AP2 FLUID, ELECTROLYTE & ACID- BASE BALANCE
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
fluid balance
taking in and eliminating equal amounts of fluid
factors affecting total body water content
Age, gender, body mass & body fat
infants
group with highest water content
males
gender with higher water content: 60%
elderly female
group with the lowest water content
ECF (extracellular fluid)
fluid found outside the cells of the body; interstitial fluid & plasma (also some transcellular fluids)
ICF (intracellular fluid)
fluid within cells; 2/3rds of all water content
ECF (extracellular fluid)
compartment with the highest sodium ion Na+ concentration
ICF (intracellular fluid)
compartment with the highest postassium ion K+ concentration
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
2.5 L
average daily intake & output of water
water intake sources
Ingested fluid (60%) and solid food (30%)
Metabolic water or water of oxidation (10%)
water output
urine (60%), insensible water loss (lost through skin and lungs), perspiration, and feces
thirst center
region in hypothalamus that monitors osmolarity and dehydration to regulate fluid intake
osmolality
reflects the number, not the type, of particles (solute) in a solution
hypothalamus
location of thirst center; captain - makes ADH stored in posterior pituitary.
ADH effect
reduces urine output = low volume of concentrated urine; increases water retention - you pee less
No ADH present
distal and collecting tubules impermeable to water; water excess excreted = high volume of dilute urine - you pee more
high specific gravity
urinalysis result that shows urine is concentrated; possibly due to dehydration or other causes
low specific gravity
urinalysis result that shows urine is dilute; possibly due to high fluid intake or diabetes insipidus
diuresis
increased output of urine
dehydration
An abnormally low amount of water in the body; condition where water loss is greater than water intake
dehydration
infants and elderly exhibit the greatest risk for ___?
water intoxication
a dangerous dilution of the body's fluids resulting from excessive ingestion of plain water; hypotonic hydration - get brain swelling
edema
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces of tissues.
electrolytes
a substance that dissociates in water into cations and anions: Na+, Cl-, Ca+2, K+
electrolyte balance
Condition when the quantities of electrolytes entering the body equal those leaving it
foods
Main electrolyte input is through ___.
pica
an abnormal craving or appetite for abnormal substances, such as dirt, paint, or ice; may indicated servere electrolyte deficiency
urine
Greatest electrolyte ouput is through ______.
general causes for electrolyte deficiency
poor diet or poor absorption of nutrients and LOSS from the GI tract: vomitting, diarrhea or gastric suction, renal disease

hypertension
High sodium diets are associated with what health conditions? Increased blood volume = ?
aldosterone
hormone that increases sodium reabsorption & potassium excretion; increases blood volume & blood pressure
aldosterone
hormone released when blood pressure is low, potassium is high or during times of stress
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
hormone released by the heart when blood pressure is high - kidneys excrete more Na+ and water, thus decreasing blood pressure & blood volume - it makes you Pee
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
increases blood calcium by increasing absorption of calcium from DCT, stimulating osteoclasts & increasing calcium absorption from the small intestine
kidney disease, dietary intake (high or low), loss from GI tract
sources of electrolyte imbalance
neurological & muscular dysfunction
What electrolyte imbalances of Na+, K+ and Ca+2 will cause.
hypernatremia
excessive sodium in the blood; hypertonic ECF - cells shrivel - usually caused by low water volume
hypernatremia
electrolyte imbalance caused by dehydration, diabetes insipidus (too little ADH) or hyperaldosteronism (Cushings)
hyponatremia
low sodium in the blood; hypotonic ECF - brain swells
hyponatremia
electrolyte imbalance caused by water intoxication or SIADH (too much ADH)
potassium
most abundant intracellular cation - most important in setting resting membrane potential
sodium
most abundant extracellular cation - controls ECF volume & water distribution

hyperkalemia
excessive potassium in the blood
hyperkalemia
electrolyte imbalance caused by hypoaldosteronism (Addison's) or kidneys' failure to excrete potassium
hypokalemia
deficient potassium in the blood
hypokalemia
electrolyte imbalance caused by hyperaldosteronism or kidneys over secretion of potasium
hypercalcemia
excessive calcium in the blood
hypercalcemia
electrolyte imbalance caused by hyperparathyroidism
hypercalcemia
electrolyte imbalance that decreases neuromuscular excitability, increases the risk of kidney stones and in some cases causes osteoporosis & increase risk of fractures
hypocalcemia
low calcium in the blood
hypocalcemia
electrolyte imbalance caused by hypoparathyroidism & diet low in vitD resulting in poor absorption.
hypocalcemia
electrolyte imbalance that increases neuromuscular excitability and can lead to muscle cramps and tetany; osteomalacia with possible fractures & bruising
acidosis
condition with low blood pH <7.35
alkalosis
condition with high blood pH >7.45
acidosis
condition caused by high CO2 or low HCO3- (bicarbonate)
alkalosis
condition caused by low CO2 or high HCO3- (bicarbonate)
acid
what most metabolic processes make

3 buffers in the body
bicarbonate, phosphate and proteins
bicarbonate buffer
maintains pH of extracellular fluid; HCO3- & H2CO3
protein buffer
Most plentiful buffer in body cells including RBCs
increased rate and depth of breathing
respiratory response to low pH/acid
decrease rate and depth of breathing
respiratory response to high pH/alkaline
excretion of H+ and reabsorption of HCO3-
renal response to low pH/acid
reabsorption of H+ and excretion of HCO3-
renal response to high pH/alkaline
renal compensation
kidney varies acid (H+) secretion and bicarbonate (HCO3-) reabsorption depending on pH of ECF; eg. kidney removes excess acid from plasma
respiratory compensation
changes in ventilation change pH by increasing or decreasing CO2 levels; eg, lungs exhale plasma acid as CO2
buffers
weak acid base pairs that resist changes in pH; in place and FASTEST acting
renal excretion of hydrogen ions
active hours to days; SLOWEST but MOST POWERFUL; only way to rid body of metabolic acids
respiratory acidosis
A drop in blood pH due to hypoventilation (too little breathing) and a resulting accumulation of CO2.
respiratory alkalosis
Arise in blood pH due to hyperventilation (excessive breathing) and a resulting decrease in CO2.
metabolic acidosis
decreased pH in blood due to an increase in non-respiratory acids or excessive loss of bases through GI tract
metabolic alkalosis
increased pH in blood due to loss of hydrogen ions H+ by emptying of stomach or overdose of anti-acids
ECF (extracellular fluid)
plasma and interstitial fluid are part of ____?
female
group with 50% water content
hypercapnea
high amounts of CO2 in the blood
hypocapnea
condition of deficient carbon dioxide in the blood
potassium
levels controlled by aldosterone; imbalances of this ion are easily seen on an ECG (echocardiogram)
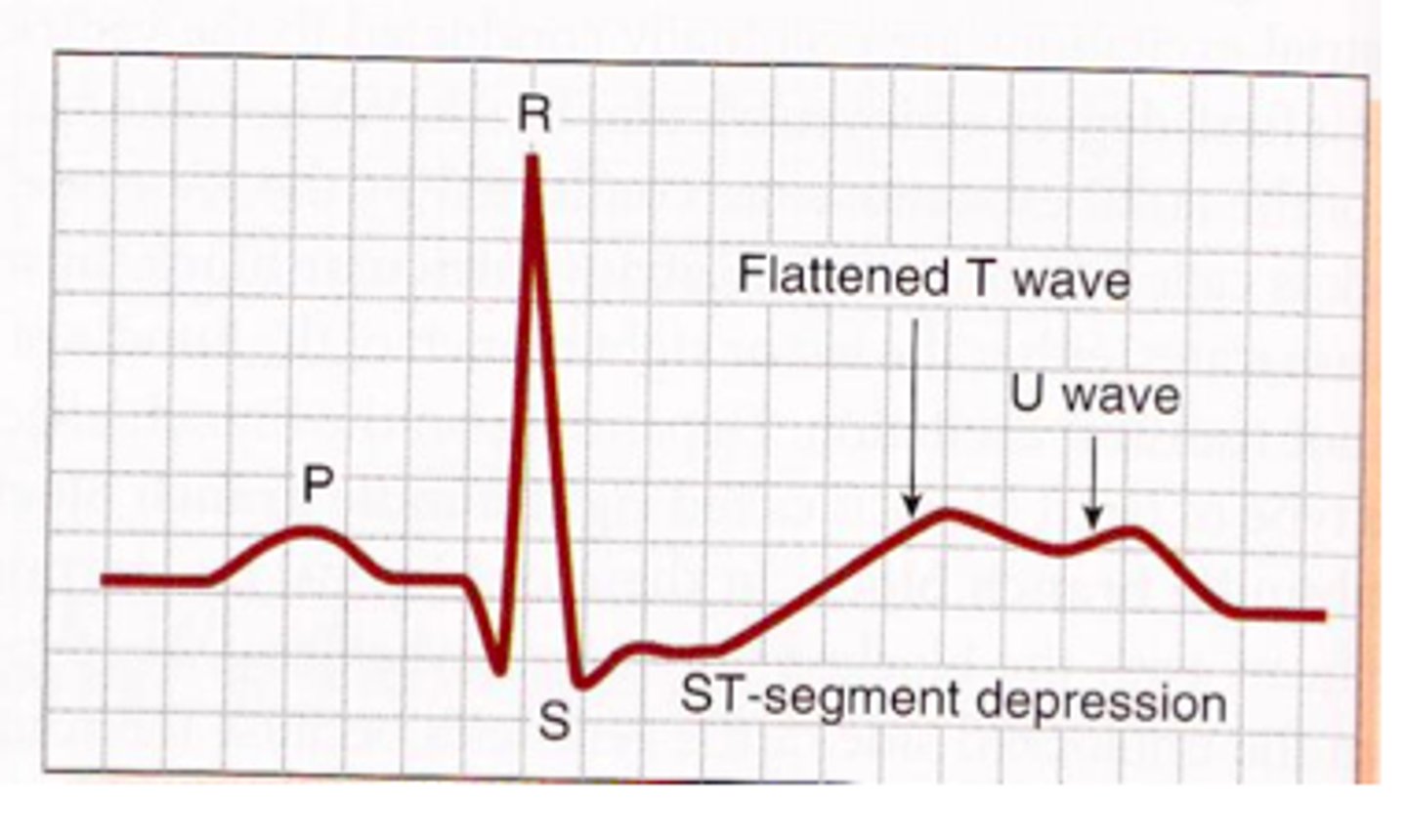
sodium
reabsorption controlled by aldosterone
calcium
levels controlled by parathyroid hormone PTH
1.5 L
average amount of urine that is excreted each day
diabetes insipidus
low ADH, antidiuretic hormone; high urine output & intense thirst; may lead to dehydration
SIADH
syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone; too much ADH - water retention leads to hyponatremia & brain swelling