BMS Section 2 - Endocrine System Pt. I
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Exchange of ions and molecules of adjacent cells
Across gap junctions with the same cells
Transfer of information from cell to cell
Chemical signals within a single tissue
Hormones are transported to target cells
Through the bloodstream
Hormone
Any chemical that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs
Types of cellular communication
Autocrine, Paracrine, Endocrine, Direct
Autocrine
Cell releases a signaling molecule that binds to receptors on its own surface, influencing its own behavior
Ex. positive self talk, someone is influencing their self only
Paracrine
Cell releases chemical messenger molecules that diffuse short distances to act on neighboring cells, influencing their behavior and function
Ex. Coach talking to players in a huddle, coach is only influencing the players near him
Direct
Cells to communicate through physical contact to transfer small molecules, or by the binding of surface proteins on adjacent cells
Ex. Someone shaking you awake, only making sure you are awake
Endocrine
When specialized cells, or endocrine glands, release chemical messengers called hormones into the bloodstream
Ex. Making a phone call, can be short distance or long distance to specific cells
Glandular Epithelium
Make up endocrine and exocrine glands, specialized epithelial tissue that secretes substances
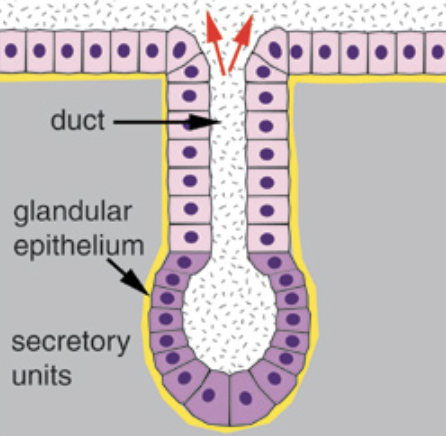
Exocrine glands
release contents through a duct that leads to epithelial surface
Merocrine
Part - release by exocytosis
sweat and salivary glands
Apocrine
Away - release by exocytosis, part of the cell is pinched off
mammary and odorous sweat glands
Holocrine
Whole - release by entire cell rupturing
sebaceous glands
Classes of hormones
Amino acid derivatives, peptide hormones, lipid derivatives
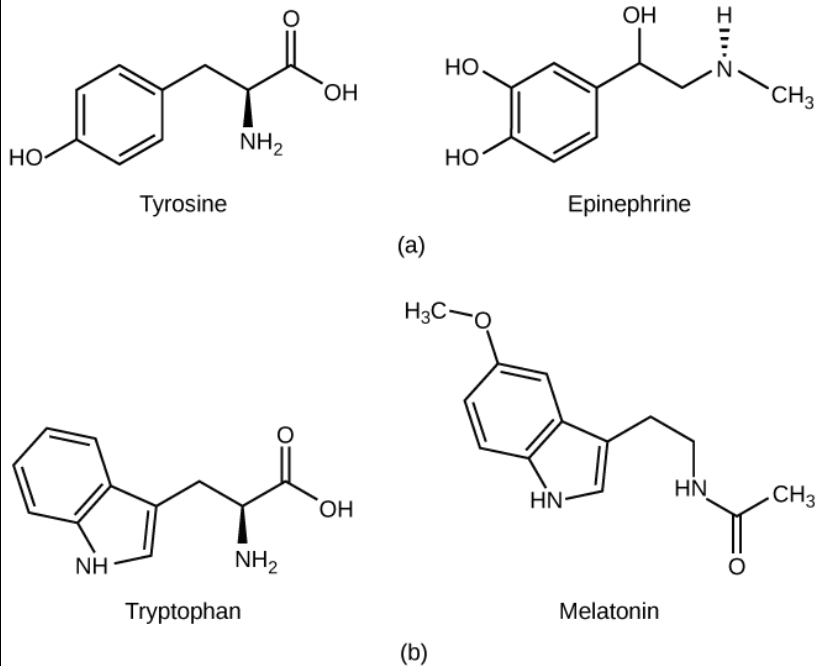
Amino acid derivatives
Derived from amino acids
Tryptophan (→ melatonin) and
Tyrosine (→ thyroid hormones) (hydrophobic) vs catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) (hydrophilic)
Peptide hormones
Derived from amino acids, linked by peptide bonds
Peptides (2-50 amino acids) vs protein hormones (<50 amino acids)
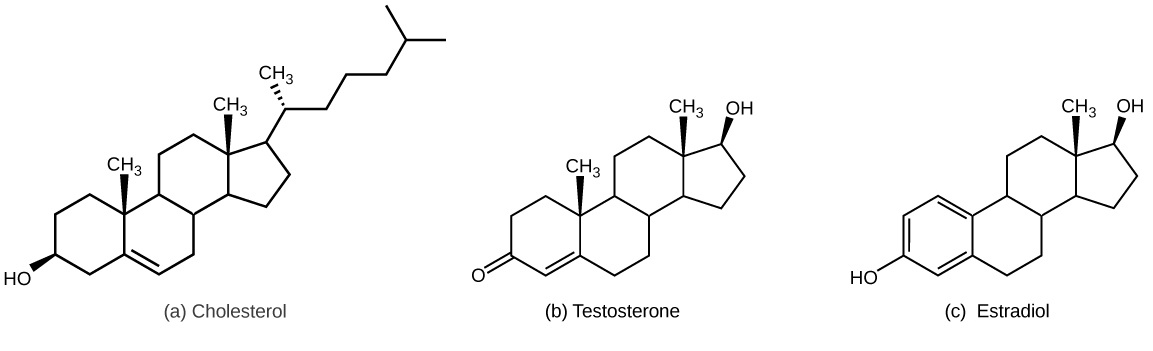
Lipid derivatives
Derived from fatty acid molecules
steroid hormones → derived from cholesterol
Mechanisms of catecholamine and peptide hormones
Not lipid soluble, cannot penetrate plasma membrane. Binds to receptor proteins on outer surface of plasma membrane (extracellular receptors)
Mechanisms of steroid and thyroid hormones
Lipid soluble, diffuses across plasma membrane. Binds to receptors inside the cell (intracellular receptors)
Mechanisms of G protein coupled receptors
Hormones uses an intracellular intermediary to bring affects. Once activated, these proteins increase cyclic AMP levels, acting as a second messenger within the cell
Effects of the secondary messengers
How G protein activation impacts metabolic activity of a cell
G protein activation increases
Accelerate the activity of the cell
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, ADH, ACTH, FSH, LH, TSH
Activating enzymes, opening ion channels
G protein activation decreases
Decrease cAMP levels in the cytoplasm resulting in an inhibitory effect on the cell
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Transport of hormones
Can circulate freely or be bound to special carrier proteins.
Bloodstream contains a substantial reserve of bound it
Free hormone activation
Remain functional for less than an hour and proceed to be inactivated when
diffuse out of bloodstream and bind to receptors on target cells
are absorbed and broken down by liver or kidneys
are broken down in blood or intestinal fluids
Thyroid and steroid hormones functionality
Remain functional for much longer
Geonomic effects of hormones and intracellular receptors
Steroid hormones can alter rate of DNA transcription in nucleus, Alterations in synthesis of enzymes of structural proteins
can directly affect activity and structure of target cell
Non-geonomic effects of hormones and intracellular receptors
Thyroid hormones bind to receptors within nucleus and on mitochondria
activates genes or change rate of transcription, increases rate of ATP production
Down-regulation of hormone action
Presence of a hormone triggers a decrease in the number of hormone receptors
When levels of a particular hormone are high, cells become less sensitive to it
Up-regulation of hormone action
Abscence of a hormone triggers an increase in the number of hormone receptors
when levels of a particular hormone is low, cells are more sensitive to it
Hormones release triggers
Hormonal stimuli
Humoral stimuli
Neural stimuli
Hormonal stimuli
Arrival or removal of a hormone
Humoral stimuli
Change in extracellular fluid
Neural stimuli
Neurotransmitters