Ch.6+7; Skeletal Tissue + Axial Skeleton
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
now complete with the harder quizziz questions!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Bone Functions:
support
hard framework
hematopoiesis
mineral storage (i.e: calcium)
energy metabolism (osteoblasts secrete osteocytes that influence blood sugar levels)
Spongy vs Compact Bone
5 major differences in total
What are the ends of the long bone called? What about the middle part?
Proxiamal/Distal Epiphyses and Diaphysis
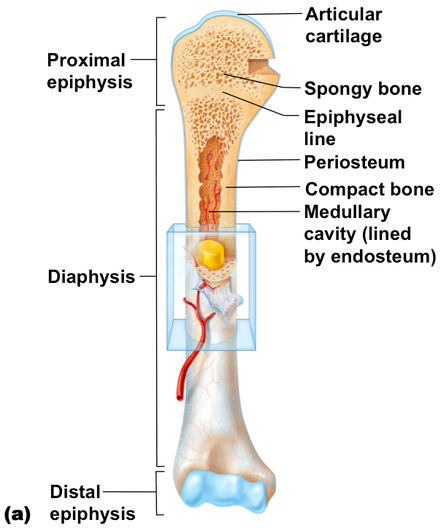
What does the medullary cavity hold, and what do they do?
Yellow: lies in dormant and only produces RBC in emergency
Red: hematopoiesis
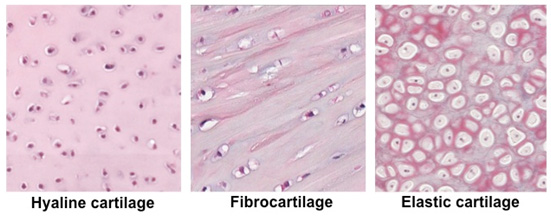
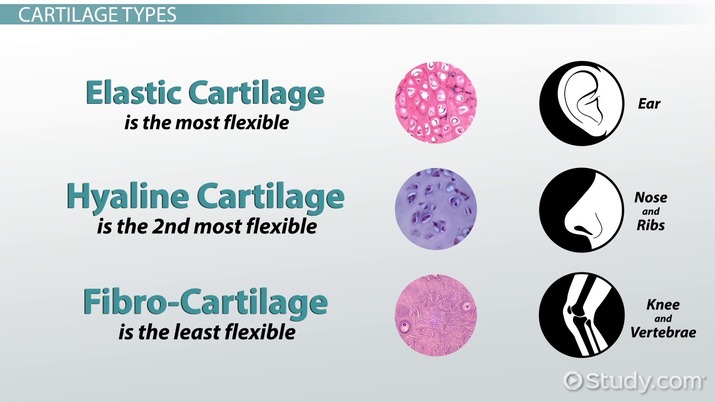
Compare the structure of the three kinds of cartilage
Hyaline: smooth and glassy appearance
Fibrocartilage: large bundles of cartilage that run linearly
Elastic: dense-network of elastic fibers, with dark-stained matrix
Compare the functions of the three kinds of cartilage
Hyaline: supports/reinforces structures + resists compression
Fibrocartilage: absorbs shock
Elastic: recoils
Compare the locations of three kinds of cartilages
Hyaline: nose and trachea
Fibrocartilage: intervertebral disc and pubic symphysis
Elastic: external ear and epiglottis
Bone Tissue Function:
bone support/protection
levers for muscles to act on
stores calcium/minerals/fat inside marrow inside for hematopoiesis
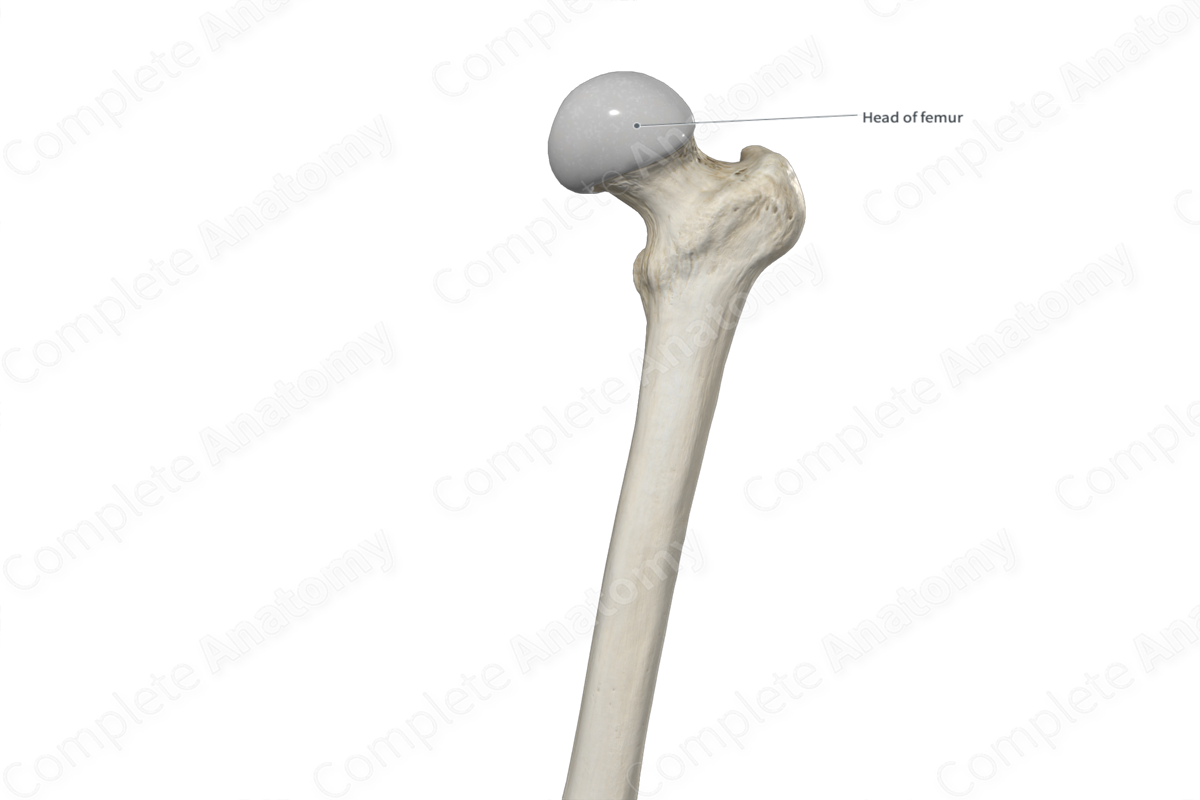
Surfaces that form joints: Head
bony extension carried on a narrow neck
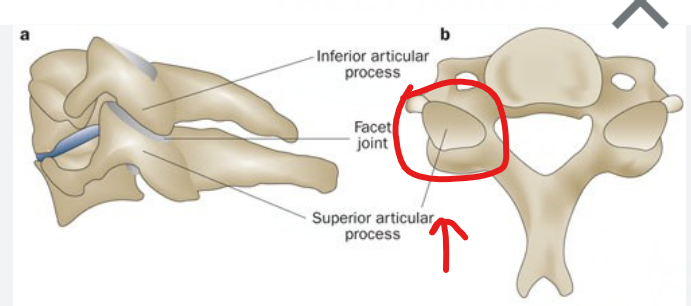
Surfaces that form joints: Facet
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
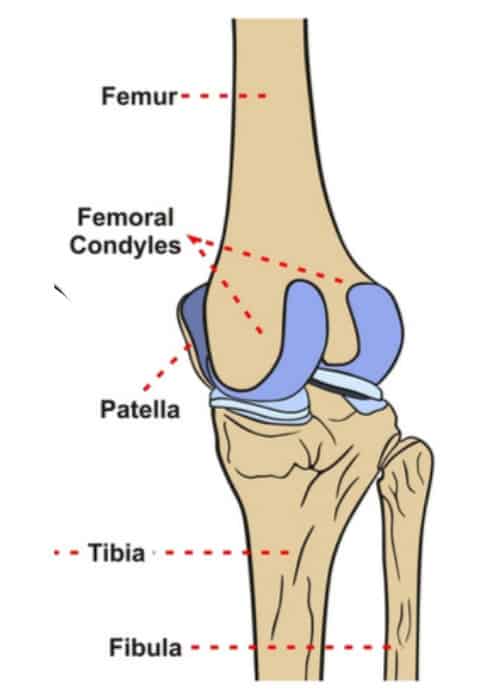
Surfaces that form joints: Condyles
rounded articular projection, usually articulaes with corresponding fossa
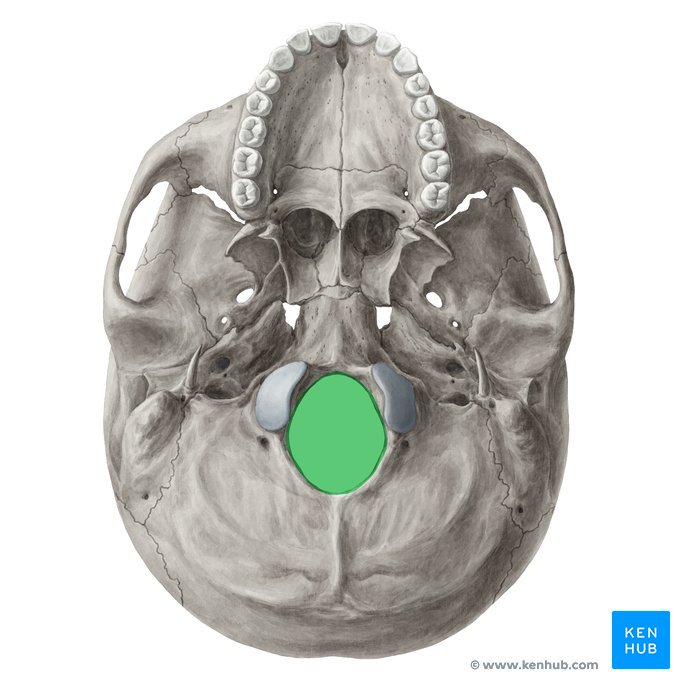
Depressions/Openings: Foramen
round/oval opening through a bone
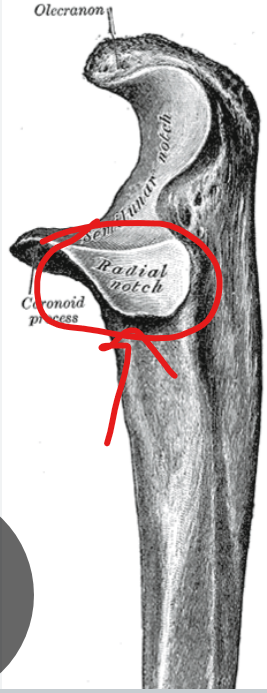
Depressions/Openings: Notch
indentation at the edge of a structure
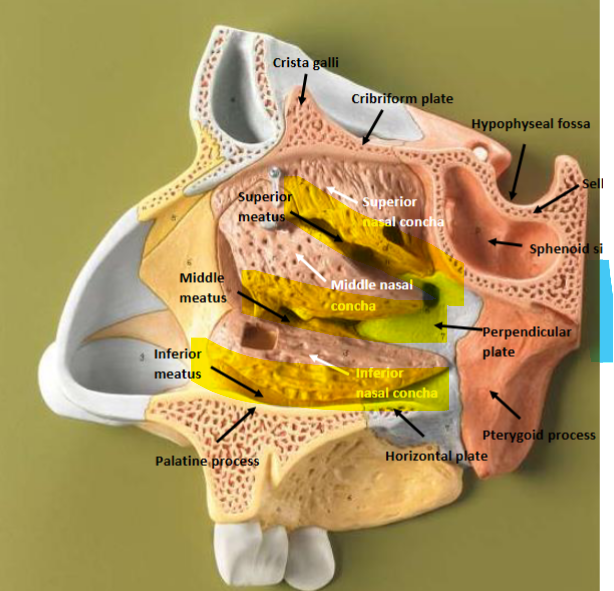
Depressions/Openings: Meatus
Canal-like passageway
Depressions/Openings: Sinus
cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
Facial Bones:
Unpaired: Mandible, Vomer
Paired: Maxillae, Lacrimal, Nasal, Inferior Nasal Conchae, Zygomatic process, palatine
Cranial Bones:
Unpaired: Frontal, Occipital
Paired: Parietal, Temporal, Sphenoid, Ethmoid
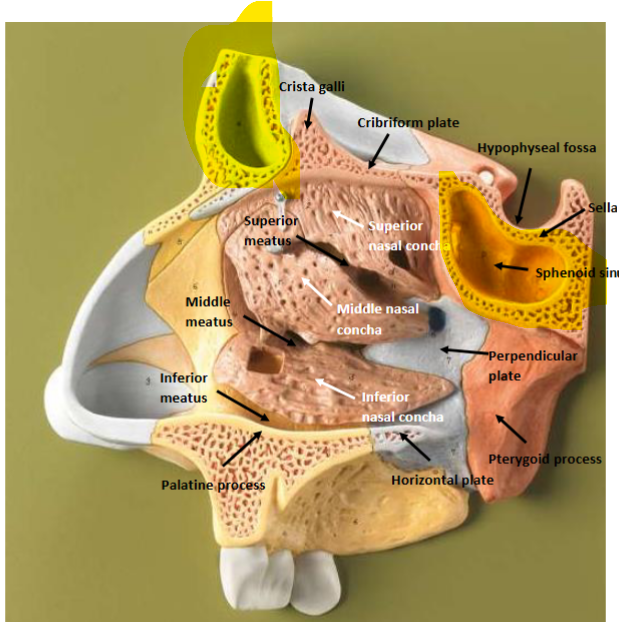
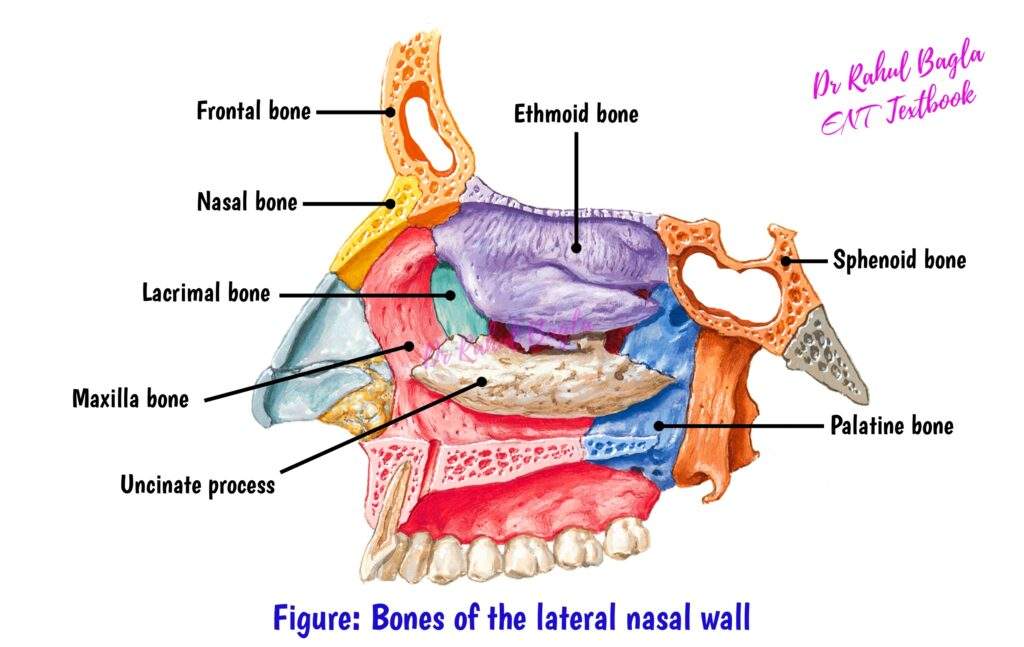
Describe the bony boundaries of the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses
The nasal cavity is bordered by the frontal, nasal, lacrimal, maxilla, sphenoid and palatine bone. The paranasal sinuses are found inside the frontal and sphenoid bone.
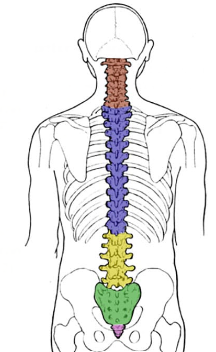
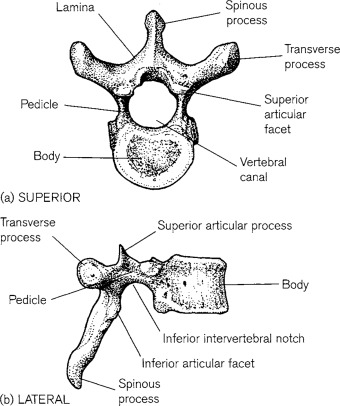
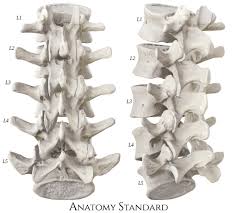
General Structure of the Vertebrae
The vertebrate is composed of 26 total bones in an adult.
Invertebrate discs act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae.
C1-C7, T1-T12, L1-L5, Sacrum and Coccyx
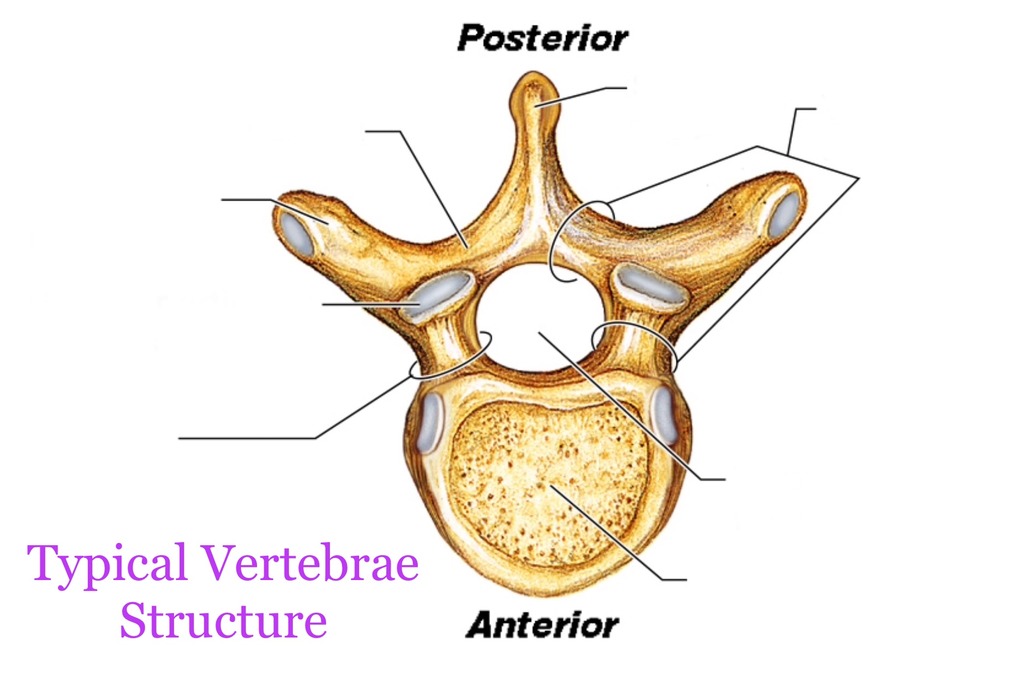
Typical Vertebrae:
spinous process
vertebral arch
superior articular process and facet
inferior articular process and facet
body
intervertebral foramen
transverse process
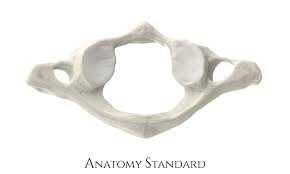
C1 - Atlas
ring shaped
no body
smallest
nods “yes”
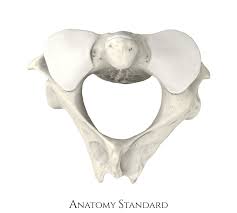
C2 -Axis
dens to fit into atlas
shakes head “no”
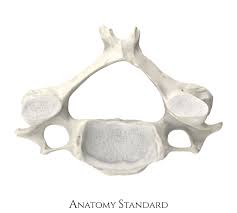
C3-C6
all Cranial Vertebrae have transverse foramen
bifid spinous process
body
C7 - prominens vertebrae
no bifid process
large spinous process
largest body out of all C
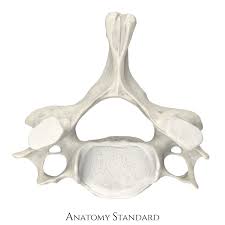
T1-T12:
spinous process points inferior
articulates with the rib
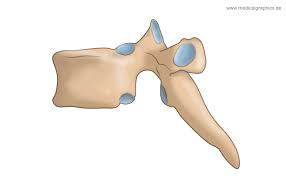
L1-L5
largest body
hatchet shaped spinous process
thin and tapered process
Sacrum and Coccyx
attaches to the pelvis
last part of the vertebral column
previously 5 bones e/ before adulthood
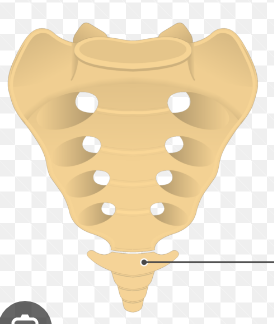
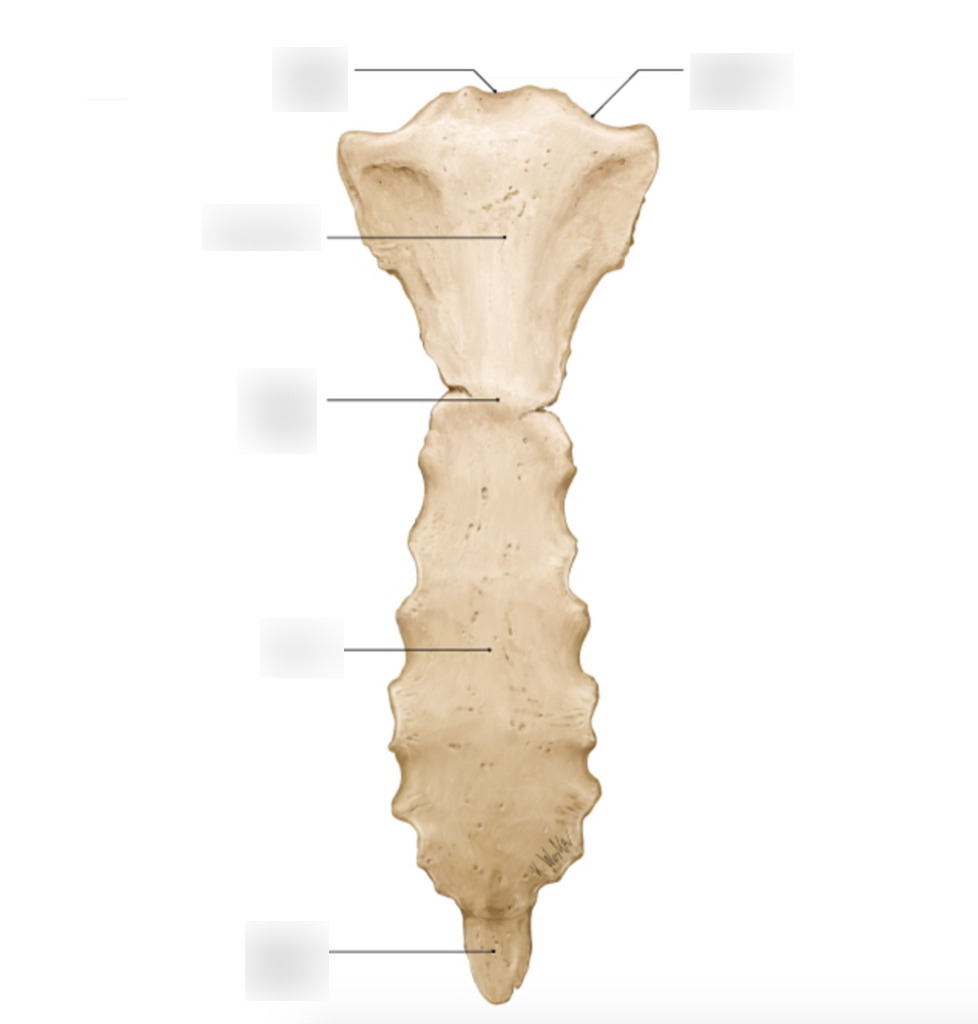
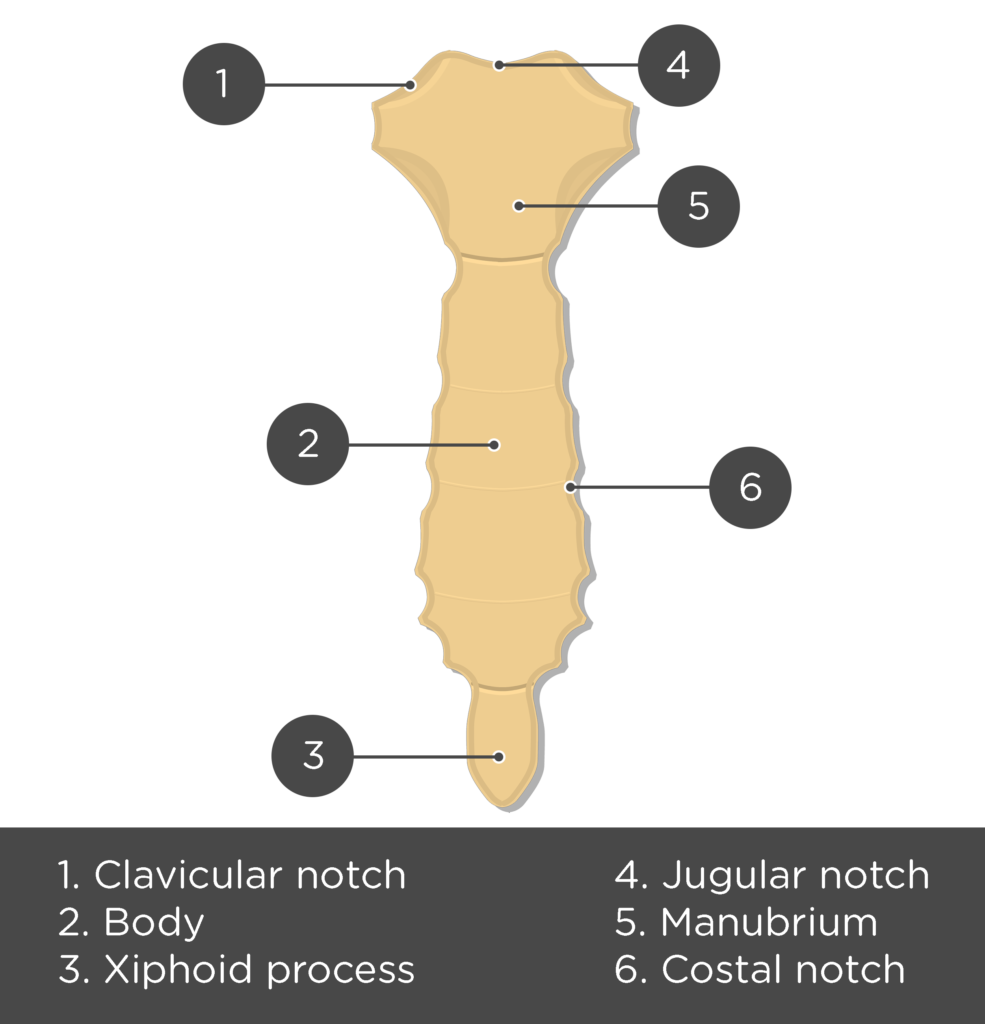
Sternum
manubrium connects to the ribs
body
xiphoid process
jugular notch
clavicular notch
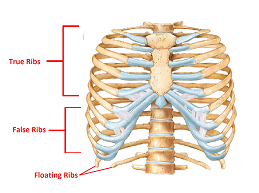
True Vs False Ribs
Trues (1-7): attach directly to the sternum w costal cartilage
False Ribs (8-12): connect indirectly to sternum
Floating ribs (11-12): don’t connect to sternum at all to protect kidneys/flexibility to trunk
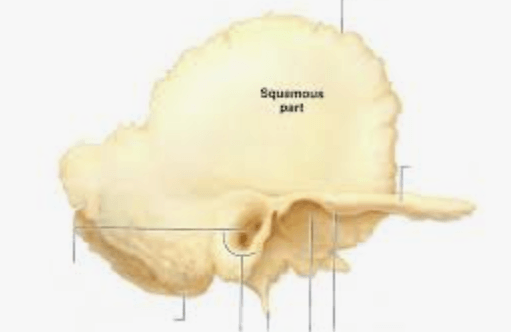
Q. What bone is this?
temporal
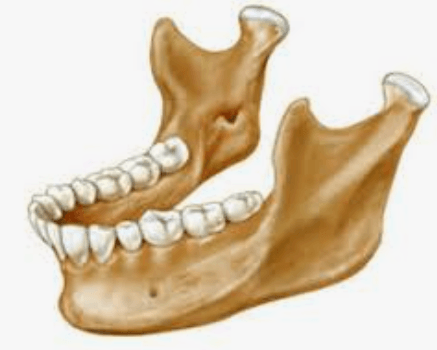
Q. Above is the mandible. What other bone fits the same category?
Nasal Bone
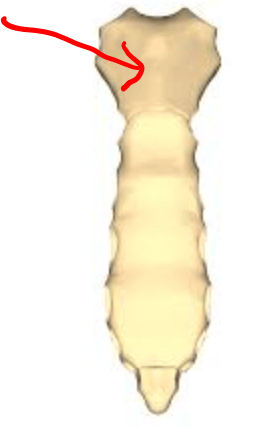
What is the arrow pointing to?
Manubrium
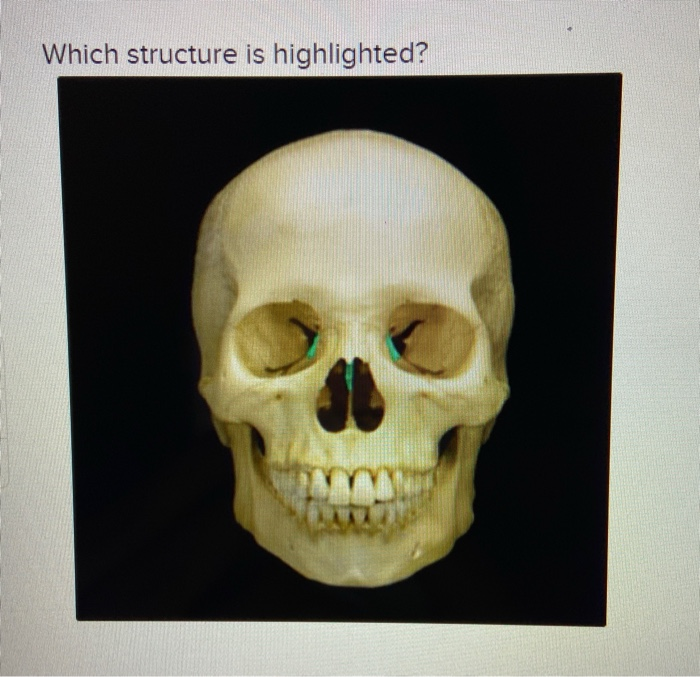
Q. What structure is highlighted?
Ethmoid bone
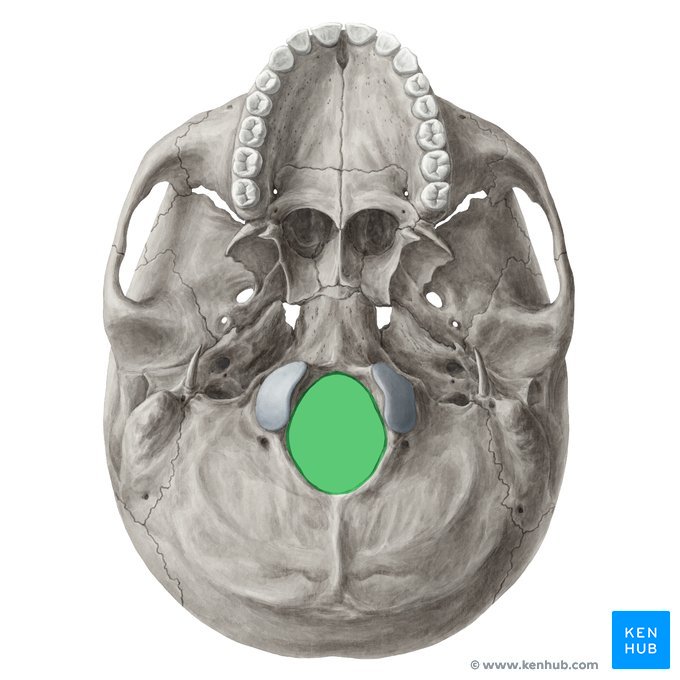
Q. What’s the highlighted portion called?
Foramen Magnum
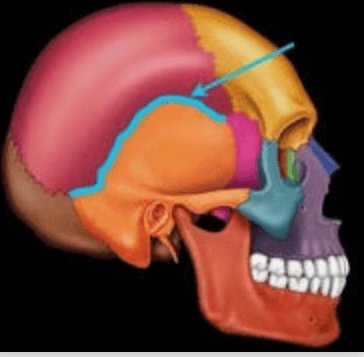
Q. What suture is this?
Squamous
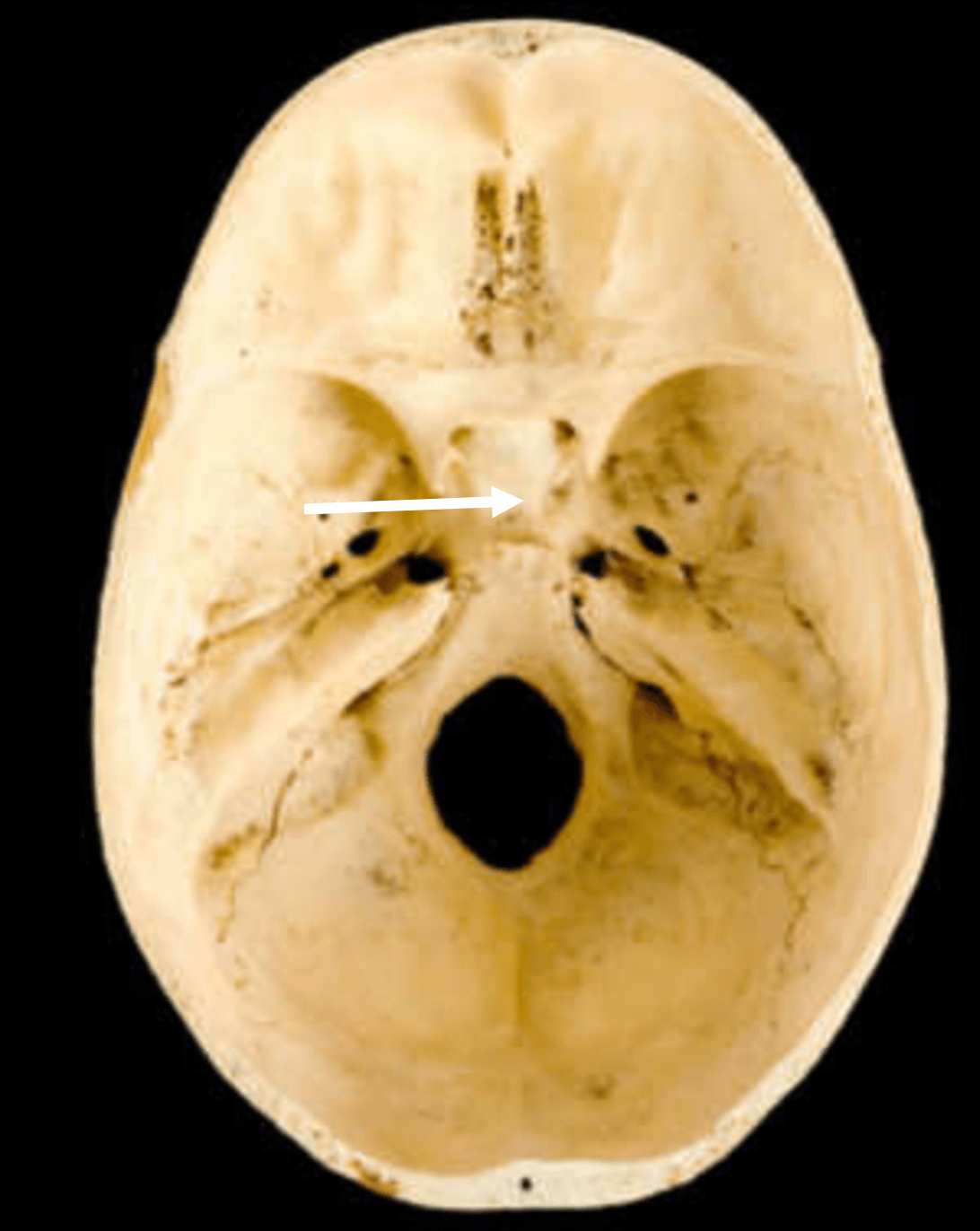
Q. What’s the arrow pointing to?
sella turcica
sphenoid bone
cranial bone
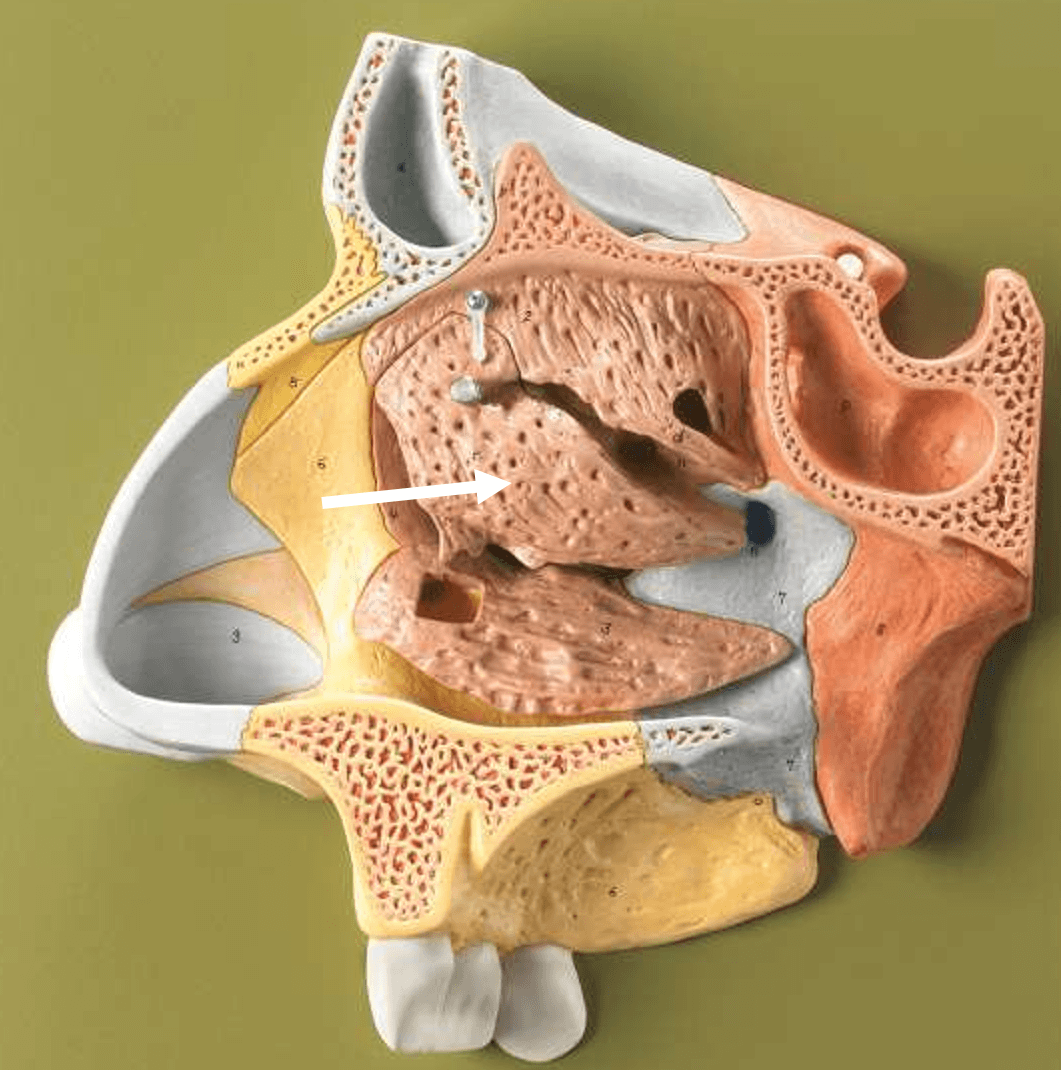
Q. What’s it pointing to?
Ethmoid Bone + Middle Nasal Concha
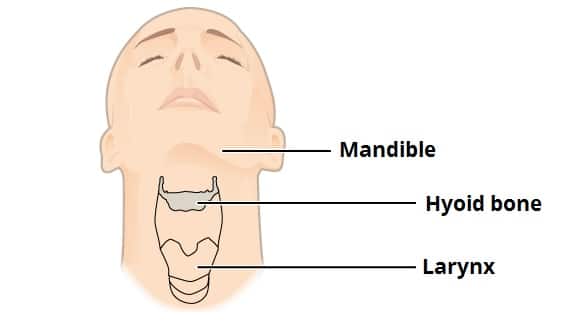
Hyoid Bone
doesn’t articulate with ANYTHING
functions: breathing, swallowing, speaking
Sacrum (ID 5)
ala, sacral promontory, anterior sacral foramina, auricular surface (lateral), posterior sacral foramina
Name all the sutures needed for class! (Hint: there’s 5)
Coronal, Sagittal, Lambdoid, Squamous, Occipitomastoid
Q. Osteoporosis can’t be treated by..
Bone graft surgeries
Q. Elastic cartilage can be found in…
the external ear
Q. What’s FALSE about the spongy bone?
it’s avascular
Q. What term is not related to the sternum?
auricular surface
Q. Which of these is NOT part of the Sphenoid process?
Crista Galli
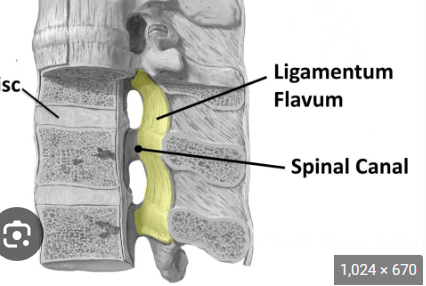
Q. What is the ligamentum flavum?
The ligament that connects adjacent ligaments running in the vertebrae
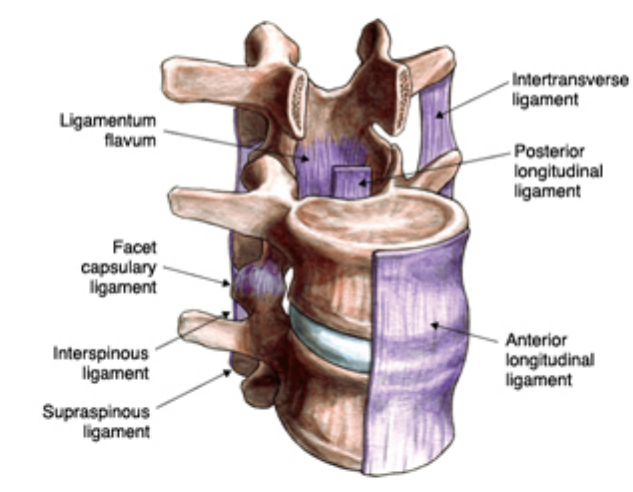
Q. What do the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments do?
They limit spinal extension and reinforce intervertebral discs.
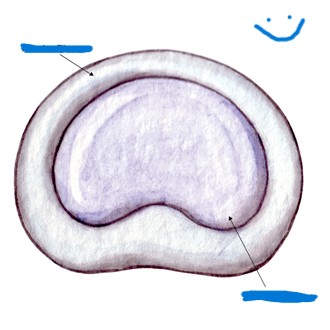
What’s the outside arrow pointing to? What about the inner arrow?
Annulus Fibrosus, Nucleus Pulposus