IOA2 Exam 3 - Visual Pathway Pt 1
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
What is the visual pathway?
A group of cells and synaptic connections that carry visual information from the environment to the brain for processing
What is the first step of the visual pathway?
Light from the external world is converted into electrical signals by photoreceptors in the retina
After photoreceptors convert light into electrical signals, how does the signal travel?
Through RGCs, which form the optic nerve
Where does the signal travel thru after reaching the optic nerve?
Optic chiasm, where some fibers cross over
Which fibers cross over at the optic chiasm?
Fibers from the nasal retina cross to the opposite hemisphere, while temporal fibers remain uncrossed
Which area is the continuation of optic nerve fibers after the optic chiasm, and where does this carry visual information to?
Optic tract carries visual info to the thalamus (LGN)
Where do optic tract fibers synapse in the brain?
LGN of the thalamus (diencephalon)
After passing through the LGN, where does visual information go?
Visual cortex (primary and association areas), for processing
What role does the primary visual cortex play in vision?
It processes vision
Which is the first area to receive visual input, and is where initial processing occurs?
Primary visual cortex (V1)
Visual information processing doesn't stop at V1! Which other visual areas or associated areas process more complex visual information?
V1 --> V2 --> MT/V5 --> VIP, MST, or FST
V1 --> V3 --> V4 --> FST, IT, or TEO
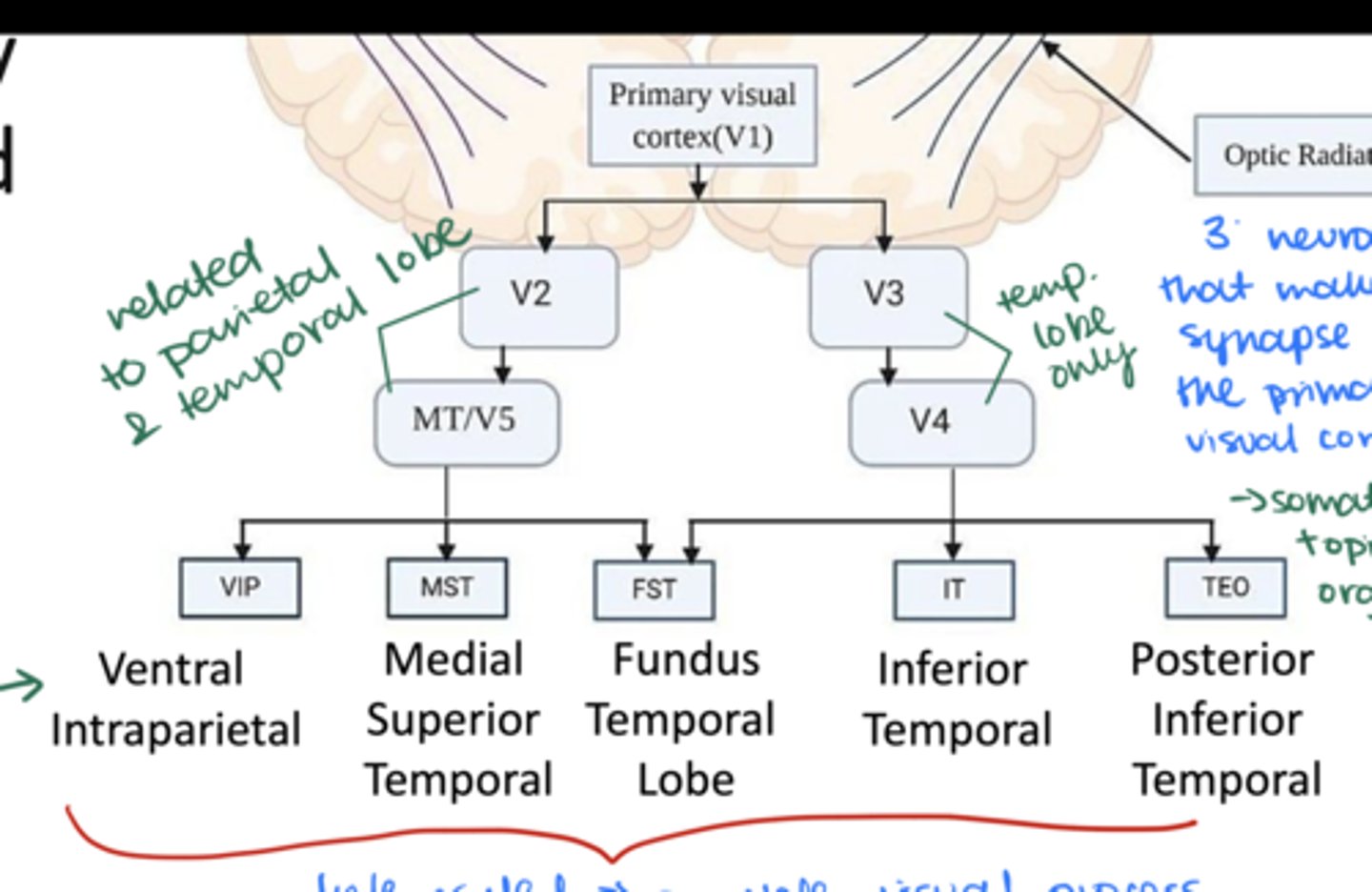
Which main structures are involved in the primary visual pathway? (ie summarize the route visual information takes from the eye to the brain for processing)
-Retina
-Optic nerve
Optic chiasm
-Optic tract
-Laternal Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
-Optic radiations
-Primary Visual Cortex (V1)
-Visual association areas

Which part of the brain is V1 located in?
Occipital lobe
Which artery is V1 located in?
Calcarine artery
What is the process of forming the neural tube called?
Neurulation
At what week during nervous system development does neurulation occur?
3-8 weeks
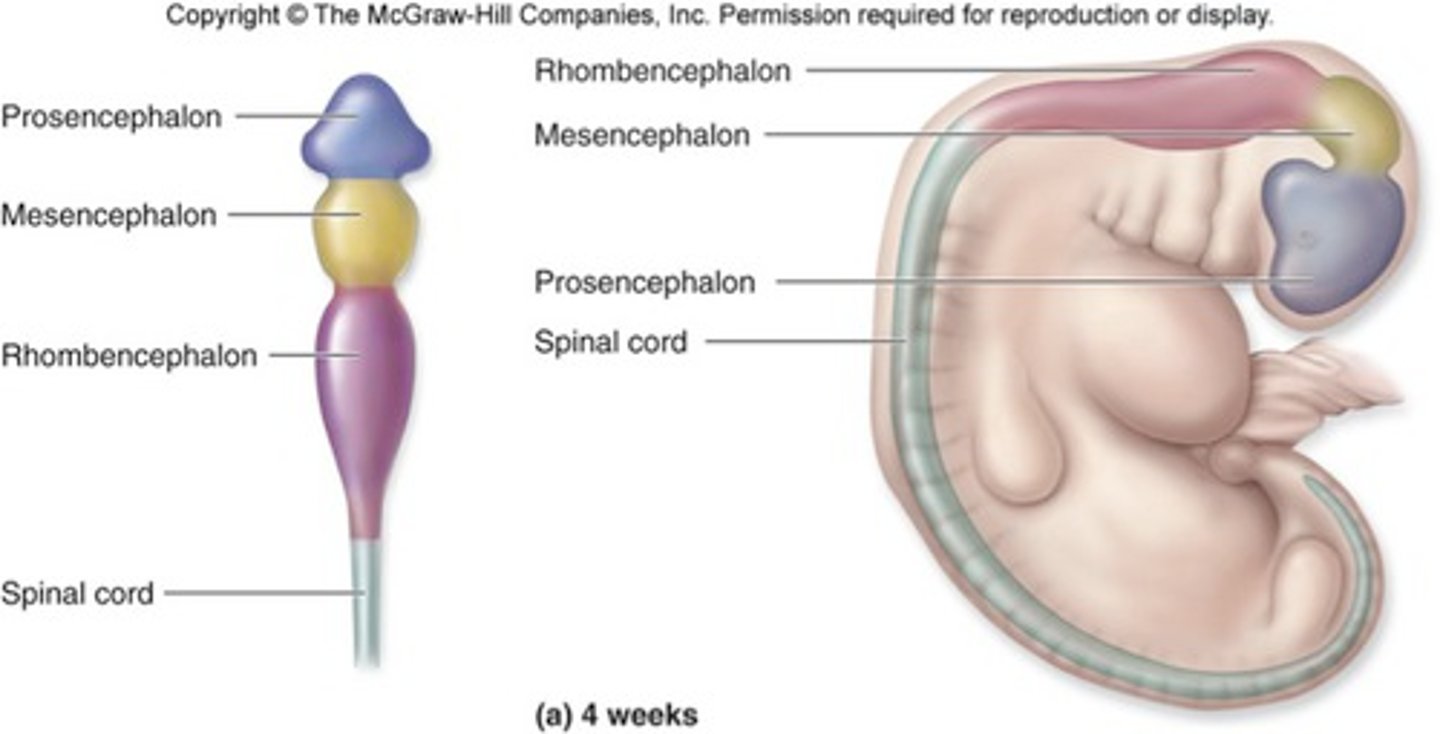
In the early embryo (3-4 weeks), the neural tube forms
3 primary brain vesicles
List the 3 primary vesicles formed by the neural tube
-Prosencephalon (forebrain)
-Mesencephalon (midbrain)
-Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
Forebrain =
Prosencephalon
Midbrain =
Mesencephalon
Hindbrain =
Rhombencephalon
Which of the 3 primary vesicles are considered part of the brainstem?
-Midbrain or Mesencephalon
-Hindbrain or Rhombencephalon
What occurs in the embryo at 5 weeks?
The 3 primary brain vesicles differentiate into 5 secondary brain vesicles
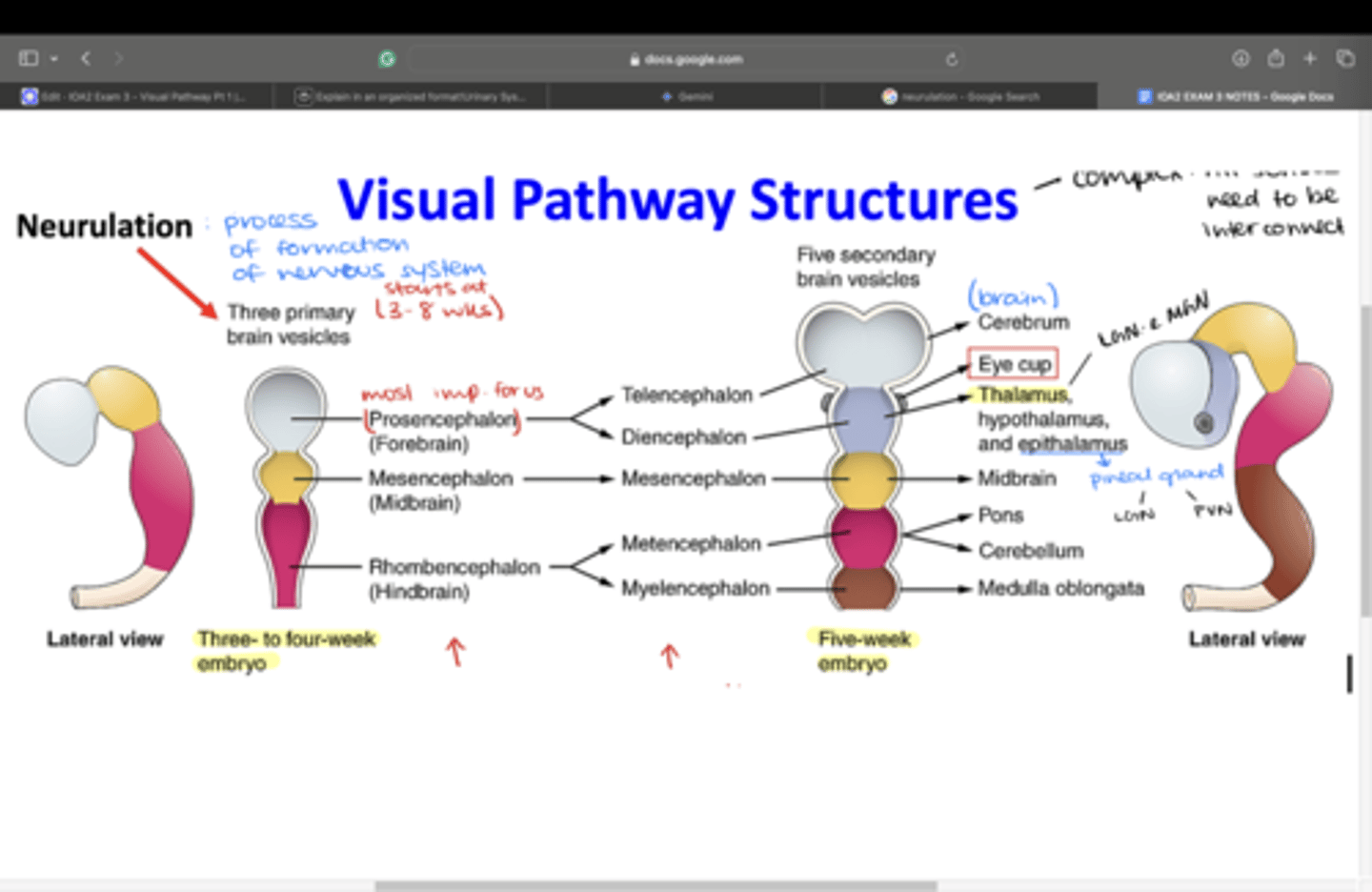
Which secondary brain vesicles differentiate from the prosencephalon?
-Telencephalon
-Diencephalon
The two areas of the forebrain (telencephalon and diencephalon) are separated by the ________ in the adult brain.
optic chiasm
Which structures does the telencephalon give rise to?
-Optic tracts
-Optic radiations
-LGN
-Cerebral cortex (cerebellum)
Which structures does the diencephalon give rise to?
-Optic cup
-Optic stalk
-Optic chiasm
-Epithalamus (pineal gland)
-Thalamus --> LGN + MGN
-Hypothalamus
Which secondary brain vesicle develops from the mesencephalon?
Mesencephalon (stays the same)
Which structures does the mesencephalon give rise to?
-Midbrain
-Tectum
-Superior colliculi
-Inferior colliculi
Which secondary brain vesicles differentiate from the rhombencephalon?
-Metencephalon
-Myelencephalon
Which strucutres does the metencephalon give rise to?
-Pons
-Cerebellum
Which structures does the myelencephalon give rise to?
Medulla oblongata
What structure does the optic nerve develop from?
Optic stalk
Which cells form the optic nerve?
Axons of ganglion cells
What develops at the center of the optic cup?
Optic fissure develops into the optic disc
What penetrates the optic fissure, and what does this eventually develop into?
Hyaloid vessels, which develops into the CRA
What does the neural ectoderm develop?
-Optic cup (retina, iris, CB)
-Optic stalk
The neural crest cells (NCCs) interact with the _______ and ________ to contribute to the development of the optic nerve and optic. stalk.
optic vesicle and surface ectoderm
The neural crest cells (NCCs) interact with the optic vesicle and surface ectoderm to contribute to the development of the _______ and _______.
optic nerve and optic stalk
The neural crest cells (NCCs) also develop the _________ to contribute to the formation of the corneal endothelium, eyelids, iris, and ciliary body.
optic nerve meninges
The neural crest cells (NCCs) also develop the optic nerve meninges to contribute to the formation of the (4):
-corneal endothelium
-eyelids
-iris
-CB
Defects in NCCs migration and differentiation can lead to eye diseases like...
-Axenfeld-Rieger Syndrome
-Peters Anomaly
Both Axenfeld-Rieger Syndrome and Peters Anomaly are:
A: Autosomal dominant
B: Autosomal recessive
C: X-linked dominant
D: X-linked recessive
Autosomal recessive
3 multiple choice options
What part of the eye is primarily affected in Axenfeld-Rieger Syndrome?
Anterior segment of the eye
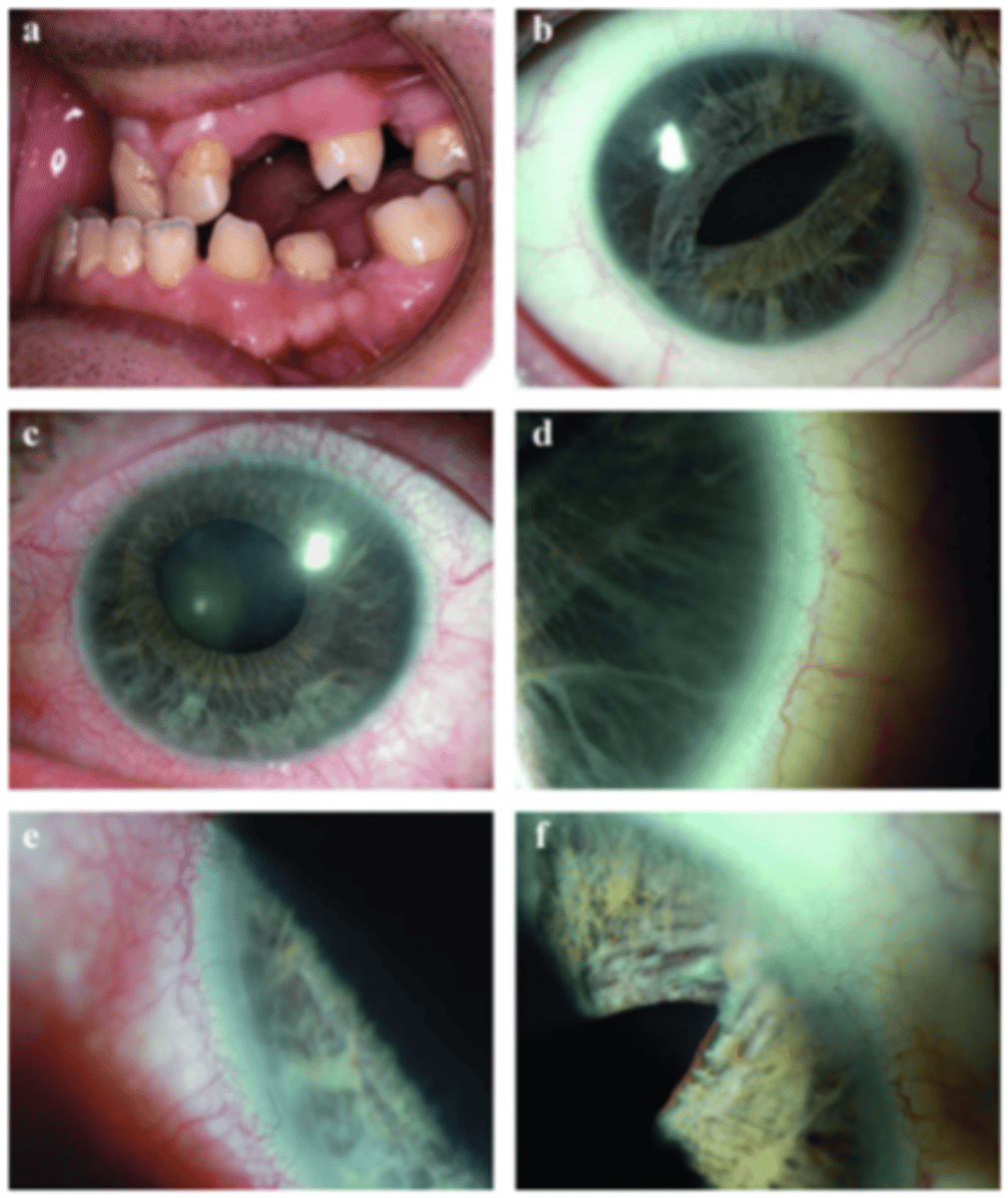
Which abnormalities in the anterior segment of the eye can lead to Axenfeld-Rieger Syndrome?
-Aniridia
-Glaucoma (50% of cases)
-Childhood
-AR
Which gene mutations are associated with Axenfeld-Rieger Syndrome?
-PITX2
-PAX6
-FOXC1
-RIEG2
What are the underlying NCCs defects in Axenfeld-Rieger Syndrome?
Defects in NCCs
-migration
-differentiation
-cell cycle arrest in the anterior chamber, facial bones, and CV system
What is Peters Anomaly?
Rare congenital disorder characterized by central corneal opacity with a clear peripheral cornea
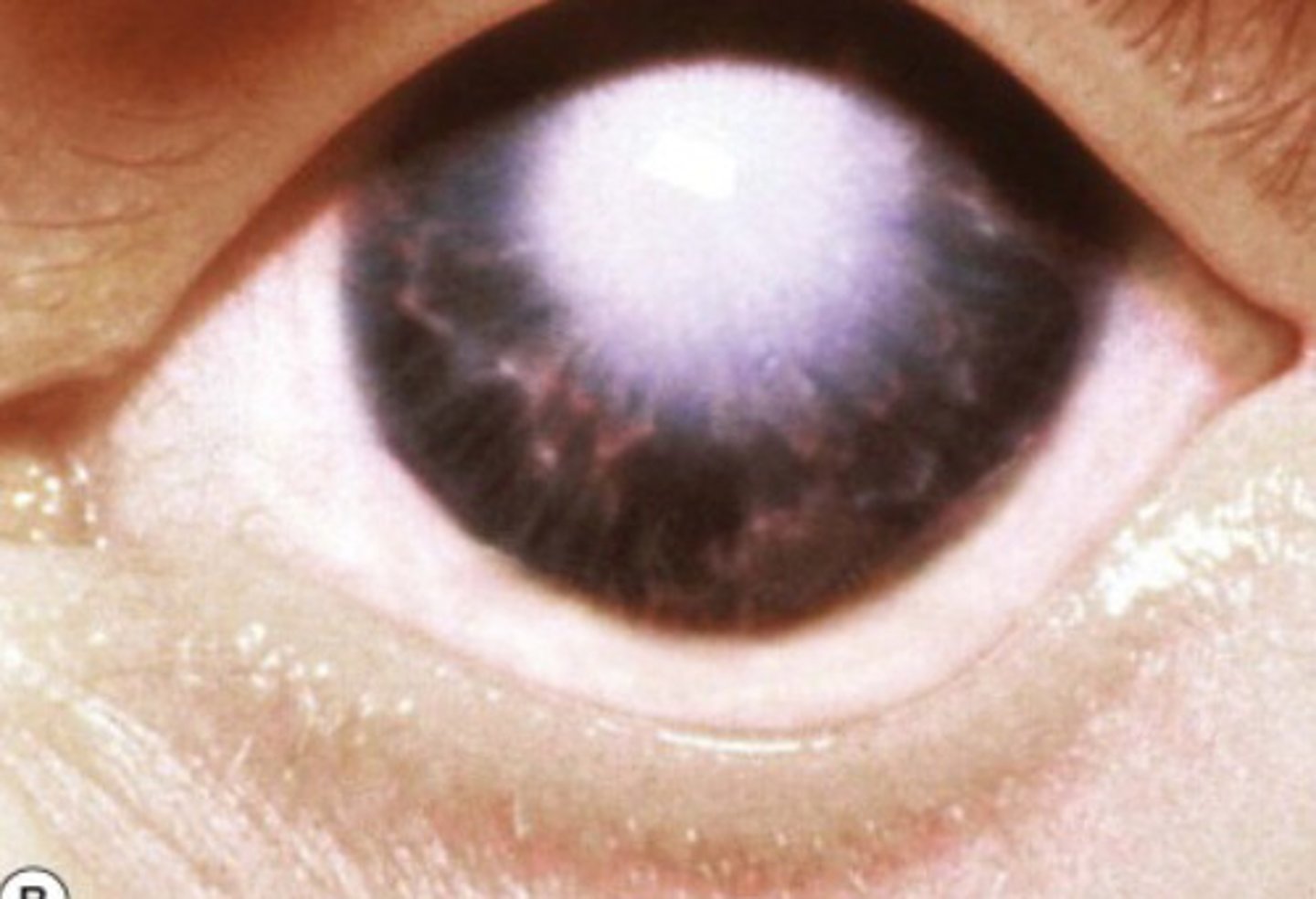
What is the tx for Peters Anomaly?
Surgery of corneal transplantation
What happens during weeks 6-8 of embryological development?
Increase of differentiation of visual structures from the neuroectoderm and NCCs
What visual structures differentiate from neuroectoderm and NCCs during weeks 6-8?
-Neural retina
-Future RPE
-Sclera
-Choroid
-Optic nerve sheaths
-Ganglion cell axons in optic nerve
When does myelination of the axons within the optic nerve begin?
Shortly before birth and continues after birth
What are the first cells in the visual pathway that convert light energy into neuronal signals?
Photoreceptors
Name the types of photoreceptors in the retina
-Blue cones
-Green cones
-Red cones
-Rods
Photoreceptors convert light energy into neuronal signals that is passed to the:
bipolar cell --> ganglion cell layer --> ON
What cells modulate signals between photoreceptors and bipolar cells?
Horizontal cells
What cells modulate signals between bipolar cells and retinal ganglion cells?
Amacrine cells
What are the output neurons of the retina whose axons form the optic nerve?
Retinal ganglion cells
Where are all the cells and synapses of the visual pathway located?
Within the retina
Where do retinal ganglion cells project, and where do their fibers exit?
-Project into the NFL
-Fibers exit retina via the ON
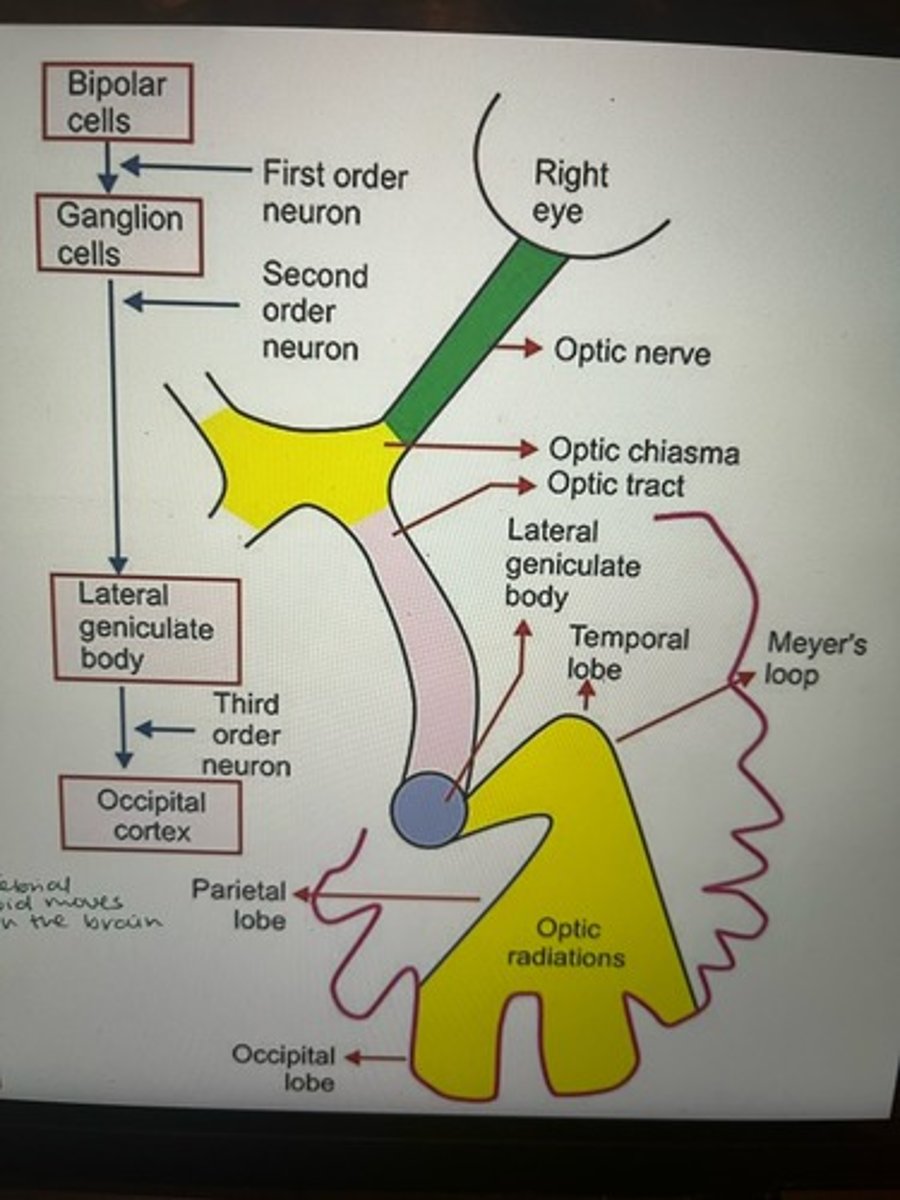
What is Meyer's Loop?
A bundle of white matter fibers that runs from the thalamus to the occipital cortex, looping around the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle
Meyer's loop runs from the _______ to the _______
thalamus --> occipital cortex
What does Meyer's loop loop around?
Temporal horn of the lateral vesicle
Part of Meyer's loop which is a broad white band of white matter that carries visual info from the retina
Optic radiation
What type of cell is the first order neuron in the visual pathway connected to?
Bipolar cells
What type of cell is the second order neuron in the visual pathway connected to?
Ganglion cells
Where is the third order neuron in the visual pathway located?
Lateral geniculate body
What are the steps of the flow of visual information, for light entering the right eye?
1) Light enters the Right Eye
2) Bipolar Cells and Ganglion Cells process the signal
3) First and Second Order Neurons transmit the signal
4) Optic Nerve carries information from the eye
5) Optic Chiasma: Nerves cross over
6) Optic Tract carries information onward
7) Lateral Geniculate Body (LGB) processes information (Third Order Neuron)
8) Optic Radiations carry information to the cortex
9) Meyer's Loop (part of radiations) loops around the temporal horn
10) Occipital Cortex interprets the visual information
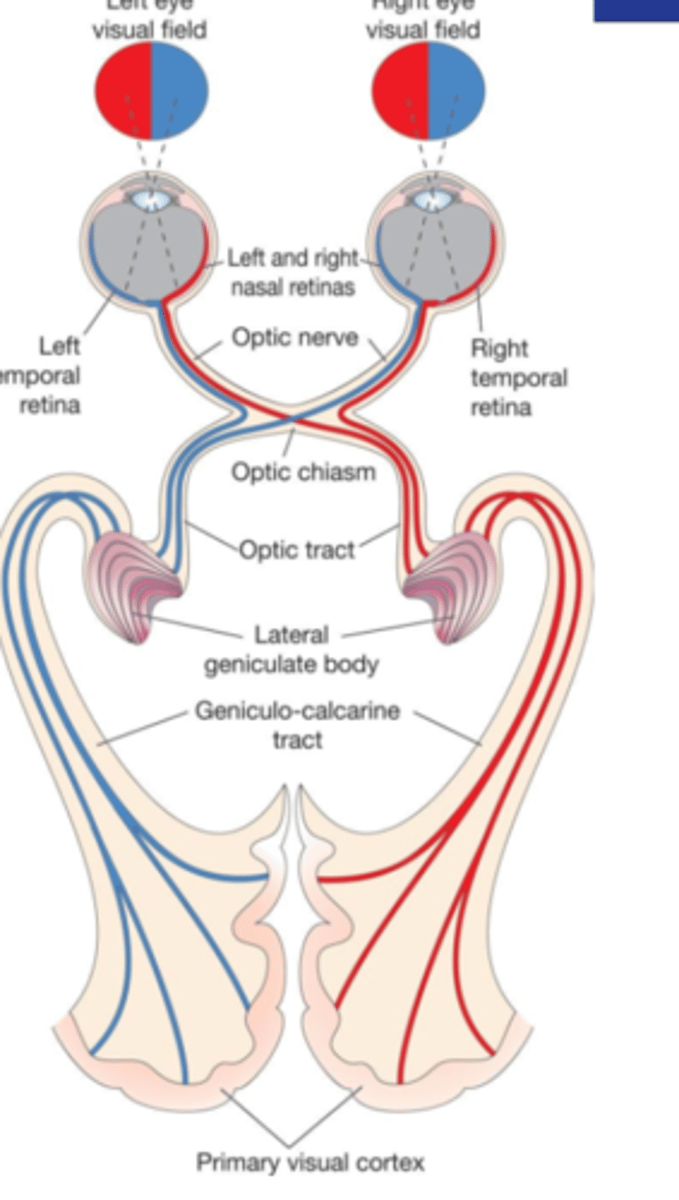
How are corneal and retinal quadrants anatomically oriented relative to the optic disk?
-Nasal (towards nose)
-Temporal (towards temporal bone)
-Superior
-Inferior
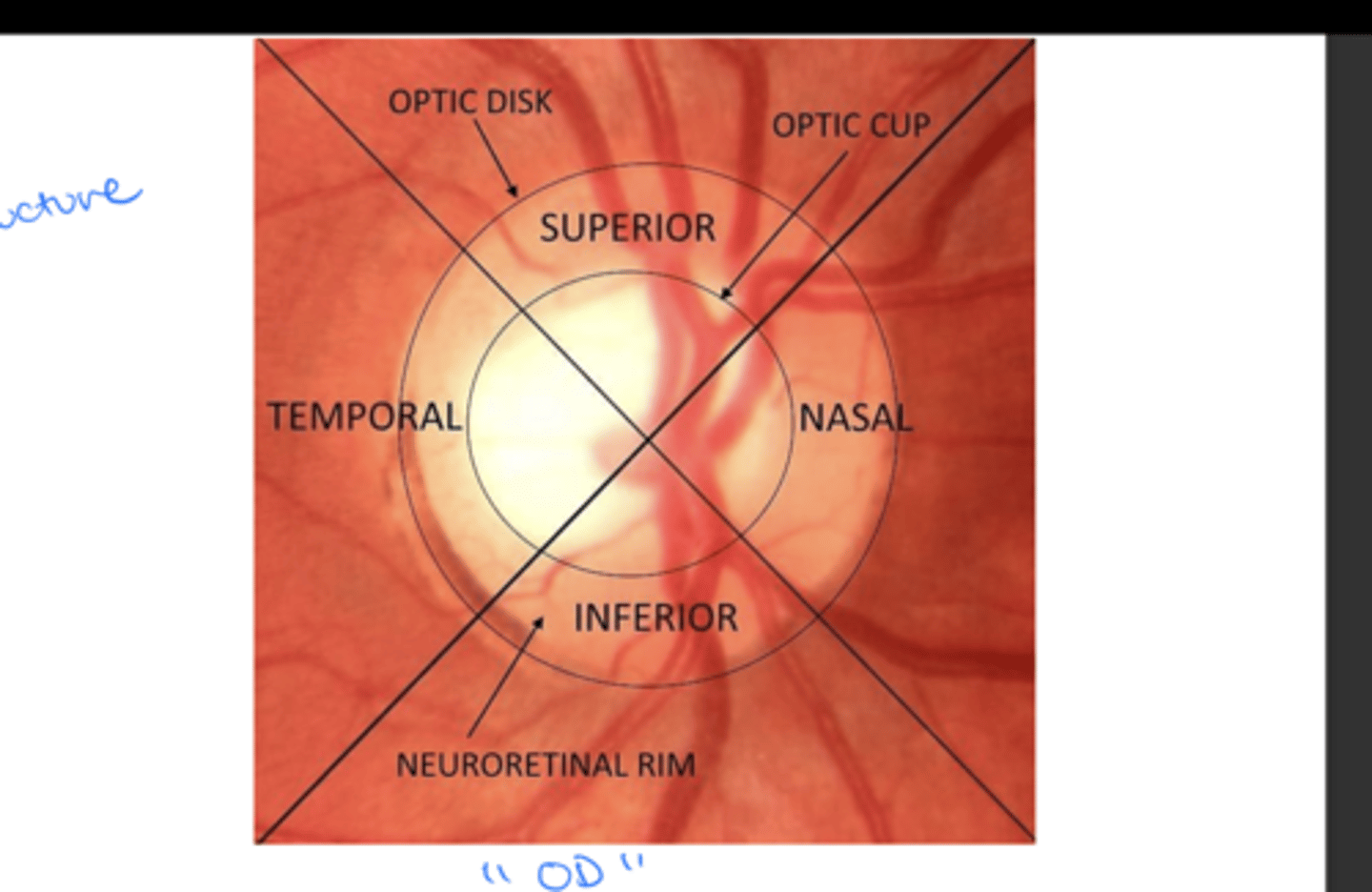
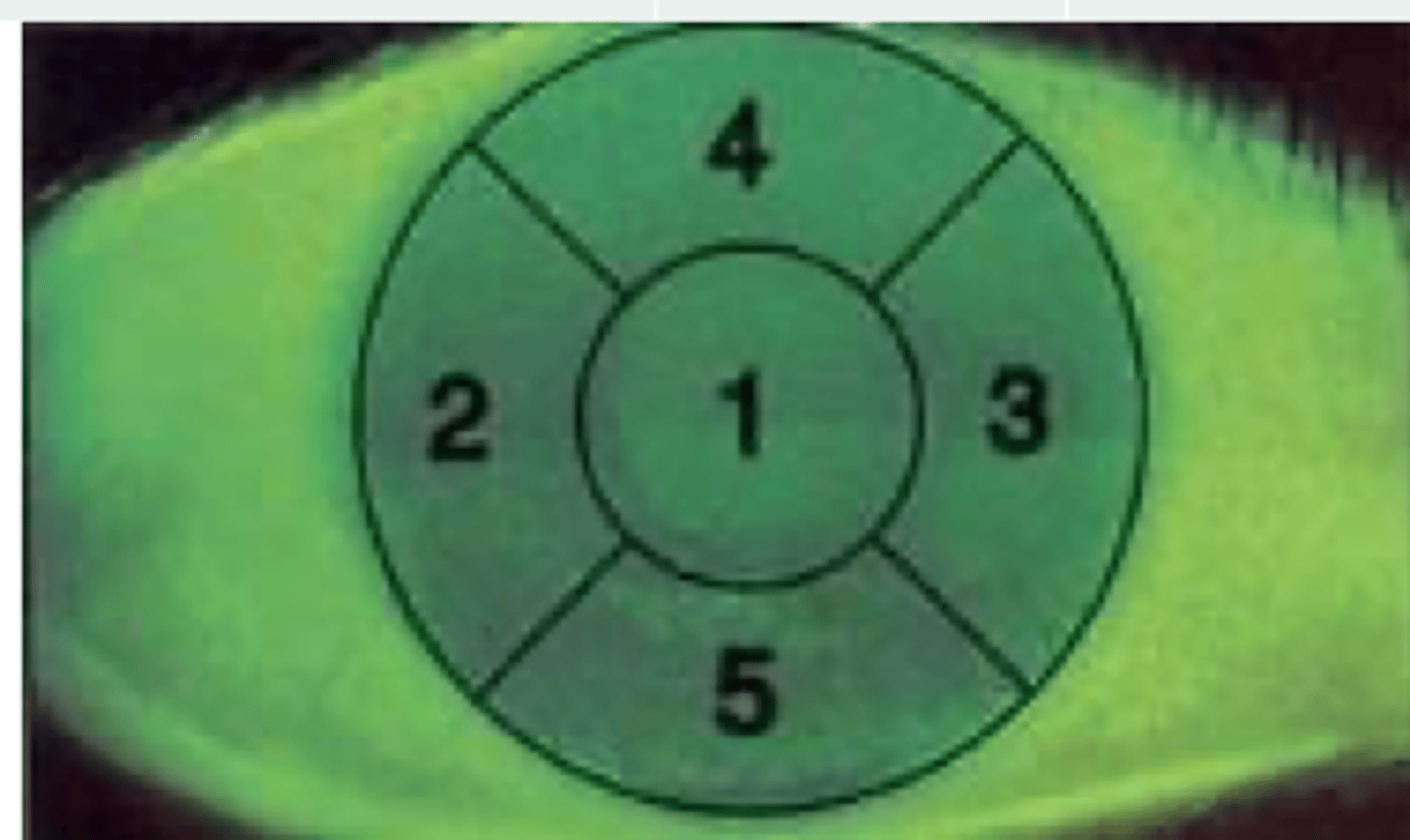
OD:
2 = Temporal
3 = Nasal
4 = Superior
5 = Inferior
OS:
2 = Nasal
3 = Temporal
4 = Superior
5 = Inferior
Label #2-5 in a right eye vs left eye:

What happens to the nasal information from RGC axons at the optic chiasm?
Contralateral nasal information of RGCs axons crosses at the level of the optic chiasm (optic nerve decussation)
Where do nasal RGCs axons synapse?
At the opposite (contralateral) side of the brain
What type of information does the optic nerve contain?
Info ONLY from one eye (ipsilateral nasal and temporal)
What type of information does the optic tract contain?
Mixed info from both eyes
-ipsilateral from temporal RGC axons
-contralateral from nasal fibers of the opposite eye
Where in the forebrain do the RGC fibers in the optic tract synapse?
-LGN
-Pulvinar
-Superior colliculus (SC)
-Tectal areas
Where do the fibers that project from the LGN synapse?
As optic radiations, they synapse at the PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX (V1) in the occipital lobe
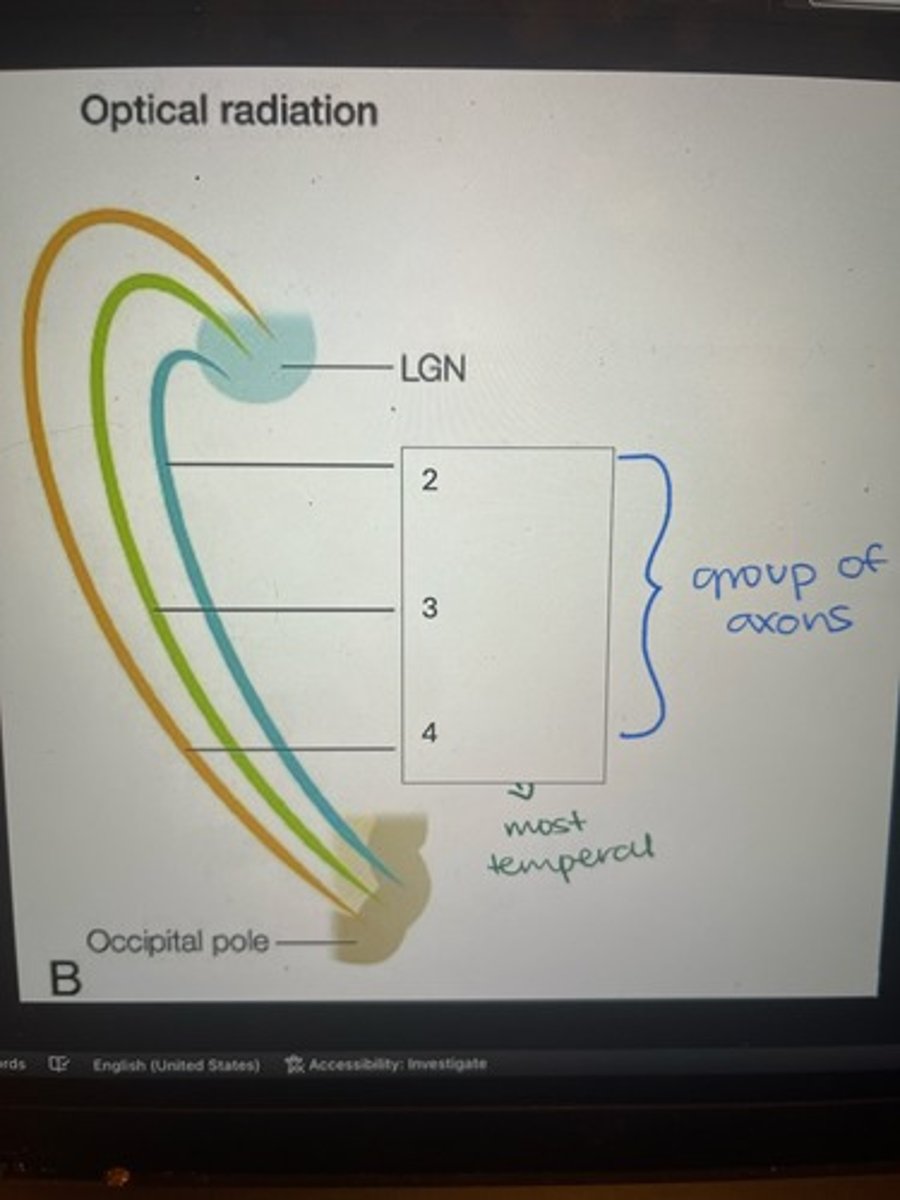
2) Dorsal bundle
3) Central bundle
4) Meyer's loop
Label the components of optical radiation (#2-4)
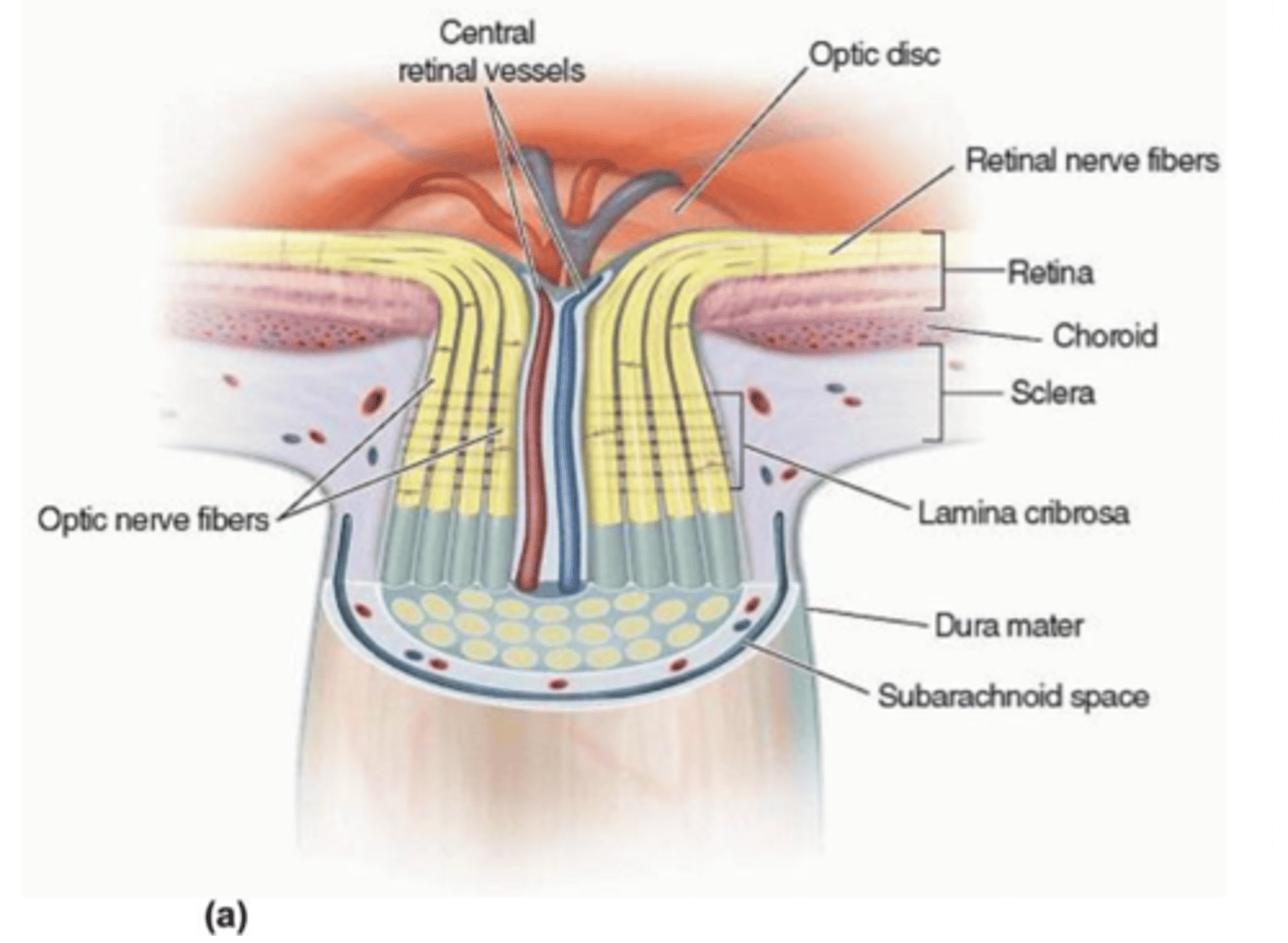
How do retinal nerve fibers exit the eye?
Retinal nerve fibers make a 90 degree turn at the optic disc and exit as the optic nerve
Which type of fibers does the optic nerve consist of?
RGCs fibers
Where do 90% of optic nerve fibers synapse?
LGN
Where do 10% of optic nerve fibers project to?
Areas controlling pupil responses or the circadian rhythm
How many nerve fibers are in the optic nerve?
1.0 - 1.3 million
What is the length of the optic nerve?
5-6 cm long
What is the diameter of the optic nerve when IOP <20mmHg?
3.5-5 mm
The optic nerve extends from the _______ to the _______.
eye --> optic chiasm
What 4 segments is the optic nerve divided into?
-Intraocular
-Intraorbital
-Intracanalicular
-Intracranial
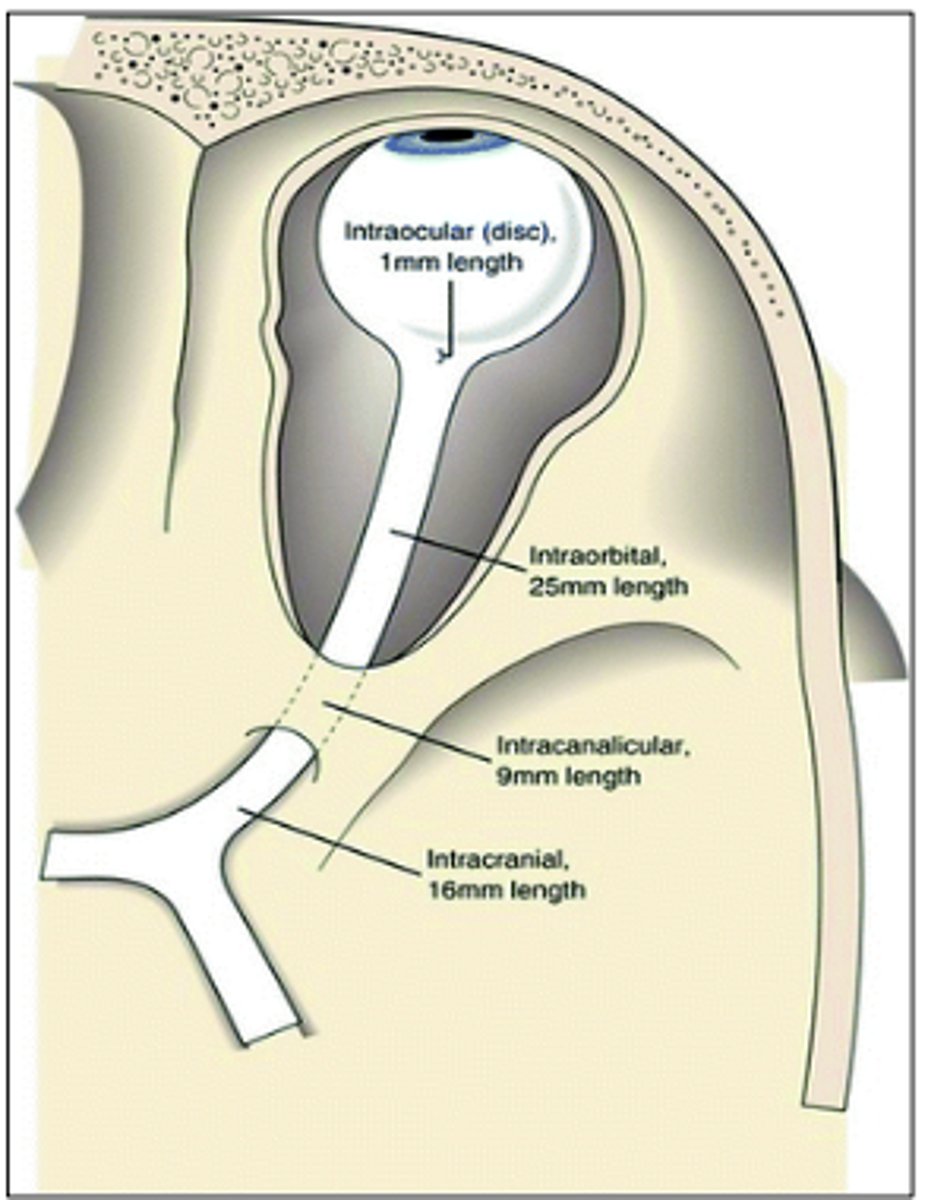
What is the length of the intraocular (disc) segment of the optic nerve?
0.7 - 1 mm
What are the regions of the intraocular segment of the optic nerve?
-Prelaminar
-Laminar (lamina cribosa)
-Retrolaminar
1) Prelaminar region
2) Laminar region
3) Retrolaminar region
Label the regions of the intraocular segment of the optic nerve
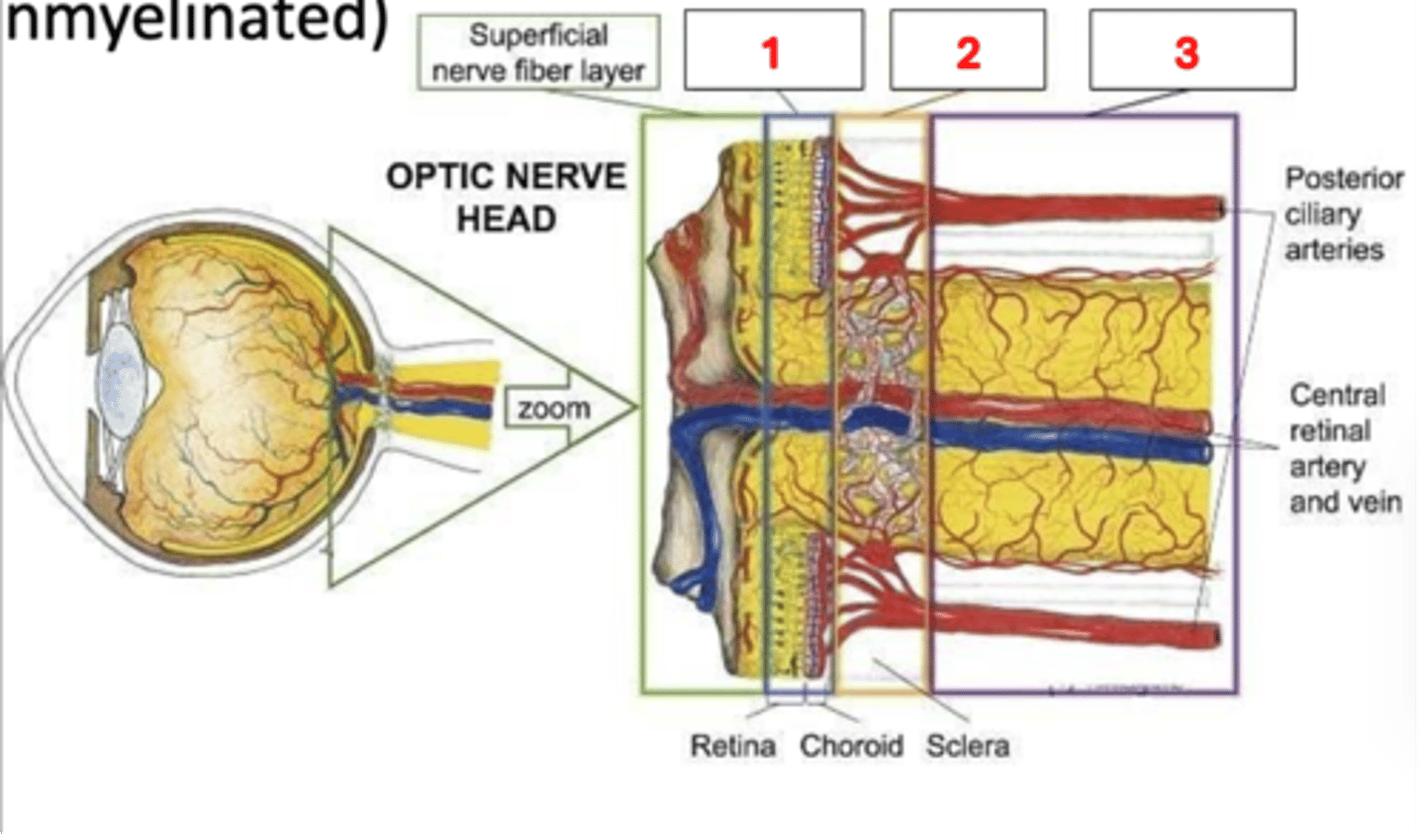
What does the prelaminar region contain?
Unmyelinated axons
What does the laminar region contain?
Unmyelinated axons
What does the retrolaminar region contain?
Myelinated axons
What is the length of the intraorbital segment of the optic nerve?
25 - 30 mm
What is the length of the intracanalicular segment of the optic nerve?
6 - 10 mm
What is the length of the intracranial segment of the optic nerve?
10 - 16 mm
What is the optic nerve head aka?
Blind spot
Why is the optic nerve head called the blind spot?
There are no rods or cones (photoreceptors) overlying it
Name the common diseases related to the ONH
-Optic nerve glioma
-Glaucoma
A: Optic nerve head
B: Retina
C: CRA / CRV
D: Bundles of RGC axons forming optic nerve
E: Lamina cribosa
F: Retina
G: Choroid
H: SPCA / SPCV
I: Pial sheath
J: Arachnoid sheath
K: Dural sheath
L: Intervaginal spaces
M: RGCs
Label each component of the optic nerve head
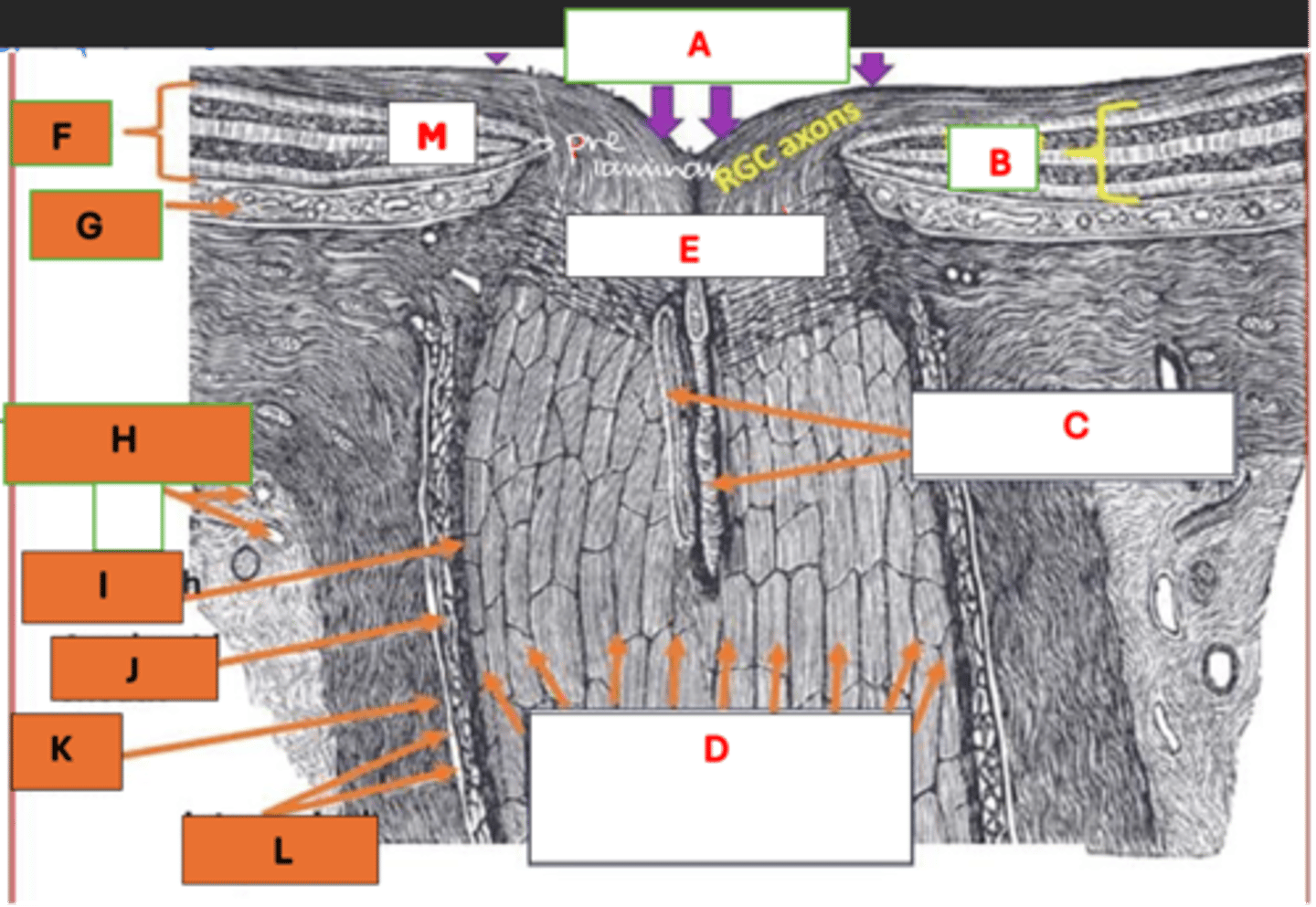
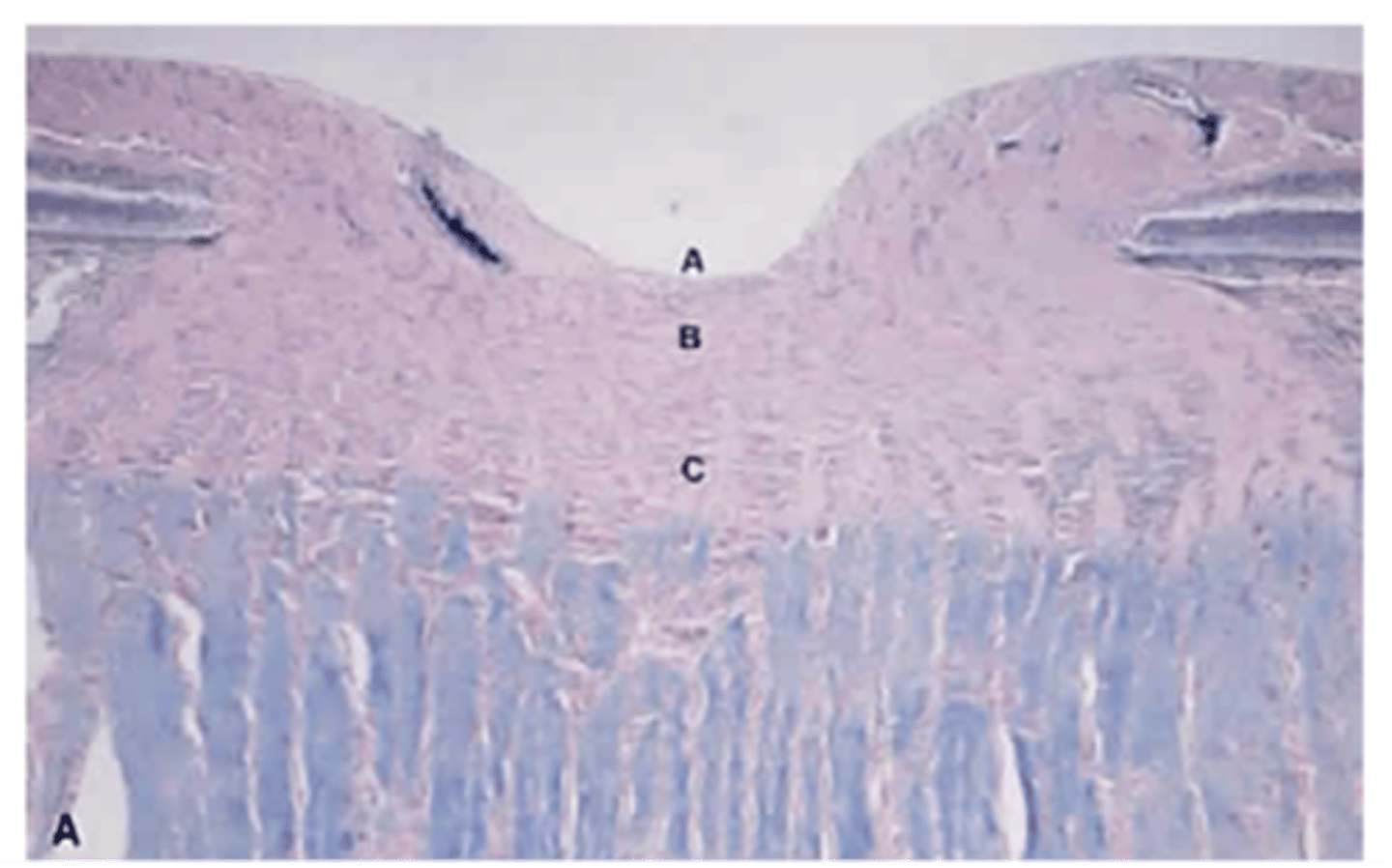
A: Surface NFL and physiologic cup
B: Prelaminar region
C: Laminar cribosa region
Label each histological component of the longitudinal section of the optic nerve head (A, B, C)