09.0 BIO, HN UNIT 9 Genetics (ALL)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Inheritance
The process in which genetic material is passed from parents to their offspring
Genetics
The study of heredity

Trait
A specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another
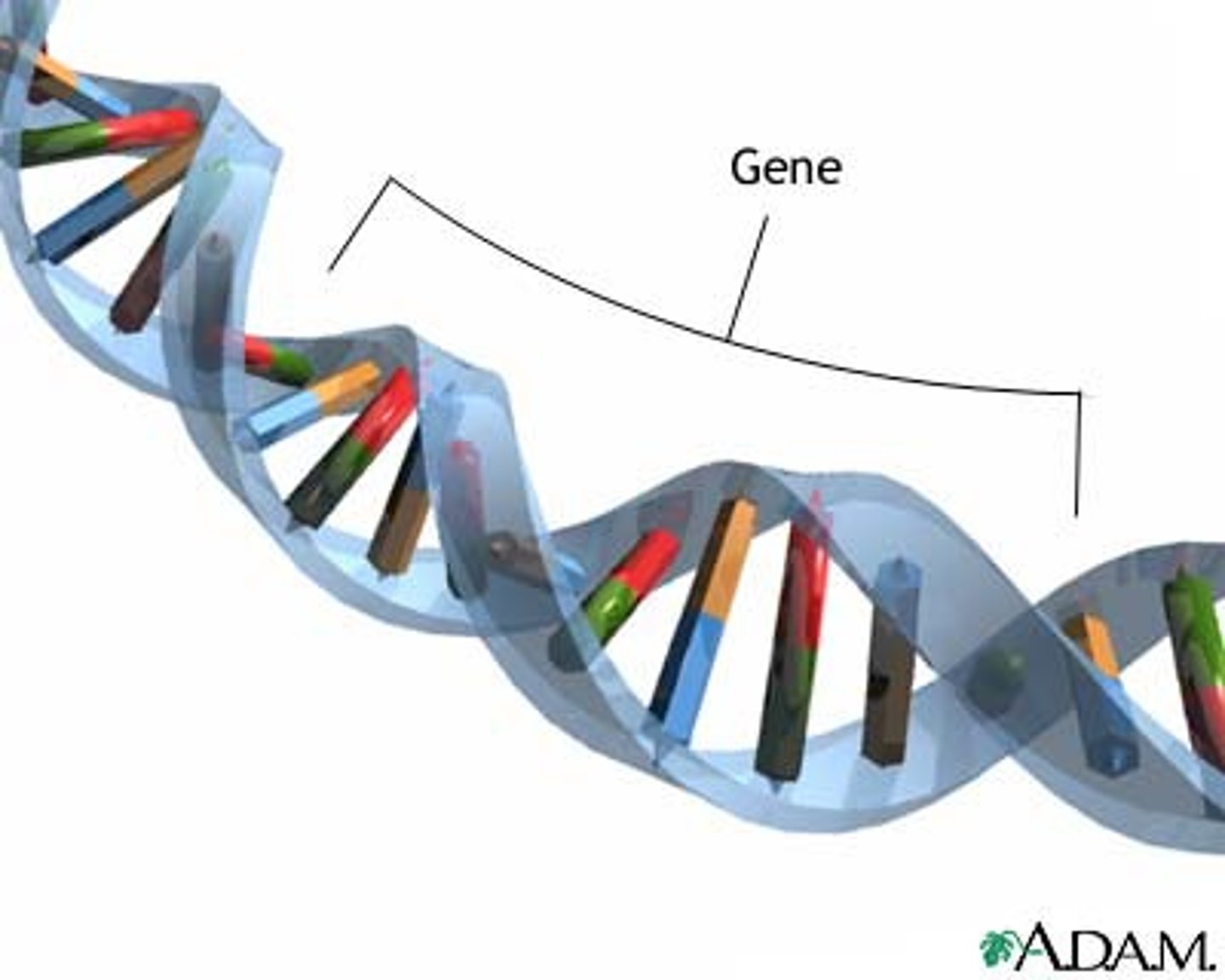
Gene
The sequence of nucleotides on a chromosome that codes for a protein and determines a trait
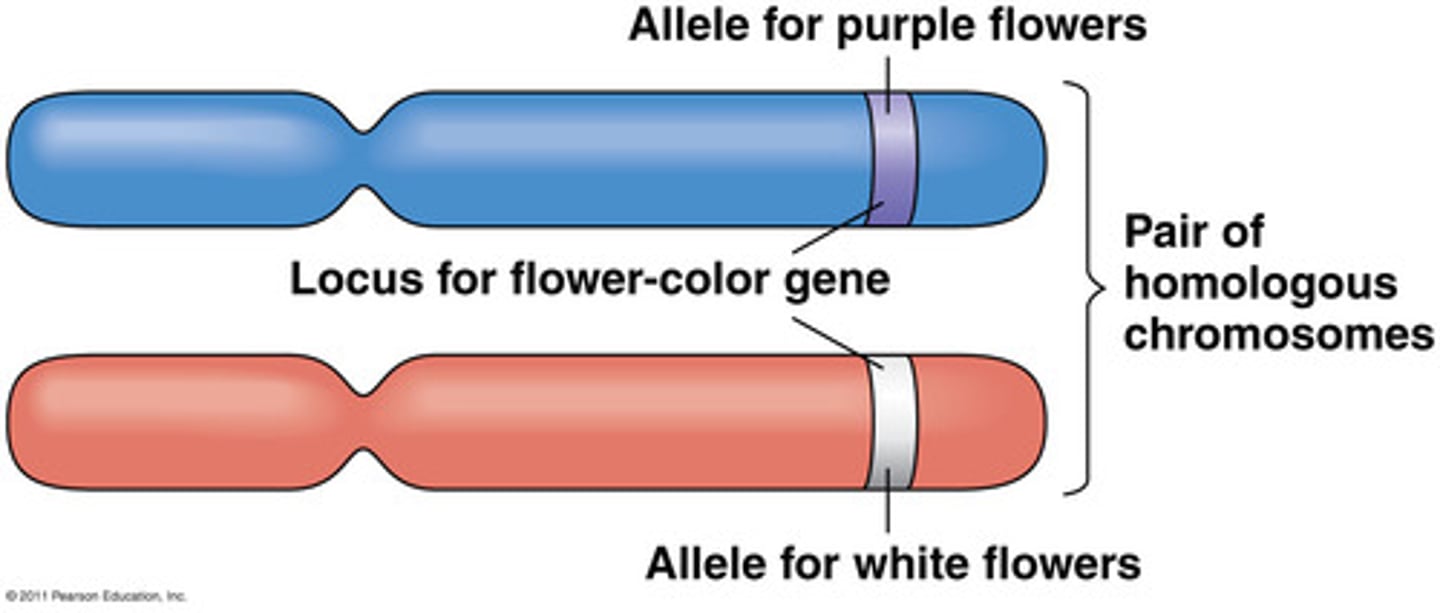
Allele
A form of a gene; for example, the gene for flower color could produce either purple flowers or white flowers
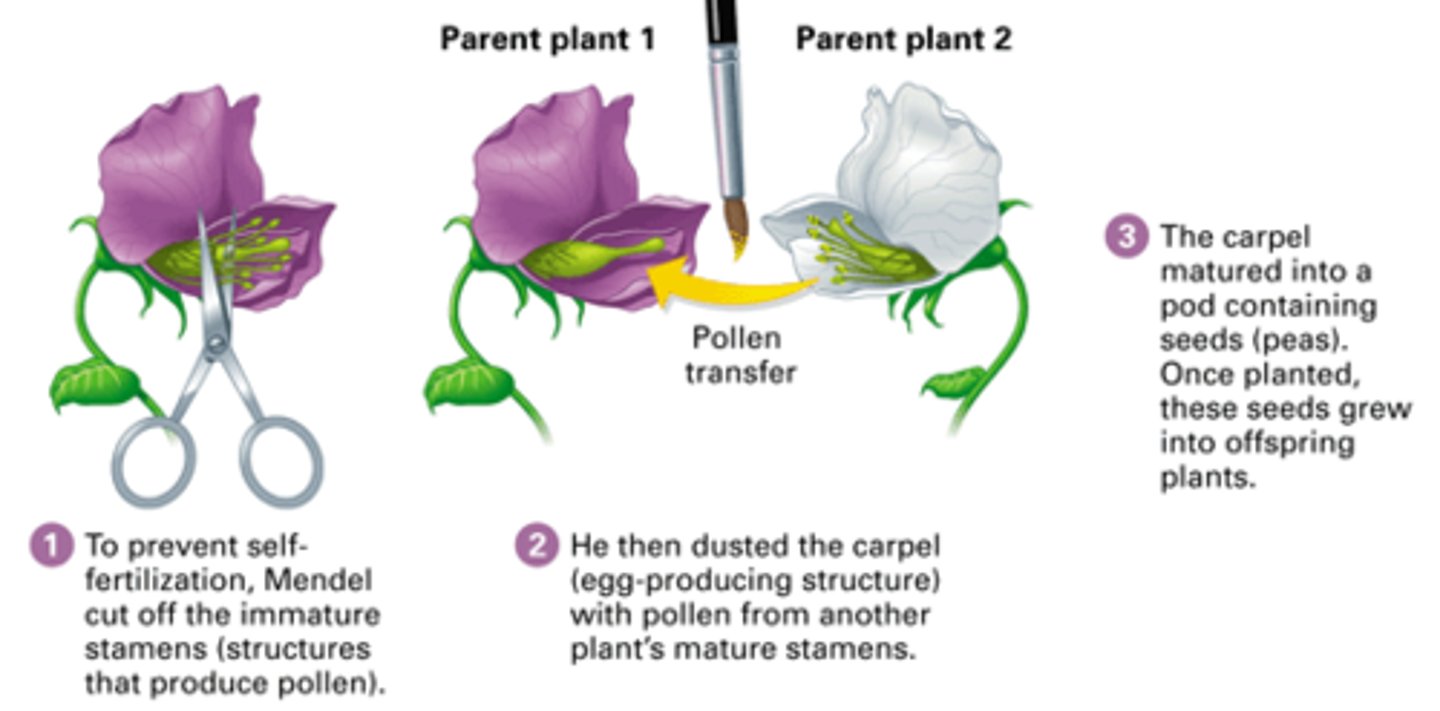
Self-pollination
The fusion of sperm and egg produced by the same individual organism
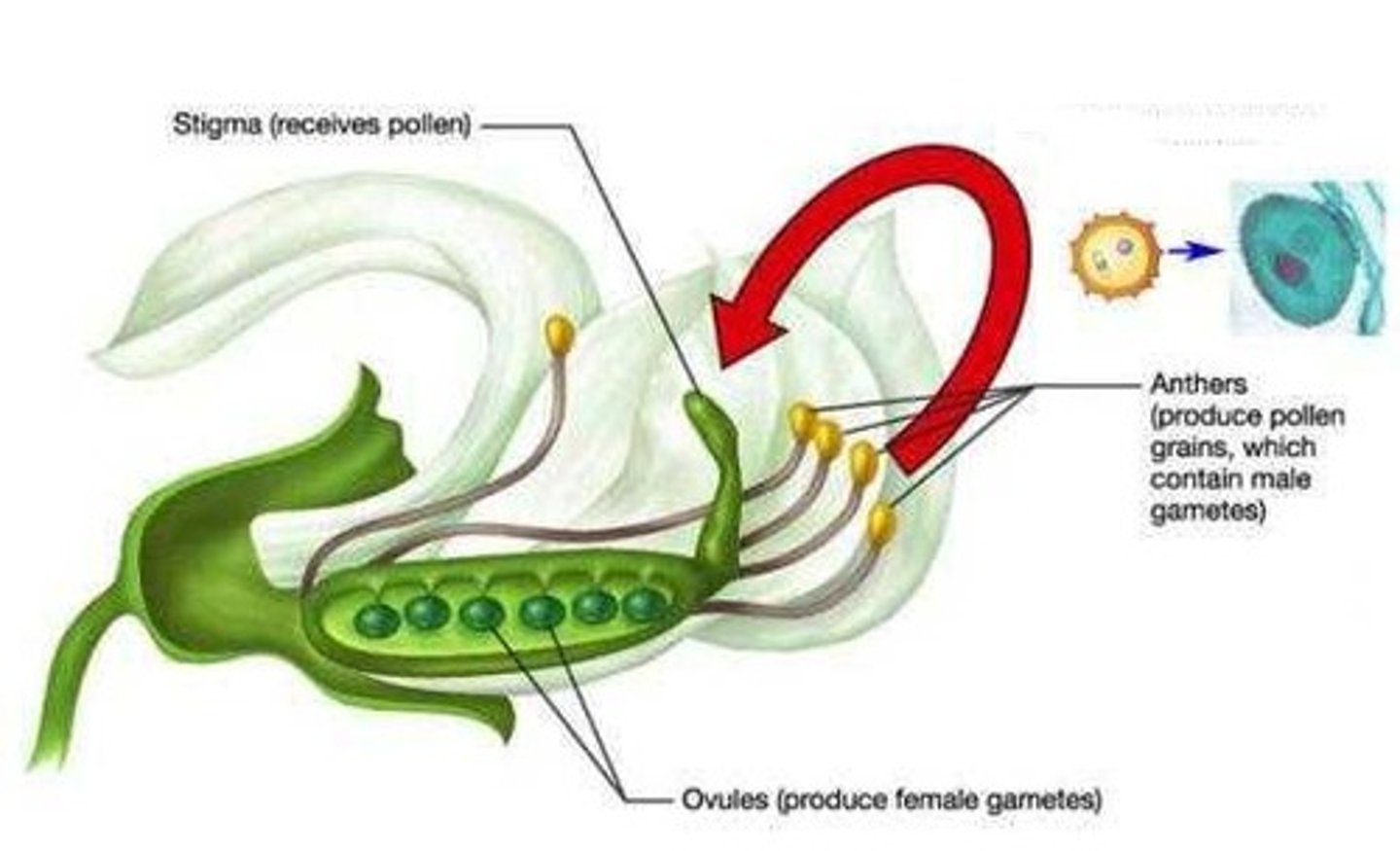
Cross-pollination
The process by which sperm from one flower's pollen fertilizes the eggs in a flower of a different plant; also known as cross-fertilization
Dominant
A trait that will show up in an organism's phenotype if gene is present
Recessive
A trait that will only appear in the phenotype if organism inherits two of them; covered up by the dominant gene
True-breeding
Inherited two identical alleles for a trait; homozygous or purebred
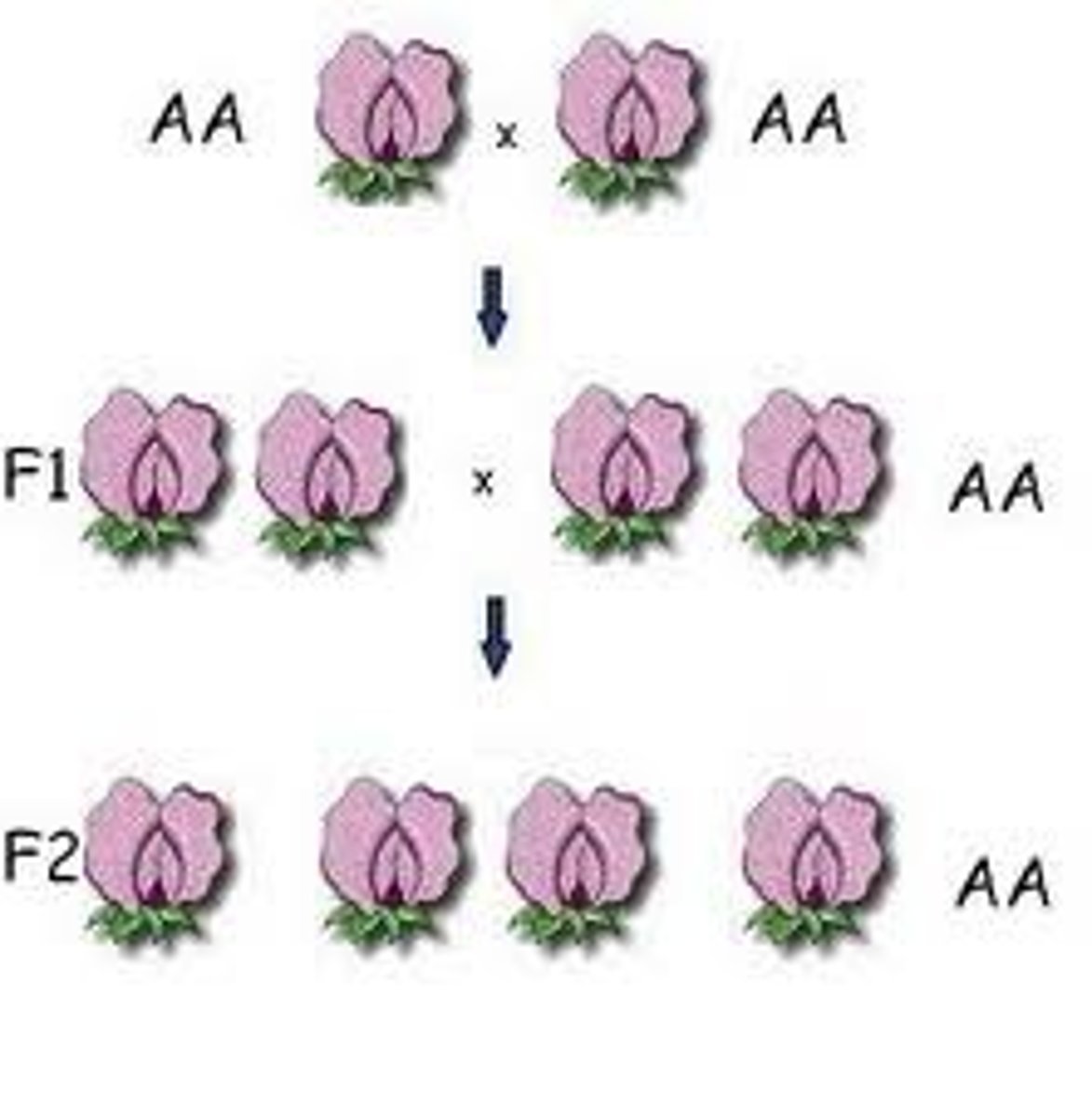
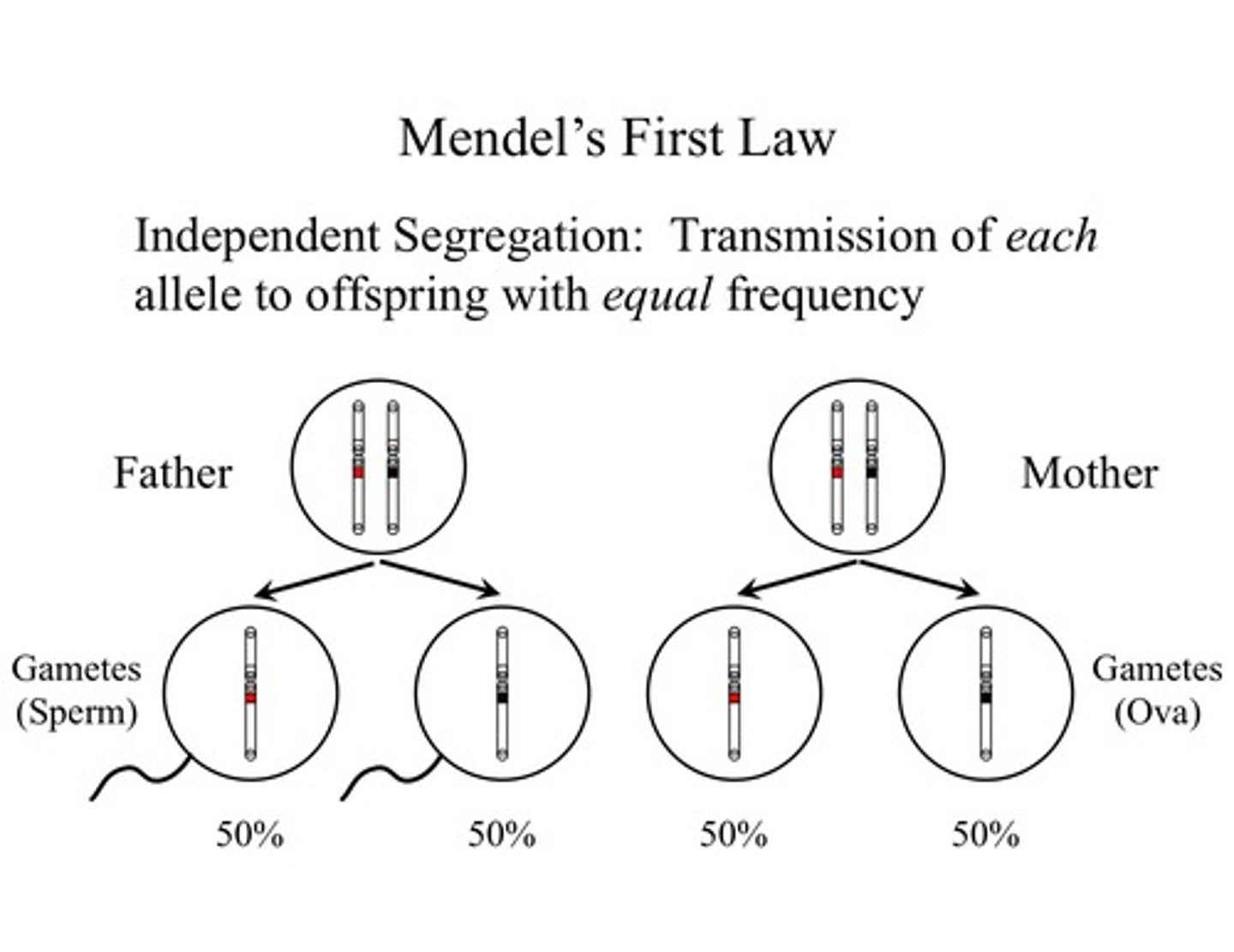
Segregation
The separation of alleles during meiosis or gamete formation
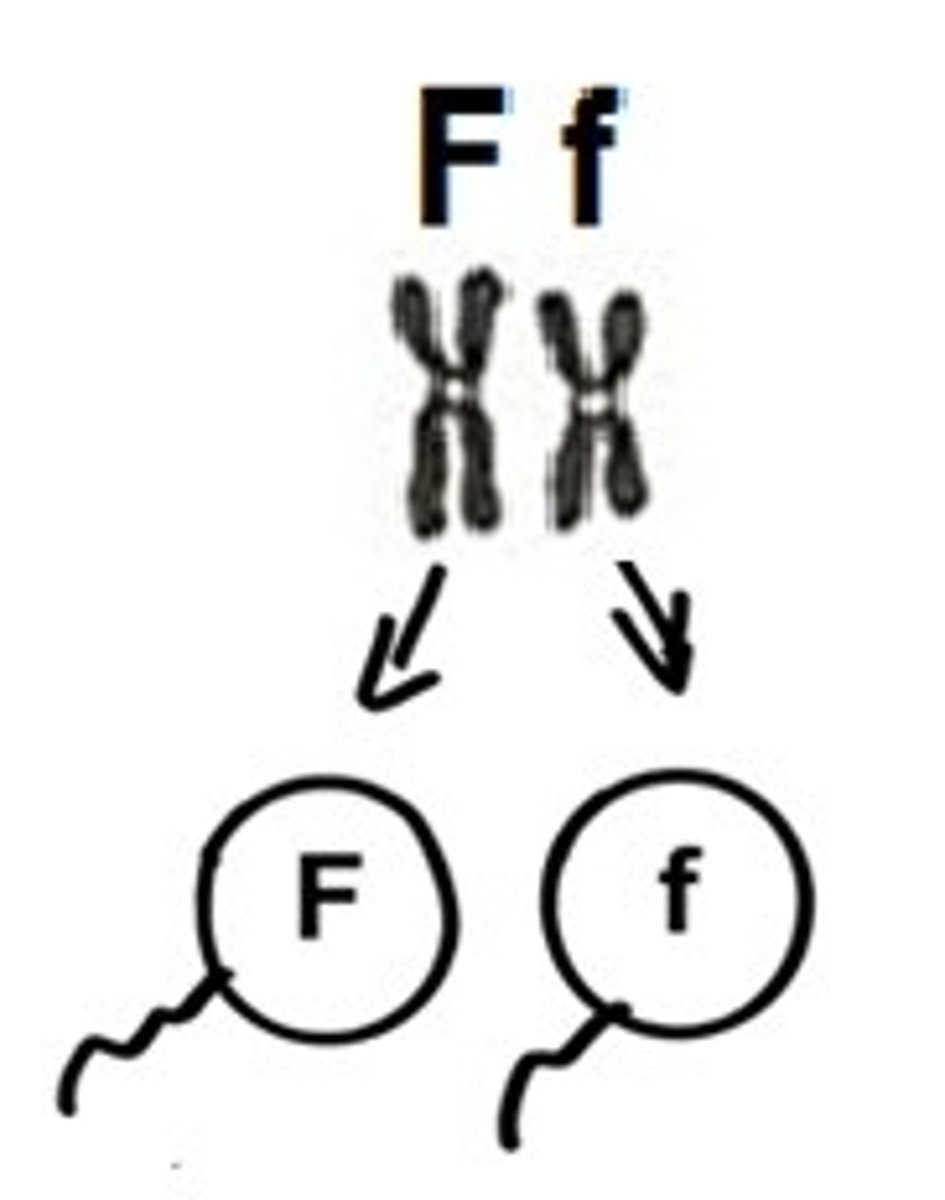
Gamete
Sex cell; sperm or egg
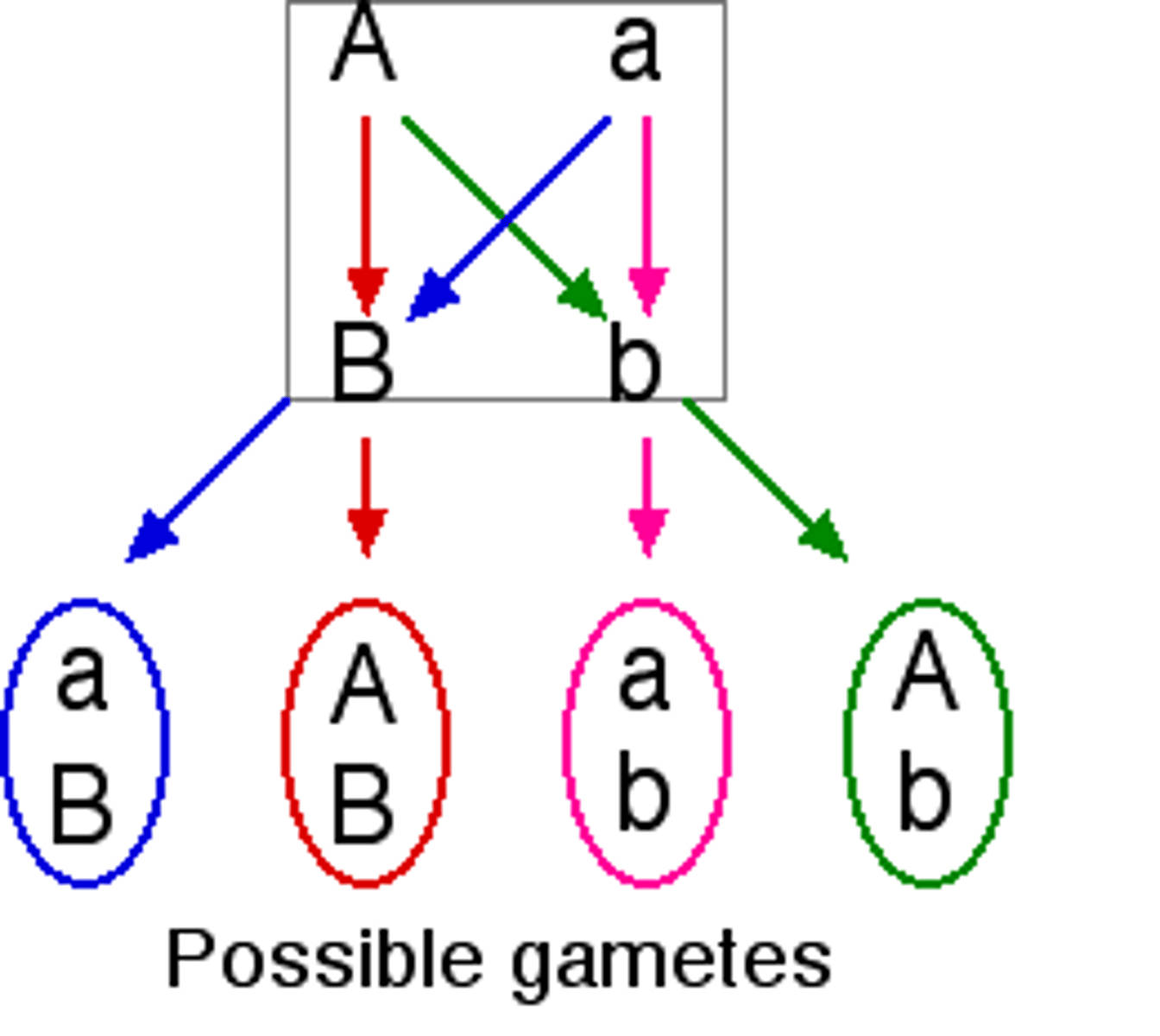
Independent assortment
A principle that genes do not influence each other's inheritance because they are separated independently during meiosis
Hybrid
The offspring of a cross between parents with different traits; heterozygous
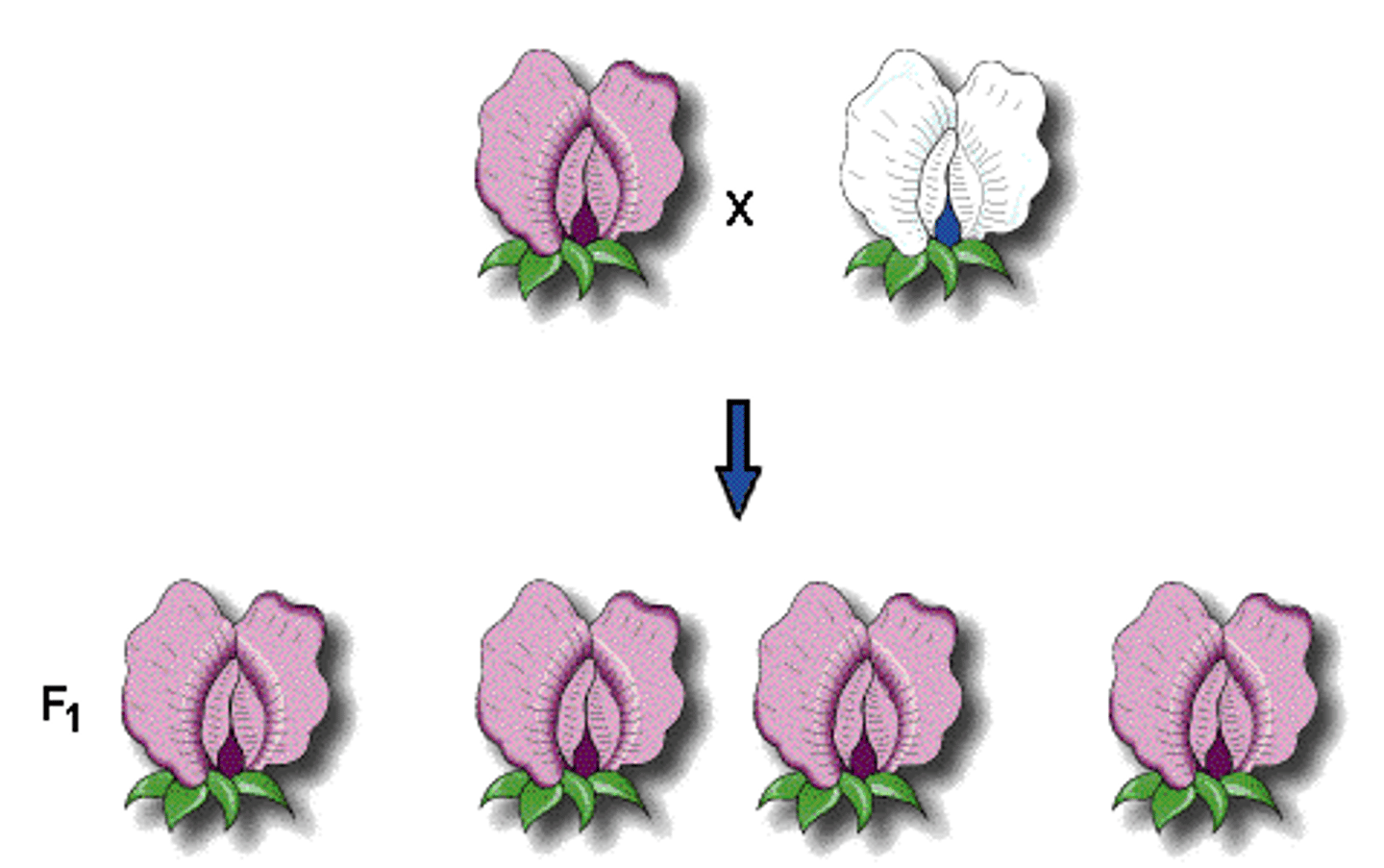
Principle of Dominance
Mendel's conclusion that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
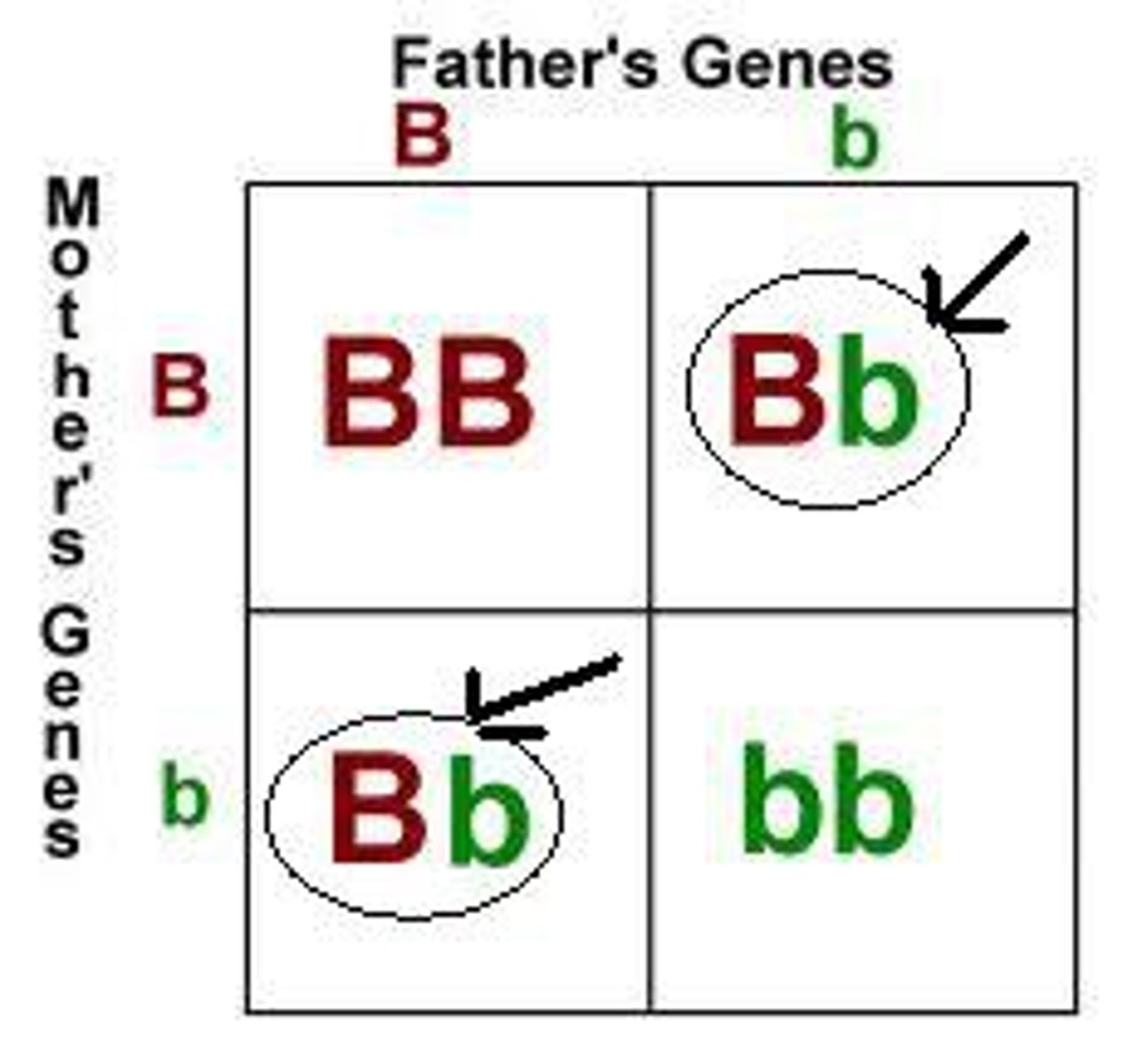
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
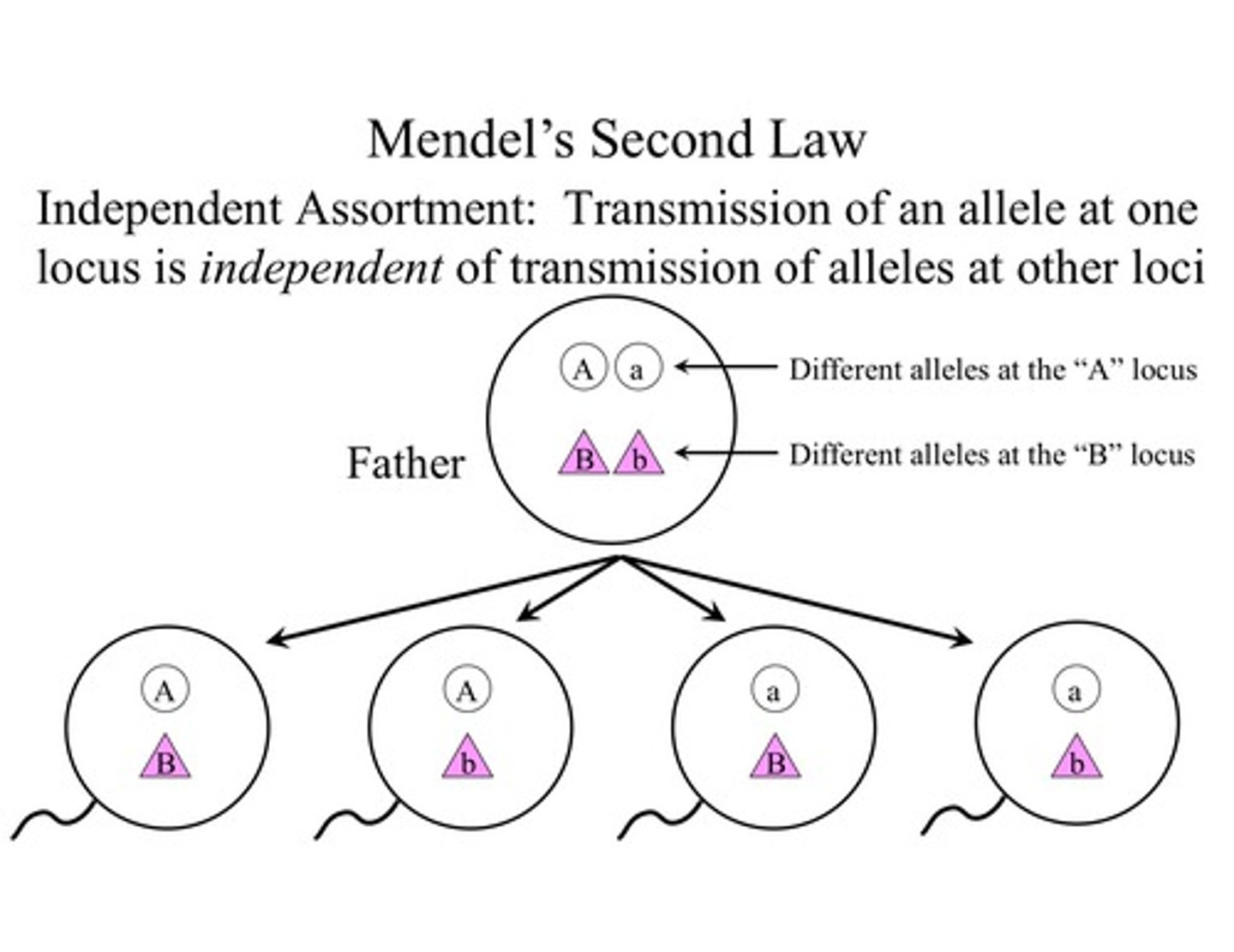
Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel's second law, stating that each allele pair segregates independently during gamete formation; applies when genes for two characteristics are located on different pairs of homologous chromosomes
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to his eventual recognition as founder of the science of genetics (1822-1884); experiments with pea plants led to the law of dominance, independent assortment, and segregation.

Flower
Reproductive structure of the plant
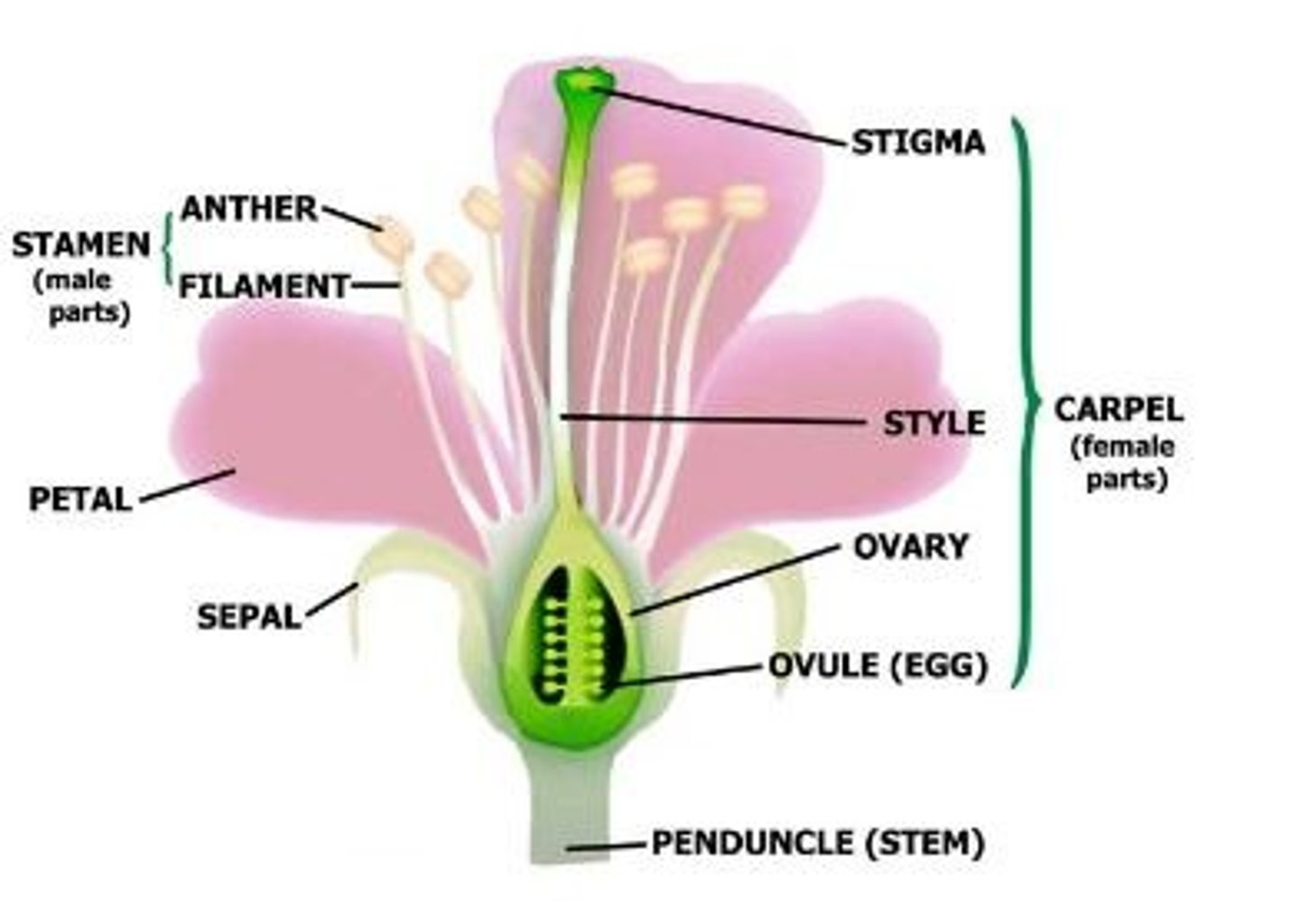
Stamen
Male parts of the plant that include the anther, filament and pollen

Carpel
Female parts of the plant that include the stigma, style, ovary, ovule

Pollen
A fine powdery substance, typically yellow, consisting of microscopic grains produced by the male part of a flower; each grain contains a male gamete that can fertilize the female ovule, when transported by the wind, insects, or other animals; male gamete

Ovule
A structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant that contains the female germ cell and after fertilization becomes the seed; female gamete

P Generation
Parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
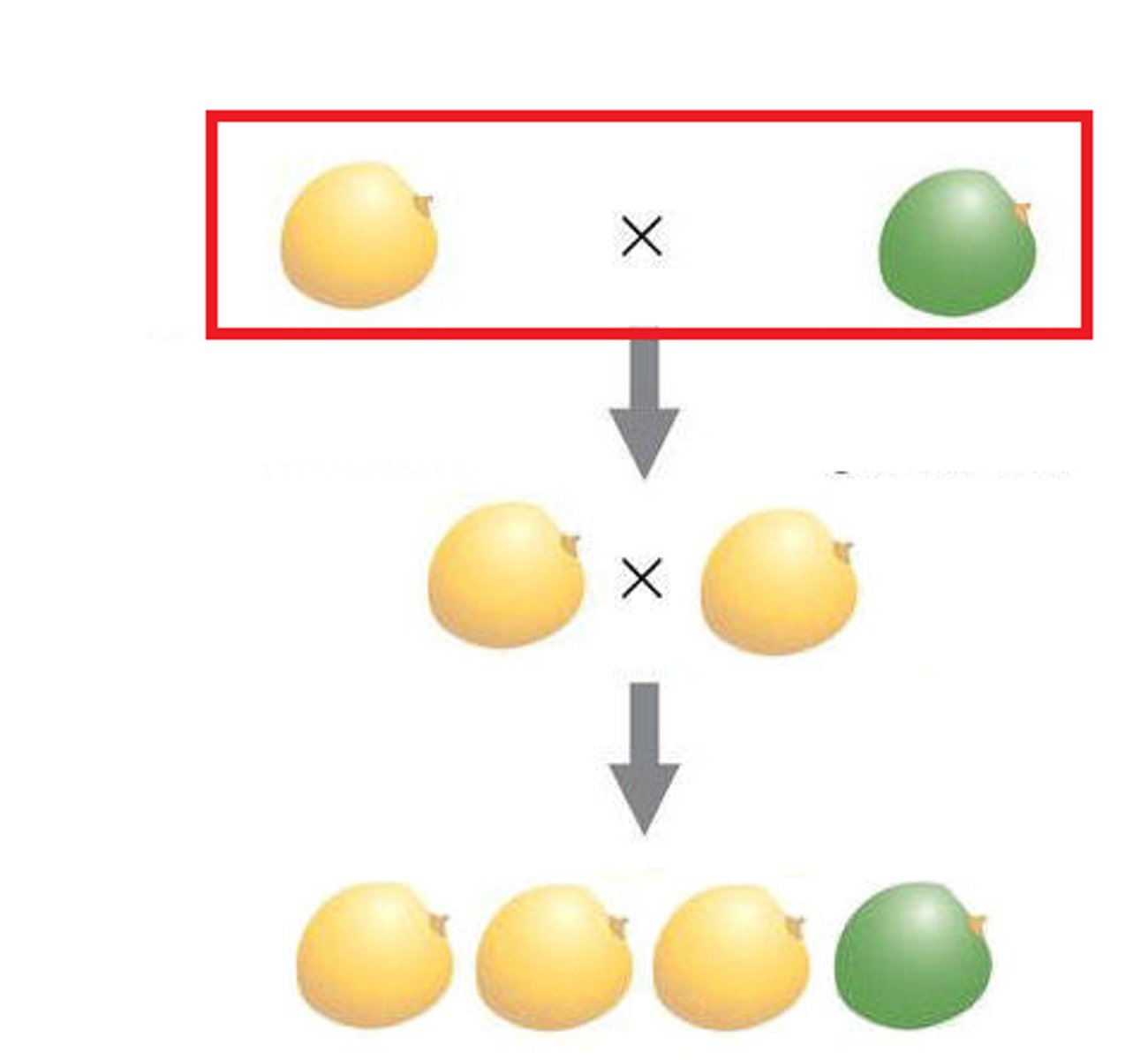
F1 Generation
The first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
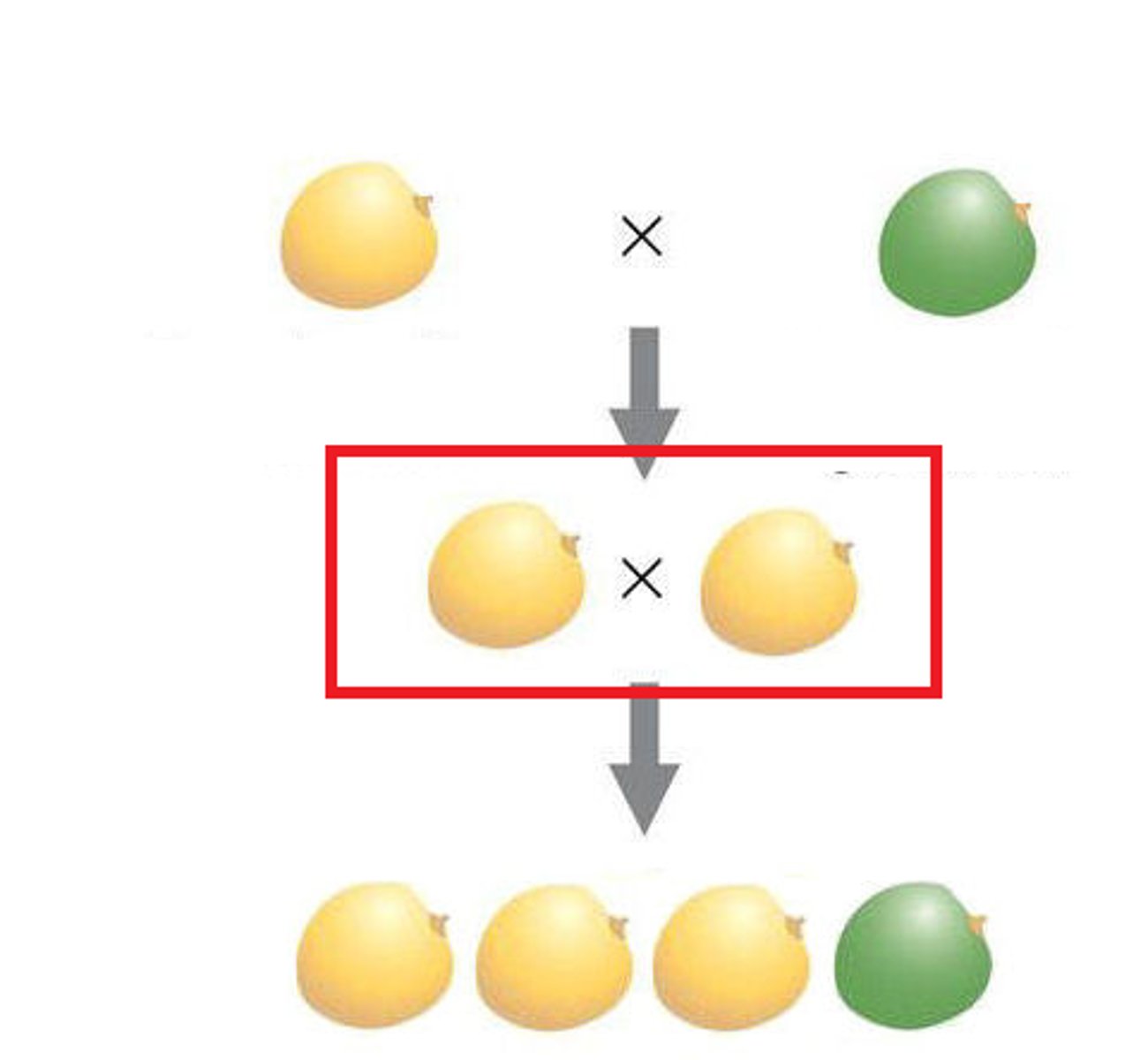
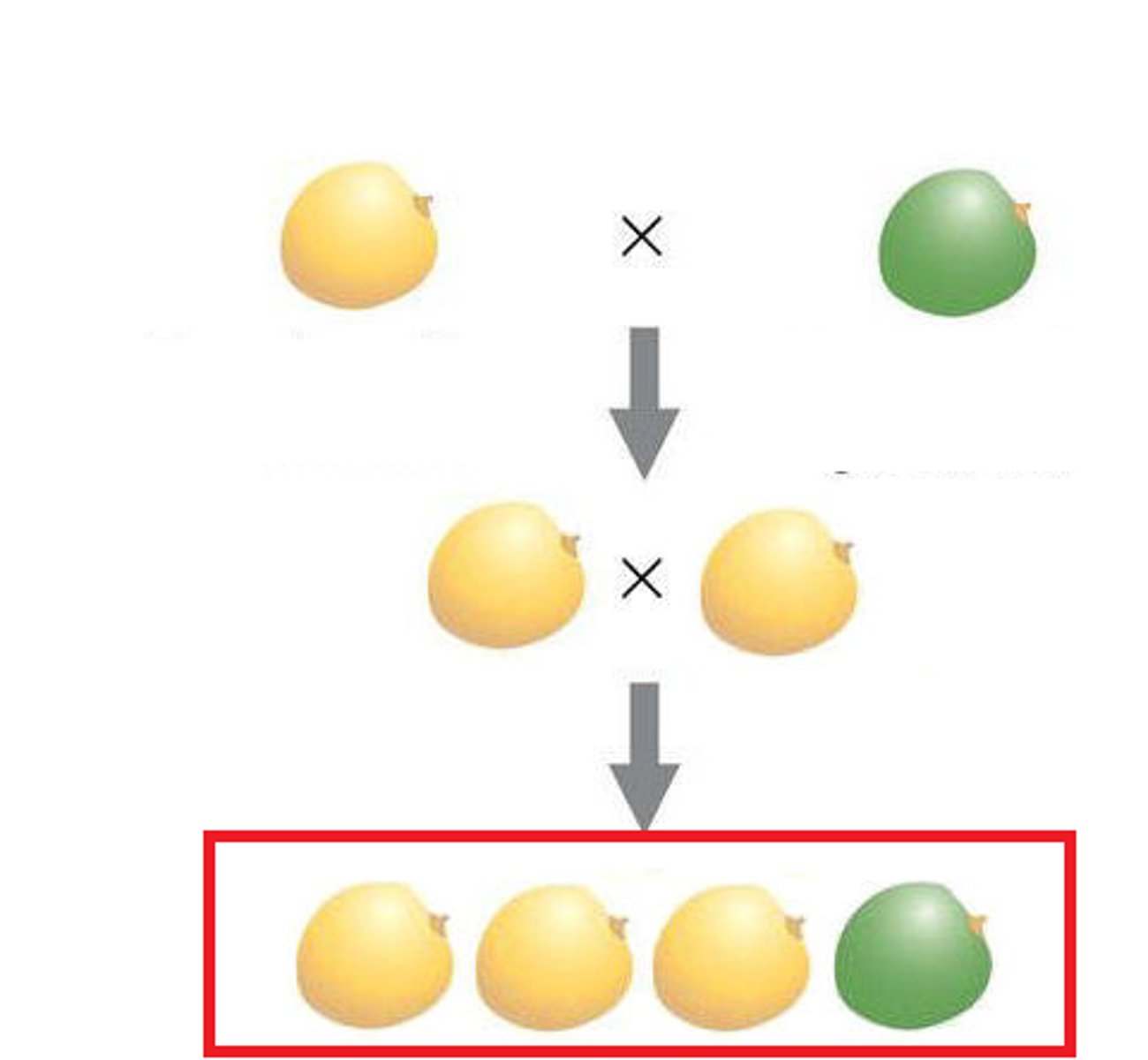
F2 Generation
The second generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two F1 organisms
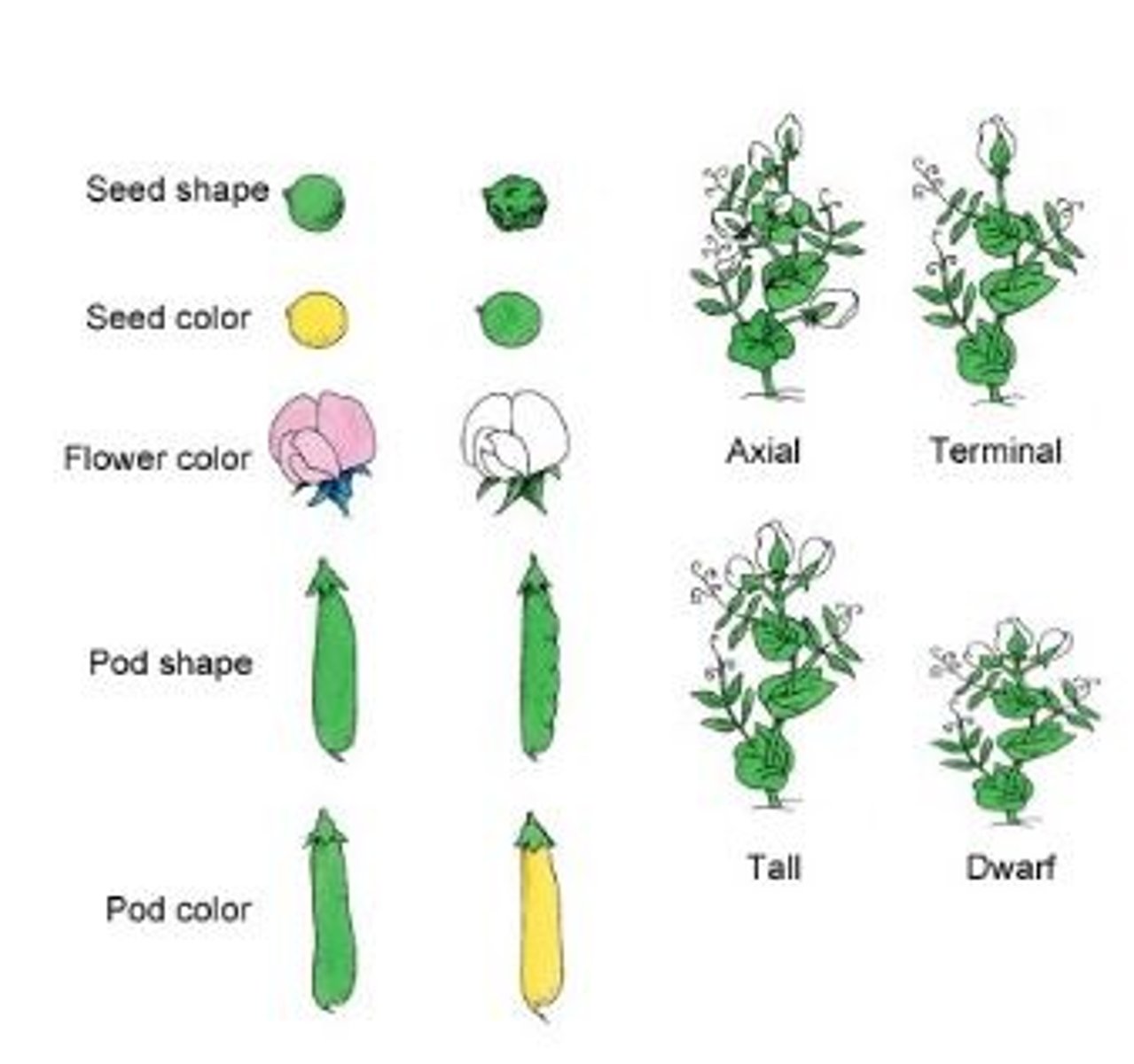
Pea Traits (Examples)
Seed shape
Seed color
Flower color
Pod shape
Pod color
Flower Location
Plant height
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
The physical characteristics of an organism
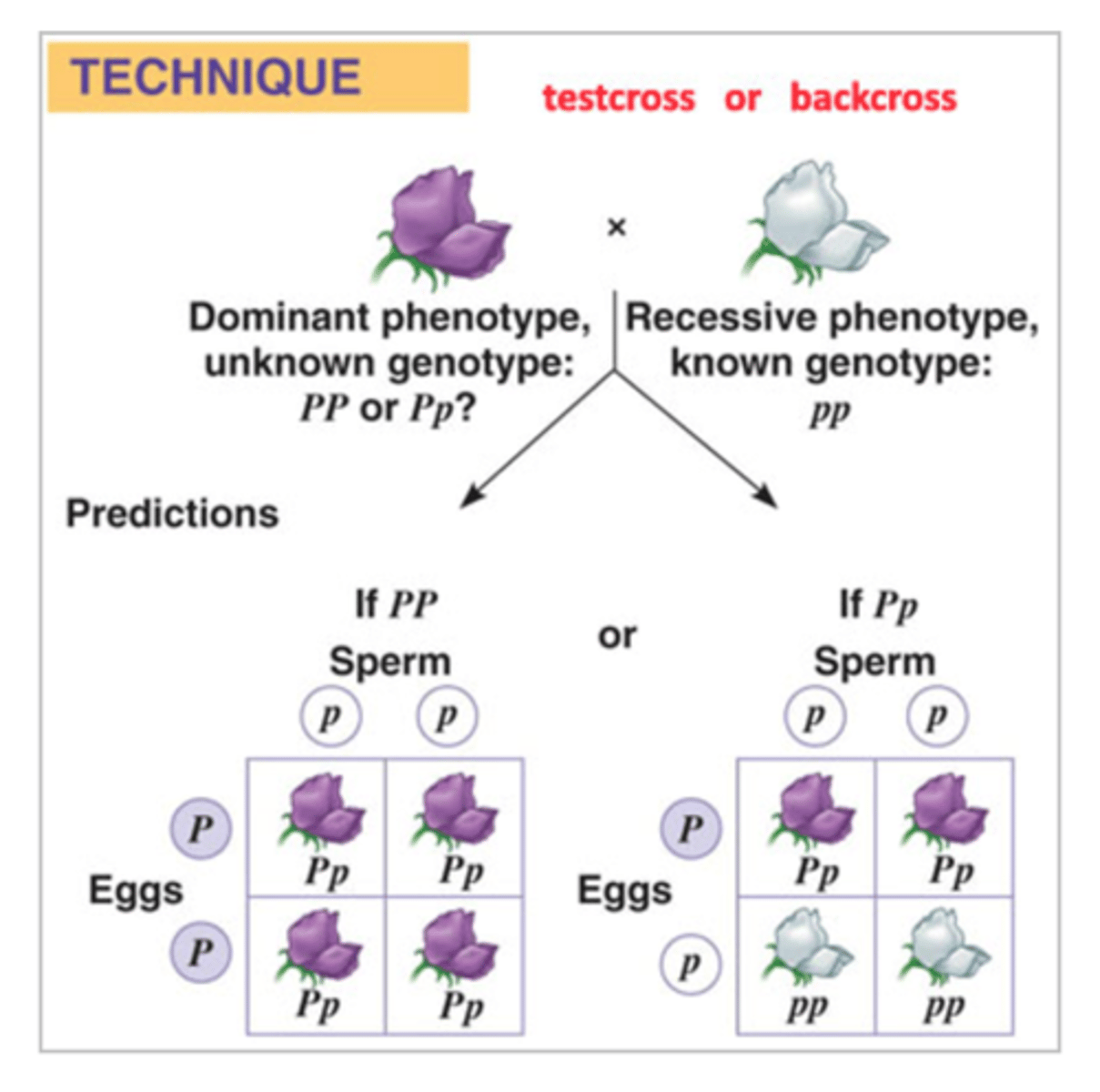
Testcross
A cross between an organism whose genotype for a certain trait is unknown and an organism that is homozygous recessive for that trait so the unknown genotype can be determined from that of the offspring
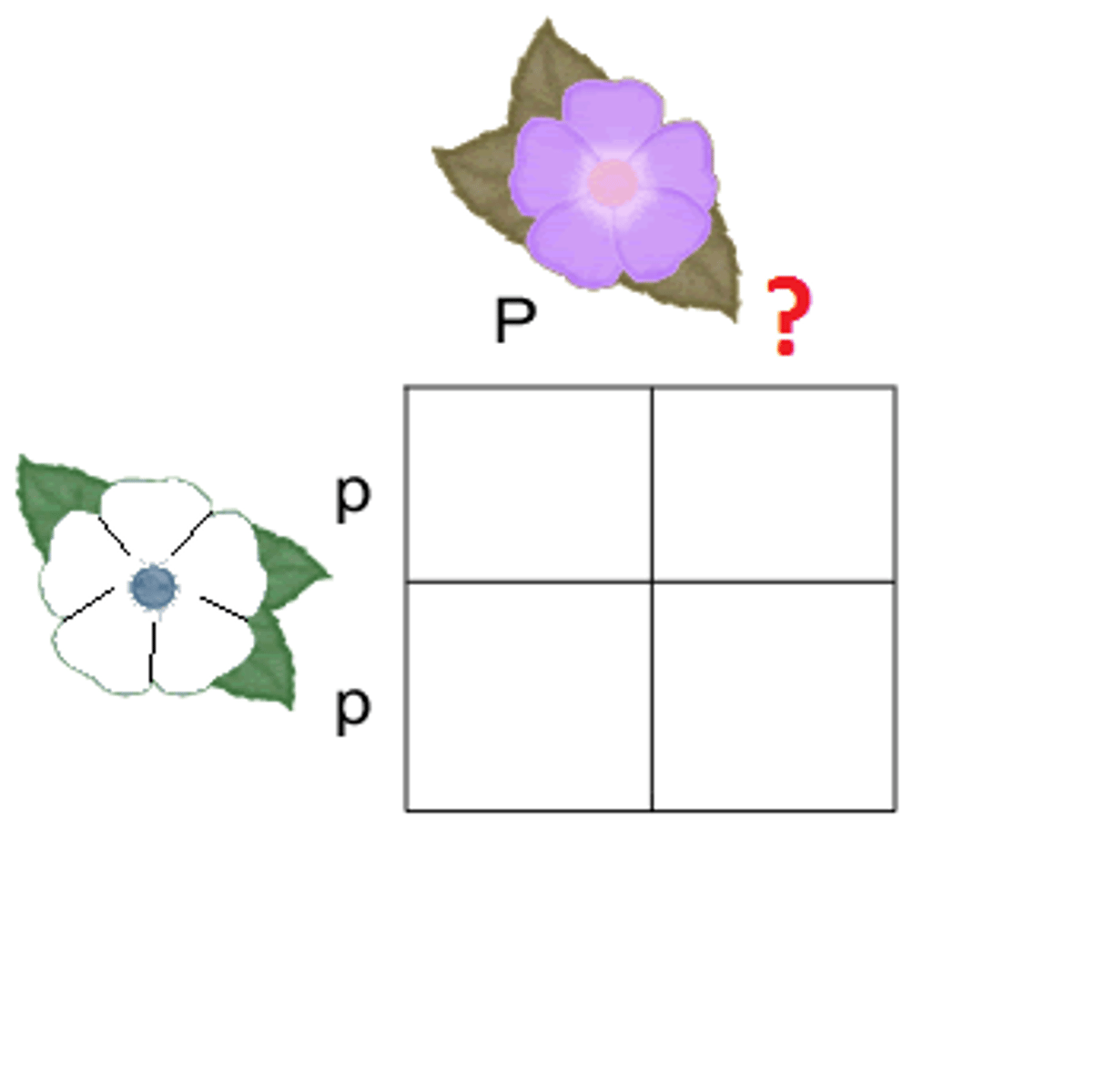
Monohybrid cross
A cross between two individuals, concentrating on only one trait
Dihybrid cross
A cross between two individuals, concentrating on two traits
Probability
The likelihood an event will occur
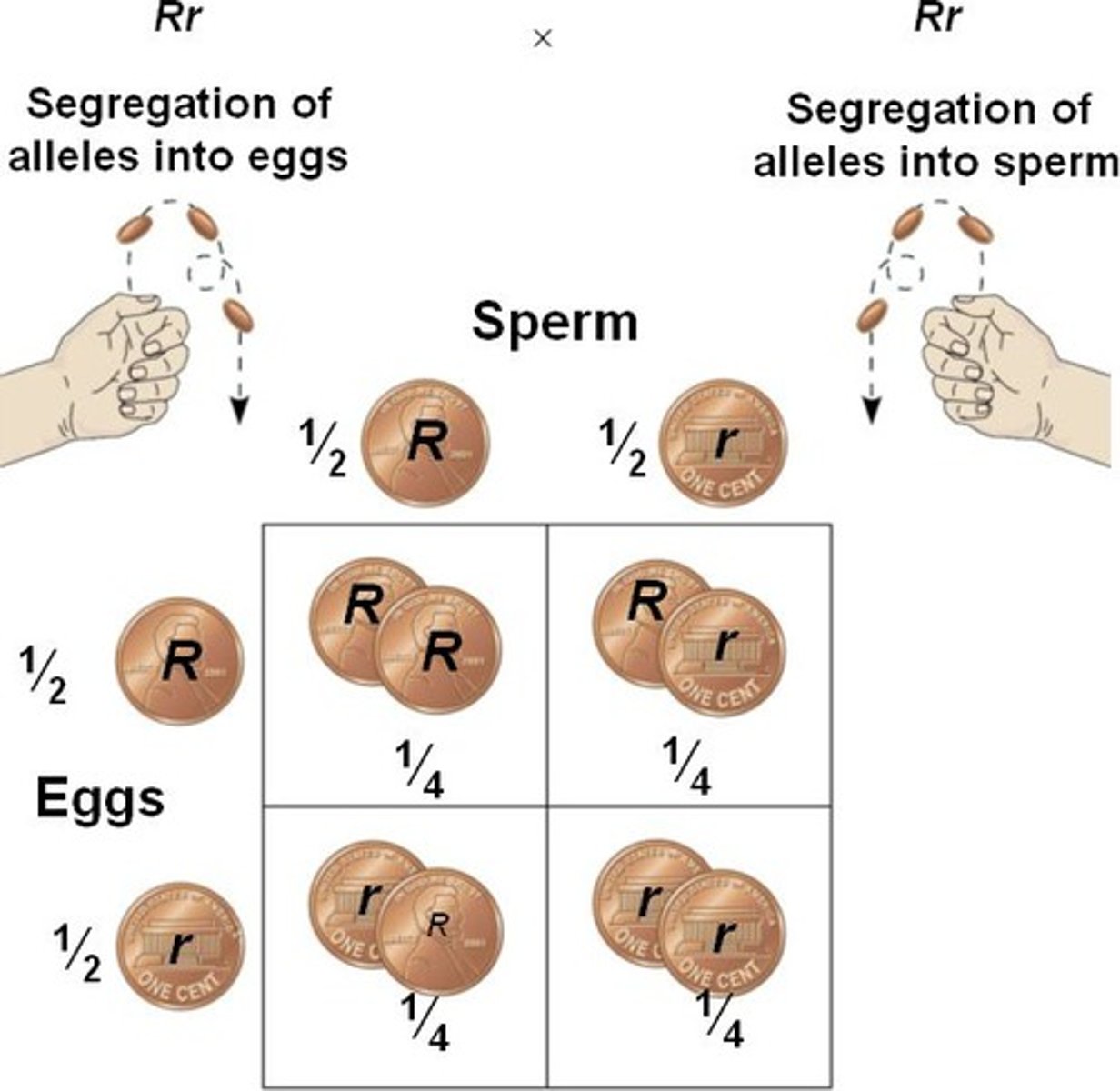
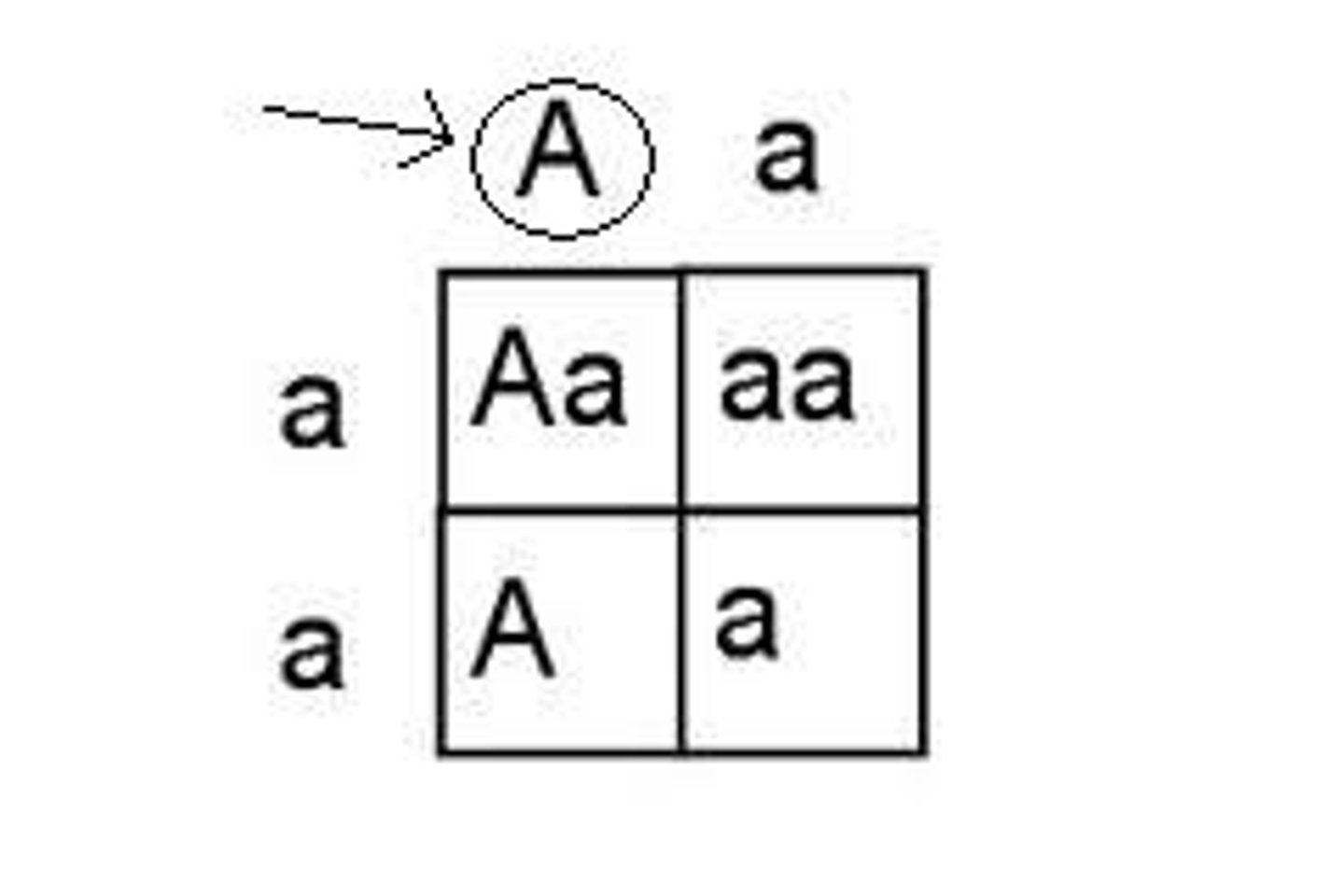
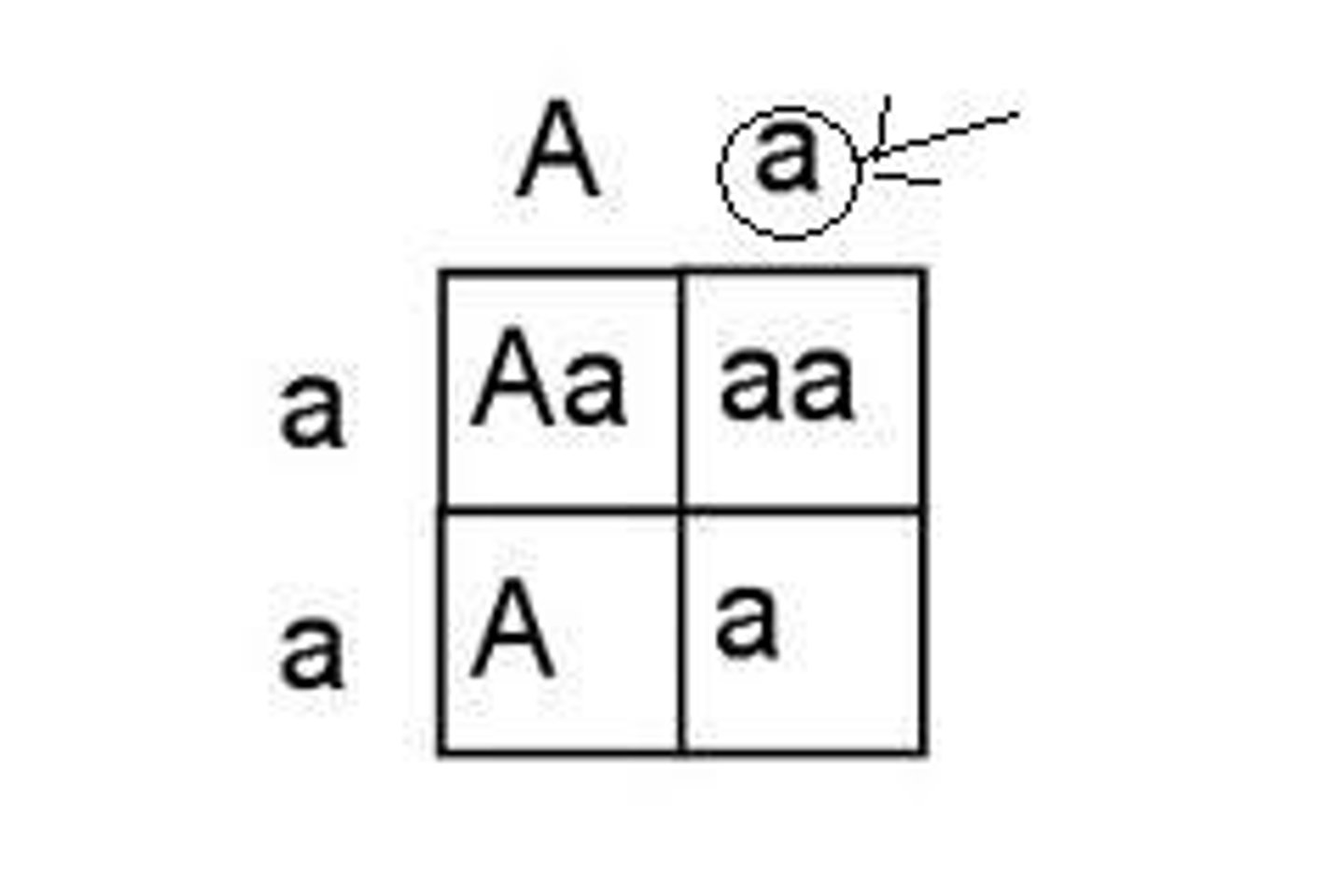
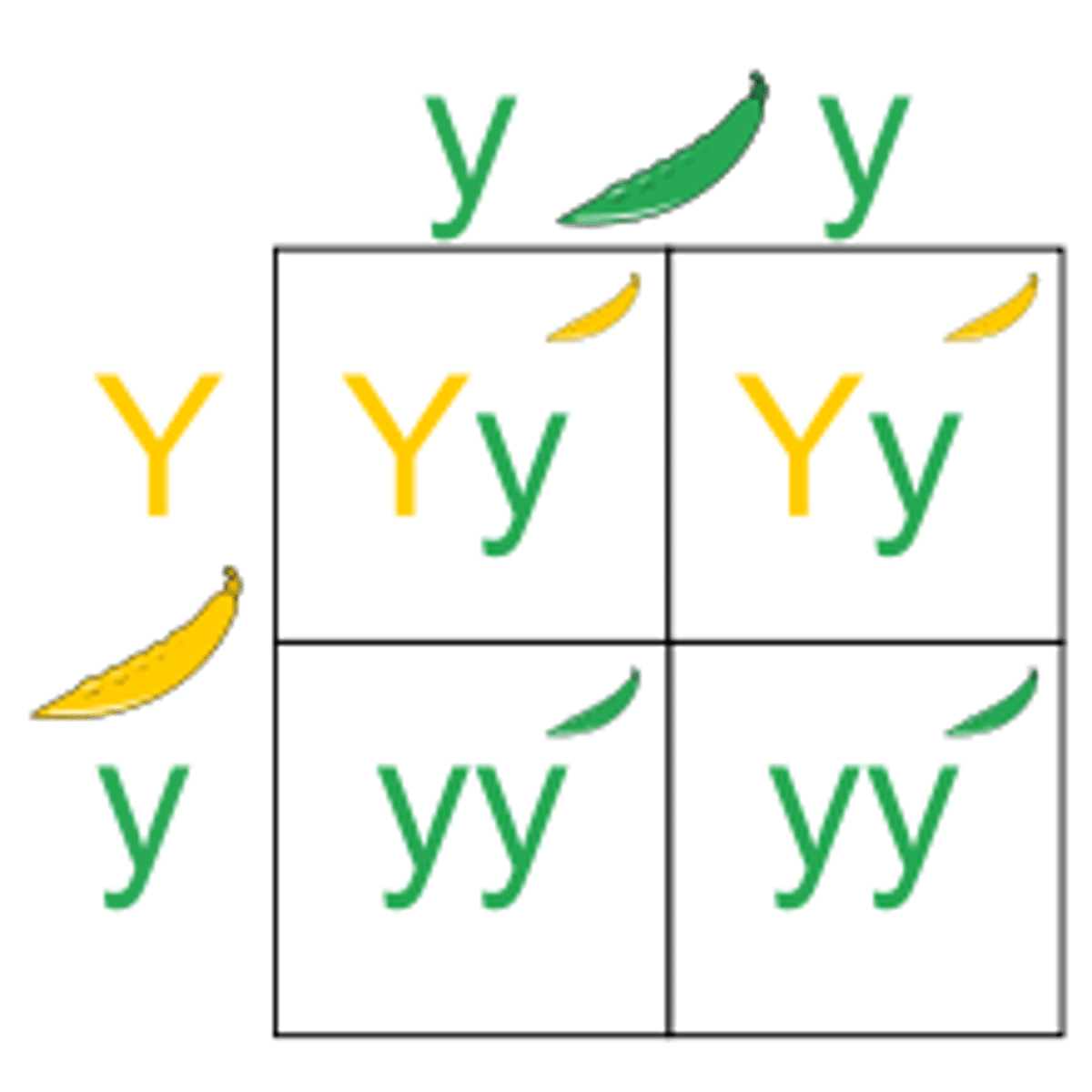
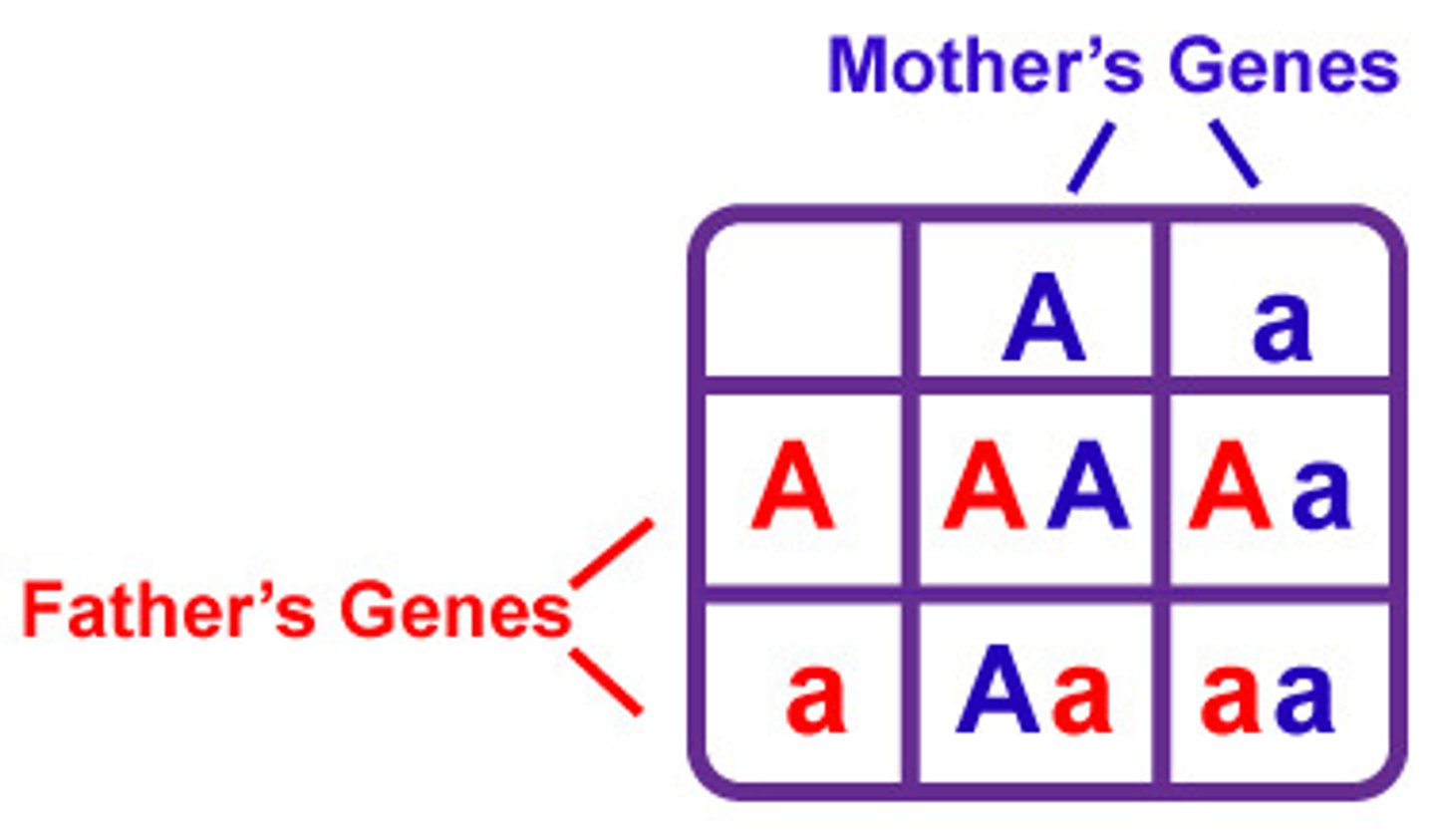
Punnett square
A diagram that shows the possible results of a genetic cross; parents' gametes on top and left, offsprings' genotypes inside
Ratio
The quantitative relationship between two amounts showing the number of times one value contains or is contained within the other; i.e three to 1 (3:1) or one to two to one (1:2:1)
Percentage
A part of a whole expressed in hundredths
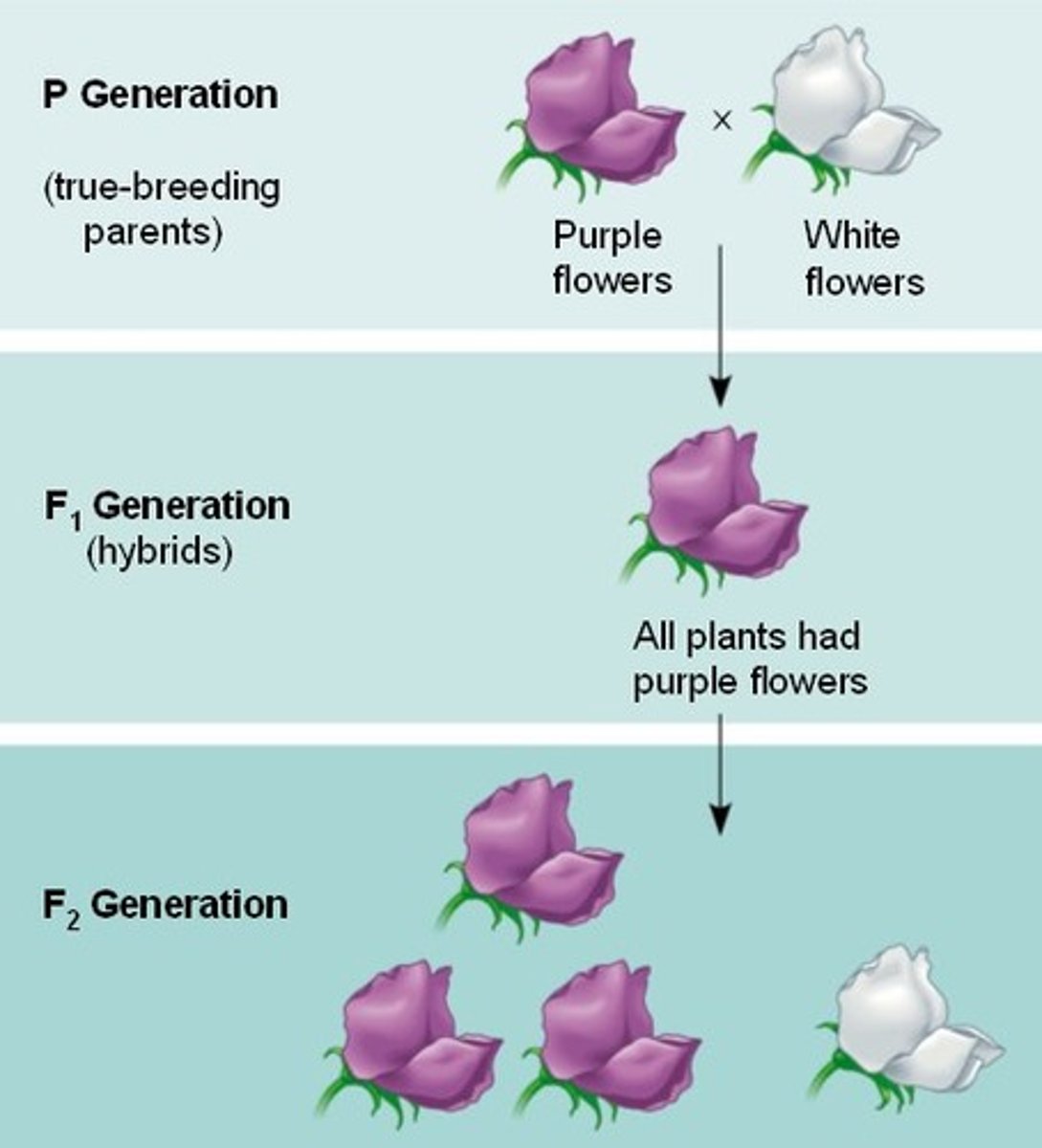
Monohybrid Cross
A cross that examines the inheritance of only one specific trait;
For example, flower color
Purple flower color is dominant = R
White flower color is recessive = r
Test Cross
A cross in which an individual with a dominant phenotype is crossed with a homozygous individual to determine the unknown genotype
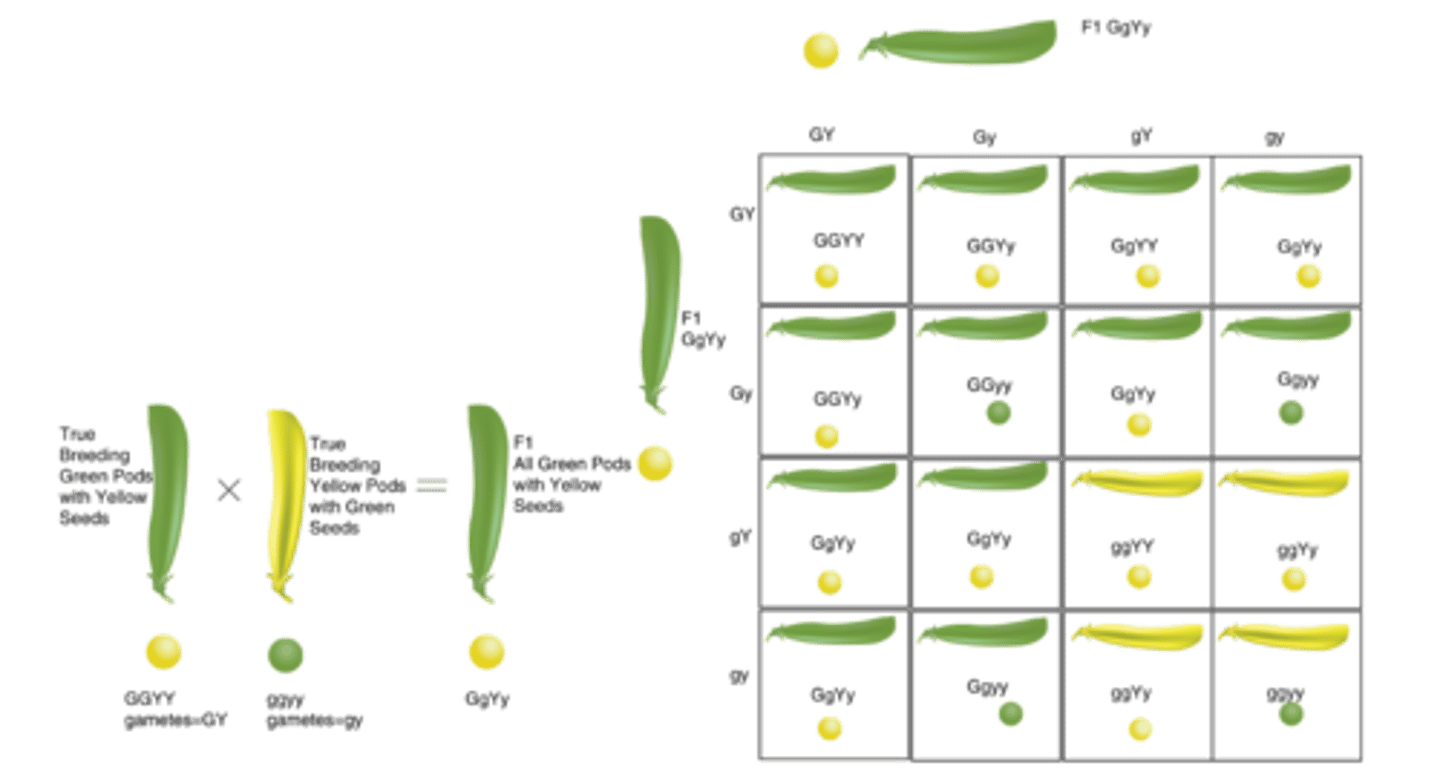
Dihybrid Cross
A cross that examines the inheritance of TWO specific traits;
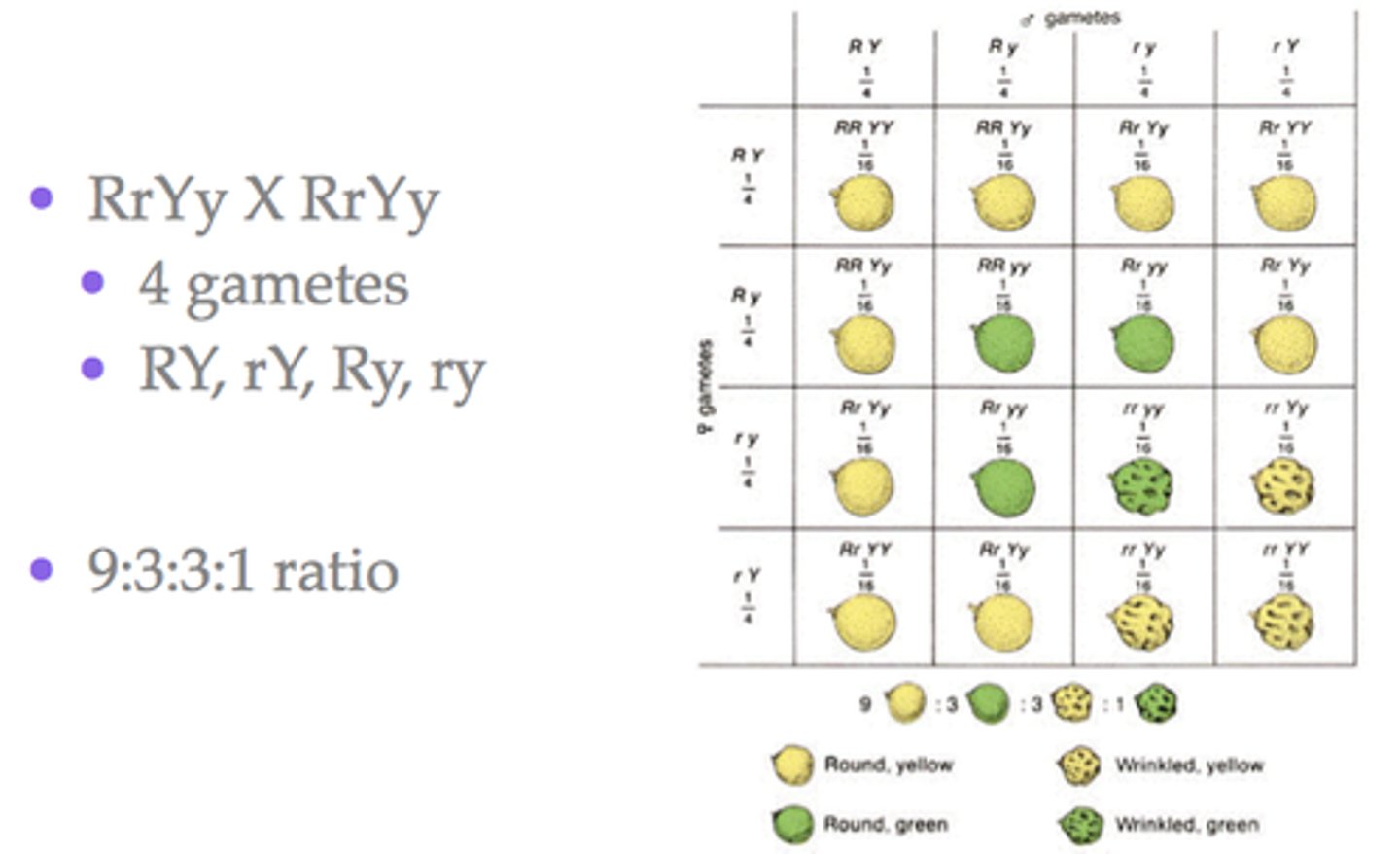
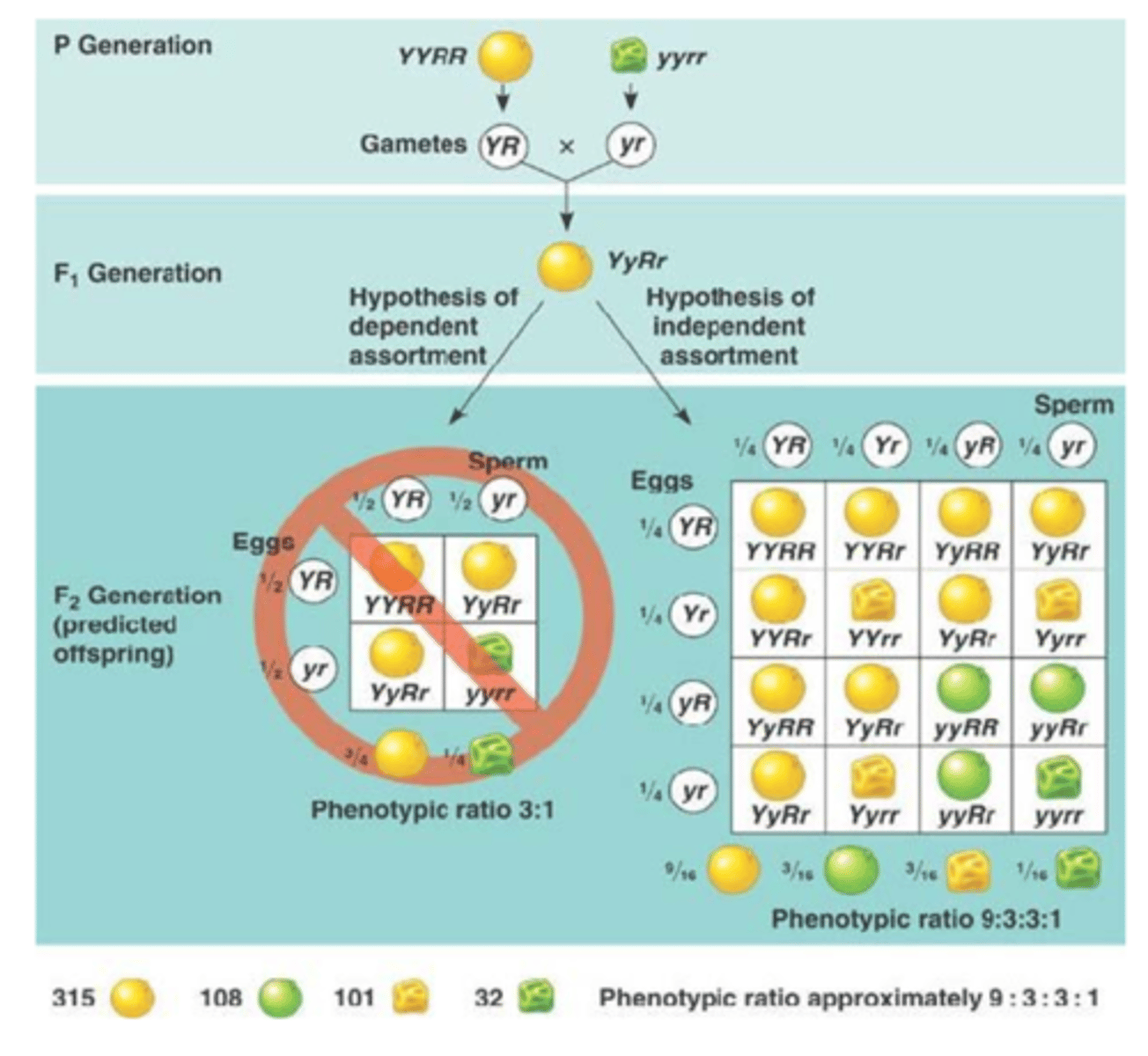
Mendel's Theory of Independent Assortment
Mendel hypothesized that two different traits like seed color (yellow/green) and seed shape (round/wrinkled) would be inherited independently of one another
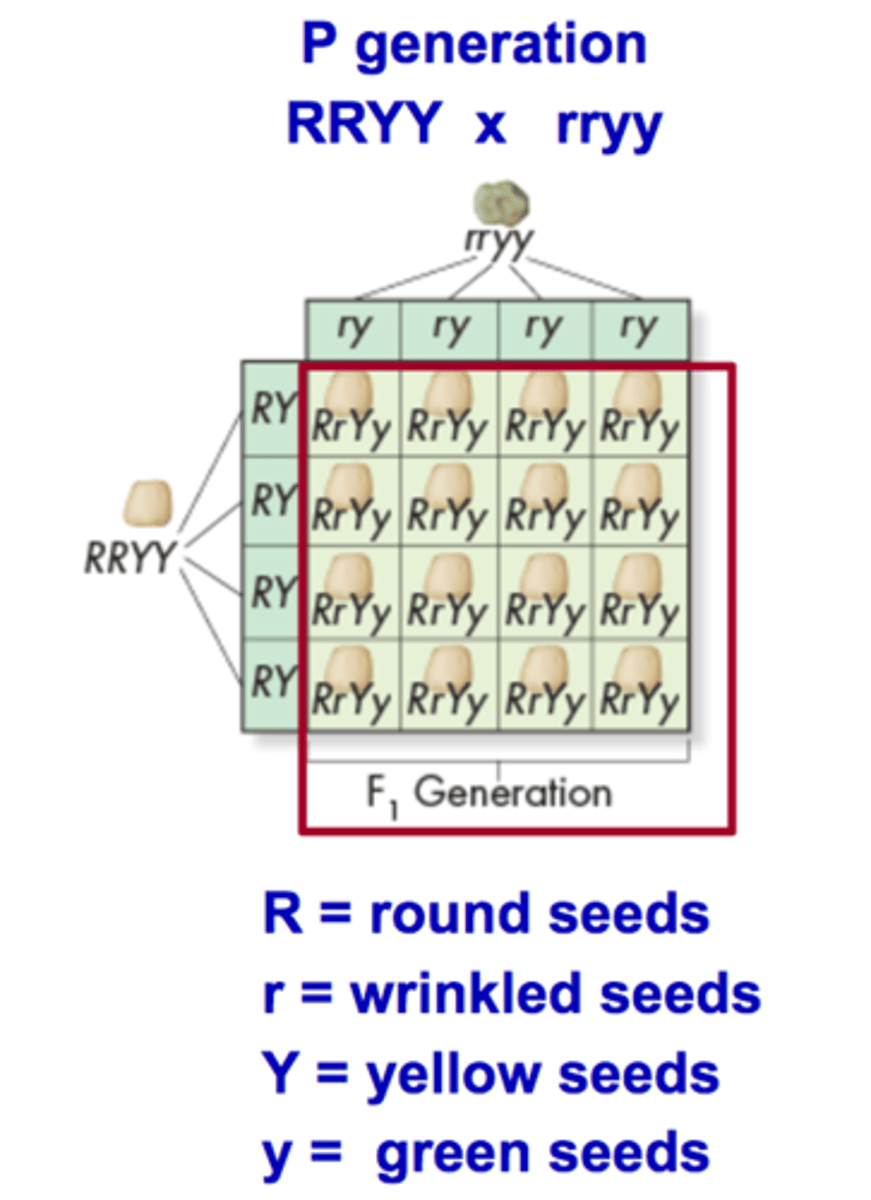
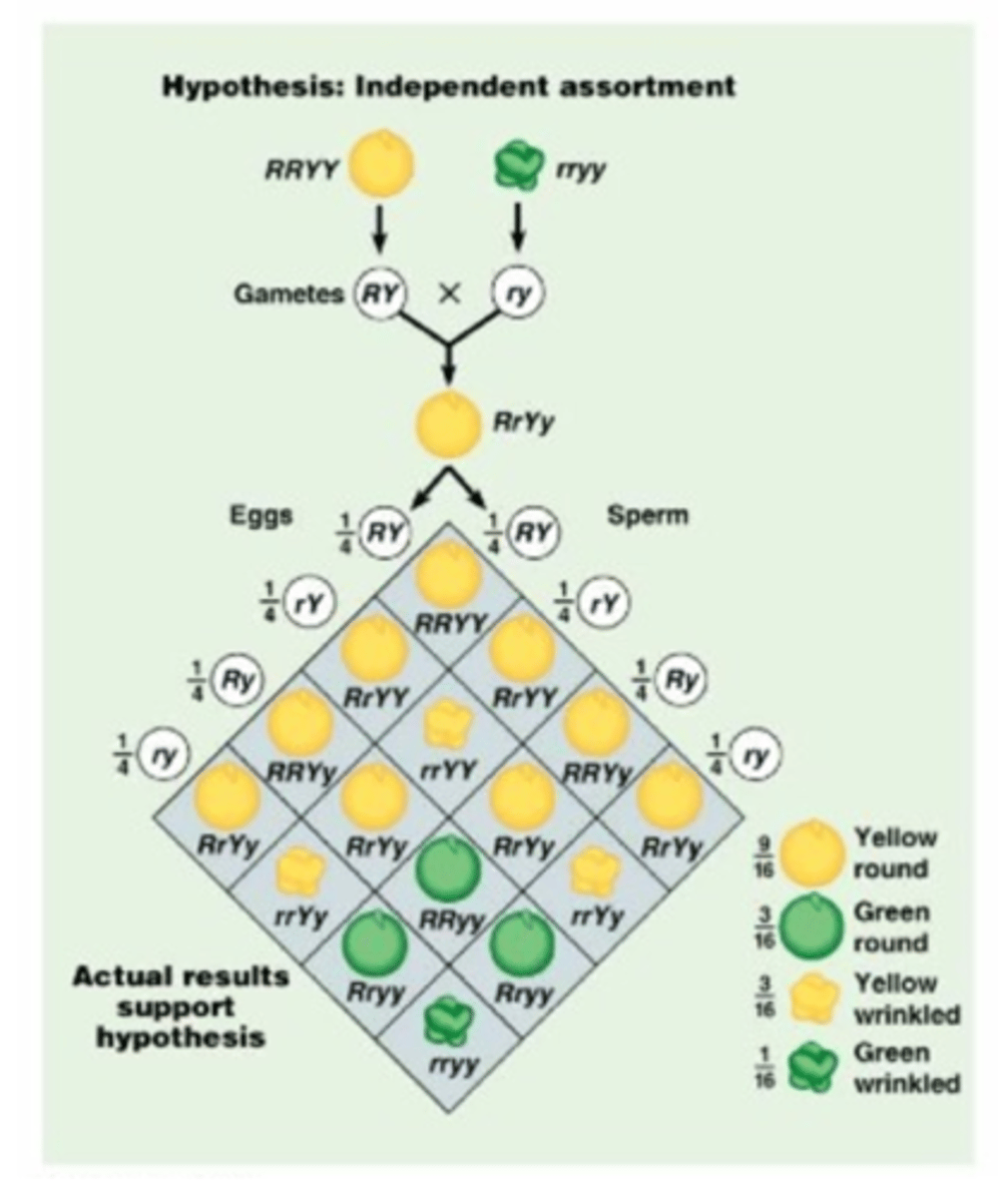
Mendel's Dihybrid Cross - F1 Results
In Mendel's dihybrid cross all of the F1 offspring produced round yellow peas. These results showed that the alleles for yellow and round peas are dominant over the alleles for green and wrinkled peas; the genotype of each F1 offspring was RrYy, heterozygous for both seed shape and seed color
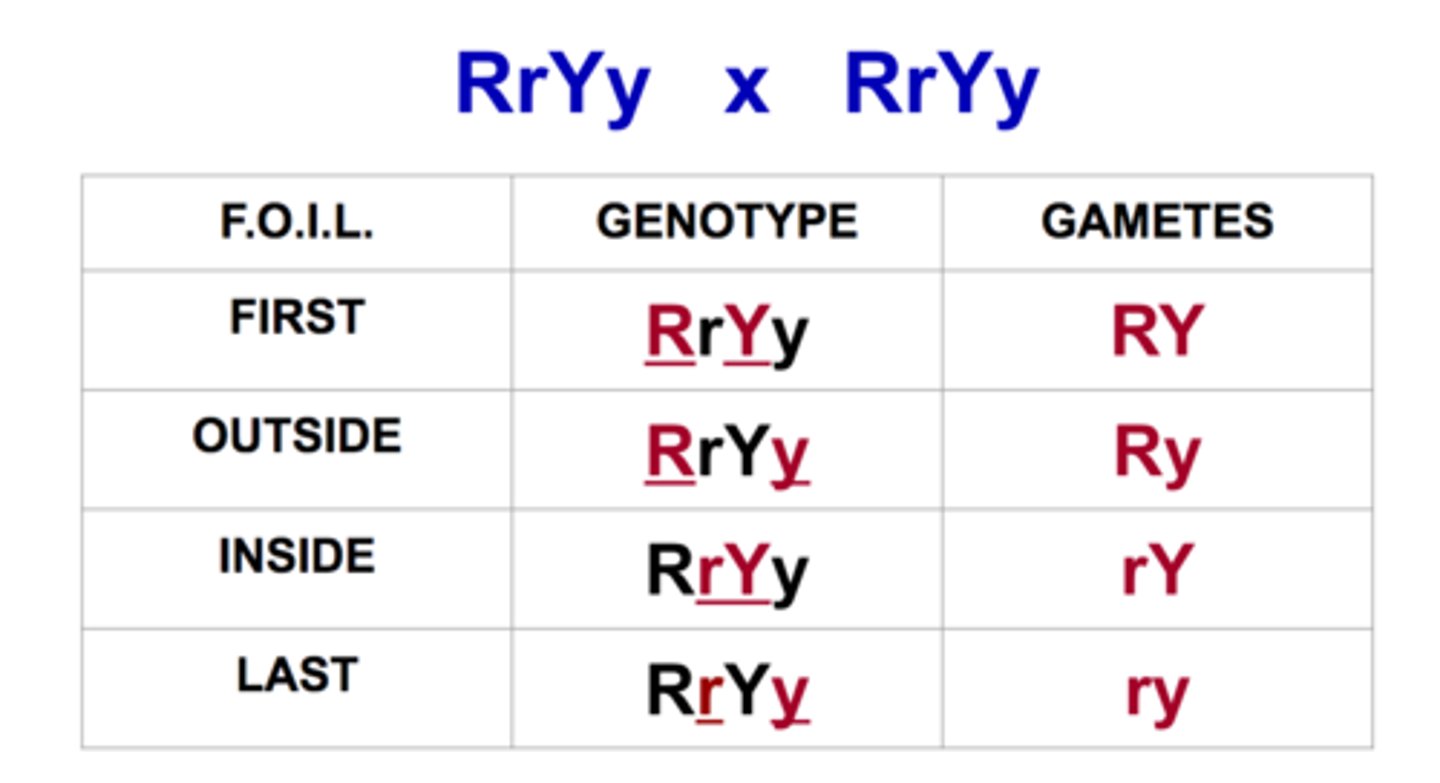
FOIL Method to Determine Possible Gametes
First, Outside, Inside, Last
Mendel's Dihybrid Cross - F2 Results
Mendel's experimental F2 results were very close to the 9:3:3:1 ratio that the Punnett square shown predicts
Law of Dominance
Alleles can be either dominant or recessive
Dominant factors mask recessive factors
Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles for different traits are distributed to gametes independently from one another (as long as alleles are located on different chromosomes or far apart)
Law of Segregation
Each pair of alleles is separated during gamete formation so that each gamete only has one form of the gene
Beyond Mendelian Genetics
Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive.
Many genes exist in several different forms, and are therefore said to have multiple alleles.
Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes.
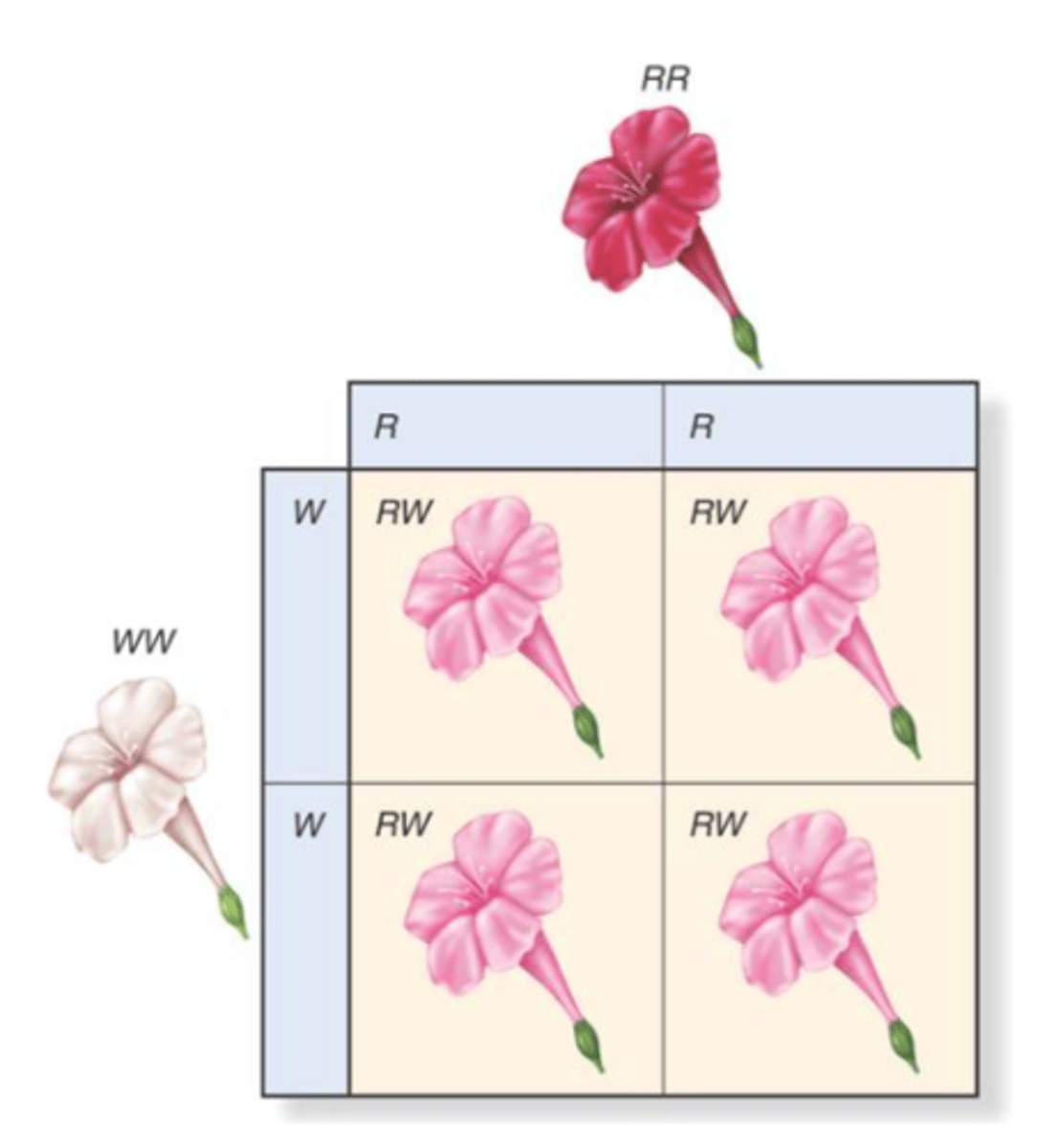
Incomplete Dominance (Description)
A type of inheritance in which a blending of the two homozygous phenotypes occurs when the genotype is heterozygous; results in three phenotypes (i.e. red, pink and white); alleles are represented by all capital letters
Incomplete Dominance (Examples)
Examples of this type of inheritance include:
Flower color (four o'clocks, snapdragons, carnations)
Sickle cell anemia in humans
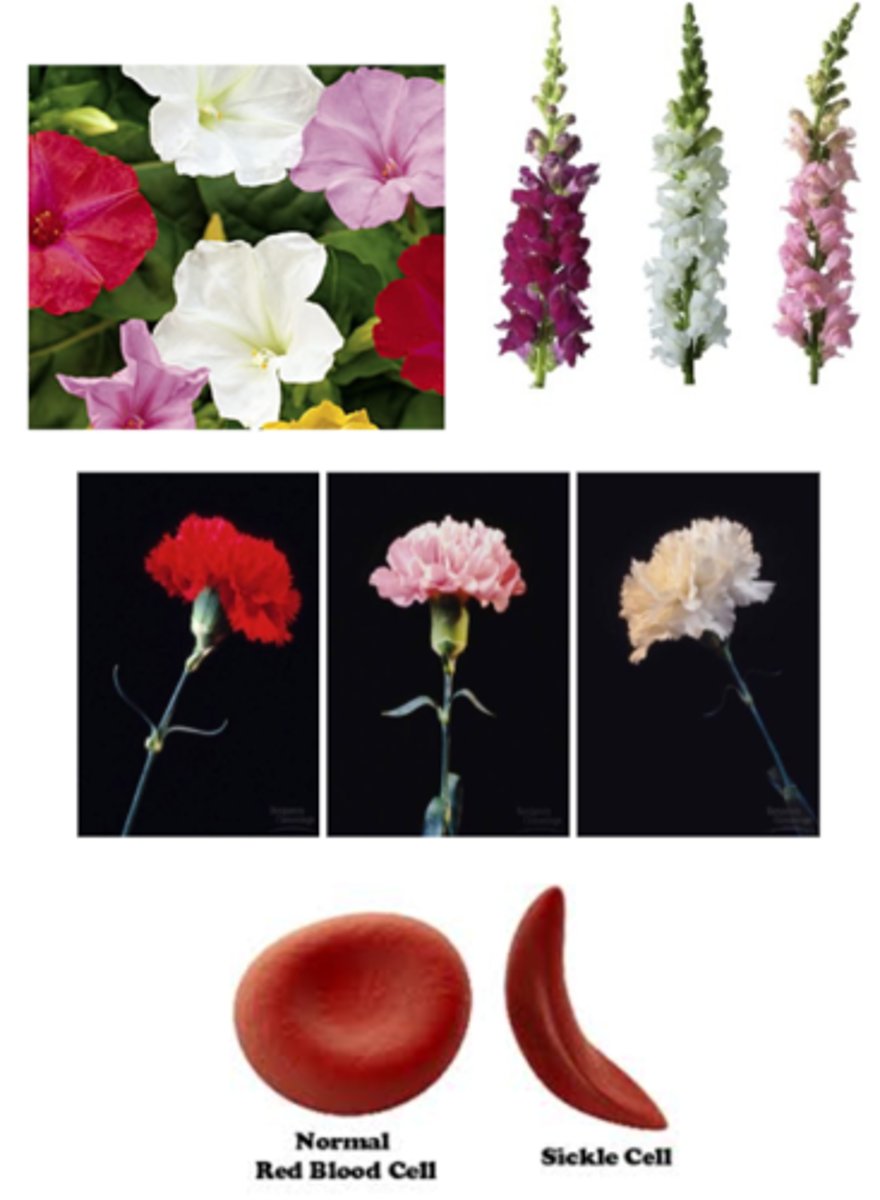

Codominance (Description)
A type of inheritance in which both traits are dominant so BOTH traits appear when the genotype is heterozygous; results in three phenotypes (i.e. red, red and white and white); alleles are represented by all capital letters
Codominance (Examples)
Examples of this type of inheritance include:
Checkered Chicken (BW)
Roan Cow (RW)
Red and White Rhododendron (RW)
Blood Type (AB)

Multiple Alleles (Description)
A gene that has more than two alleles (possible forms of the trait)
Multiple Alleles (Examples)
Examples of this type of inheritance include:
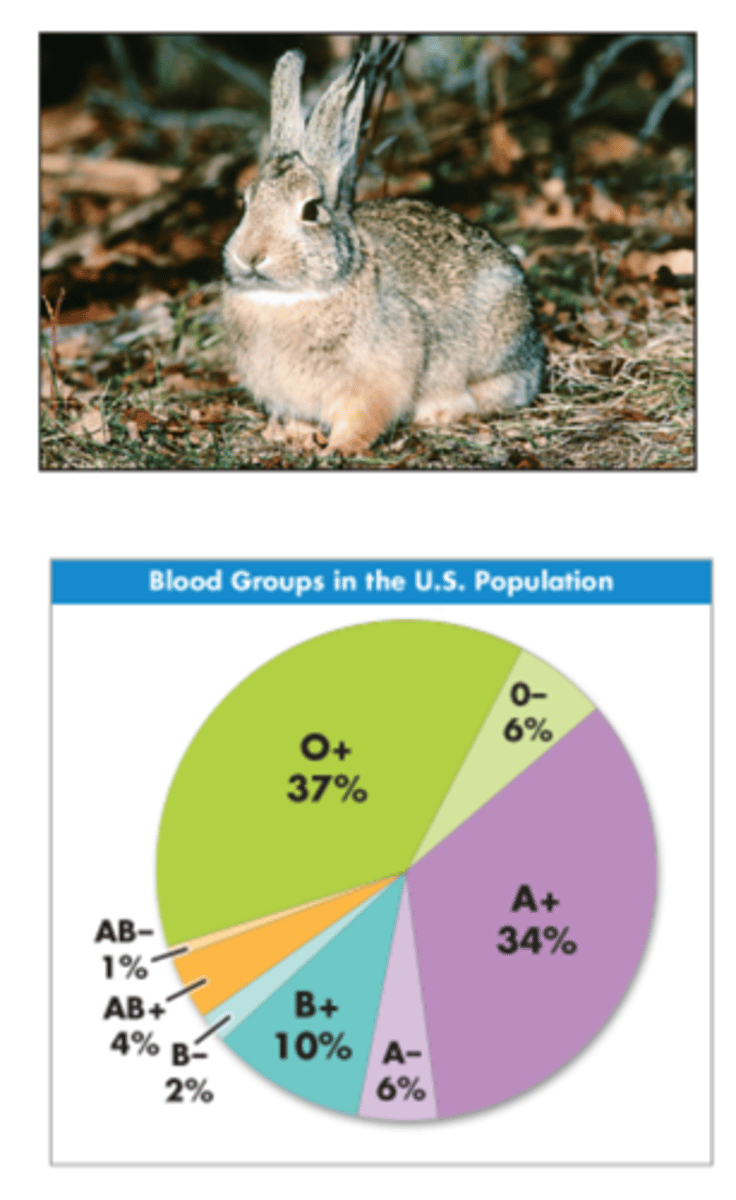
Rabbit fur (C-agouti, cch - chinchilla, ch - himalayan and c - colorless)
Blood type (Type A, B, AB, O)
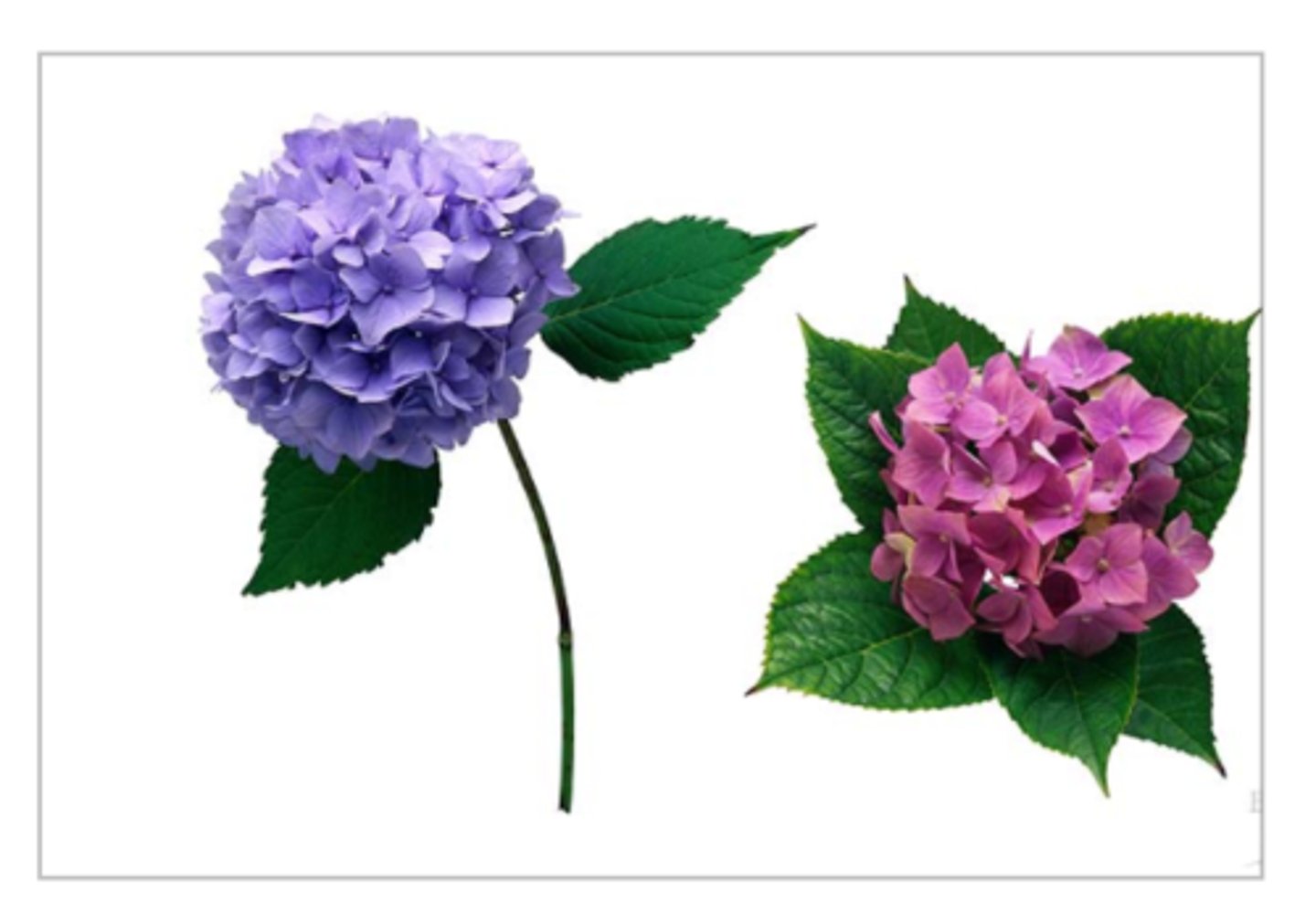
Genes & the Environment (Description)
Environmental conditions can affect gene expression and influence genetically determined traits
Genes & the Environment (Examples)
The pH of the soil will change the color of hydrangea flowers from blue to pink; Western White Butterfly wing color changes depending upon when they hatch

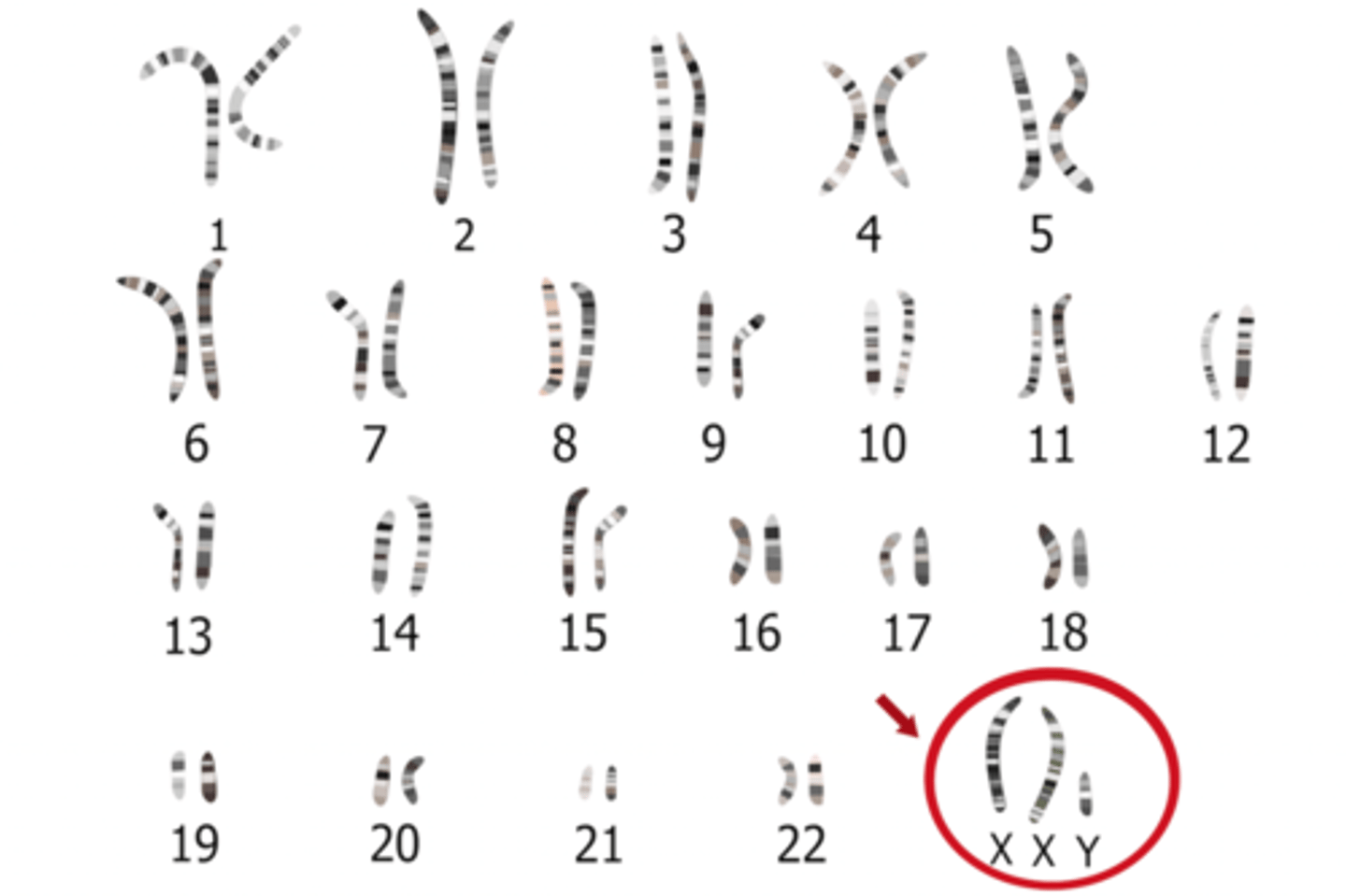
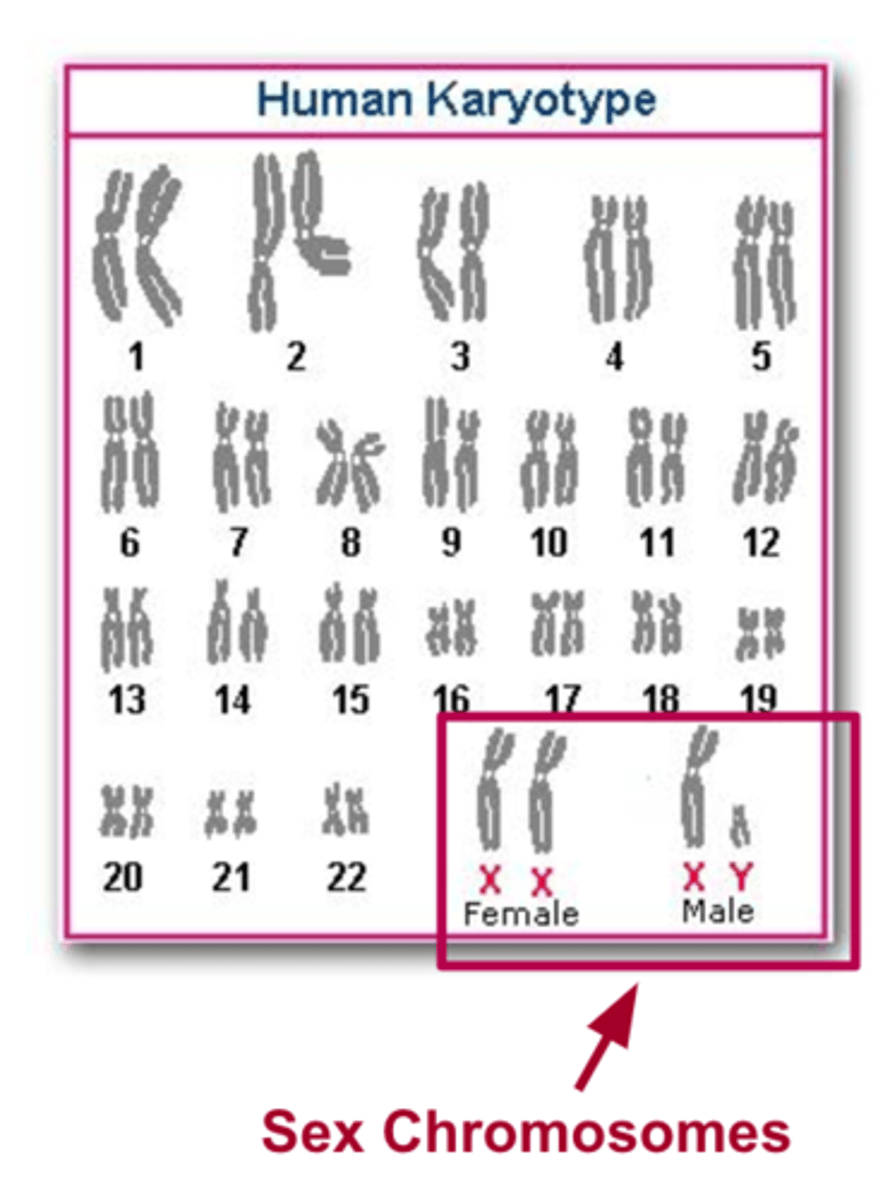
Karyotype
A photograph in which the pairs of homologous chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size
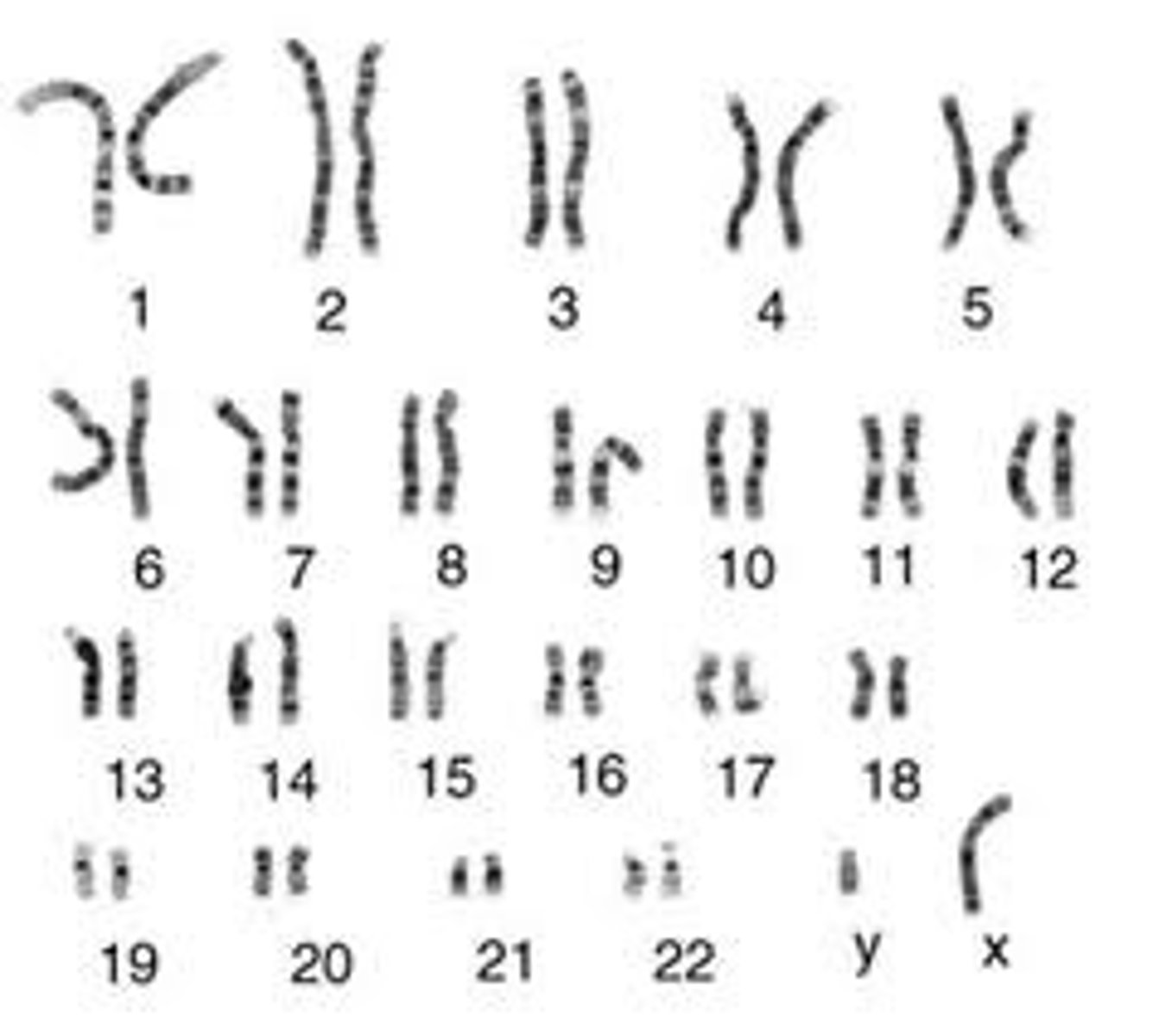
Sex chromosomes
The pair of chromosomes (X & Y) responsible for determining the sex of an individual
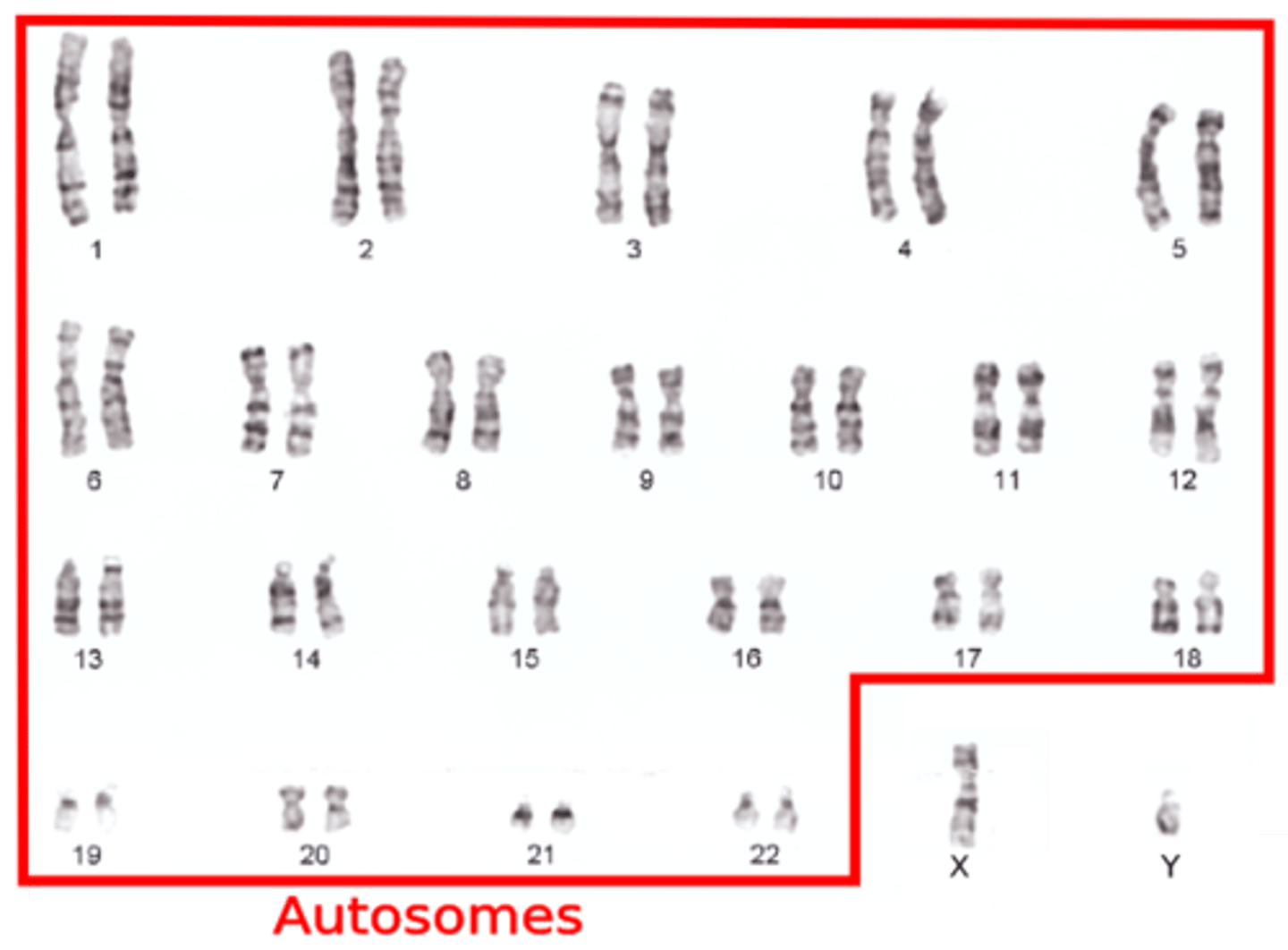
Autosomes
All chromosomes, except the sex chromosomes, that occur in pairs in all somatic cells
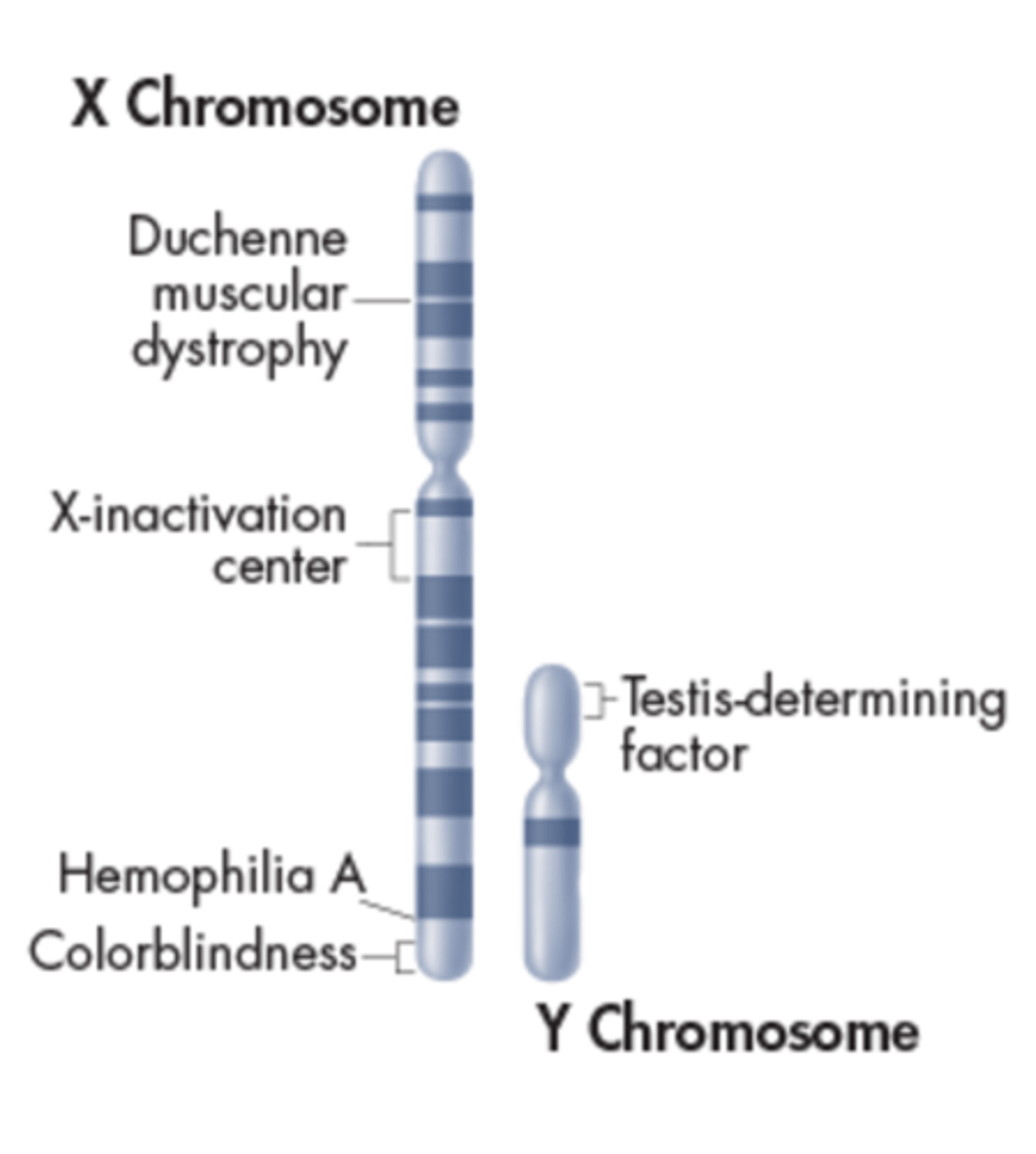
X and Y Chromosomes
More than 1200 genes are found on the X chromosome, some of which are shown.
The human Y chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome and contains only about 140 genes, most of which are associated with male sex determination and sperm development.
Human Pedigrees
A chart used to analyze pattern of inheritance that shows relationship in a family
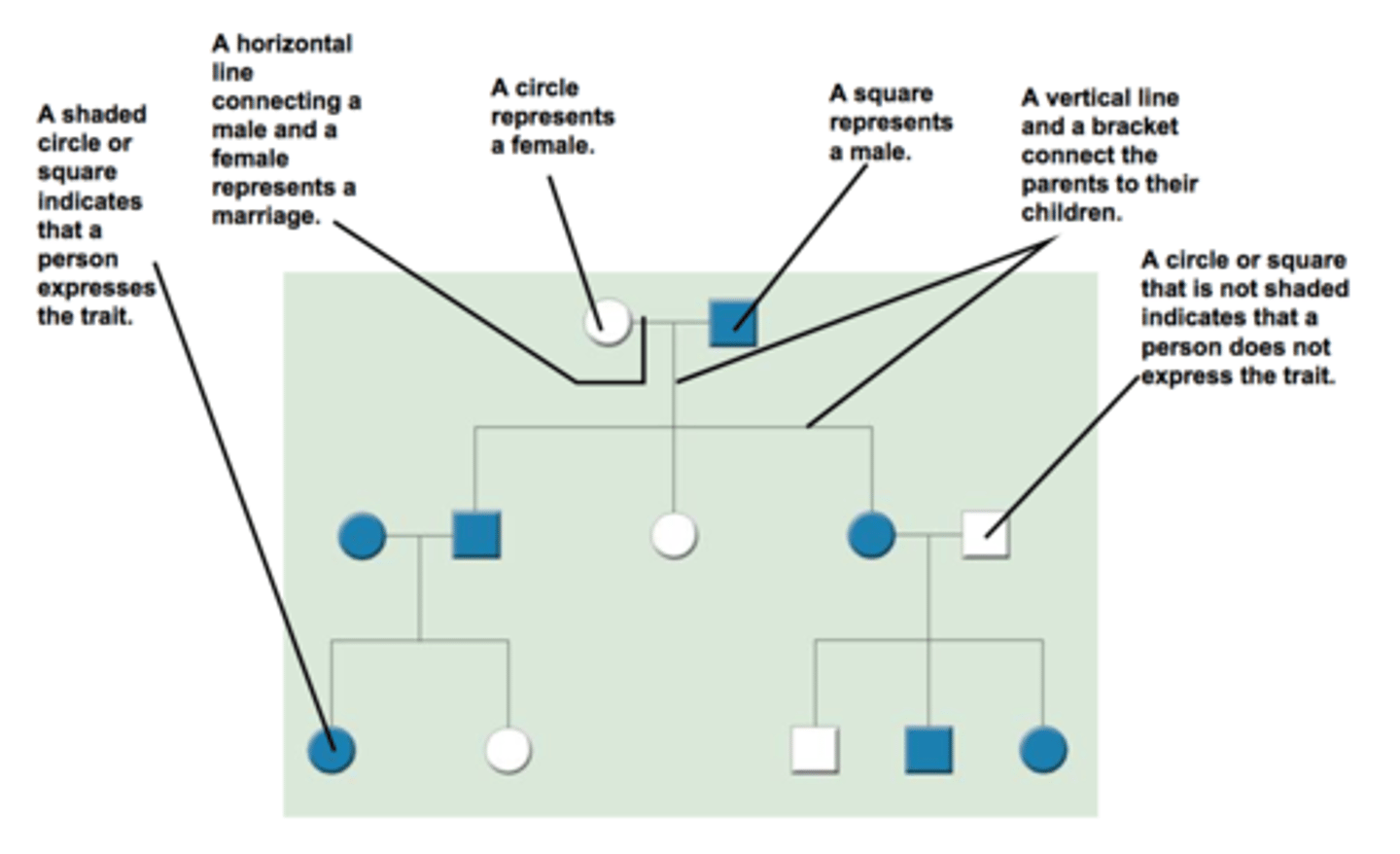
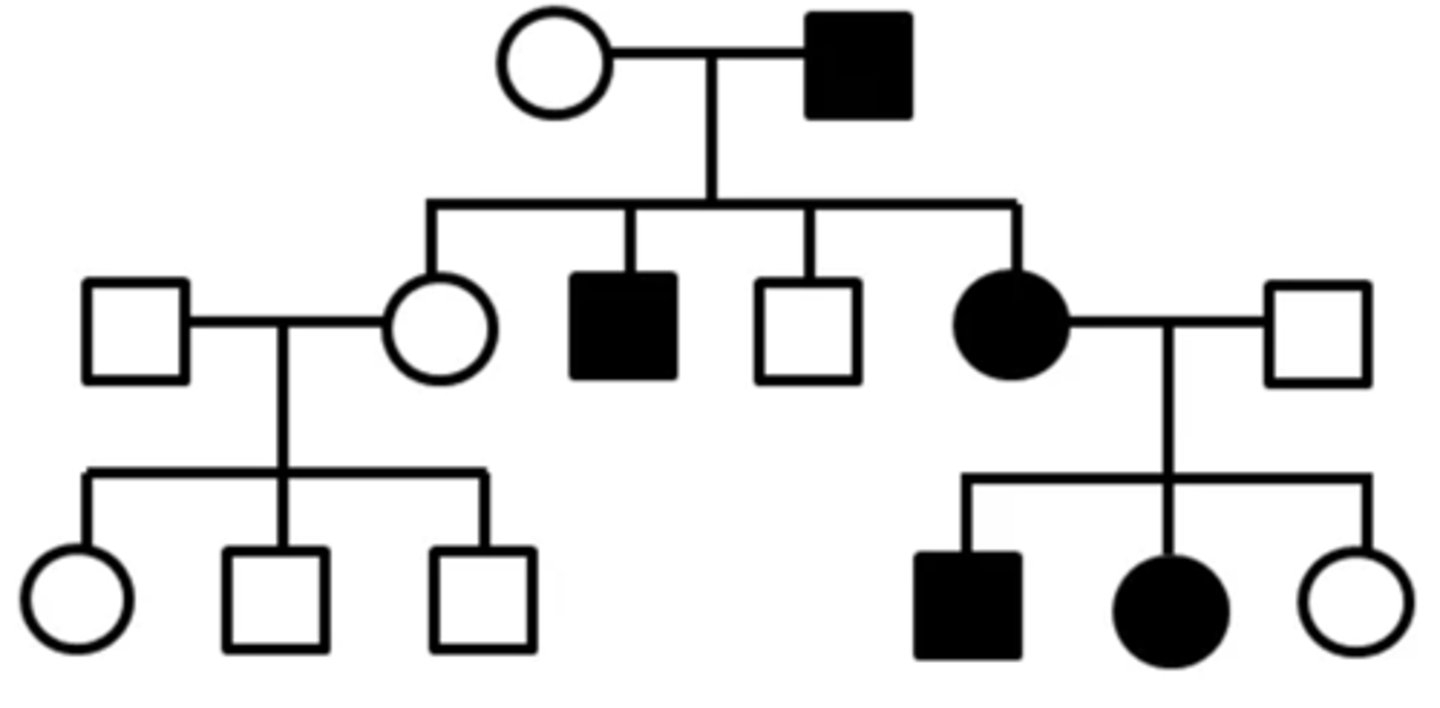
Common Pedigree Patterns (Autosomal Dominant)
One parent is affected; trait does not skip a generation; only half the children are affected; male and female are affected equally
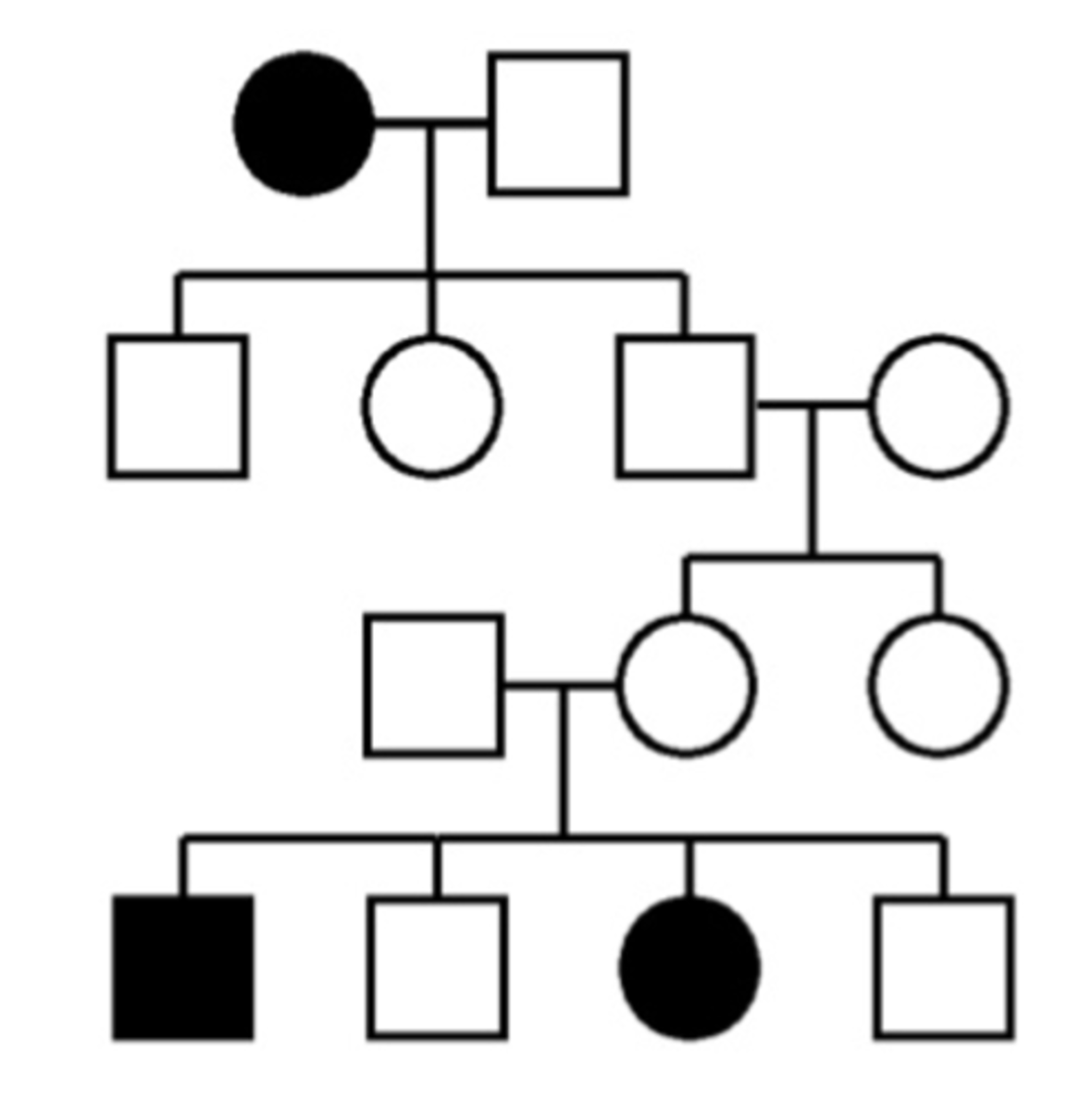
Common Pedigree Patterns (Autosomal Recessive)
Both parents must be heterozygous or homozygous recessive; trait may skip generations; both males and females are affected equally
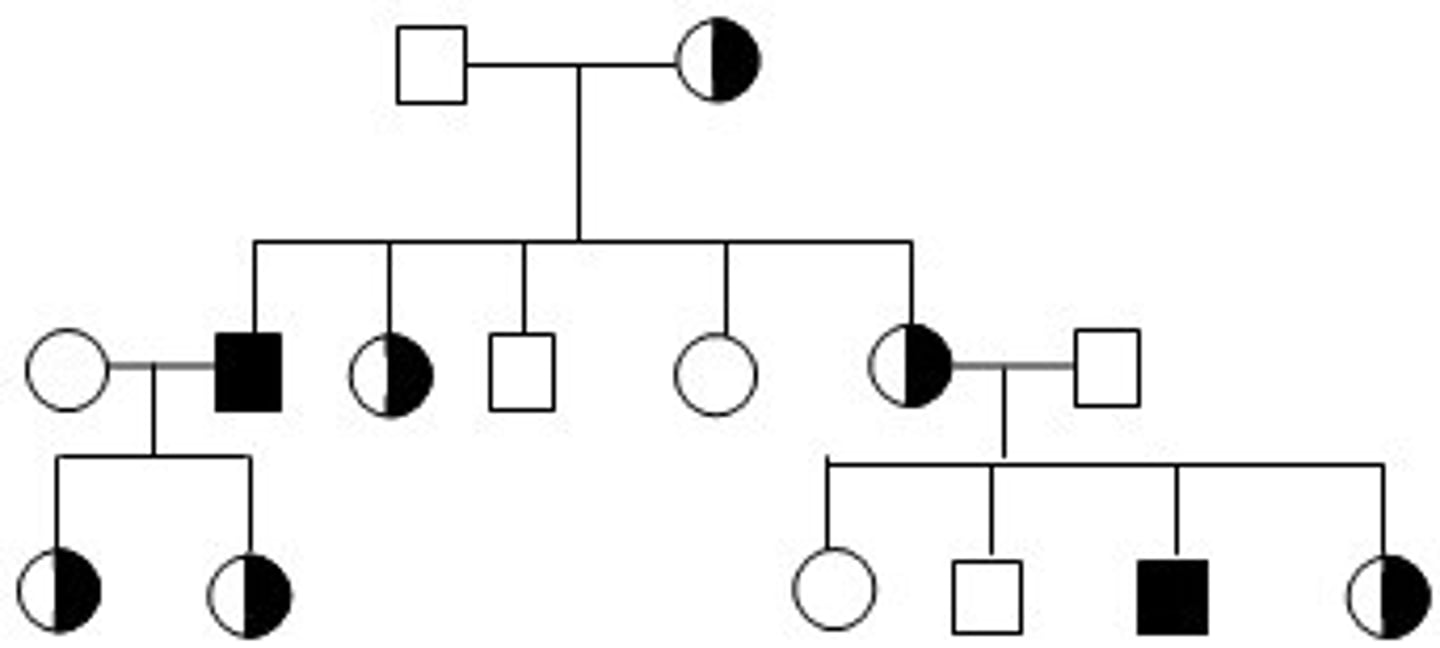
Common Pedigree Patterns (X-linked Recessive Traits)
There is NO father to son transmission; trait skips generations; there are more males than females affected
Simple Dominance in Humans (Examples)
Examples include:
Widow's peak, free earlobe, longer second toe, freckles, dimples. hair color, Rh factor
Codominance & Multiple Alleles in Humans (Examples)
ABO blood group, determined by a gene with three alleles: IA, IB, and i. These alleles are also often written as A, B and O. However AB are codominant while O is a recessive allele.
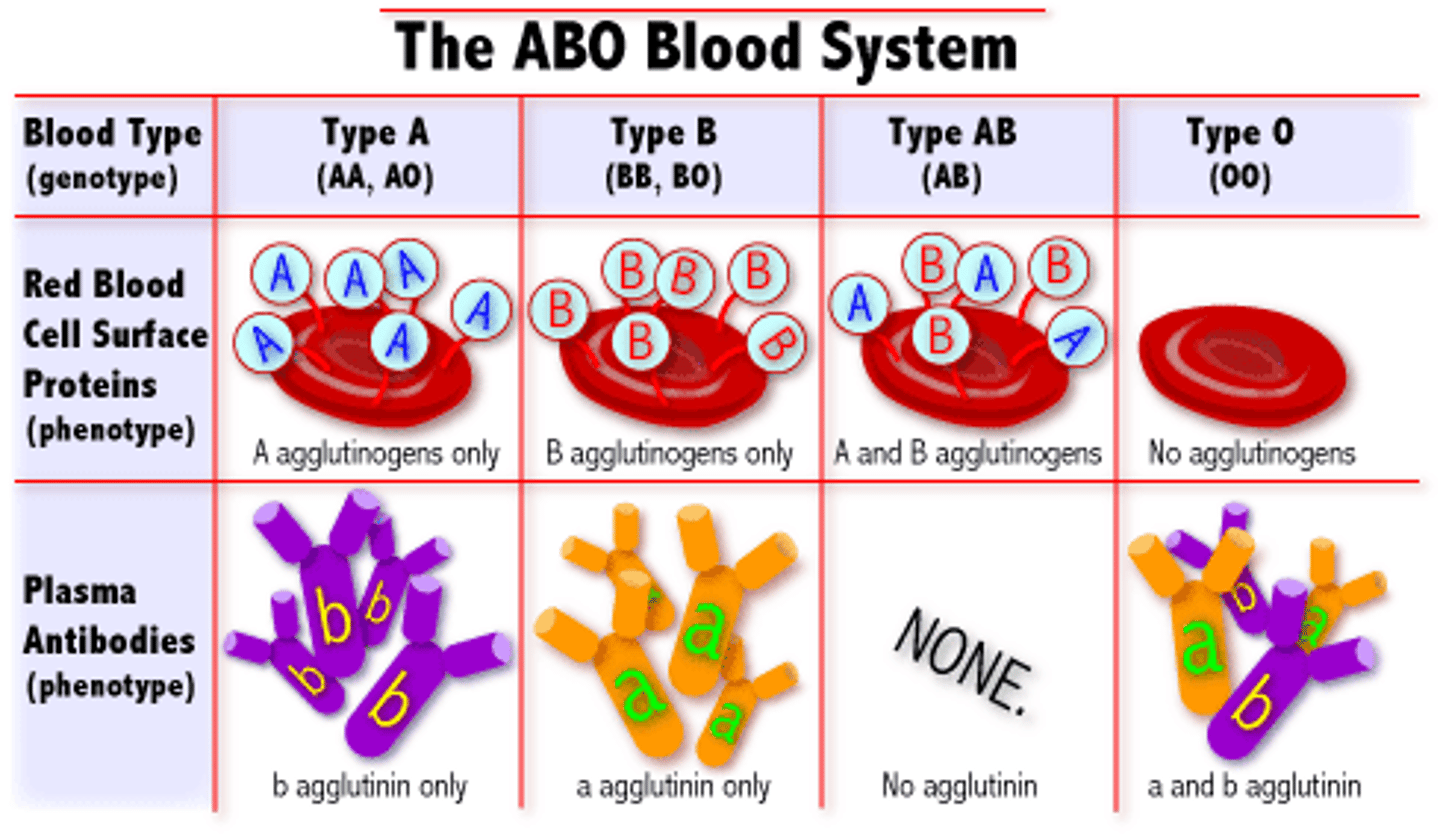
Blood Types
Blood type indicates what types of proteins (called antigens) are located on the surface of the red blood cell.
Type A blood has type A antigens
Type B blood has type B antigens
Type AB blood has A & B antigens
Type O blood has NO antigens
Antigen
Proteins found on the surface of a cell that identify the cell as self or foreign
Antibody
A protein produced in response to an antigen that helps to destroy any foreign antigen
Blood Transfusion
Transfer of blood from one person to another; must ensure blood is compatible to prevent a transfusion reaction
Agglutination
A process by which cells or other particles adhere to each other to form clumps
Blood Transfusions Reactions
People have negative reactions to blood transfusions because some people's blood contains antibodies that react with specific blood cell antigens
Universal Donor
Type O- blood
Universal Recipient
Type AB+ blood
Person with Rh positive blood
Can receive blood from either Rh+ or Rh- donor
Person with Rh negative blood
Can only receive Rh- blood
Two most common blood types
A+ and O+ blood
Sex-linked Traits (Description)
A gene located on either the X or Y chromosomes that determine sex of an individual
Sex-linked Traits in Humans (Examples)
Examples include:
X-linked dominant traits - Klinefelter's Disorders
X-linked recessive traits - Hemophilia & Colorblindness
Hairy ears - Y-linked traits
X-linked Traits
Genes are found on the X chromosome so can be passed to the offspring by either the mother (XX) or the father (XY).
Y-linked Traits
Genes are found on the Y-chromosome so can only be passed to offspring by the father (XY)
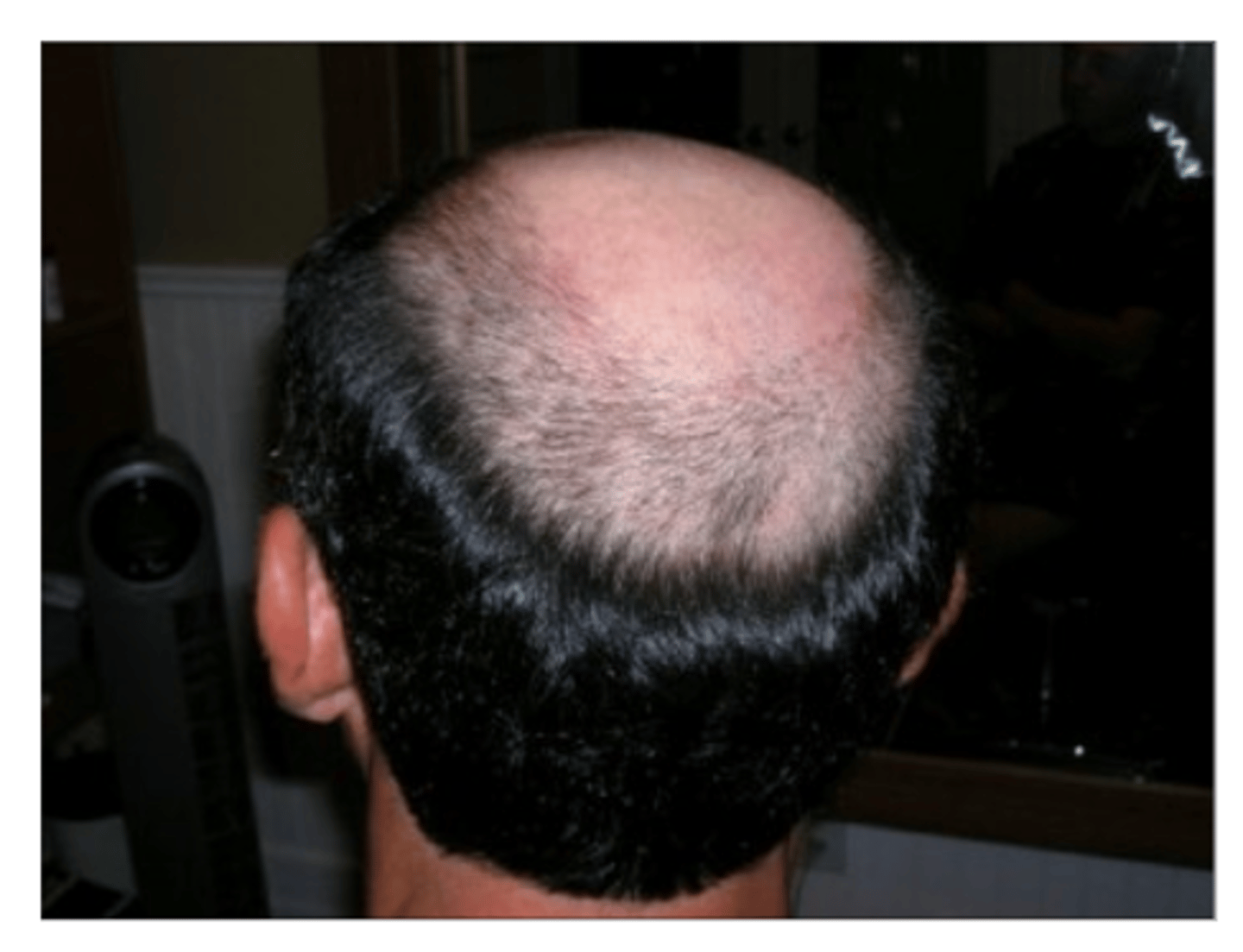
Sex-Influenced Traits in Humans (Description)
Male or female hormones influence the expression of traits, resulting in different phenotypes even when the same genotype is shared
Sex-Influenced Traits in Humans (Examples)
Baldness is a dominant trait in males and females must receive two recessive alleles to get the trait
In the presence of high levels of testosterone the gene is expressed so more men than women experience
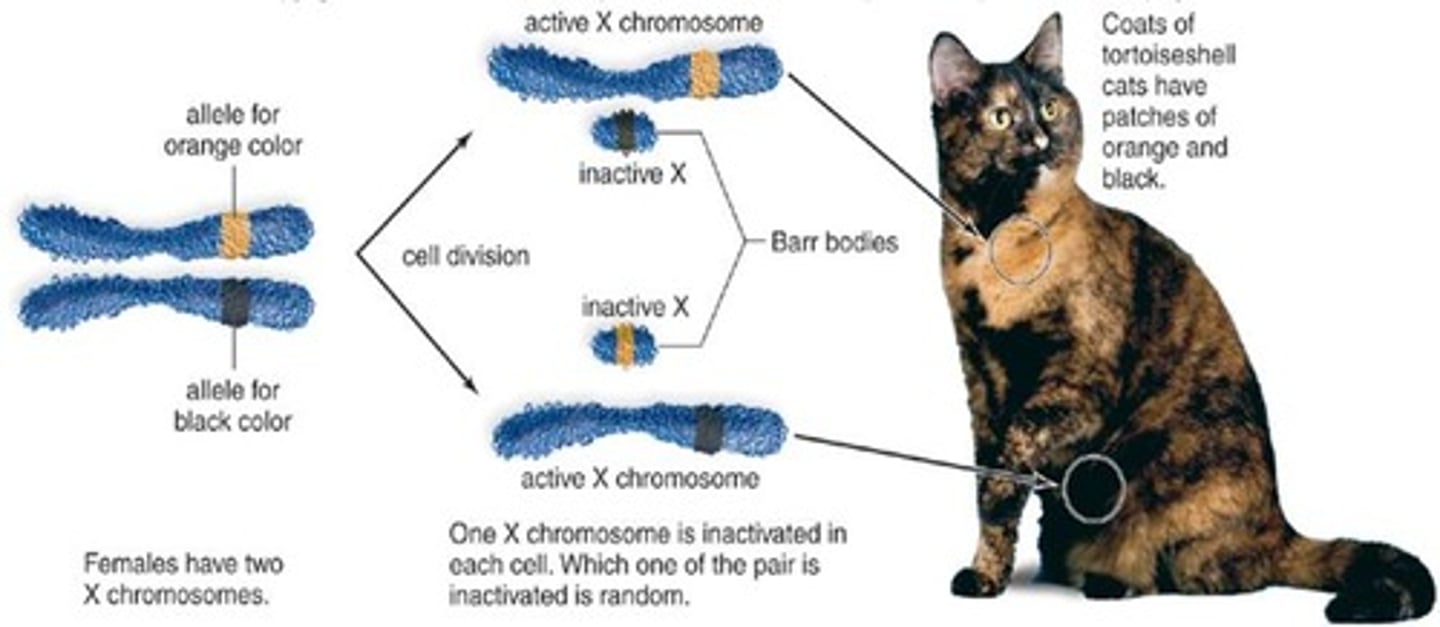
X-Chromosome Inactivation (Description)
In female cells, most of the genes in one of the X chromosomes are randomly switched off, forming a dense region in the nucleus known as a Barr body.
Barr bodies are generally not found in males because their single X chromosome is still active.
X-Chromosome Inactivation (Example)
One X chromosome may have an allele for orange spots and the other X chromosome may have an allele for black spots.
In cells in some parts of the body, one X chromosome is switched off. In other parts of the body, the other X chromosome is switched off. As a result, the cat's fur has a mixture of orange and black spots.
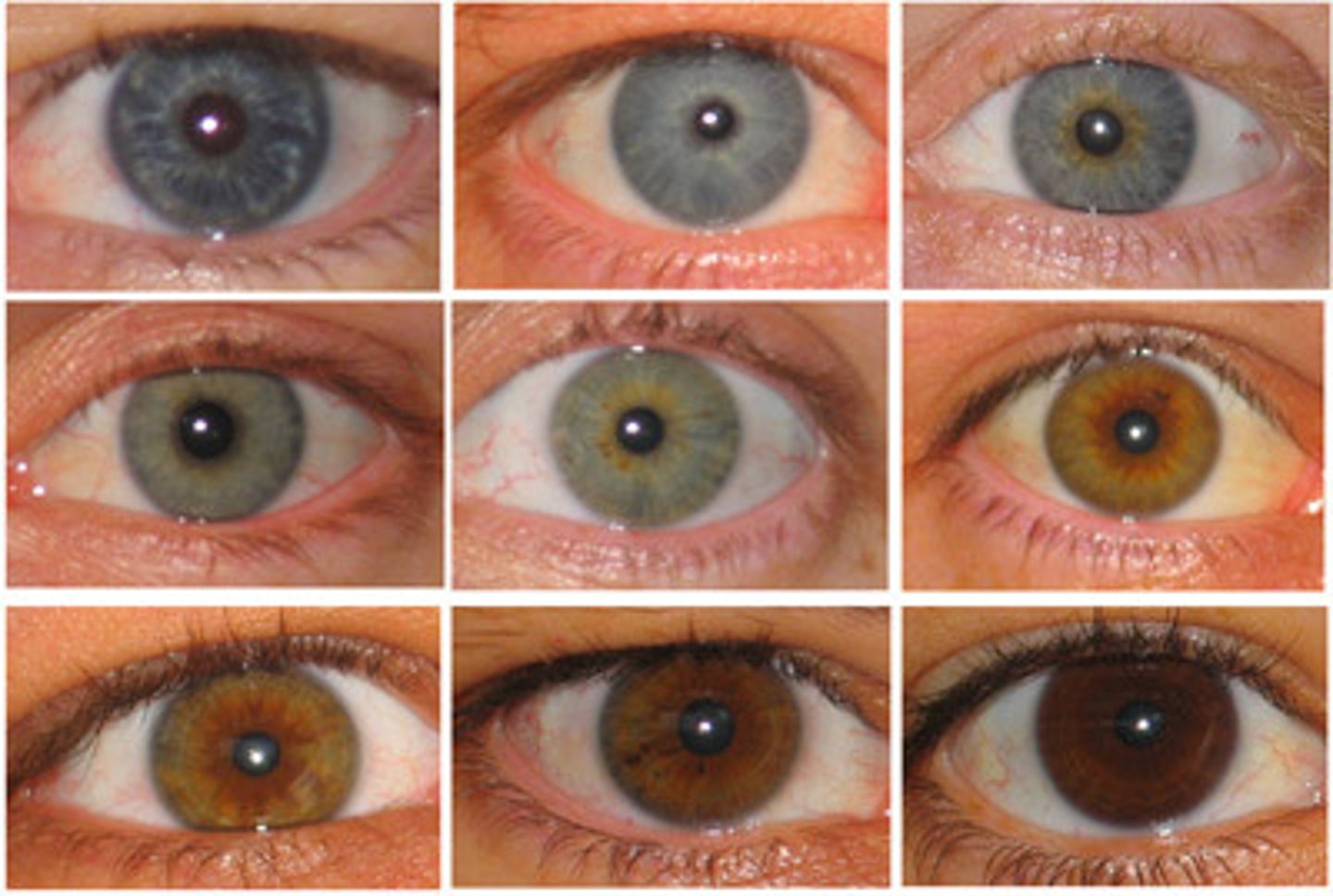
Polygenic trait (Description)
Traits controlled by two or more genes
Polygenic trait (Examples)
Examples include:
skin color, eye color, height
Single Allele Dominant Disorders (Examples)
Huntington Disease
Dwarfism
Cataracts
Polydactyly
Single Allele Recessive Disorders (Examples)
Albinism
Cystic Fibrosis
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Hereditary Deafness
X-linked Disorders (Examples)
Colorblindness
Hemophilia
Muscular dystrophy
Scaly skin
Nondisjunction (Examples)
Down Syndrome
- Trisomy-21
Klinefelter's Syndrome
- XXY
Nondisjunction (Description)
The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis
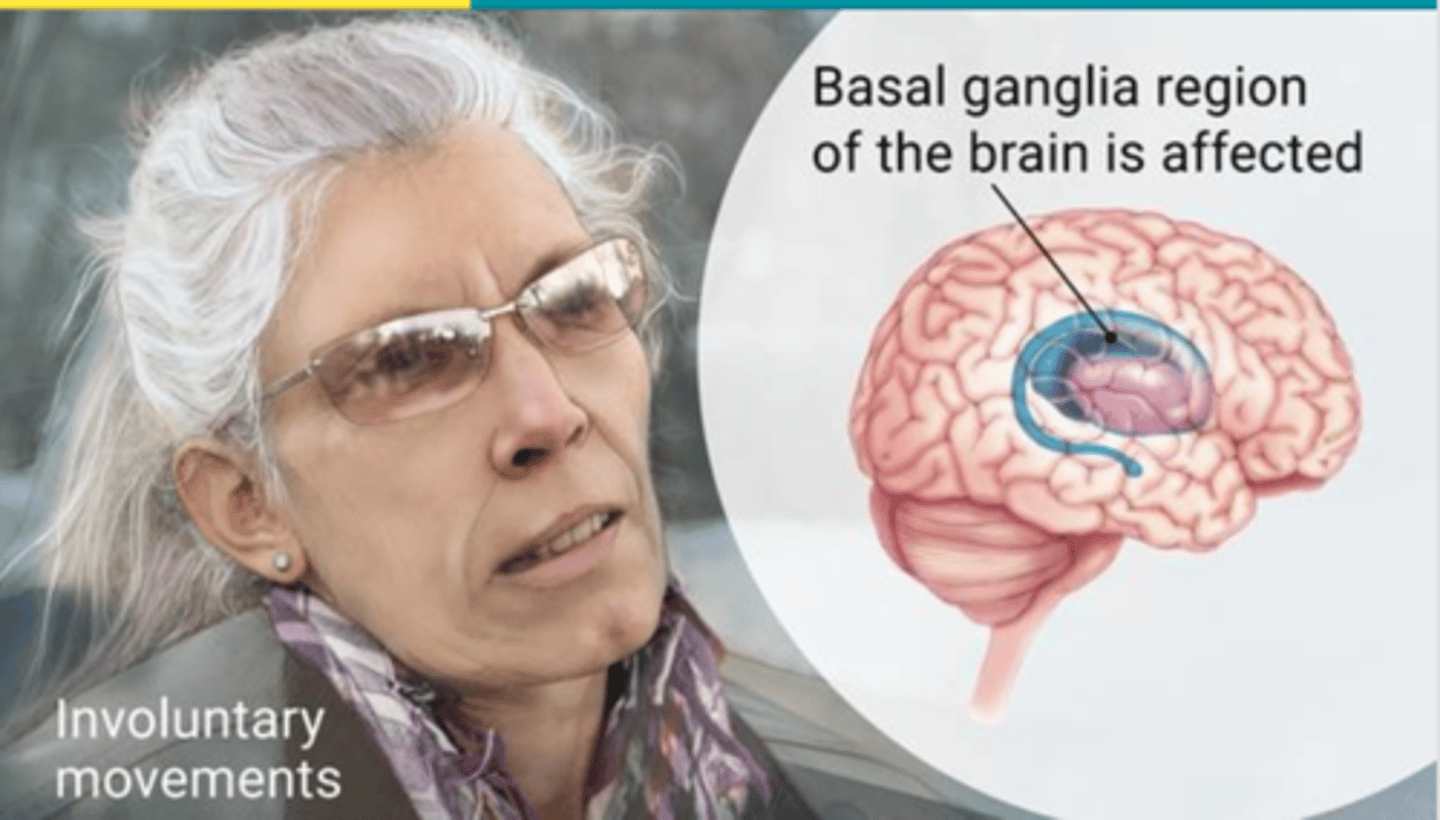
Huntington's Disease
A human genetic disease caused by a dominant allele that causes the progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain; those affected develop signs and symptoms in their 30s or 40s. But the disease may emerge earlier or later in life; treat symptoms but no cure
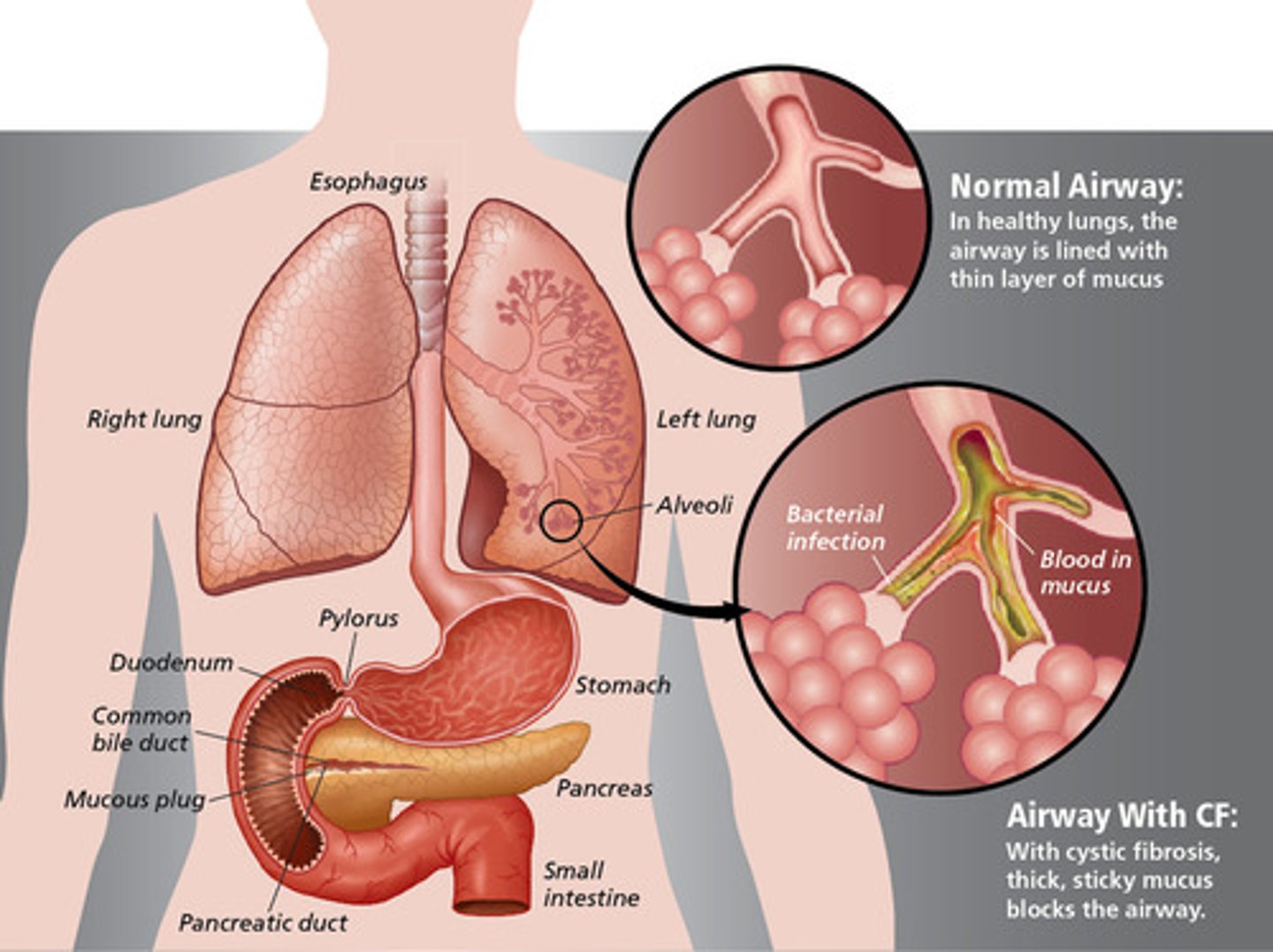
Cystic fibrosis
A human genetic disease that is caused by mutations in a recessive allele; most cases result from the deletion of just three bases in the gene for a protein called CFTR that prevents the cell membrane from transporting chloride ions (Cl-); causes a thick, sticky buildup of mucus in the lungs, pancreas, and other organs. In the lungs, the mucus clogs the airways and traps bacteria leading to infections, extensive lung damage, and eventually, respiratory failure. In the pancreas, the mucus prevents the release of digestive enzymes that allow the body to break down food and absorb vital nutrients; common among people of European descent
Sickle Cell Anemia
A common genetic disorder caused by an incomplete dominant trait; commonly found in African Americans and characterized by the bent and twisted shape of the red blood cells
Alleles are typically represented as:
N = normal
S = Sickle Cell anemia
People who are homozygous for sickle cell allele (SS) get sickle cell anemia while people who heterozygous (NS) for the sickle cell allele are generally healthy and they are resistant to malaria.

Cystic fibrosis (Genetic Advantage)
Individuals that are heterozygous for this genetic disorder are protected from the typhoid bacterium
Sickle Cell Anemia (Genetic Advantage)
Individuals that are heterozygous for this genetic disorder are protected from malaria
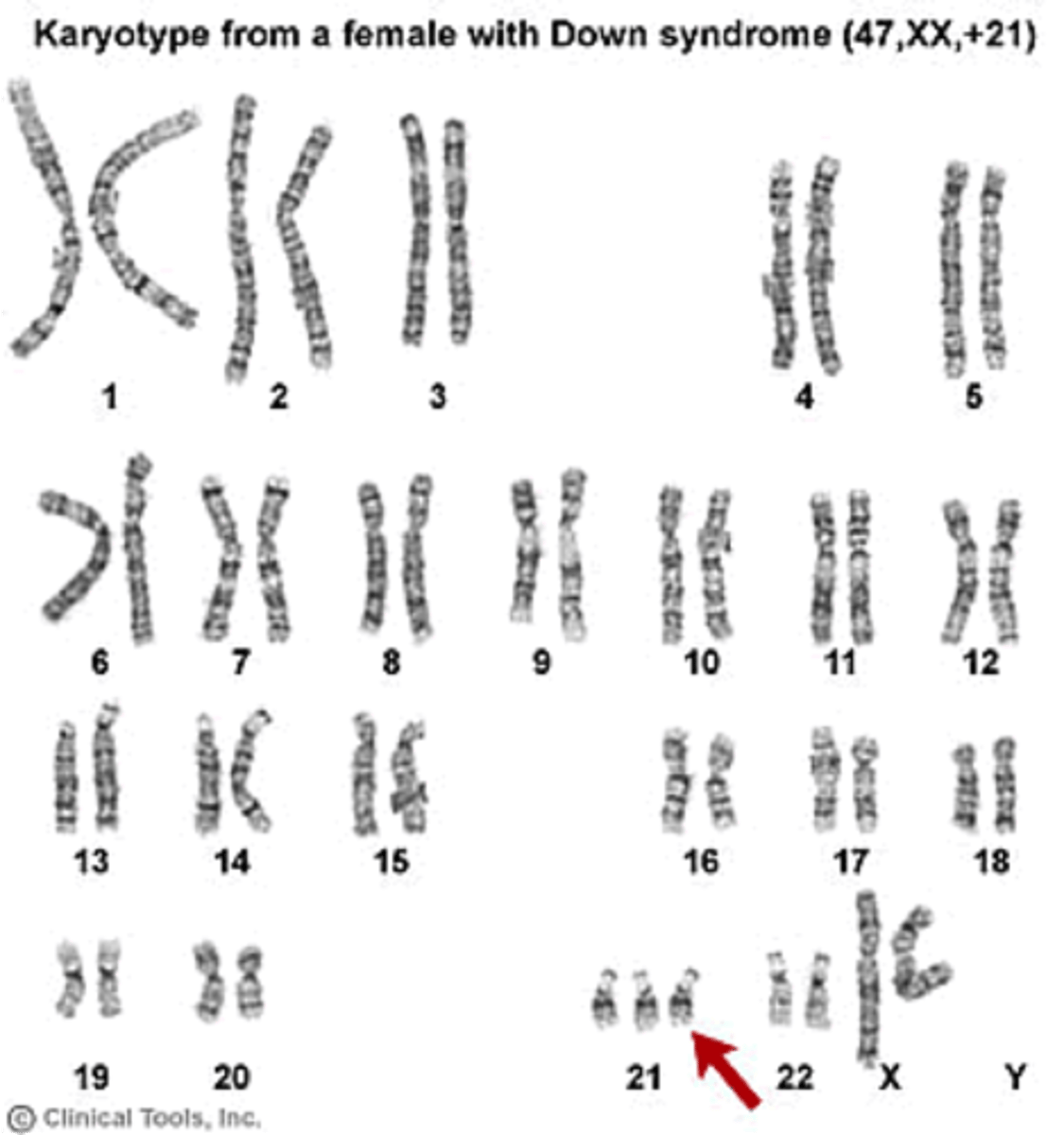
Down's Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by an extra copy (complete or partial) of chromosome 21; causes developmental delays and physical disabilities
Klinefelter Disease
A genetic disorder caused when a male inherits an extra X chromosome; results in sterility