºC.
Temperature of the upper mantle is approximately
1,000 ºC to 3,700 ºC.
Temperature of the lower mantle ranges from