Signal transduction by protein hormones
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a hormone
Chem regulatory subst secreted by ductless glands (Endocrine glands)
Passes through bloodstream to reach target tissues which contains specific receptor of that hormone
What are hormone receptors and the 2 types based (on location)
Hormone receptors are cell associated recog proteins.
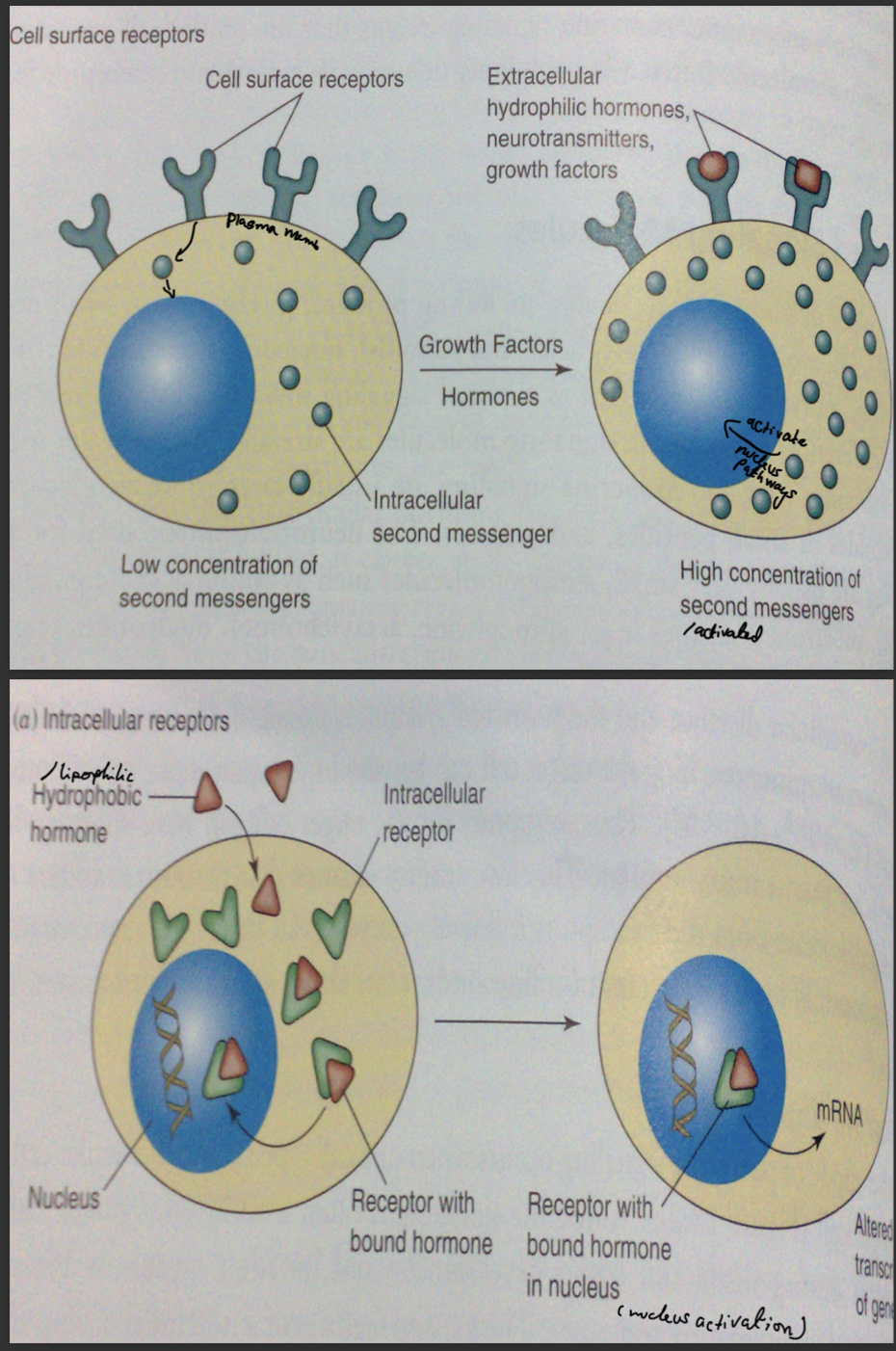
Cell (plasma) membranes receptors
Intracellular receptors (Cytosol/Nucleus)
3 types of Hormones based on chemical nature
Protein hormones
Amino acid derived hormones
Steroid hormones
Types of protein hormones
List
Large polypeptides
Small polypeptides
Glycoproteins
Large polypeptides = Insulin , Glucagon
Small polypeptides = ADH , Oxytocin
Glycoproteins = FSH , LH
Types of Amino acid derived hormones
Thyroid hormones & catecholamines —> derived from Tyrosine
Melatonin —> derived from Tryptophan
What are steroid hormones derived from and its types
Steroid hormones derived from cholesterol (makes them Lipophilic & bound to carrier proteins)
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids
Sex hormones (Progesterone, Testosterone, Estrogen)
How are hormones classified by action mechanisms
Hormones that bind to memb receptors (Protein/Amino acid ( besides thyroid hormones)
Hormones that bind to intracellular receptors (Steroid hormones + Thyroid hormones)
Characteristics of hormones that bind to intracellular receptors and name key examples
Lipophilic hormones
Need transport proteins to reach target tissue
Long plasma ½ life (hrs to days)
Action mediated by forming hormone-receptor complex.
Hormones that bind to intracellular receptors
Hormones include:
Steroid hormones
Thyroid hormones
Calcitirol (active Vit D)
Retinoids (vit A derivatives)
Mechanism of Action of hormones bind to intracellular receptors
Hormone diffuse across target cell plasma memb
Binds to specific cytosol like steroid hormone/ nuclear like thyroid hormone receptor
—> forms hormone receptor complex
hormone receptor complex accumulates,dimerizes and binds to HRE (on DNA)
Causes promoter activation/inhibition and ↑/↓ transcription of targeted gene (depending on the hormone)
Define HRE
Hormone response element is a specific regulatory DNA sequence (its on DNA)
Characteristics of Hormones which bind to cell membrane receptors
Hydrophilic hormones
Dont need transport proteins to reach target tissues
Short plasma ½ Life (mins)
Action mediated by second messenger
What is second messenger and the examples
Second messenger is intracellular signal produced when hormones (1st messenger) bind to its specific cell memb receptor on target cell. It amplifies signal and mediates effects of the hormone.
Examples
cAMP (Cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
cGMP (Cyclic guanosine monophosphate)
Calcium / phoshpatidyl inositol
Protein kinase cascades
cAMP pathway steps
Hormone bind to specific cell memb receptor (on target tissue)
Binding cause GDP + G protein —> activates Gs protein (GTP + G protein)
Active G protein —> activates/inhibits adenylate cyclase enzyme
Adenylate cyclase enzyme (if active) causes active G protein —> GDP + Pi and ATP—> cAMP
cAMP —> Activates PKA/ binds to CREB
Hormone effects mediated
cAMP hydrolysed by phosphodiesterase into AMP to terminate cAMP
Hormones that activate and inhibit adenylate cyclase enzyme
Activate
FSH, LH, TSH, HCG
Glucagons
B catecholamines (epinephrine/norepinephrines)
PTH and calcitonin (Ca2+ homeostasis)
Inhibit
Somatostatin
Angiotensin II
a2 catecholamines
What effects does cAMP mediate on cells and how
Affects:
Neuronal funct
Muscular contraction
Secretion
Growth and differentiation
Immune mechanisms
cAMP mediates effects by mechanisms:
Protein Kinase (PKA)
Gene expression (CREB)
Protein Kinase characteristic and what it does on activation?
cAMP dependent protein kinase is an inactive R2C2 tetrameter
(2 regulatory subunits [R] , 2 catalytic subunits [C])
On activation 4 cAMP bind to 2 R subunits leaving 2 C subunits free to act
Active protein kinase transfers phosphate group from ATP to serine or threonine amino acid residues of specific protein causing its phosphorylation
Phosphorylated protein (eg:enzyme) mediates hormonal effect
How does cAMP do Gene expression?
cAMP bind to cAMP response element binding protein.(CREB protein)
cAMP + CREB protein complex bind to specific HRE on DNA —> affect gene transcription
This affects amount of specific protein —> mediates hormonal effect
What does Phosphodiesterase do and what inhibits it?
After medicating hormonal effects cAMP hydrolysed by cAMP dependent phosphodiesterase enzyme into 5’AMP.
Phosphodiesterase inhibited by methyl xanthines (eg: caffeine)
what is Cyclic GMP (cGMP) and what does it cause
Def: cGMP is 2nd messenger of Atriopeptins (hormone group) eg: ANF/ANP
(ANF = Atrial natruiuretic factor)
They cause:
Natiuresis (Na excretion)
Diuresis (Urine production)
Vasodilation
Inhibition of aldosterone (adrenal gland) secretion
cGMP pathway steps
Hormone binds to its specific receptor —> Activates memb bound guanylate cyclase
Active guanylate cyclase catalyses formation of cGMP from GTP
cGMP activates cGMP-dependent protein kinase
Active protein kinase phosphorylates proteins
Phosphorylated proteins mediate effect of atriopeptins
After medicating effect cGMP hydrolysed by cGMP dependent phosphodiesterase enzyme 5’GMP
Which compounds stimulates soluble cytosolic form of guanylate cyclase? and cause what?
Compounds
Nitric oxide
Nitroglycerine
Nitroprusside
Sodium azide
Sodium nitrite
Stimulate soluble cytosolic form of guanylate cyclase causing:
Smooth muscle relaxation
Vasodilation
Which hormones use Calcium or Phosphatidyl inositols
Gonadotropin releasing hormones (GnRH)
Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
Vasopressin/Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
a1 adrenergic catecholamines
Calcium or phosphatidyl inositols pathway steps
Hormone binds to its specific receptor —> activates Gq protein
Active G protein activates phospholipase C enzyme (PLC) **
Active PLC hydrolyses phosphatatidyl inositol 4,5 biphosphate (PIP2) → 1,2 Diacyl glycerol (DAG) or Inositol triphosphate (IP3)
DAG —> activates protein kinase C —> active PK C phosphorylates specific substrates (eg:enzymes) —> mediates hormone effect
IP3 —> releases Ca2+ from intracellular storage sites (mitochondria, ER) —> Ca2+ acts as second messenger.
** GTP —> GDP (inactive) + pi
Protein Kinase cascade: What is Tyrosine kinase and where can it be found?
Tyrosine kinases is a group of enzymes which phosphorylates their substrates on tyrosine residue —> become activated
Tyrosine kinase may be
Intrinsic part of receptor (eg: Insulin receptor)
Intracellular associated with receptor but not intrinsic part of it
How does Insulin receptor work (receptor with intrinsic tyrosine kinase)
Binding of hormone to its receptor
—> tyrosine kinase activation
—> receptor autophosphorylation
—> Phosphorylates Insulin receptor substrates (IRS) on tyrosine residues
—> Phosphorylated IRS activates PI3-kinase or MAP Kinase Cascade
Active Phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase (PI3-kinase) activates numerous molecules which mediates effects of hormone
Mitogen activated protein kinase cascade (MAP kinase cascade): Phosporylated IRS cause cascade activation: RAS → RAF → MEK → MAP kinase Active MAP kinase affects certain transcription factors & ribosomal subunits → mediate effect of hormone
Remember: MAP kinase cascade Is a cascade system (series of reactions where 1 enzyme affects the next…etc)