BIO 2 exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:02 AM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
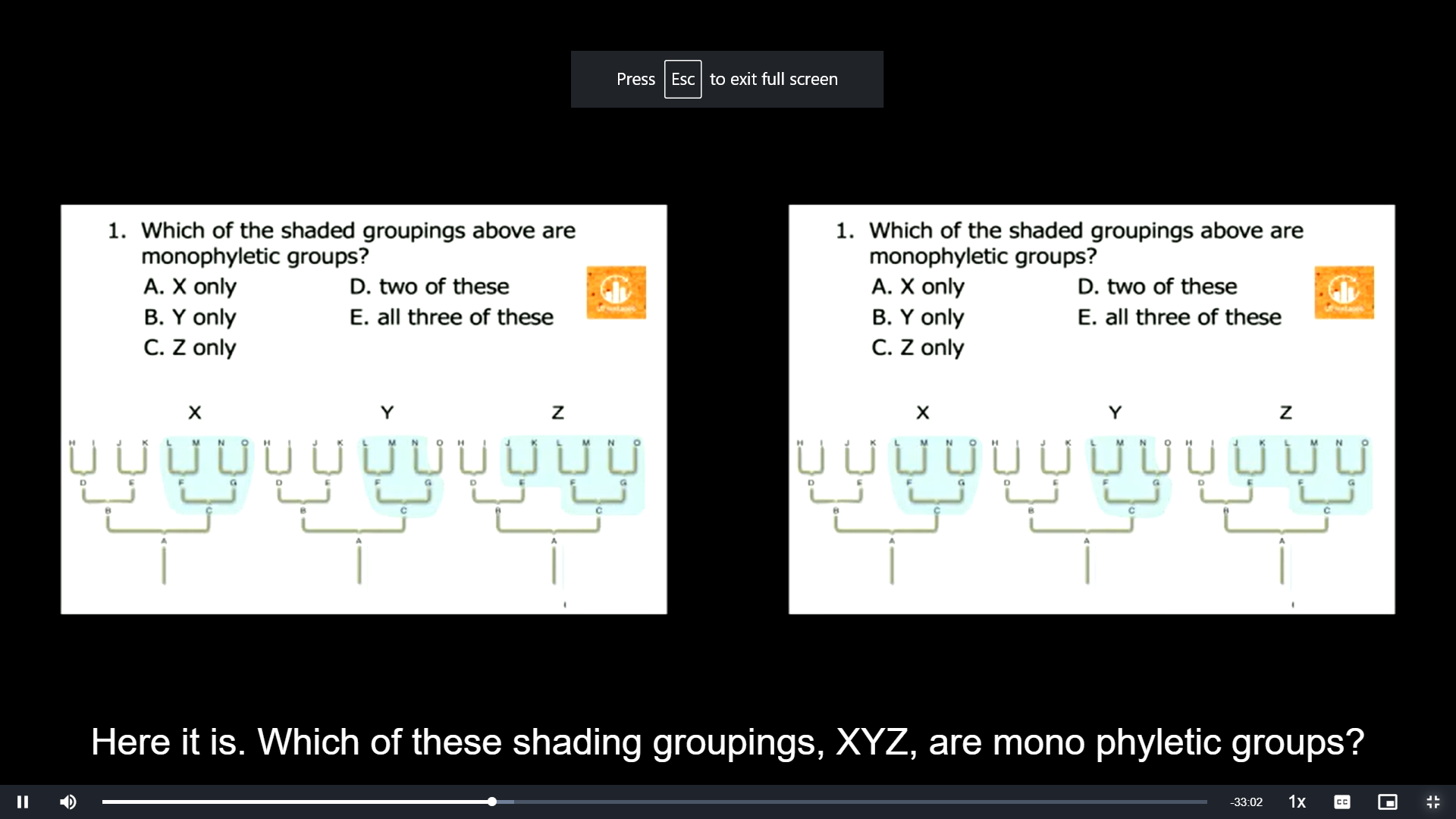
\
Which of the shaded groupings above are monophyletic groups?
\
A. X only
B. Y only
C. Z only
D. two of these
E. all three of these
Which of the shaded groupings above are monophyletic groups?
\
A. X only
B. Y only
C. Z only
D. two of these
E. all three of these
A. X only
2
New cards
\
Which of the following is an example of convergent evolution?
\
A. animals with the same homologous traits
B. two mosquito species with the same mutation conferring pesticide resistance
C. fins of a fish and fins of a whale (mammal)
Which of the following is an example of convergent evolution?
\
A. animals with the same homologous traits
B. two mosquito species with the same mutation conferring pesticide resistance
C. fins of a fish and fins of a whale (mammal)
C. fins of a fish and fins of a whale (mammal)
3
New cards
\
What is the reason for using an “__outgroup”__ in a phylogenetic tree?
\
A. to be sure there is a sufficient number of taxa (species)
B.. to decide which form of a trait is ancestral or derived
C.to decide which taxon (species) is the most derived
D. because it is easier to find fossil data for the outgroup
E. because every group needs something that doesn’t belong
What is the reason for using an “__outgroup”__ in a phylogenetic tree?
\
A. to be sure there is a sufficient number of taxa (species)
B.. to decide which form of a trait is ancestral or derived
C.to decide which taxon (species) is the most derived
D. because it is easier to find fossil data for the outgroup
E. because every group needs something that doesn’t belong
B.. to decide which form of a trait is ancestral or derived
4
New cards

\
From the chart of traits in this figure, which species has __none__ of the derived traits a-e?
\
A. Species 1
B. species 3
C species 5
D. two of the 6 species shown
From the chart of traits in this figure, which species has __none__ of the derived traits a-e?
\
A. Species 1
B. species 3
C species 5
D. two of the 6 species shown
C species 5
5
New cards

\
According to the time line implied in this figure (reading from left to right), which of these __traits__ appeared __earliest__ in this group of species?
\
A. trait a
B. trait b
C. trait c
D. trait d
E. trait e
According to the time line implied in this figure (reading from left to right), which of these __traits__ appeared __earliest__ in this group of species?
\
A. trait a
B. trait b
C. trait c
D. trait d
E. trait e
D. trait d
6
New cards

\
In this phylogeny the two closest “sister species” (because they branched most recently) share what derived trait in common, which they do not share with any other species in the group?
\
A. trait a
B. trait b
C. trait c
D. trait d
E. trait e
In this phylogeny the two closest “sister species” (because they branched most recently) share what derived trait in common, which they do not share with any other species in the group?
\
A. trait a
B. trait b
C. trait c
D. trait d
E. trait e
A. trait a
7
New cards
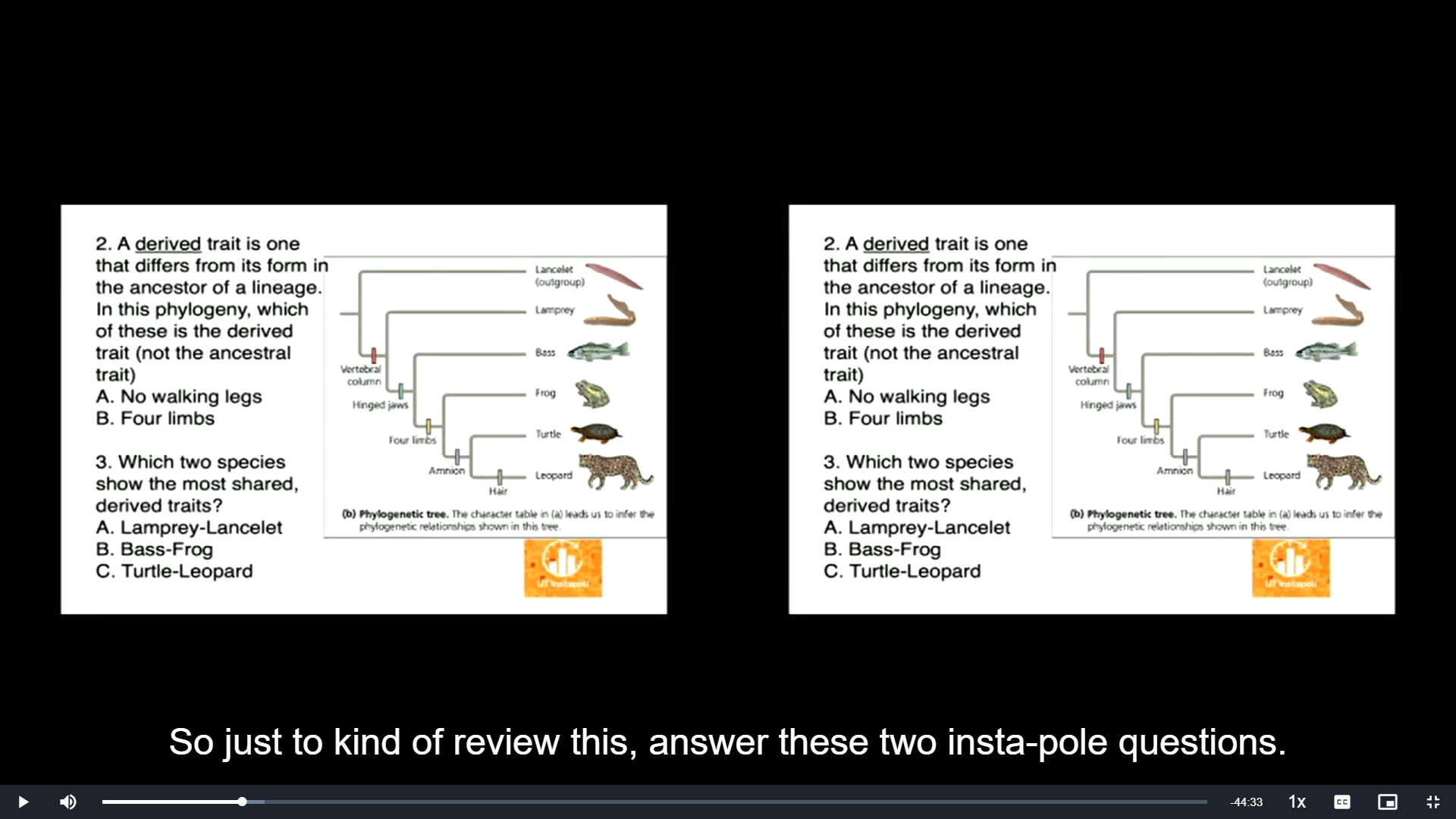
A derived trait is one that differs from its form in the ancestor of a lineage. In this phylogeny, which of these is the derived trait (not the ancestral trait)
A. No walking legs
B. Four limbs
A. No walking legs
B. Four limbs
B. Four limbs
8
New cards
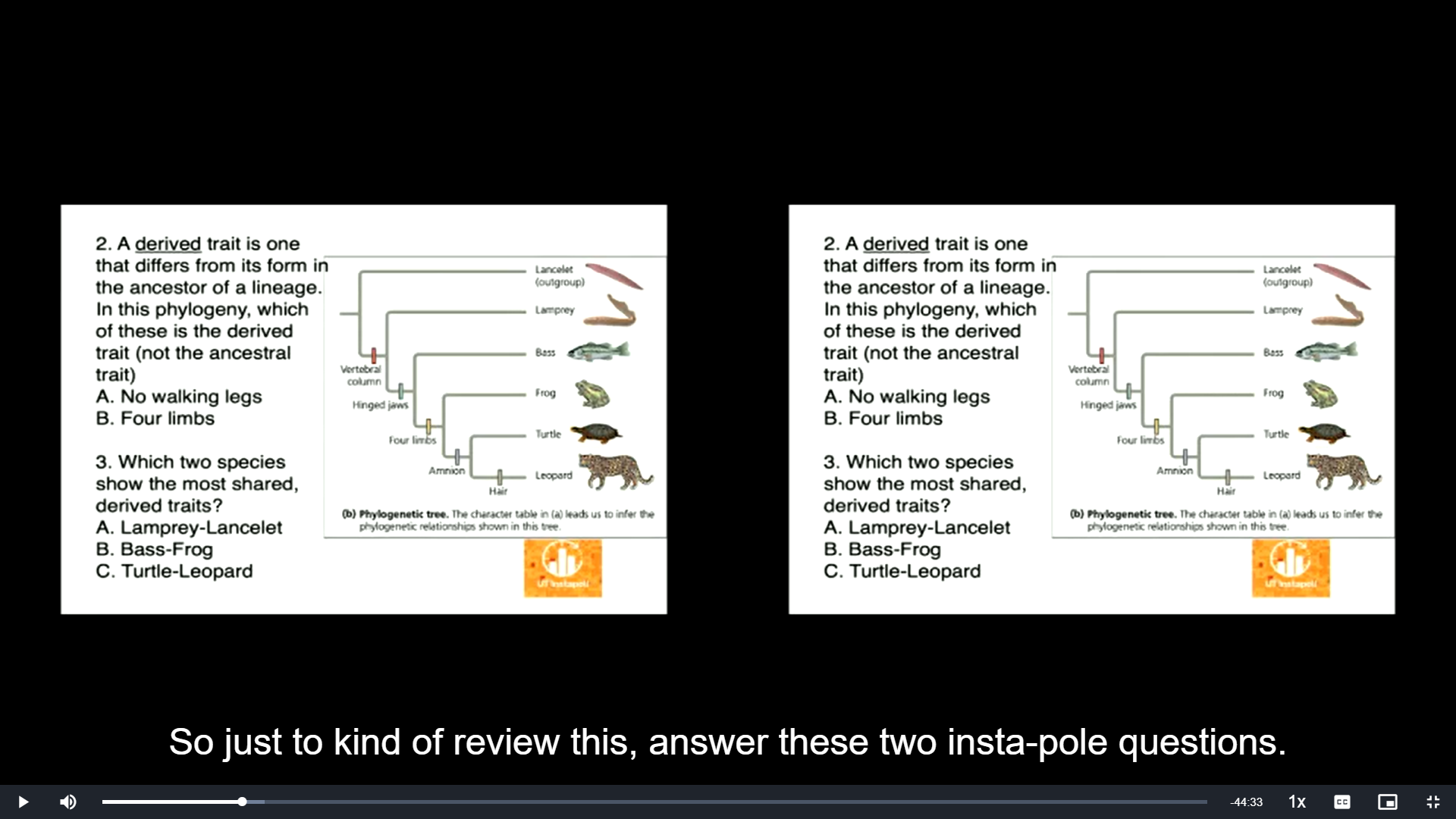
Which two species show the most shared, derived traits?
A. Lamprey-Lancelet
B. Bass-Frog
C. Turtle-Leopard
A. Lamprey-Lancelet
B. Bass-Frog
C. Turtle-Leopard
C. Turtle-Leopard
9
New cards
What are homologous traits?
A. traits that are for the same function
B. traits that have a similar shape/form
C. traits that are easy to measure
D. traits derived from the same ancestral trait
E. more than one of these are true for homologous traits
A. traits that are for the same function
B. traits that have a similar shape/form
C. traits that are easy to measure
D. traits derived from the same ancestral trait
E. more than one of these are true for homologous traits
D. traits derived from the same ancestral trait
10
New cards
To study evolutionary relationships between widely divergent organisms, such as prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes, which homologous gene sequences would be best to use?
A. Genes for specific cell wall types
B. Genes for specific ribosome rRNAs
C. Genes for specific membrane proteins
A. Genes for specific cell wall types
B. Genes for specific ribosome rRNAs
C. Genes for specific membrane proteins
B. Genes for specific ribosome rRNAs
11
New cards
At which of these relative times did the oxygen revolution occur?
A. Before the origin of life?
B. After A but before the origin of Bacteria?
C. After B but before the origin of Eukarya?
D. After C but before the origin of Animals?
A. Before the origin of life?
B. After A but before the origin of Bacteria?
C. After B but before the origin of Eukarya?
D. After C but before the origin of Animals?
C. After B but before the origin of Eukarya?
12
New cards
\
Why is the chemical process of nitrogen fixation so important for organisms?
\
A. it is the diffusion of atmospheric N2 across membranes into cells for their use
B. it is the essential first step to get atmospheric N2 into a compound like NH3
C. It is the only way animal cells can build amino acids from atmospheric N2
Why is the chemical process of nitrogen fixation so important for organisms?
\
A. it is the diffusion of atmospheric N2 across membranes into cells for their use
B. it is the essential first step to get atmospheric N2 into a compound like NH3
C. It is the only way animal cells can build amino acids from atmospheric N2
B. it is the essential first step to get atmospheric N2 into a compound like NH3
13
New cards
Most of these are examples of ecological interactions between species that could affect natural selection of bacteria. Which is not?
A. Competition for specific sugar molecules
B. Production of antibiotic that limits growth of other species
C. Adaptation to growth at human body temperature
A. Competition for specific sugar molecules
B. Production of antibiotic that limits growth of other species
C. Adaptation to growth at human body temperature
C. Adaptation to growth at human body temperature
14
New cards
This phylogeny from rRNA sequences tells us that eukaryotic nuclear rRNA genes are closest to which?
A. Mitochondrial rRNA genes
B. Archaeal rRNA genes
C. Bacterial rRNA genes
A. Mitochondrial rRNA genes
B. Archaeal rRNA genes
C. Bacterial rRNA genes
B. Archaeal rRNA genes
15
New cards
This phylogeny from rRNA sequences tells us that Mitochondrial rRNA is closest to
A. Eukaryotic nuclear rRNA genes
B. Archaeal rRNA genes
C. Bacterial rRNA genes
D. Chloroplast rRNA genes
A. Eukaryotic nuclear rRNA genes
B. Archaeal rRNA genes
C. Bacterial rRNA genes
D. Chloroplast rRNA genes
C. Bacterial rRNA genes
16
New cards
Under which conditions would there be a fitness advantage of asexual reproduction?
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
A. a stable, favorable environment
17
New cards
Under which conditions would there be a fitness advantage of sexual reproduction?
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
18
New cards
What cellular adaptations would you expect to find in multicellular organisms that are not well developed in single-celled organisms?
A. cell-cell adhesions
B. cell-cell communication
C. cell specialization for different functions
D. two of these
E. all three of these
A. cell-cell adhesions
B. cell-cell communication
C. cell specialization for different functions
D. two of these
E. all three of these
E. all three of these
19
New cards
\
Which of these describes a **quorum sensing** response in bacteria?
\
A. Cells only respond at low cell density
B. Cells only respond when receptors detect many inducer signals
C. Cells only respond when they detect other species of bacteria present
Which of these describes a **quorum sensing** response in bacteria?
\
A. Cells only respond at low cell density
B. Cells only respond when receptors detect many inducer signals
C. Cells only respond when they detect other species of bacteria present
B. Cells only respond when receptors detect many inducer signals
20
New cards
\
Penicillin is an important antibiotic that kills bacteria with *very few side effects* on human cells *because it*:
\
A. Inhibits formation of peptidoglycan
B. Inhibits phospholipid bilayer function
C. Inhibits eukaryotic ribosomes
D. Is a strong oxidizing agent, like bleach
E. more than one of these is an important reason
Penicillin is an important antibiotic that kills bacteria with *very few side effects* on human cells *because it*:
\
A. Inhibits formation of peptidoglycan
B. Inhibits phospholipid bilayer function
C. Inhibits eukaryotic ribosomes
D. Is a strong oxidizing agent, like bleach
E. more than one of these is an important reason
A. Inhibits formation of peptidoglycan
21
New cards
\
How an anti-fungal treatment could harm *fungal* parasites (like ringworm, athlete’s foot) but *not humans* (animals)?
\
A. It inhibits formation of peptidoglycan
B. It inhibits chitin cell wall formation
C. It inhibits eukaryotic ribosomes
D. It is a strong oxidizing agent, like bleach
E. More than one of these is an important reason
How an anti-fungal treatment could harm *fungal* parasites (like ringworm, athlete’s foot) but *not humans* (animals)?
\
A. It inhibits formation of peptidoglycan
B. It inhibits chitin cell wall formation
C. It inhibits eukaryotic ribosomes
D. It is a strong oxidizing agent, like bleach
E. More than one of these is an important reason
B. It inhibits chitin cell wall formation
22
New cards
By which normal processes does sexual reproduction lead to genetic variability in offspring?
A. independent assortment during meiosis
B. random mutation
C. random fertilization
D. A and B
E. B and C
F. A and C
G. all three of these
A. independent assortment during meiosis
B. random mutation
C. random fertilization
D. A and B
E. B and C
F. A and C
G. all three of these
F. A and C
23
New cards
Under which environmental conditions would there be a relative fitness advantage of __sexual__ reproduction?
\
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
\
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
24
New cards
\
Under which conditions would there be a relative fitness advantage of __asexual__ reproduction, offspring all genetically identical to parent organism?
\
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
Under which conditions would there be a relative fitness advantage of __asexual__ reproduction, offspring all genetically identical to parent organism?
\
A. a stable, favorable environment
B. a changing, harsher environment
A. a stable, favorable environment
25
New cards
\
Which of these describes a **quorum sensing** response in bacteria?
\
A.Cells only respond at low cell density
B. Cells only respond when receptors detect many inducer signals
C. Cells only respond when they detect other species of bacteria present
Which of these describes a **quorum sensing** response in bacteria?
\
A.Cells only respond at low cell density
B. Cells only respond when receptors detect many inducer signals
C. Cells only respond when they detect other species of bacteria present
B. Cells only respond when receptors detect many inducer signals
26
New cards
Which of the following is/are a diverse monophyletic group that evolved from a Protistan ancestral group?
\
A. Animal Kingdom only
B. Plant Kingdom only
C. Fungi Kingdom only
D. Archaea Kingdom only
E, A and B only
F. A, B, and C only
G. A, B, C, and D
\
A. Animal Kingdom only
B. Plant Kingdom only
C. Fungi Kingdom only
D. Archaea Kingdom only
E, A and B only
F. A, B, and C only
G. A, B, C, and D
F. A, B, and C only
27
New cards
\
What is the major function of hox genes?
\
A. determine body size
B. determine major body structures
C. determine early embryonic cell layers
D. determine cell-cell adhesions
What is the major function of hox genes?
\
A. determine body size
B. determine major body structures
C. determine early embryonic cell layers
D. determine cell-cell adhesions
B. determine major body structures
28
New cards
The era when Animal groups first became abundant and diverse was *closest to*:
A. 3 billion years ago
B. 2 billion years ago
C. 600 million years ago
D. 60 million years ago
A. 3 billion years ago
B. 2 billion years ago
C. 600 million years ago
D. 60 million years ago
C. 600 million years ago
29
New cards
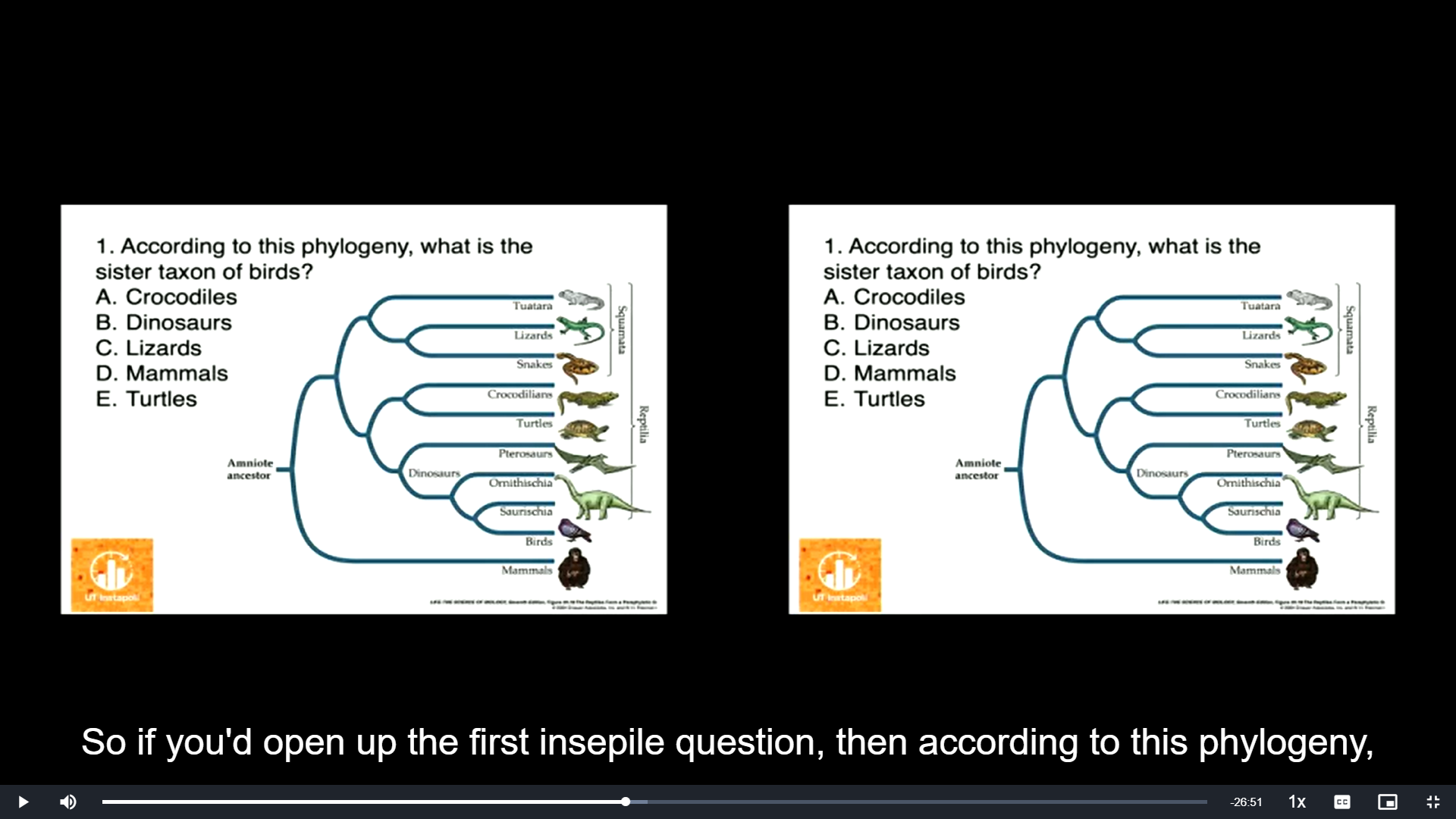
\
According to this phylogeny, what is the sister taxon of birds
\
A. Crocodiles
B. Dinosaurs
C. Lizards
D. Mammals
E. Turtles
According to this phylogeny, what is the sister taxon of birds
\
A. Crocodiles
B. Dinosaurs
C. Lizards
D. Mammals
E. Turtles
B. Dinosaurs
30
New cards
Which of the following is the set of taxa (vertebrate classes) that have amniotic eggs?
\
A. Birds, Mammals, and Reptiles
B. Amphibia, Bony Fish, and Reptiles
C. Birds and Reptiles
D. Amphibia, Birds, Mammals and Reptiles
E. All classes of vertebrates
\
A. Birds, Mammals, and Reptiles
B. Amphibia, Bony Fish, and Reptiles
C. Birds and Reptiles
D. Amphibia, Birds, Mammals and Reptiles
E. All classes of vertebrates
A. Birds, Mammals, and Reptiles
31
New cards
\
Which of these is one defining trait of members of the Plant Kingdom, distinguish them from Protistan ancestors?
\
A. Have more than one cell
B. Conduct photosynthesis with chlorophyll
C. Have cellulose cell walls
D. Multicellular embryos develop on parent
E. Cannot move around
Which of these is one defining trait of members of the Plant Kingdom, distinguish them from Protistan ancestors?
\
A. Have more than one cell
B. Conduct photosynthesis with chlorophyll
C. Have cellulose cell walls
D. Multicellular embryos develop on parent
E. Cannot move around
D. Multicellular embryos develop on parent
32
New cards
\
Which of the following was an __advantage__ for the earliest plants to live on land?
\
A. Extra strong UV radiation available
B. Easier to support body weight of plant
C. Easier to reproduce, with swimming sperm
D. Easier for chlorophyll to absorb light energy
E. More than one of these was advantageous
Which of the following was an __advantage__ for the earliest plants to live on land?
\
A. Extra strong UV radiation available
B. Easier to support body weight of plant
C. Easier to reproduce, with swimming sperm
D. Easier for chlorophyll to absorb light energy
E. More than one of these was advantageous
D. Easier for chlorophyll to absorb light energy
33
New cards
\
Which of the following is a good match of a challenge of living on land with a Plant adaptation to solve that challenge?
\
A. Absorb light --> roots to absorb water
B. Too much water loss --> waxy cuticle
C. Competition for light -> grow closer together
Which of the following is a good match of a challenge of living on land with a Plant adaptation to solve that challenge?
\
A. Absorb light --> roots to absorb water
B. Too much water loss --> waxy cuticle
C. Competition for light -> grow closer together
B. Too much water loss --> waxy cuticle
34
New cards
In which way do plants grow at meristem regions?
A. By mitosis and cytokinesis
B. By cleavage of large cells into smaller ones
C. By cell elongation
A. By mitosis and cytokinesis
B. By cleavage of large cells into smaller ones
C. By cell elongation
A. By mitosis and cytokinesis
35
New cards
Which of these describes the general function of plant stems?
A. Main organ for photosynthesis
B. Main organ for food storage
C. Transport materials up from roots
D. Gas exchange with surrounding air
E. Anchor plant in the soil
A. Main organ for photosynthesis
B. Main organ for food storage
C. Transport materials up from roots
D. Gas exchange with surrounding air
E. Anchor plant in the soil
C. Transport materials up from roots
36
New cards
\
How do relative concentrations of abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellins (GA) control the extent of seed dormancy? \n 1. Is in charge of promoting **seed dormancy**
\
A. parent plant
B. seed (embryo plant)
How do relative concentrations of abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellins (GA) control the extent of seed dormancy? \n 1. Is in charge of promoting **seed dormancy**
\
A. parent plant
B. seed (embryo plant)
A. parent plant
37
New cards
How do relative concentrations of abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellins (GA) control the extent of seed dormancy? \n 2. Is in charge of promoting **seed germination**
\
A. parent plant
B. seed (embryo plant)
\
A. parent plant
B. seed (embryo plant)
B. seed (embryo plant)
38
New cards
\
3. Which of these always happens first in seed germination.
\
A. starch is digested into sugars
B. hormone signal binds to receptor
C. target cells secrete enzymes
D. seed takes in water (imbibition)
3. Which of these always happens first in seed germination.
\
A. starch is digested into sugars
B. hormone signal binds to receptor
C. target cells secrete enzymes
D. seed takes in water (imbibition)
D. seed takes in water (imbibition)
39
New cards
\
Which of these does NOT occur in seed germination
\
A. starch is digested into sugars
B. hormone signal binds to receptor
C. target cells secrete enzymes
D. embryo secretes GA gibberellins
E. embryo secretes ABA abscisic acid
Which of these does NOT occur in seed germination
\
A. starch is digested into sugars
B. hormone signal binds to receptor
C. target cells secrete enzymes
D. embryo secretes GA gibberellins
E. embryo secretes ABA abscisic acid
E. embryo secretes ABA abscisic acid
40
New cards
Which of these is the most accurate description of phototropism?
A. Plant shoot bends towards the light.
B. Plant shoot grows towards the light
C. Plant shoot bends towards warmth
D. Plant shoot grows towards warmth
A. Plant shoot bends towards the light.
B. Plant shoot grows towards the light
C. Plant shoot bends towards warmth
D. Plant shoot grows towards warmth
B. Plant shoot grows towards the light
41
New cards
If your hypothesis is that phototropism response requires blue light, which is the specific null hypothesis?
A. Blue light does not cause phototropism
B. Blue light has no effect on phototropism
C. Either of these works as a null hypothesis
A. Blue light does not cause phototropism
B. Blue light has no effect on phototropism
C. Either of these works as a null hypothesis
B. Blue light has no effect on phototropism
42
New cards
If your hypothesis is that phototropism response requires blue light, which of these are important to control? (same for treatment & control groups)
A. angle/position of the light
B. brightness/intensity of the light
C. Amount of water given the seedling
D. A and B
E. A, B, and C
A. angle/position of the light
B. brightness/intensity of the light
C. Amount of water given the seedling
D. A and B
E. A, B, and C
D. A and B
43
New cards
Besides light energy, what substances are used up in photosynthesis?
A. CO2
B. O2
C. H2O
D. CO2 & O2
E. CO2 & H20
A. CO2
B. O2
C. H2O
D. CO2 & O2
E. CO2 & H20
E. CO2 & H20
44
New cards
What do you think is the main source of O2 for aerobic respiration in underground root cells?
A. O2 taken into leaves from the air
B. O2 produced in photosynthesis
C. O2 diffusing in from air pockets in soil
A. O2 taken into leaves from the air
B. O2 produced in photosynthesis
C. O2 diffusing in from air pockets in soil
C. O2 diffusing in from air pockets in soil
45
New cards
What are the two types of forces that move water in plants?
A. Osmosis and Diffusion
B. Osmosis and Fluid Pressure
C. Fluid Pressure and Cell Walls
A. Osmosis and Diffusion
B. Osmosis and Fluid Pressure
C. Fluid Pressure and Cell Walls
B. Osmosis and Fluid Pressure
46
New cards
Which of these would cause water to enter a plant cell?
A. increased solute concentration inside the cell
B. decreased solute concentration inside the cell
C. higher fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
D. lower fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. A and D
A. increased solute concentration inside the cell
B. decreased solute concentration inside the cell
C. higher fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
D. lower fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. A and D
G. A and D
47
New cards
What is the name for the major upward pull on water in plants?
A. root pressure
B. photosynthesis
C. transpiration
D. translocation
A. root pressure
B. photosynthesis
C. transpiration
D. translocation
C. transpiration
48
New cards
Which happens when stomata are closed?
A. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration increases
B. CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
C. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration decreases
D. CO2 intake increases; transpiration decreases
A. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration increases
B. CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
C. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration decreases
D. CO2 intake increases; transpiration decreases
C. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration decreases
49
New cards
\
Which of these would cause __water to enter a plant cell__?
\
A. increased solute concentration inside the cell
B. decreased solute concentration inside the cell
C. higher fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
D. lower fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. A and D
Which of these would cause __water to enter a plant cell__?
\
A. increased solute concentration inside the cell
B. decreased solute concentration inside the cell
C. higher fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
D. lower fluid pressure inside the cell than outside
E. A and C
F. B and C
G. A and D
G. A and D
50
New cards
The action of proton pumps in root hairs is to
A. Transport H+ ions out of the cell by passive facilitated diffusion
B. Transport H+ ions into the cell by passive facilitated diffusion
C. Transport H+ ions out of the cell by using ATP.
D. Transport H+ ions into the cell by using ATP
A. Transport H+ ions out of the cell by passive facilitated diffusion
B. Transport H+ ions into the cell by passive facilitated diffusion
C. Transport H+ ions out of the cell by using ATP.
D. Transport H+ ions into the cell by using ATP
C. Transport H+ ions out of the cell by using ATP.
51
New cards
\
After proton pump action has created an electrical gradient, then __in response to that electrical gradient (no more ATP spent)__:
\
A. Cations like K+ can enter the cell passively
B. Anions like NO3- can enter the cell passively
C. Water can enter the cell passively
D. Two of these (A, B, C) are true
E. All of these (A, B, and C)
After proton pump action has created an electrical gradient, then __in response to that electrical gradient (no more ATP spent)__:
\
A. Cations like K+ can enter the cell passively
B. Anions like NO3- can enter the cell passively
C. Water can enter the cell passively
D. Two of these (A, B, C) are true
E. All of these (A, B, and C)
A. Cations like K+ can enter the cell passively
52
New cards
\
Which happens when stomata are __opened__?
\
A. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration increases
B. CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
C. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration decreases
D. CO2 intake increases; transpiration decreases
Which happens when stomata are __opened__?
\
A. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration increases
B. CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
C. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration decreases
D. CO2 intake increases; transpiration decreases
B. CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
53
New cards
\
Which __by itself__ causes net movement of __water__ crossing a membrane?
\
A. Electrical gradient
B. Solute gradient
C. Proton gradient
D. A and B
E. B and C
F. A and C
G. all of these (A,B,and C)
Which __by itself__ causes net movement of __water__ crossing a membrane?
\
A. Electrical gradient
B. Solute gradient
C. Proton gradient
D. A and B
E. B and C
F. A and C
G. all of these (A,B,and C)
B. Solute gradient
54
New cards
\
When sucrose is loaded __into__ phloem near the source, water then moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
When sucrose is loaded __into__ phloem near the source, water then moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
55
New cards
\
When sucrose is moved out of phloem into a sink cell, water moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
When sucrose is moved out of phloem into a sink cell, water moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
56
New cards
\
When sucrose is loaded __into__ phloem near source, water moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
When sucrose is loaded __into__ phloem near source, water moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
57
New cards
\
When sucrose is moved __out of__ phloem into a sink cell, water moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
When sucrose is moved __out of__ phloem into a sink cell, water moves
\
A. into phloem there, increasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
B. out of phloem there, decreasing its fluid pressure
58
New cards
Water moves within sieve tubes from area near the source to area near the sink because:
A. gravity (sink is always lower)
B. pumping of water from cell to cell in sieve tube
C. movement of water from area of higher fluid pressure to area of lower fluid pressure
D. movement of water across membranes from area of low solutes to area of high solutes
A. gravity (sink is always lower)
B. pumping of water from cell to cell in sieve tube
C. movement of water from area of higher fluid pressure to area of lower fluid pressure
D. movement of water across membranes from area of low solutes to area of high solutes
C. movement of water from area of higher fluid pressure to area of lower fluid pressure
59
New cards
The four products of meiosis in the male flower part
A. are diploid
B. Immediately grow by mitosis
C. Immediately become fertilized
A. are diploid
B. Immediately grow by mitosis
C. Immediately become fertilized
B. Immediately grow by mitosis
60
New cards
Of the four products of meiosis in the female flower part
A. All four survive to be megaspores
B. Only one survives to be a megaspore
C. One immediately becomes fertilized
A. All four survive to be megaspores
B. Only one survives to be a megaspore
C. One immediately becomes fertilized
B. Only one survives to be a megaspore
61
New cards
Cells in the petal are
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
B. diploid 2n
62
New cards
Cells in the pollen grain are
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
63
New cards
Cells in the embryo sac are
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
64
New cards
Cells in the endosperm (food for embryo) are
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
C. triploid 3n
65
New cards
Cells in the ovary wall (will become fruit) are
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
A. haploid n
B. diploid 2n
C. triploid 3n
D. don't know
B. diploid 2n
66
New cards
Of the following, which of the following systems provides the LEAST genetic variability?
A. fertilization within single flower on same plant;
B. fertilization between two flowers on same plant
C. fertilization between flowers on different plants in same species
D. asexual (vegetative) reproduction
A. fertilization within single flower on same plant;
B. fertilization between two flowers on same plant
C. fertilization between flowers on different plants in same species
D. asexual (vegetative) reproduction
D. asexual (vegetative) reproduction
67
New cards
In phylogenetic analysis we must be careful to look for the presence or absence of traits that are homologous to each other in different groups. What are __homologous__ traits?
A.traits derived from the same ancestral trait
B. traits that are for the same function
C. traits that have a similar shape
D. traits that are easy to measure
E. two of the above describe homologous traits
A.traits derived from the same ancestral trait
B. traits that are for the same function
C. traits that have a similar shape
D. traits that are easy to measure
E. two of the above describe homologous traits
A.traits derived from the same ancestral trait
68
New cards
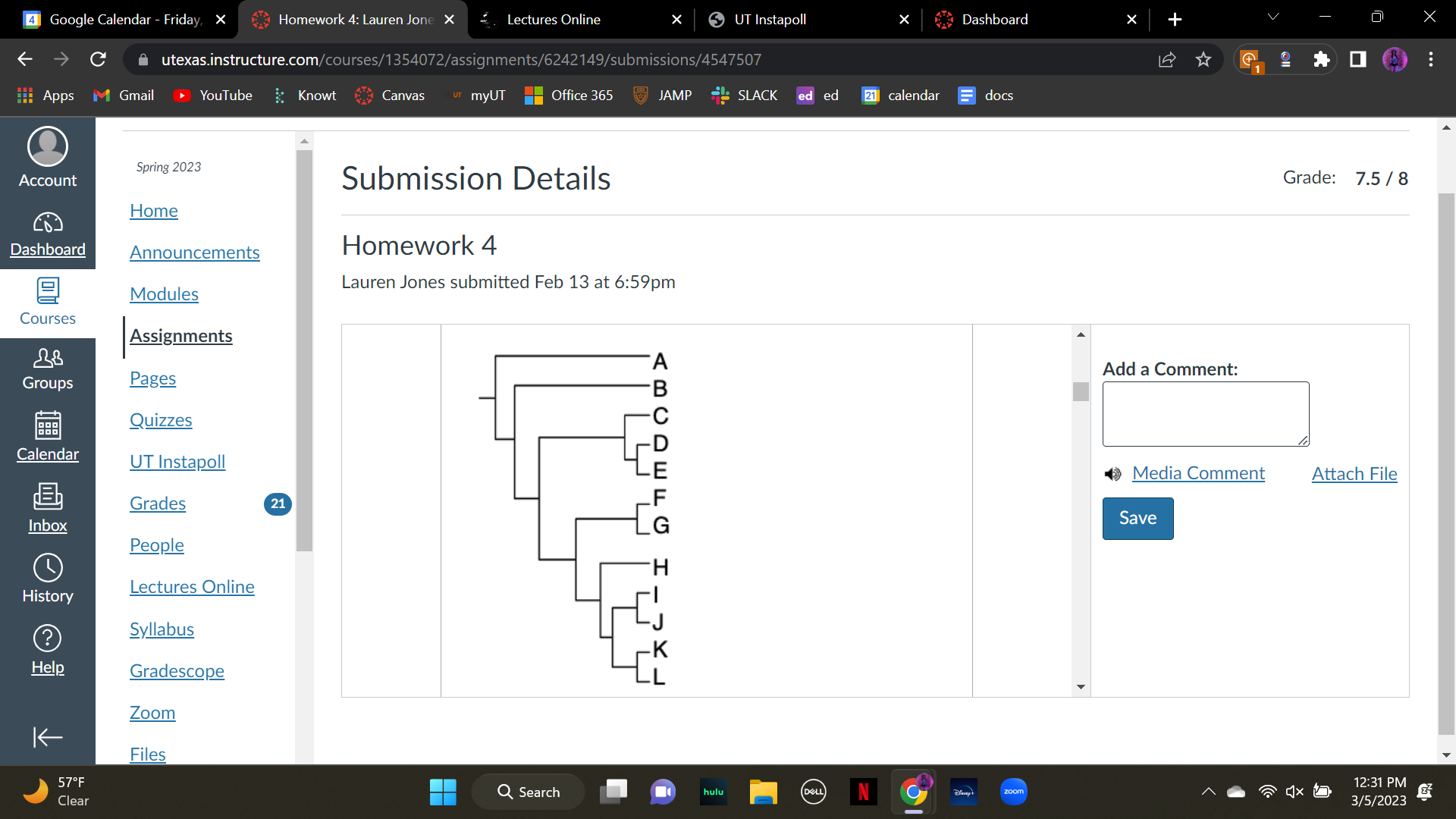
According to this phylogeny, **species H** shares more derived traits with which of these groups?
A. F & G
B. I & J
C. K & L
\
D. I & J & K & L
E. equally with F-L
A. F & G
B. I & J
C. K & L
\
D. I & J & K & L
E. equally with F-L
D. I & J & K & L
69
New cards
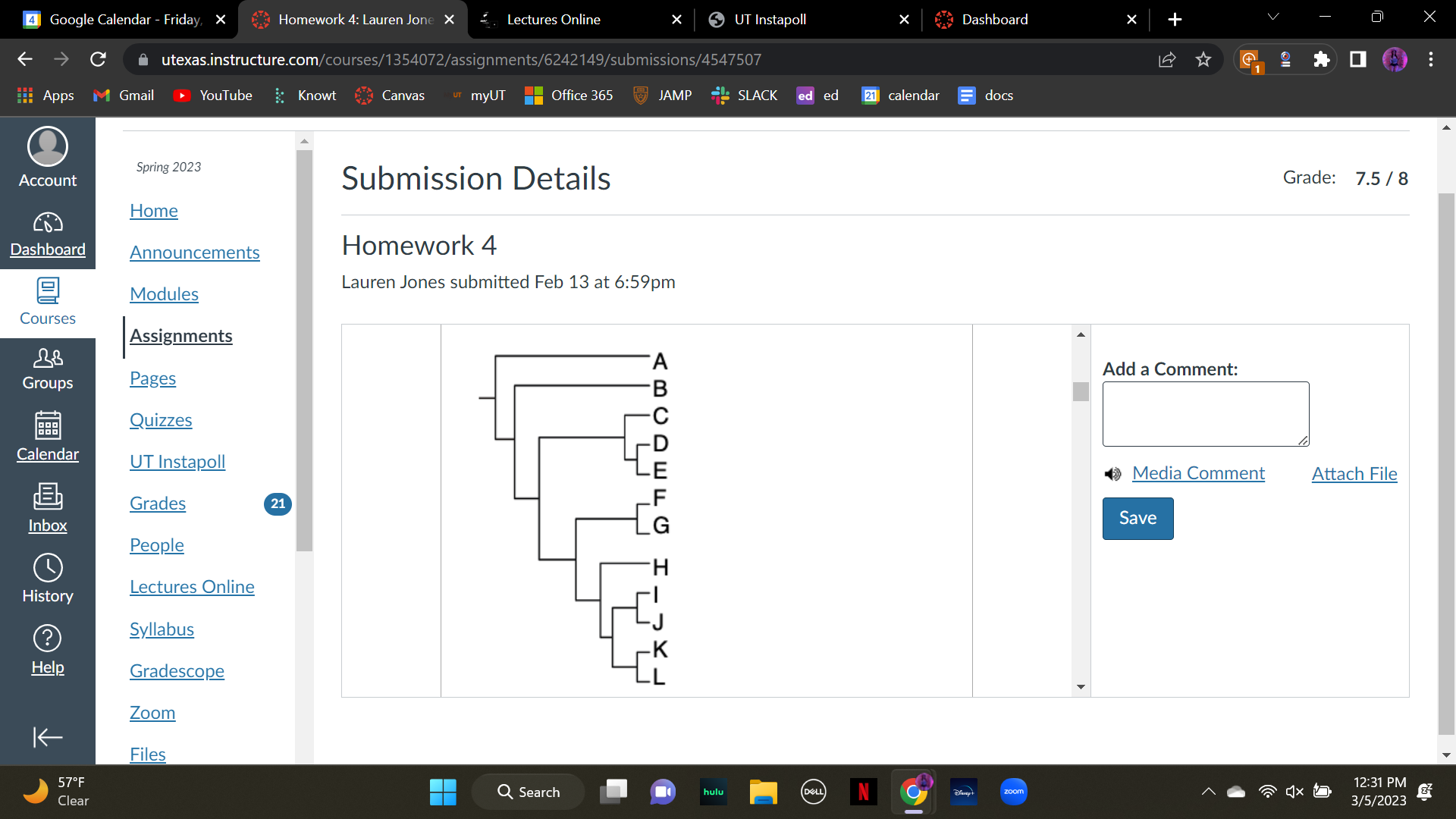
Which of the following sets of species consists of a monophyletic group? (also known as a clade)
A. A-E (A through E)
B. B-L
C. C-G
D. H and I
E. H-J
A. A-E (A through E)
B. B-L
C. C-G
D. H and I
E. H-J
B. B-L
70
New cards
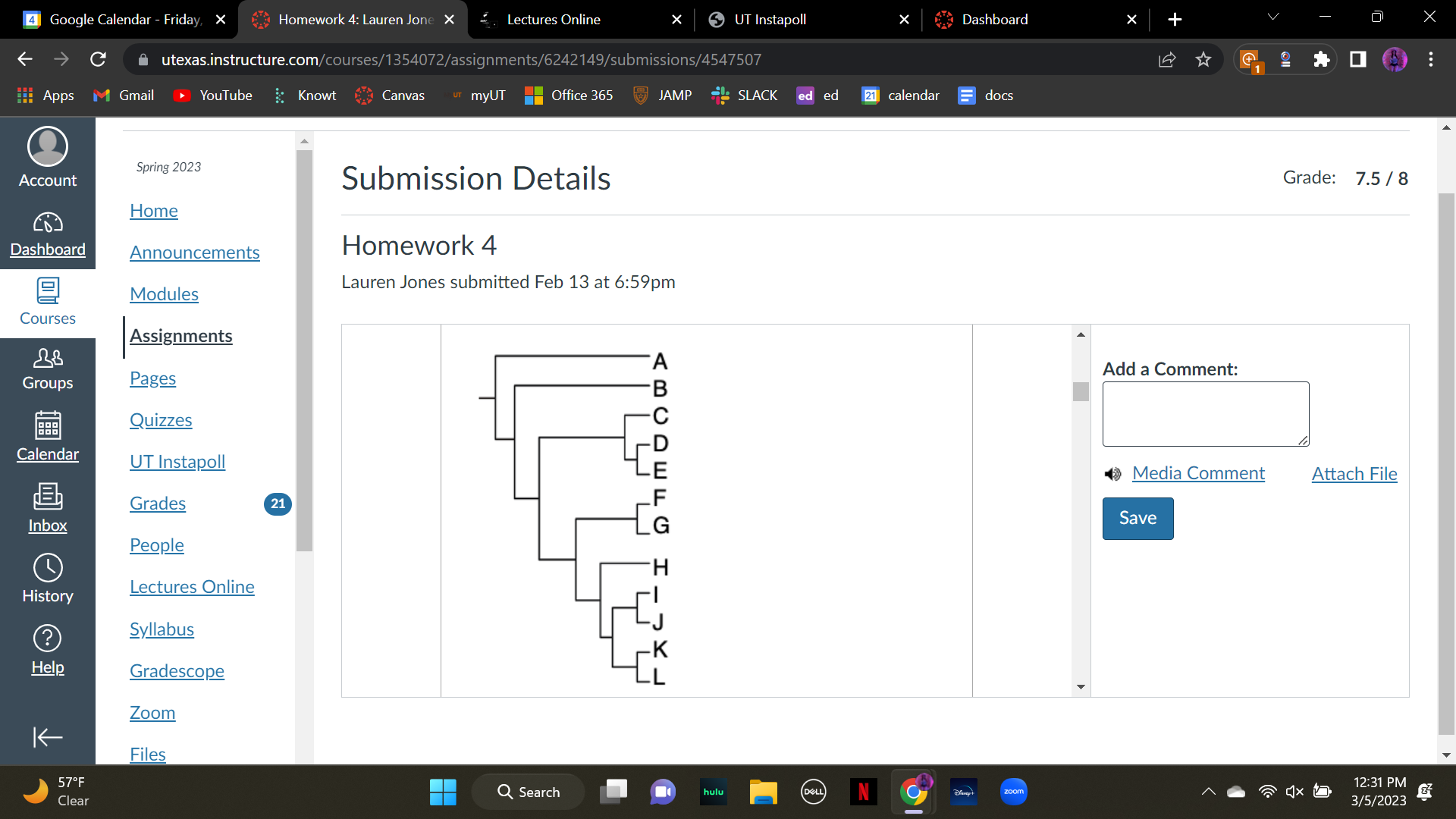
A biologist is studying phylogenetic relationships among __these species, C-L__ (C through L). In order to best determine which traits are ancestral vs. derived she should use *which of these* as the outgroup?
A. B
B. C
C. L
D. any species within her study group C-L
A. B
B. C
C. L
D. any species within her study group C-L
D. any species within her study group C-L
71
New cards
In a phylogenetic tree of species the term “sister taxa” refers to any two species
\
A. with the most shared, derived traits
B. that evolved from the most ancient common ancestor
C. that belong to the same large monophyletic group
D. that have the same function in the ecosystem
E. that currently live in the same geographic region
\
A. with the most shared, derived traits
B. that evolved from the most ancient common ancestor
C. that belong to the same large monophyletic group
D. that have the same function in the ecosystem
E. that currently live in the same geographic region
A. with the most shared, derived traits
72
New cards
Biologists now routinely test for homology between __genes__ in different species. If genes are determined to be homologous, how are they related to each other?
A. by chance mutations
B. in function but not structure
C. because of convergent evolution
D. by descent from a common ancestor
A. by chance mutations
B. in function but not structure
C. because of convergent evolution
D. by descent from a common ancestor
D. by descent from a common ancestor
73
New cards
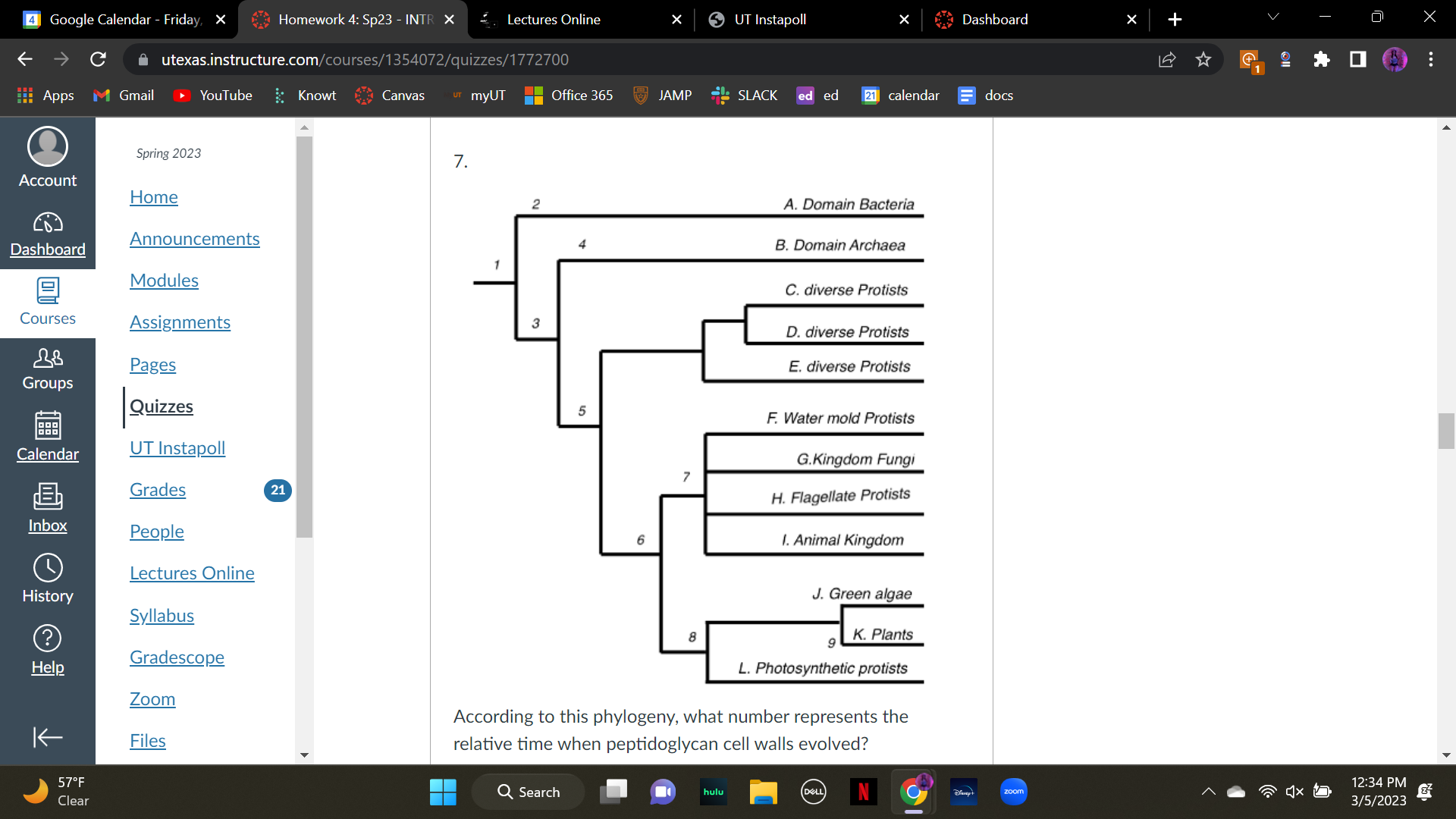
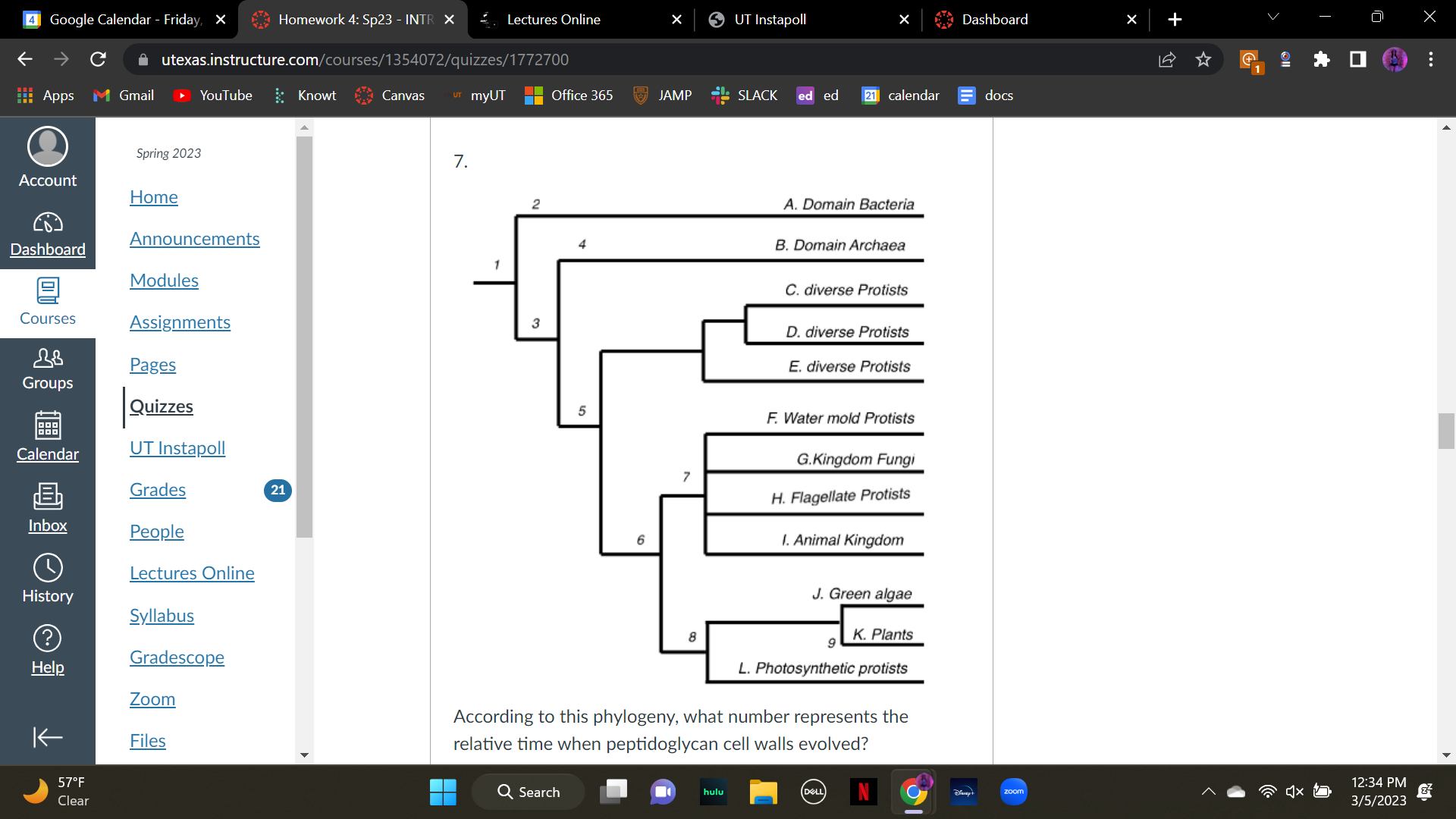
According to this phylogeny, what number represents the relative time when peptidoglycan cell walls evolved?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
B. 2
74
New cards
According to this phylogeny, what number represents the relative time when eukaryotic cell structure evolved?
A. 2
B. 3
C.4
\
D. 5
E. 6
A. 2
B. 3
C.4
\
D. 5
E. 6
D. 5
75
New cards
Which one of these groups of the domain Archaea lives in a variety of environments on earth, not just extreme conditions where only highly adapted cells can live?
A. halophilic, salt-loving
B. thermophilic, heat-loving
C. methane-generating
A. halophilic, salt-loving
B. thermophilic, heat-loving
C. methane-generating
C. methane-generating
76
New cards
Which of these traits are shared by cells of all organisms? \n
A. use ATP as energy currency
B. genome of DNA
C. cell walls present
\
D. two of these are true for all
E. all three of these are true for all
A. use ATP as energy currency
B. genome of DNA
C. cell walls present
\
D. two of these are true for all
E. all three of these are true for all
D. two of these are true for all
77
New cards
The origin and ecological success of which group led to the earth’s change called the “oxygen revolution”?
A. Plants
B. Archaea
C. Animals
D. Cyanobacteria
A. Plants
B. Archaea
C. Animals
D. Cyanobacteria
D. Cyanobacteria
78
New cards
Which traits are true for chemoheterotrophs?
A. energy from light, carbon from CO2
B. energy from inorganic chemicals, carbon from CO2
C. energy from light, carbon source is organic compounds
D. energy from organic compounds; carbon source is organic compounds
A. energy from light, carbon from CO2
B. energy from inorganic chemicals, carbon from CO2
C. energy from light, carbon source is organic compounds
D. energy from organic compounds; carbon source is organic compounds
D. energy from organic compounds; carbon source is organic compounds
79
New cards
Which of the following describes the nutritional mode of plants?
A. photoautotroph
B. chemoautotroph
C. photoheterotroph
D. chemoheterotroph
A. photoautotroph
B. chemoautotroph
C. photoheterotroph
D. chemoheterotroph
A. photoautotroph
80
New cards
Which of the following describes the nutritional mode of animals?
A. photoautotroph
B. chemoautotroph
C. photoheterotroph
D. chemoheterotroph
A. photoautotroph
B. chemoautotroph
C. photoheterotroph
D. chemoheterotroph
D. chemoheterotroph
81
New cards
Which of these is a chemical process accomplished only by certain Bacteria and no other organisms?
A. cellular respiration
B. photosynthesis
\
C. nitrogen fixation
D. methane production
A. cellular respiration
B. photosynthesis
\
C. nitrogen fixation
D. methane production
C. nitrogen fixation
82
New cards
A history of endosymbiosis explains the __evolutionary origin__ of
A. Bacteria
B. Chloroplasts
C. Mitochondria
D. two of the above
E. all three of the above
A. Bacteria
B. Chloroplasts
C. Mitochondria
D. two of the above
E. all three of the above
D. two of the above
83
New cards
Which of these describes all members of the “kingdom” Protista?
A. multicellular prokaryotes
B. multicellular eukaryotes
C. unicellular prokaryotes (can exist as clusters of unspecialized cells)
D. unicellular eukaryotes (can exist as clusters of unspecialized cells)
A. multicellular prokaryotes
B. multicellular eukaryotes
C. unicellular prokaryotes (can exist as clusters of unspecialized cells)
D. unicellular eukaryotes (can exist as clusters of unspecialized cells)
D. unicellular eukaryotes (can exist as clusters of unspecialized cells)
84
New cards
The Australian marsupial mole and the North American mole have similar body form, forelegs with claws specialized for digging and a snout for poking in the ground.
Which of these is the most likely explanation of their similar body structures?
A. They share a widespread, recent common ancestor with all of these traits
B. They live in similar habitats and have similar behavior. Individuals acquired these structures as they dug for food and shelter
C.They live in similar habitats and have similar behavior. Individuals with these traits had greater reproductive fitness so passed on their genes.
Which of these is the most likely explanation of their similar body structures?
A. They share a widespread, recent common ancestor with all of these traits
B. They live in similar habitats and have similar behavior. Individuals acquired these structures as they dug for food and shelter
C.They live in similar habitats and have similar behavior. Individuals with these traits had greater reproductive fitness so passed on their genes.
C.They live in similar habitats and have similar behavior. Individuals with these traits had greater reproductive fitness so passed on their genes.
85
New cards
Which of the following is NOT specific information supporting the endosymbiosis hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria from a prokaryotic ancestor?
A. Mitochondria can replicate by binary fission
B. Mitochondria have one loop chromosome
Correct!
C. Mitochondria are about the same size as bacteria
D. Mitochondria have prokaryotic-type ribosomes
E. Mitochondria have a double membrane
A. Mitochondria can replicate by binary fission
B. Mitochondria have one loop chromosome
Correct!
C. Mitochondria are about the same size as bacteria
D. Mitochondria have prokaryotic-type ribosomes
E. Mitochondria have a double membrane
C. Mitochondria are about the same size as bacteria
86
New cards
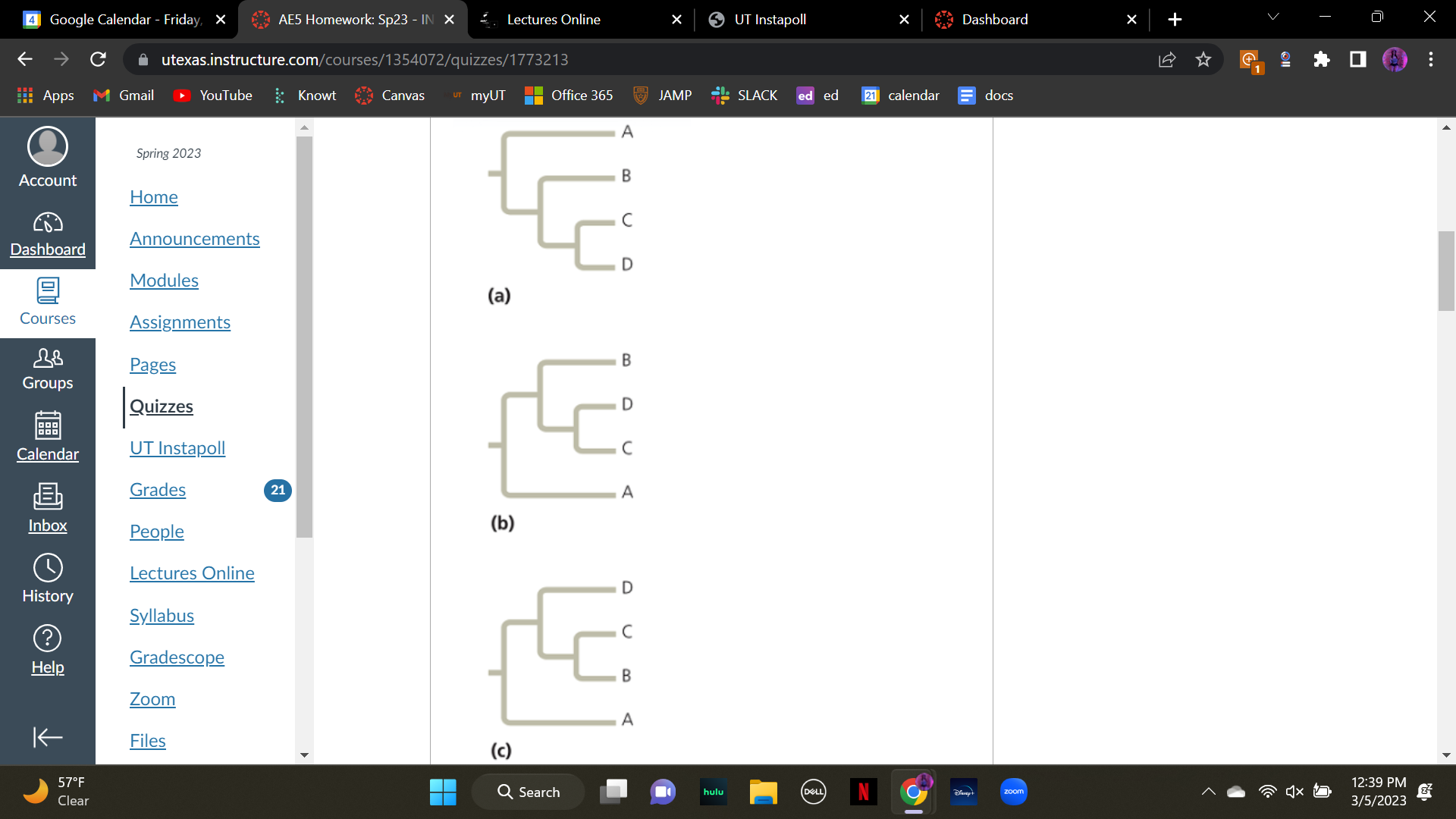
Which of the trees shown here depicts an evolutionary history different from the other two? Why? \n
A. (a) because it lists the letters in order from top to bottom, unlike the other two trees
B. (b) because the letters are not in sequence, unlike the other two trees
C. (c) because sister taxa are C and D unlike the other two trees
A. (a) because it lists the letters in order from top to bottom, unlike the other two trees
B. (b) because the letters are not in sequence, unlike the other two trees
C. (c) because sister taxa are C and D unlike the other two trees
C. (c) because sister taxa are C and D unlike the other two trees
87
New cards
Which of these features of all members of the Animal Kingdom distinguish them from other kingdoms or domains?
A. Cell-cell communication systems are present
B. Different cells in the body are specialized for specific functions
C. Cells are attached to each other to make a multicellular organism
D. Embryos have layers of cells that will develop into specific tissues and organs
E. more than one of these is true
A. Cell-cell communication systems are present
B. Different cells in the body are specialized for specific functions
C. Cells are attached to each other to make a multicellular organism
D. Embryos have layers of cells that will develop into specific tissues and organs
E. more than one of these is true
D. Embryos have layers of cells that will develop into specific tissues and organs
88
New cards
What is a feature of Plants that is NOT found in either Animals or Fungi?
A. they are autotrophs
B. their cells have cell walls
C. their cells have mitochondria
D. they have multicellular reproductive organs
E. more than one of these is true and a distinction
A. they are autotrophs
B. their cells have cell walls
C. their cells have mitochondria
D. they have multicellular reproductive organs
E. more than one of these is true and a distinction
A. they are autotrophs
89
New cards
In a group of related fungi, some species reproduce only asexually. Which of the following ways to determine whether or not two groups are distinct species would NOT be useful?
(A) cell shape and structure
(B) DNA sequences
\
(C) biological species definition
(D) chromosome movement patterns during mitosis
(E) which specific antibiotics they produce
(A) cell shape and structure
(B) DNA sequences
\
(C) biological species definition
(D) chromosome movement patterns during mitosis
(E) which specific antibiotics they produce
\n (C) biological species definition
90
New cards
Which of the following is a distinguishing trait of __all__ true animals?
A. circulatory system
B. a head or cranium
C. segments and appendages
D. embryonic cell layers
A. circulatory system
B. a head or cranium
C. segments and appendages
D. embryonic cell layers
D. embryonic cell layers
91
New cards
Which of the following is the set of taxa (vertebrate classes) that have amniotic eggs?
A. Amphibia, Bony Fish, and Reptiles
B. Birds, Mammals, and Reptiles
C. Birds and Reptiles
D. Amphibia, Birds, Mammals and Reptiles
E. All classes of vertebrates including fish
A. Amphibia, Bony Fish, and Reptiles
B. Birds, Mammals, and Reptiles
C. Birds and Reptiles
D. Amphibia, Birds, Mammals and Reptiles
E. All classes of vertebrates including fish
B. Birds, Mammals, and Reptiles
92
New cards
Researchers suggest that the evolutionary increase in the number of *hox* genes
A. led to reproductive isolation in all cases
B. could explain the evolution of color vision
C. allowed for the evolution of more complex body patterns
D.resulted in a decrease in the number of body segments in insects
E. resulted in all of the above
A. led to reproductive isolation in all cases
B. could explain the evolution of color vision
C. allowed for the evolution of more complex body patterns
D.resulted in a decrease in the number of body segments in insects
E. resulted in all of the above
C. allowed for the evolution of more complex body patterns
93
New cards
The crustacean *Daphnia* (”water flea”) reproduces clonally for some of the year (many small eggs, by mitosis) and then (when?) produces eggs by meiosis, mates and produces a few larger offspring. Is the sexual reproduction stage at the very *beginning* of summer or at the *end* of summer?
A. at the beginning of summer because growth conditions are optimal
B. at the beginning of summer because more offspring can be produced
C. at the end of summer because conditions are changing
D. at the end of summer because it’s easier for them to find mates in cooler weather
A. at the beginning of summer because growth conditions are optimal
B. at the beginning of summer because more offspring can be produced
C. at the end of summer because conditions are changing
D. at the end of summer because it’s easier for them to find mates in cooler weather
\
C. at the end of summer because conditions are changing
C. at the end of summer because conditions are changing
94
New cards
The earliest animals evolved from which type of non-animal ancestors?
A. Bacteria
B. Archaea
\
C. Protists
D. Fungi
A. Bacteria
B. Archaea
\
C. Protists
D. Fungi
C. Protists
95
New cards
A waxy cuticle is an adaptation that
A. helps prevent water loss in algae
B. aids in transport of water in plants
C. aids intake of carbon dioxide in algae
D. aids intake of carbon dioxide in plants; (E) reduces evaporation from surface of plants.
\
E. reduces evaporation from surface of plants
A. helps prevent water loss in algae
B. aids in transport of water in plants
C. aids intake of carbon dioxide in algae
D. aids intake of carbon dioxide in plants; (E) reduces evaporation from surface of plants.
\
E. reduces evaporation from surface of plants
E. reduces evaporation from surface of plants
96
New cards
Which of the following caused the “oxygen revolution”?
A. release of gases from the cooling earth
B. evolutionary origin of aerobic respiration
\
C. success of photosynthetic bacteria
D. success of photosynthetic plants
A. release of gases from the cooling earth
B. evolutionary origin of aerobic respiration
\
C. success of photosynthetic bacteria
D. success of photosynthetic plants
C. success of photosynthetic bacteria
97
New cards
Genes for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are found in the genomes of all organisms. A comparison of rRNA sequences in flowering plant chloroplast genomes would show them closest to which of these?
A. rRNA sequences in plant nuclear genomes
B. rRNA sequences in archaeal genomes
\
C. rRNA sequences in bacterial genomes
D. rRNA sequences in animal nuclear genomes
E. rRNA sequences in fungi nuclear genomes
A. rRNA sequences in plant nuclear genomes
B. rRNA sequences in archaeal genomes
\
C. rRNA sequences in bacterial genomes
D. rRNA sequences in animal nuclear genomes
E. rRNA sequences in fungi nuclear genomes
C. rRNA sequences in bacterial genomes
98
New cards
Of the following groups, the closest relatives of fungi are thought to be the
A. animals
B. vascular plants
C. mosses
D. slime molds
A. animals
B. vascular plants
C. mosses
D. slime molds
A. animals
99
New cards
Specific environmental changes that are associated with the burst of animal diversity known as the Cambrian explosion are:
NOTE: This question was regraded to give credit for any answer. The actual correct items are A and C
(A) higher oxygen levels
(B) cooler global temperatures
(C) higher dissolved minerals in sea water
\
(D) two of these
(E) all three of these
NOTE: This question was regraded to give credit for any answer. The actual correct items are A and C
(A) higher oxygen levels
(B) cooler global temperatures
(C) higher dissolved minerals in sea water
\
(D) two of these
(E) all three of these
(D) two of these
100
New cards
Which of the following was probably the LEAST important factor in bringing about the Cambrian explosion of animal diversity? \n \[similar topic in previous question; both from old exams\]
A. the emergence of predator-prey relationships
B. an increase in the concentration of atmospheric oxygen
C. availability of calcium and phosphates in sea water
D. movement of animals onto land
E. the origin of hox genes
A. the emergence of predator-prey relationships
B. an increase in the concentration of atmospheric oxygen
C. availability of calcium and phosphates in sea water
D. movement of animals onto land
E. the origin of hox genes
D. movement of animals onto land