As Level Physics - Physical Quantities and Units
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
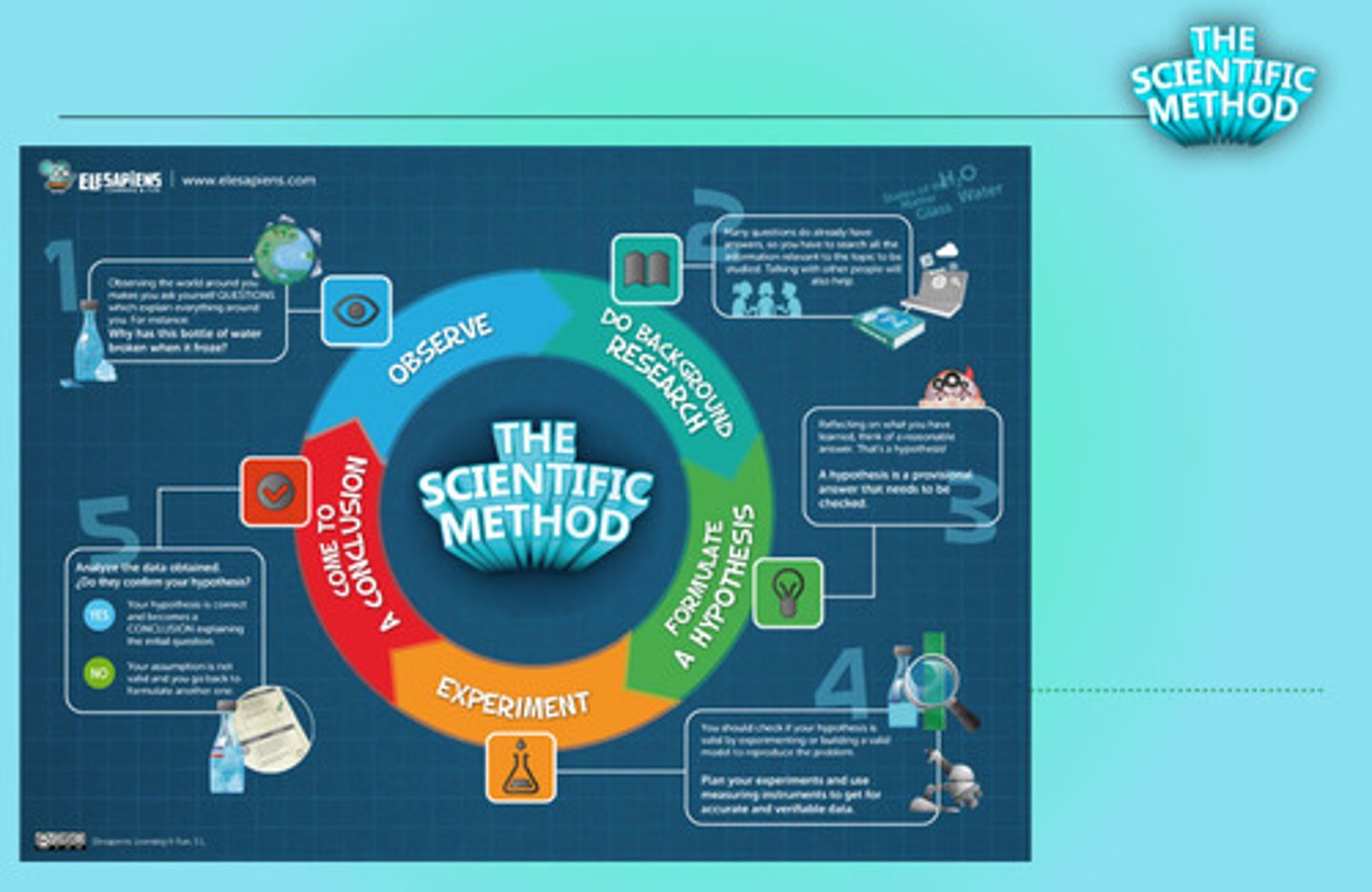
Scientific Method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions.
scientific theory
a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations
scientific law
a rule that describes a pattern in nature
physics
the study of matter and energy and how they interact
experiment
a scientific procedure undertaken to make a discovery, test a hypothesis, or demonstrate a known fact.
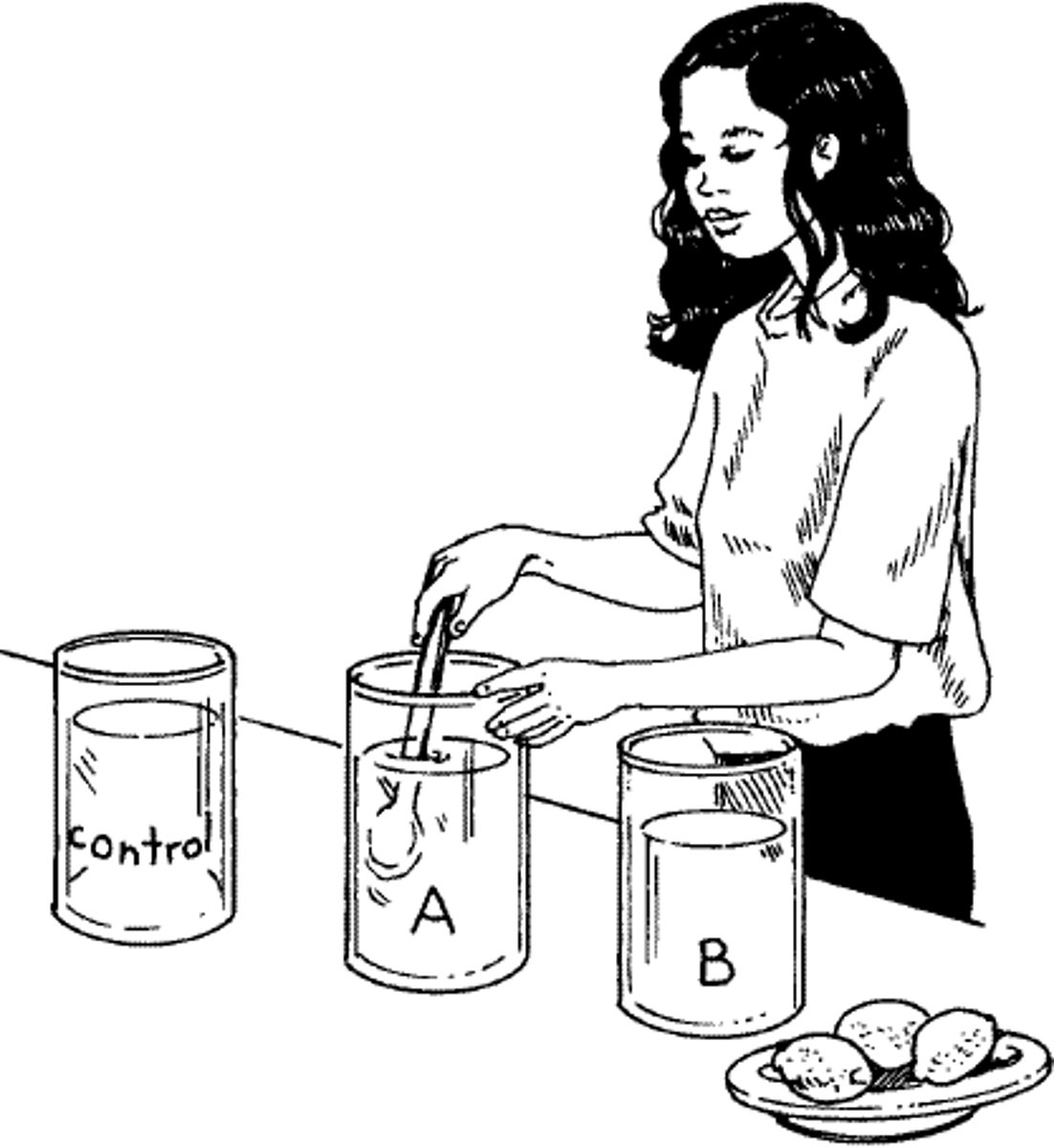

Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory

Units
standard quantities used to specify measurements
Precision
a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another
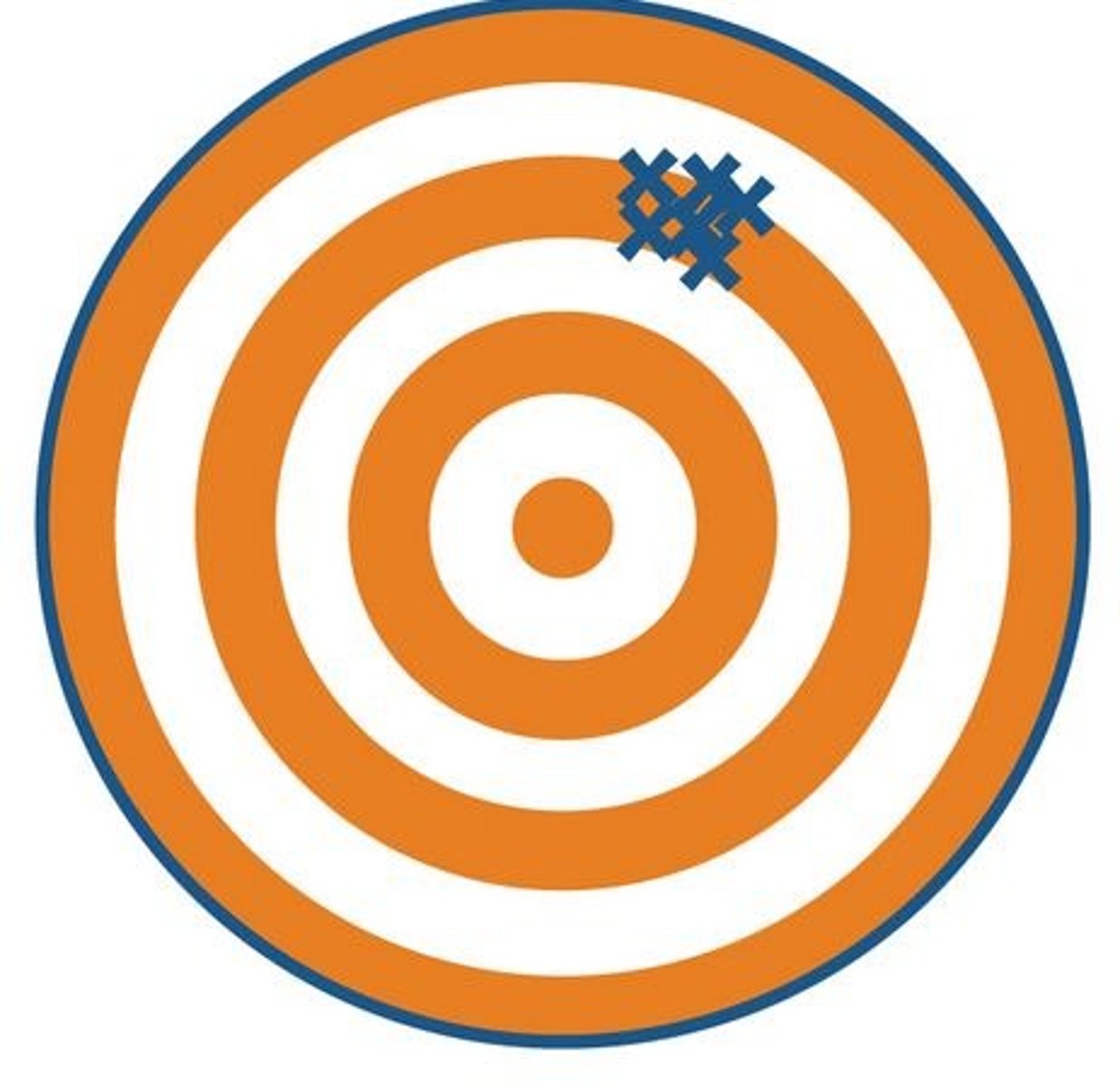

Accuracy
how close a measurement is to the true value
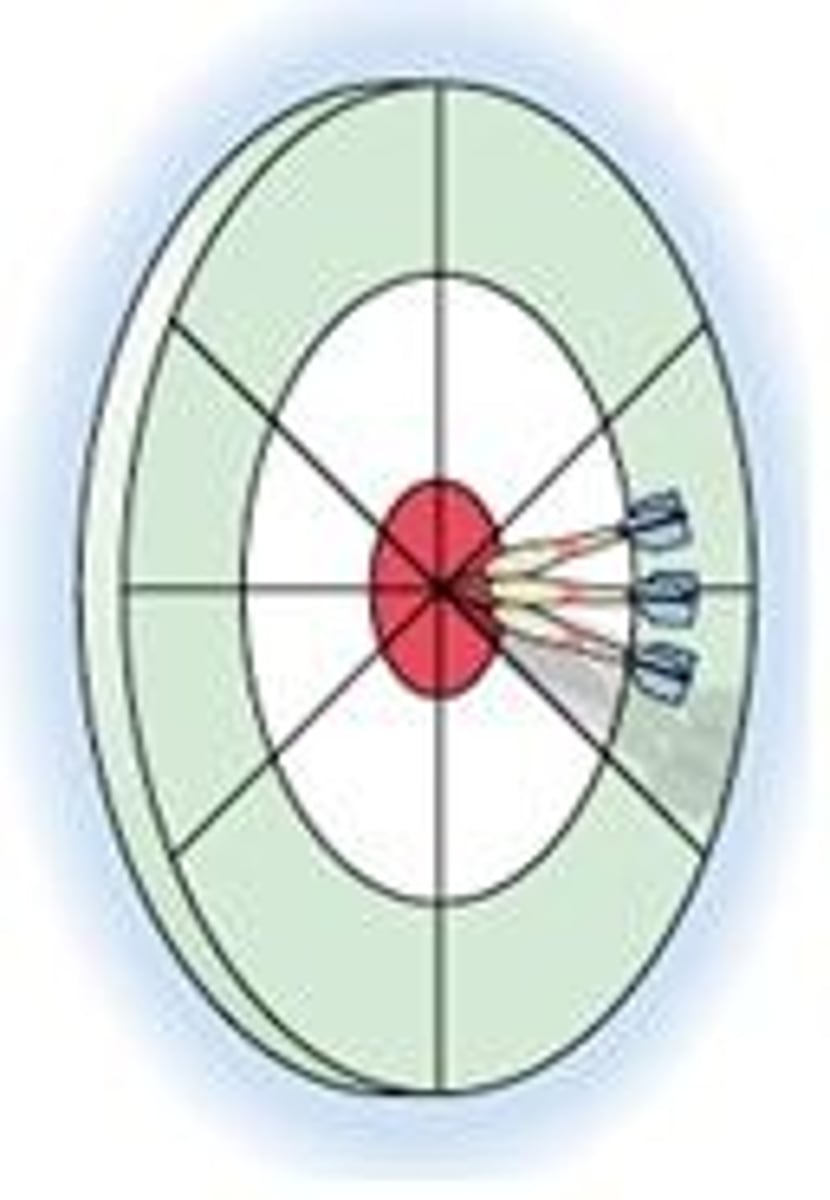
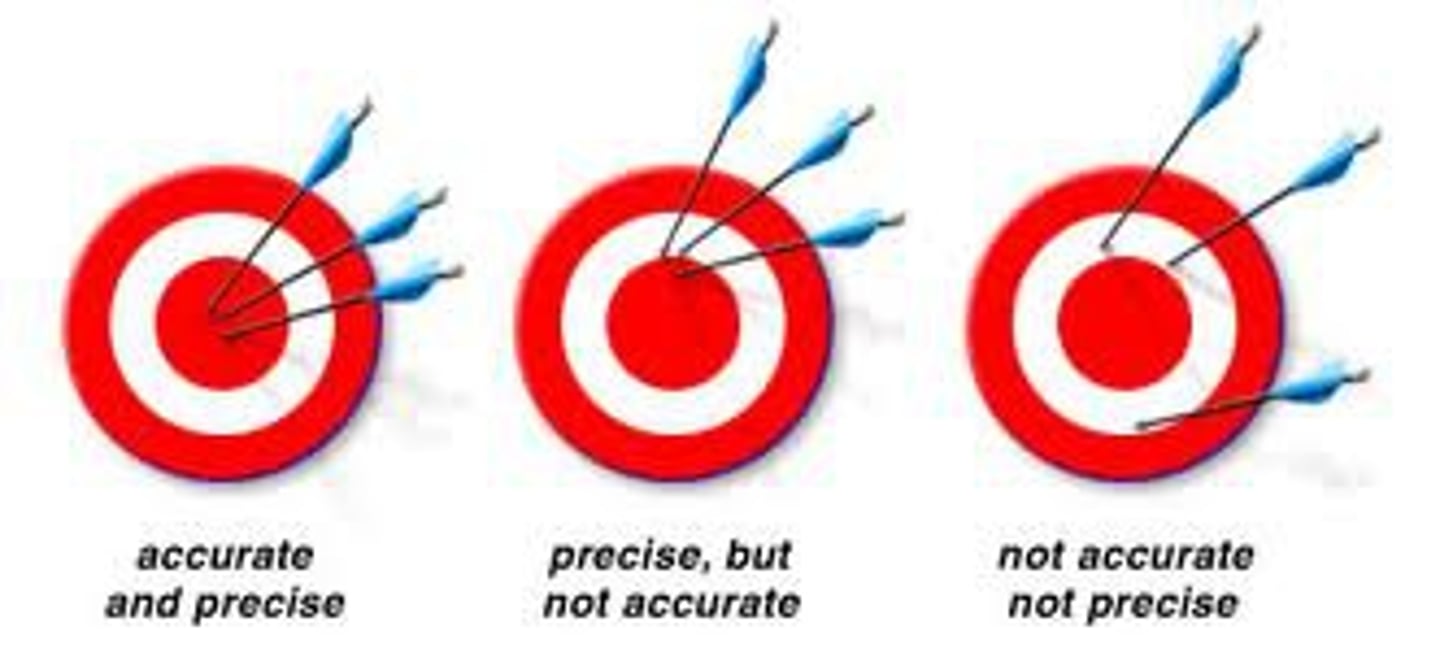
Precision vs. Accuracy
precision is consistency of output whereas accuracy is alignment with the targeted value or goal
error
the difference between the experimental value and the accepted value
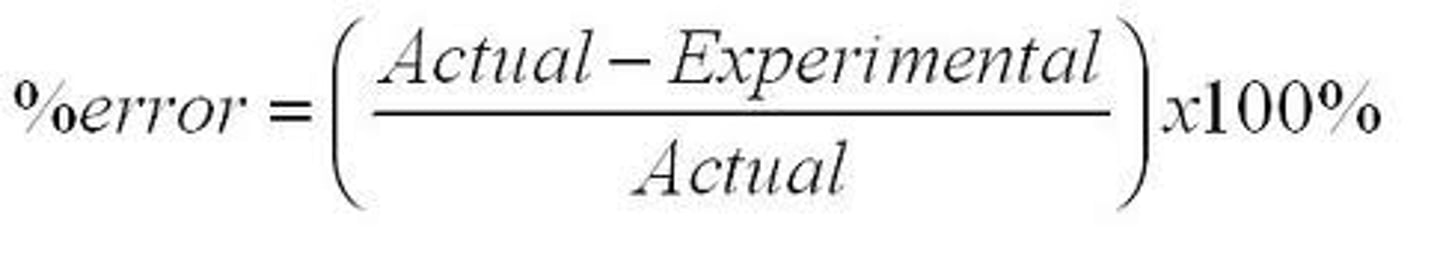
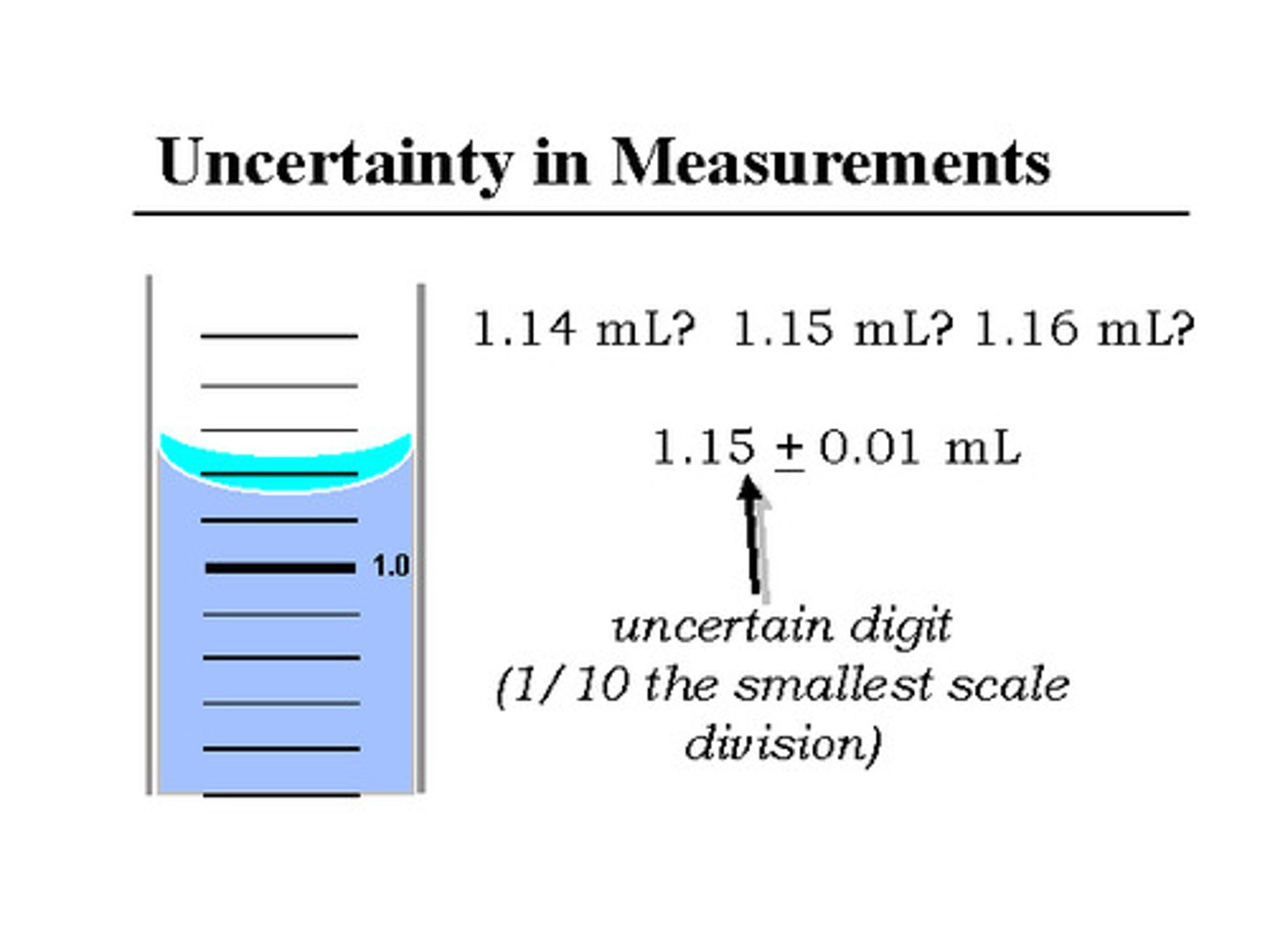
uncertainty
an estimate of how much a measured or calculated value differs from a true value
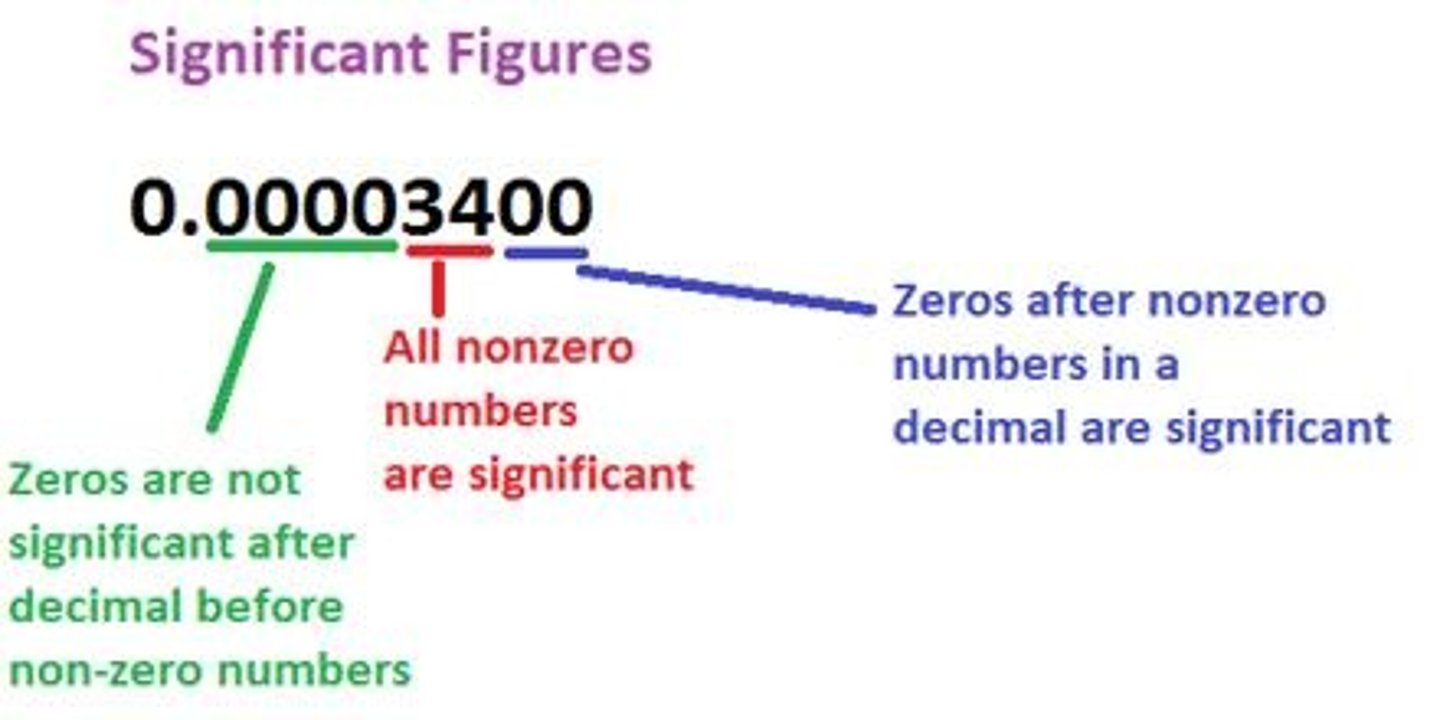
significant figures
All the digits that can be known precisely in a measurement, plus a last estimated digit
scientific notation
A method of writing or displaying numbers in terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10.

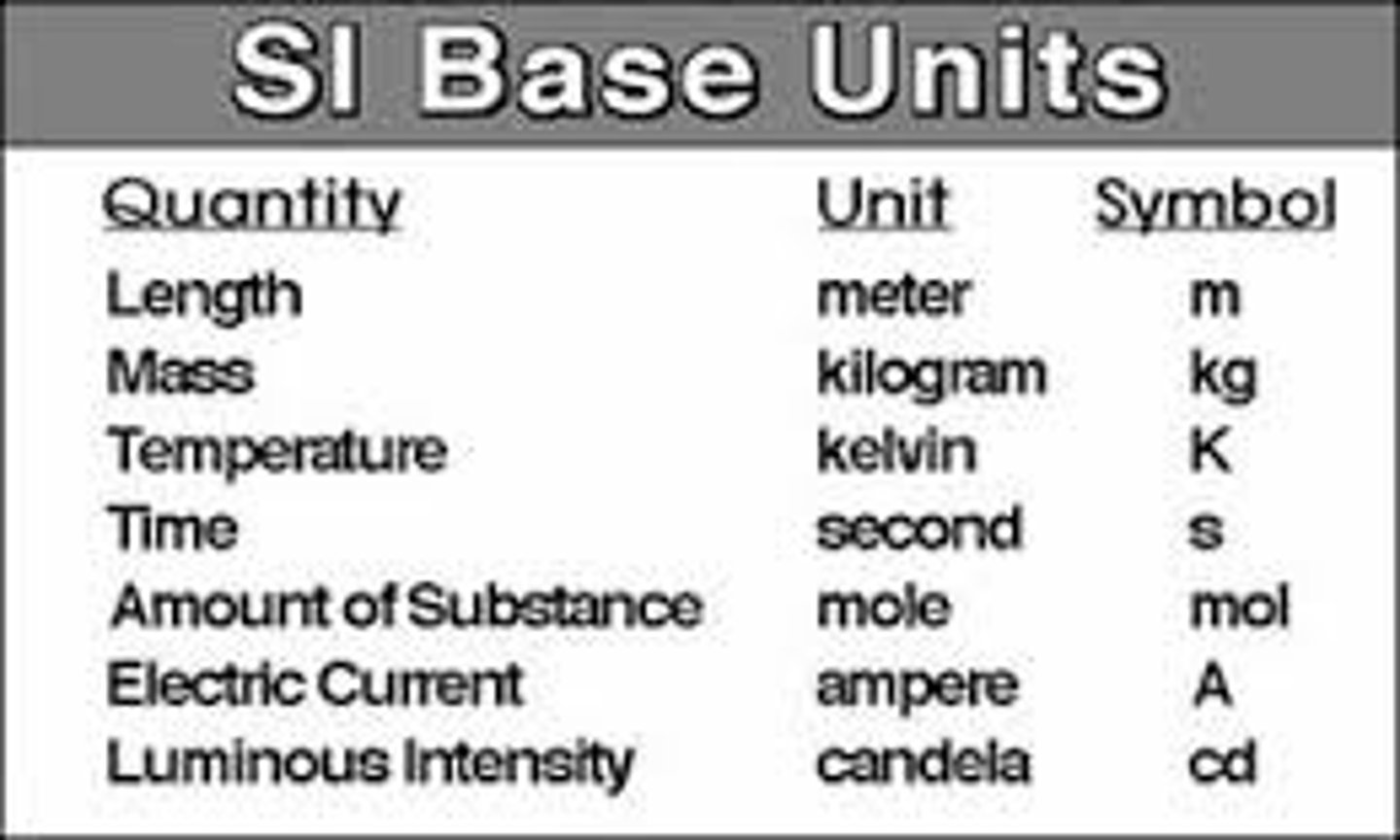
meter (m)
SI base unit of length

Kelvin (K)
SI base unit of temperature

second (s)
SI base unit for time
kilogram (kg)
the SI unit for mass, abbreviated (kg)

SI system of measurement
the International System of Units developed by scientists as a worldwide standard of measurement
kilo (k)
prefix meaning 1000 (10^3)

mega (M)
prefix meaning 1000000 (10^6)
giga (G)
prefix that is one billion; 10^9
tera (T)
prefix; 10^12
deci (d)
prefix; 10^-1
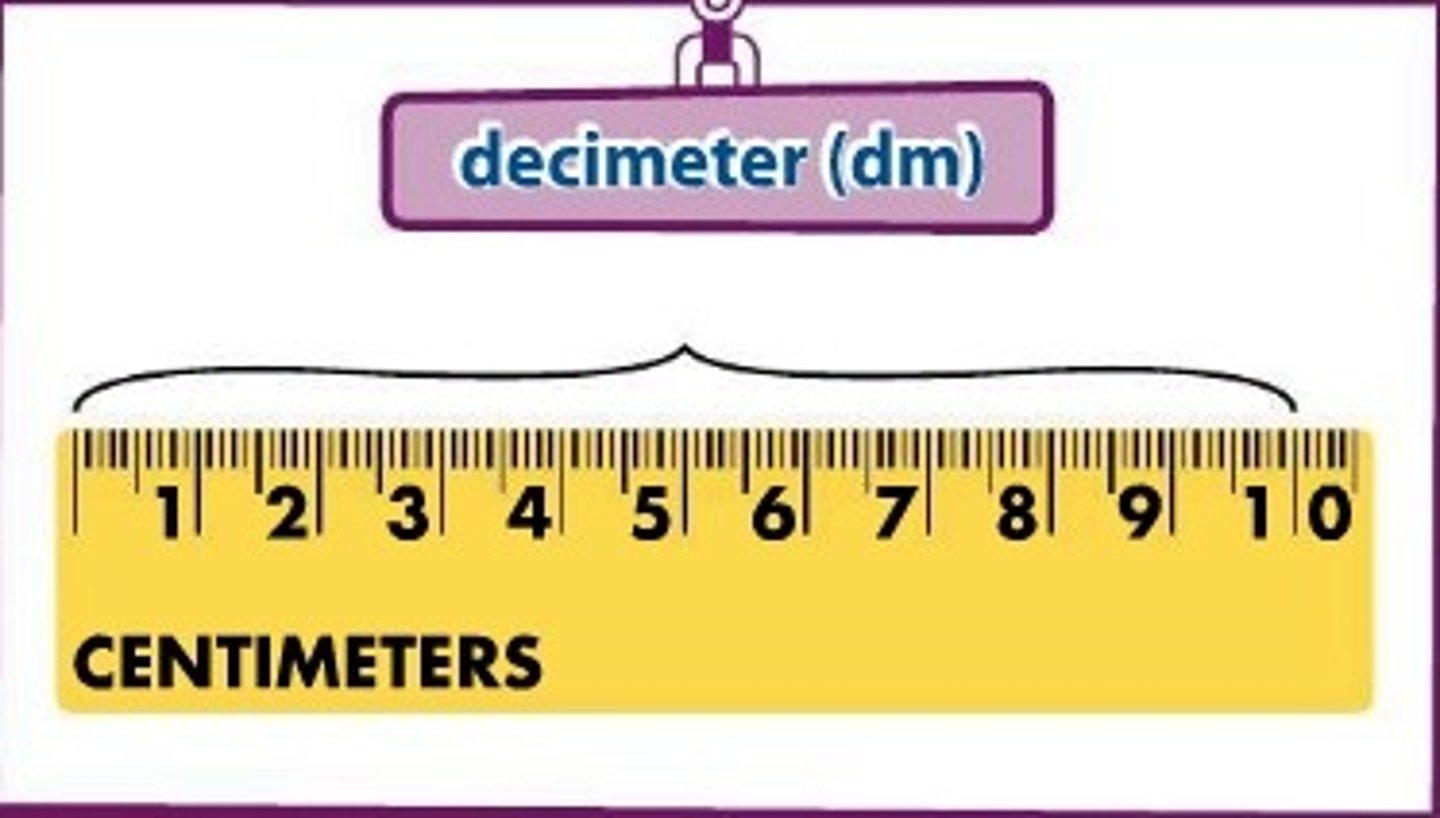
centi (c)
prefix; 10^-2
milli (m)
prefix; 10^-3

micro (μ)
prefix; 10^-6
nano (n)
prefix; 10^-9
pico (p)
prefix; 10^-12
candela (cd)
SI base unit of luminous intensity

Amperes (A)
a unit of electric current equal to a flow of one coulomb per second.
moles (mol)
SI unit of measurement represented by "n" for amount of substance
Newton (N)
SI unit of force
Pascal (Pa)
SI unit of pressure
Joules (J)
SI unit for energy
Watt (W)
SI unit of power
Hertz (Hz)
cycles or waves per second, unit for the measurement of frequency
Coulomb (C)
SI unit of electric charge
Volts (V)
unit for voltage
Ohms (Ω)
unit for electrical resistance
Tesla (T)
Unit for the magnitude of a magnetic field
Farad (F)
The SI unit for capacitance