M3: LEC 5: Pollination and Ripening
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
T/F - Anthophyta pollen have wings and are dispersed by wind.
False - they do not have wings and are not dispersed by wind
Who disperses the p. anthophyta pollen?
insects
Where does the pollen grain land?
stigma
What happens when the pollen grain lands on the stigma?
1) pollen grain germinates the pollen tube
2) pollen tube travels down the style w the sperm to the ovule w the egg
What does the ovule consist of?
seed coat (integument), central cells, eggs, and synergids
What is the func of the synergids?
attract the pollen tube
T/F - The female gametophyte is reduced to a few cells in the ovule.
True
What happens before pollination and after pollination?
Before pollination:
all the floral parts (sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels are present
After pollination:
the sepals, petals, stamen, stigma, and style have fallen off and only the base of the carpel (ovary) is present
Why is abscission important for the process of pollination?
to stop attracting insects
What happens in double fertilization?
1) one sperm fertilizes the egg —> forming a zygote
2) the other sperm fertilizes the central cell —> forming the endosperm (food)
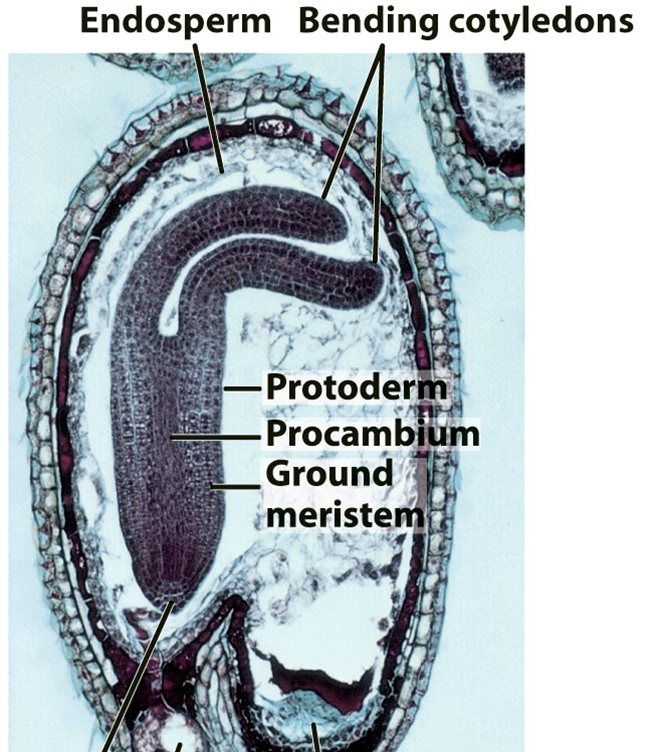
What are the differences btwn an immature and mature embryo?
immature embryo (photo attached):
1) endosperm is not completely digested
2) the embryo does not completely fill up the seed
mature embryo:
1) endosperm is completely digested
2) the embryo fills up the seed
How does the fruit know to start ripening and prepare for dispersal?
when the seed is mature and contains a mature embryo
What happens in the ripening process?
1) the ovary enlarges
2) sucrose enters the fruit
3) sucrose breaks into glucose and fructose
a) glucose for ATP
b) fructose for sweetening
4) anthocyanin and carotenoids form
a) attracting for animal dispersal
What are the different types of seed dispersal?
1) fruit dries and splits —> attract and disperse
2) forms hook —> animal dispersal
3) pressurized fruit shoot out their seed
4) growing wings —> wind dispersal
5) fruit hardens and traps air —> floatation