PSYC 322: midterm 1
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
content for midterm
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
gerontology
scientific study of the process of aging
relatively new multidisciplinary field
helps undertsand aging trends
predict future trajectories
address current and future implications of aging on society
measures of life longevity
life expectancy
healthy life expectancy
mortality rate
survival rate
life expectancy
an estimation of how long someone will live
healthy life expectancy
an estimation of how long someone will live at “full" health”
i.e. without long term diseas/illness
morality rate
number of deaths in a period in a population
survival rate
the percentage of a population that is expected to live after a certain point or incident/illness
often used in context of illness
how long you can expect to live when you are past a certain age or have a specific disease
what could explain the difference in variance between life expectancy and healthy life expectancy?
genetics
environment such as socioeconomic status
top 3 causes of deaths in females and males
alzheimer disease and other dimentias
ischaemic heart disease
trachea, bronchus, lung cancers
key factors that are considered when looking at data related to aging
continuity
individuality
survival
aging =/= illness
continuity
life span perspective
life is divided into two main stages: early and late
early phase greatly influences how later phases are
features include:
multidirectionality
plasticity
historicalcultural context
multiple causation
multidirectionality
growth and decline throughout aging process
plasticity
capacity to change is not predetermined or set
neuroplasticity
neuroplasticity
brain’s ability to rewire/create new connections thorughout lifespan
historical/cultural context
historical and/or cultural experiences throughout the lifespan can affect development
multiple causation
so many factors contribute to/affect development over the lifespan
individuality
as individuals age, differences are magnified due to many factors
personality
physical function/health
life experience
opportunities
biological factors
longitudinal studies
useful for observing continuity within the same individual/population
useful for tracking changes based on individual differences
cross-sectional studies
useful for observing potential differences between individuals/cohorts grouped by age
useful for isolating potential factors that may explain differences in development
age effects
attributing the aging process to universal
cohort effects
attributing the aging process to specific (generational) factors
primary aging
normal disease-free development during adult aging
secondary aging
developmental changes related to disease, lifestyle, environment
tertiary aging
rapid losses that occur right before death
terminal drop/mortality aging
final stages of life
personal aging
changes within an individual that reflects the passage of time on one’s development
social aging
effects of changing environment on an individual
normative age-graded influences
normative history-graded influences
non-normative influences
normative age-graded influences
experiences that one’s culture and historical context attach to certain points in the lifecycle
ex. geting married at 13 in 1800s
normative history-graded infuences
events that most people in a similar place/time experience simultaneously
ex. covid pandemic
non-normative influences
random or rare events that is significant to an individual but isn’t universally experienced
ex. winning the lottery
how can we operationalize age?
chronological age
perceived age
biological age
psychological age
sociocultural age
biological age
function of bodily functioning, organs, fitness, failty indices, etc.
psychological age
level of psychological functioning and adaptability
sociocultural age
related to social roles/norms that an individual fills in relation to others in society
biological theories of aging
programmed aging theories
metabolic theories
random error theories
programmed aging theories
aging and death are encoded within our genes
genetic timing mechanisms
declines in physiological function
evidence:
cell senescence
species-specific life spans
cell senescence
stops the division of cell division
irreversible cessation
biological process to reduce risk of uncontrolled cell proliferation (can lead to cancer)
bioproduct of shortening telomeres
results of cell senescence
thickening of artery walls
arthritis
skin changes
neurodegeneration
telemerase
enzyme that can lengthen/preserve telomere length
cells withtelomerase can slow aging process
hayflict limit
number of times a cell can divide before cell division stops
cells without hayflict limit/express telomerase
stem cells
germ cells
cancer cells
metabolic theories
organisms have a finite amount of energy to expend in lifespan
one’s metabolism → longevity
rate of living theories
evidence: caloric restriction studies
caloric restriction studies
restricting caloric intake without starvation can slow metabolism which slows the aging process
generally less energy expenditure → longevity
generally, bigger animals live longer
criticisms of caloric restriction studies
complex intracellular processes
specific mechanisms that impact aging is unclear
operationalizing caloric restriction (when/what/how much is restricted)
is it worth practicing CR if you’re sacrificing wuality of life?
random error theories
aging is not pre-programmed, it is random
accumulation of random, unpredictable damage to an organism’s cells and molecules over time
wear and tear theory
being worn down gradually by environmental factors
which then wears down our biological features and so forth
psychological theories
identity process theory
selective compensation with optimizaion model
ageism
identity process theory
identity continues to change dynamically in adulthood
less about why but HOW WE ADAPT to aging changes
events can fundamentally change how we view ourselves
threshold experience
identity
current view of oneself
threshold experience
changes due to aging
ex. illness, physical changes due to age
can lead to identity assimilation, identity balance, or identity accomodation
some thresholds carry more weight (spectrum)
identity assimilation
denial, preservation of positive identity
ex. denying age is making one look older/different
identity balance
healthy in-between
the goal
changing understanding of identity and accepting it
identity accomodation
changing approach to accomodate threshold experience
selective compensation with optimization model
as we decline with age, steps can be taken to compensate and maintain optimal performance for high priority items
while sacrificing lesser priority items
psychological approach to functional aging
what are the three components of selective compensation with optimization model?
selection
choosing a goal to prioritize
optimization
choosing which resources to allocate to achieve goals
compensation
balancing/weighing costs to maintain a level of functioning
selective compensation with optimization model
ex. early adulthood: starting a family
selection
starting a family
optimization
physical energy, external resources (eg. daycare), financial situation
compensation
financial trade-offs (less vacations/extra expenses), time off work
ageism
a set of beliefs, attitudes, social institutions, and acts that denigrate individuals or groups based on their chronological age
old age associated with disease and decline
being part of an age group leads to assumptions of advantage/disadvanage
ageist beliefs are internalized → behaviour affected
results of implicit ageism study
positive implicit associations highest for children
negative associations for older adults
sociocultural theories: first generation theories
simple, binary, functional view of aging
disengagement theory
activity theory
sociocultural theories: second generation
more focused on the individual expereince
contuity theory
bronfenbrenner’s ecological perspective
sociocultural theories: third generation
expansion on individuality
focus on social structures, lifespan perspective
disengagement theory
coping with old age is done through gradual and voluntary disengagement from social roles and activities
mutual and beneficial withdrawal of individuals and society
disengagement is normative, universal and inevitabl
ex. retiring is inevitable and normal
criticism of disengagement theory
feeds into agism
not always normative, universal, and inevitable
unfalsifiable
disregards individuality
too much focus on social normative influences
activity theory
with aging comes a reduction in social responsibility, leading to reduction in life satisfaction
new roles, friendships, and activities established later in life helps sustain life satisfaction
menec (2003) findings of activity theory
greater overall activity was related to greater happiness, better function, and reduced mortality
more solitary activities were related only to higher levels of happiness
continuity theory
people who age normally (primary aging) attempt to maintain both itnernal and external continuity to past to preserve balance in self-image
too much continuity → unpredictable, unstable
too much continuity → boring, stagnancy
criticisms of continuity theory
mostly considers primary healthy aging and largely ignores secondary/tertiary aging
ignores the impact of social structures on aging
prevents the possibility of continuity
ageism
socioeconomic factors
access to healthcare
bronfenbrenner’s ecological perspective
a person’s development is shaped by their environment
from microsystems → macrosystems, chronosystems
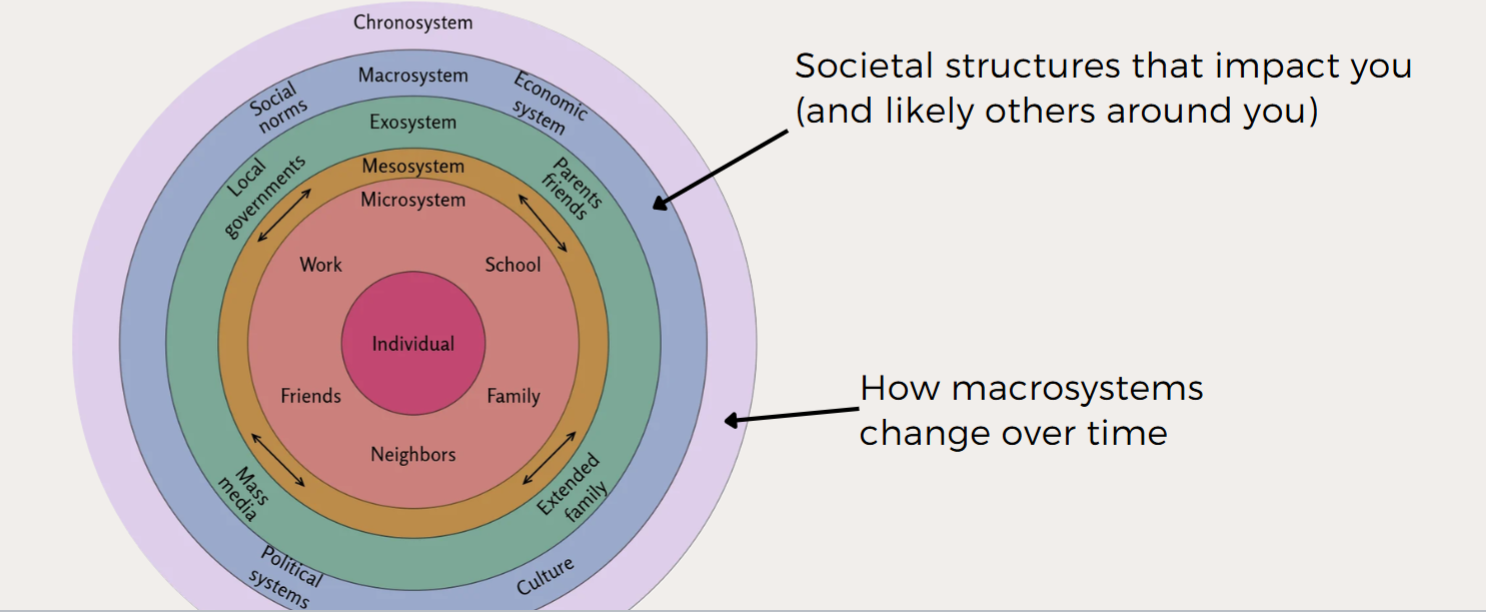
third generation of sociocultural theories
aging is not just a process suddenly experienced in later life, but is a product of an entire lfietime of experiences
more conscious and adaptive choices rather than aging “happening” to you
predatory journals
poor or dishonest publishing practices with little to no peer review process
impact factor
metric that measures how often the average article of a journal is cited throughout the scientific literature
higher IF