Concepts (*TBD Unit 5-9)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
VSEPER
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
electrons are the same charge and repel one another
2 Electron Domains
Linear
180 degrees
3 Electron Domains w/0 Lone Pairs
Trigonal Planar
120 degrees
3 Electron Domains w/1 Lone Pairs
Bent
120 degrees
4 Electron Domains w/0 Lone Pairs
Tetrahedral
109 degrees
4 Electron Domains w/1 Lone Pairs
Trigonal Pyramidal
109 degrees
4 Electron Domains w/2 Lone Pairs
Bent
120 degrees
5 Electron Domains w/0 Lone Pairs
Trigonal Bipyramidal
5 Electron Domains w/1 Lone Pairs
Seesaw
90 degrees
5 Electron Domains w/2 Lone Pairs
T-shape
90 degrees
5 Electron Domains w/3 Lone Pairs
Linear
90 degrees
6 Electron Domains w/0 Lone Pairs
Octahedral
90 degrees
6 Electron Domains w/1 Lone Pairs
Square Pyramidal
90 Degrees
6 Electron Domains w/2 Lone Pairs
Square Planar
90 degrees
6 Electron Domains w/3 Lone Pairs
T-shaped
6 Electron Domains w/4 Lone Pairs
Linear
90 degrees
Coulomb’s Law
More attraction when
Distance between charged particles is small
Magnitude of charge is greater
Potential Energy Graph
Lowest pt. = when bond is most stable
Bond Strength
Stronger when bonds are shorter/when double/triple bonds (compared to single bonds)
Structure of Ionic Solids
Lattice structure aka crystalline where you alternate between the anion and the cation
Anions are drawn larger than cations because they hold more electrons
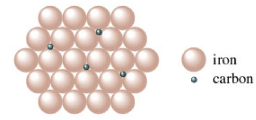
Interstitial Alloy
Occurs when there is a big difference in atom size (ex: C and Fe)
density increased
less malleable and ductile
more rigid
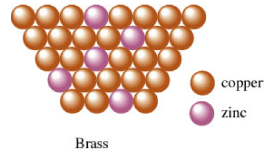
Substitutional Alloy
Occurs when there is a small difference in atom size (ex: Cu and Zn)
Resonance
When you can draw a molecule in multiple arrangements
Formal Charge
# of Valence - # of Non-bonding Electrons - # of Covalent Bonds
Hybridization
3 domains = sp2
4 domains = sp3
Sigma vs Pi Bonds
Sigma = electron pair is shared
Pi = second/second + third bond formed in a double or triple bond
Intermolecular vs Interparticle Forces
IMFs = between molecules
IPFs = within molecules
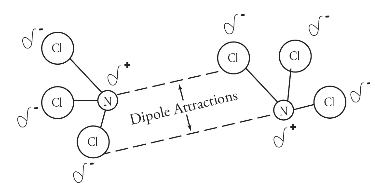
Dipole-dipole Interactions
between 2 polar molacules
lead to higher melting points and boiling points
Hydrogen Bonding
(special case of dipole-dipole)
hydrogen atom of a molecule is attracted to unshared electron pair on F, O, N of a neighboring molecule
“H-bonding is FON”
Ion-induced Dipole
attraction between charged ion and nonpolar molecule
ion distorts the electron cloud of nonpolar molecule
Dipole-induced dipole
polar and nonpolar IMF
polar induces temporary dipole
larger molecules are more polarizable (by Coulomb’s)
Induced-dipole-induced-dipole (London Dispersion Forces)
attraction between 2 nonpolar molecules because of temporary dipoles
more electrons = more polarizable = stronger attraction
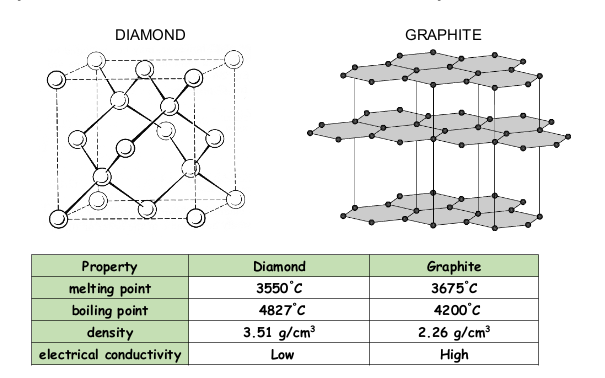
Network Covalent Solids
2-dimensional = soft and slippery
3-dimensional = interlocking layers (of carbon)
high melting point
insoluble
poor conductors except graphite
Vaporization (Evaporation)
Conversion of a liquid to a gas
aka how easy it is to break bonds
Phase Diagram
who relationships between solid, liquid, and gas
triple point = where all states exist in equilibrium
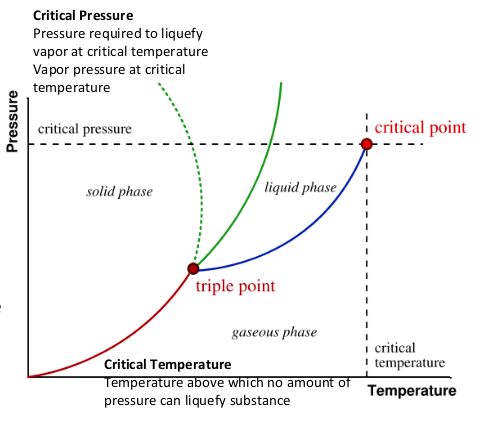
Vapor Pressue
Pressure exerted by vapor in equilibrium w/liquid
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
Boyle’s Law
Volume and pressure = inversely proportional
P1V1 = P2V2
only true at low pressures
Charles’s Law
Volume and temperature = directly proportional
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Gay-Lussac’s Law
P1/T1 = P2/T2
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
Pressure of a mixture = sum of pressures of different components
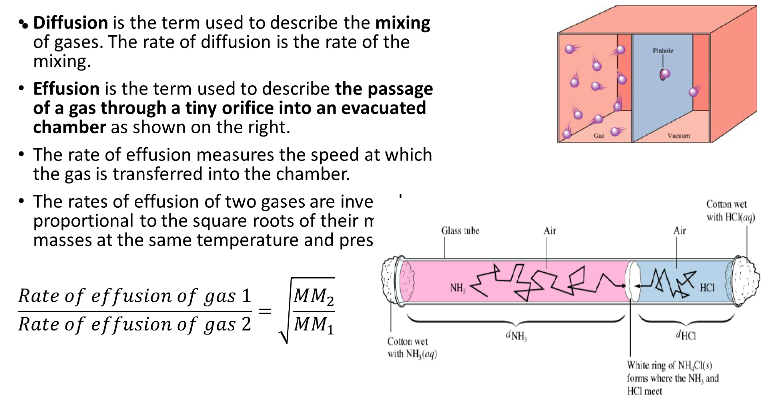
Diffusion vs Effusion
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Assumes…
all particles are in constant, random, motion
all collisions are perfectly elastic
gas particles are so small the volume is neglected
average kinetic energy is kelvin temperature
higher temperature = higher average kinetic energy
collisions with walls = pressure of gas
Deviation from Ideal Gas Law
Low temperature = moving less fast so IMFs still matter
Small volume = hit the sides more bcs of particle size
Separation of Mixtures (List Methods)
distillation = separation by IMFs and their impacts on vapor pressure
chromatography = by polarity
Chromatography
Separates by polarity
have stationary phase = paper or stuff inside the column
have mobile phase = solvent
Beer Lambert Law
relates absorption of light to molar absorptivity, path length, and concentration
pH and pOH
pH = -log[H+]
pOH = -log[OH-]
Polyprotic Acids and Bases
can donate more than one proton
Ammonium
NH4+
Acetate
CH3COO-
Nitrate
NO3-
Nitrite
NO2-
Perchlorate
ClO4- = Perchlorate
Chlorate
ClO3
Chlorite
ClO2
Hypochlorite
ClO
CN-
Cyanide
OH-
Hydroxide
MnO4-
Permanganate
SO4-2
Sulfate
SO3-2
Sulfite
HSO4-
Hydrogen sulfate
CO3-2
Carbonate
PO4-3
Phosphate
CrO4-2
Chromate
O2-2
Peroxide
SCN-
Thiocyanate