Post Transcriptional Regulation
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Post transcriptional regulation takes place when?
after transcription, but before translation
after DOES NOT mean that transcription has to be complete
can occur while transcript is still being transcribed
Structural and spatial differences in gene expression between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
eukaryotes have a nucleus (where transcription occurs), mRNA is exported to cytoplasm after post transcriptional regulation for translation
prokaryotes do not have regulation after transcription and translation
___________ intervenes between exons
introns
Exons
protein coding regions
only about 1.5% of the human genoms
Introns
noncoding region
over 23% of the genome
Most introns are ________________, they need to be removed via _________________
untranslatable, splicing
Splicing
introns are removed and exons are joined together
Where does post-transcriptional regulation occur?
nucleus
Nuclear mRNA processing involves:
capping and methylation
splicing
polyadenylylation
What happens to primary transcripts (pre-mRNAs) as soon as they are transcribed by RNA pol II?
they are capped
What caps pre-mRNAs?
guanylyl transferase using GTP as a substrate
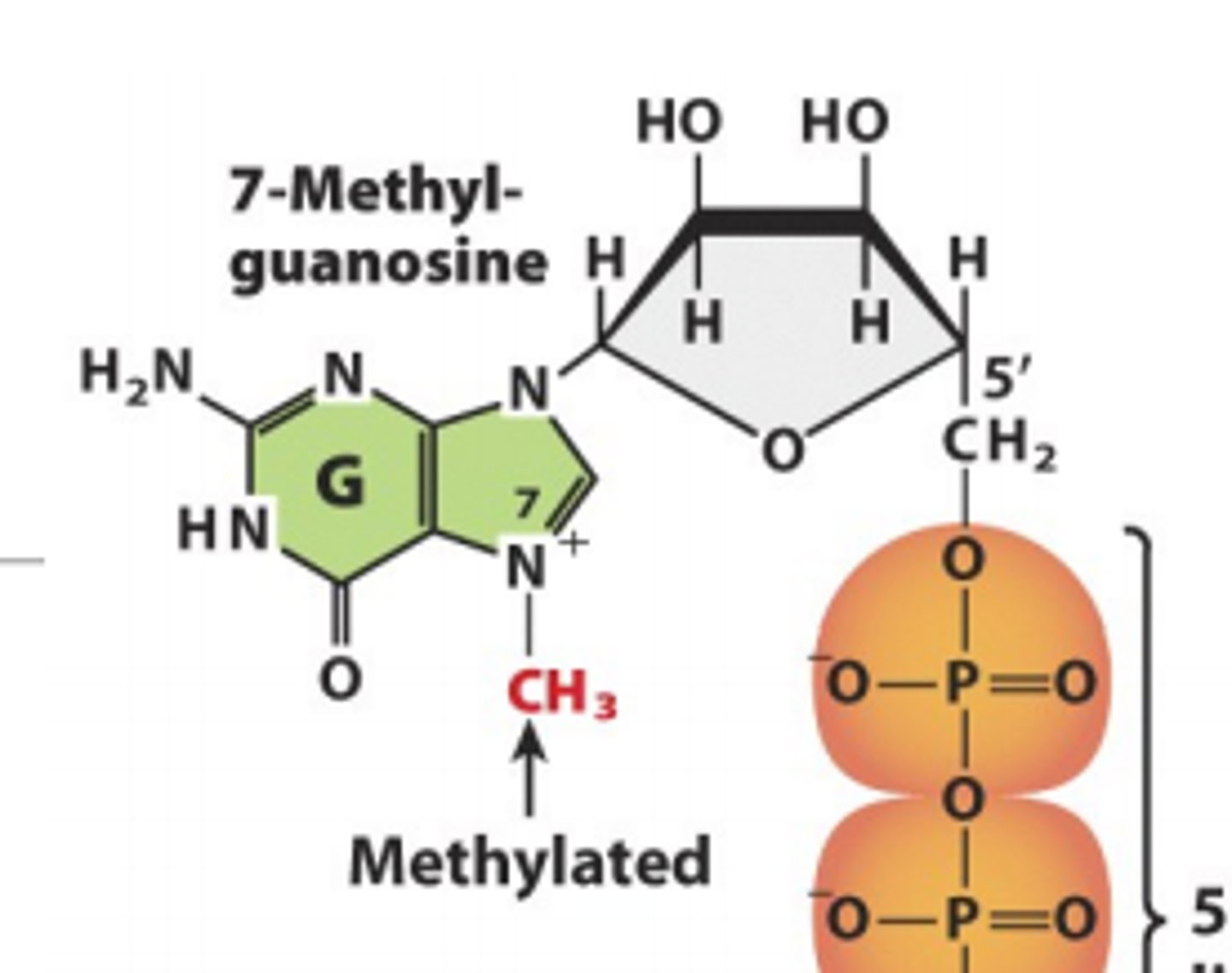
The capped G residue is _______________ at _______________ position
methylated, N7
What happens at the next two residues beside the G residue at position N7?
additional methylation occurs at C2'-O positions at the next two residues and at 6-amino group of the first adenine
A cap with only a single -CH3 on the guanyl is termed
cap 0
What does cap 0 occur in?
all eukaryotic mRNA
If a methyl is also added to the 2'-O position of the first nucleoside after the cap, what structure is generated?
cap 1
(predominant cap form in all multicellular eukaryotes)
In the capping of eukaryotic pre-mRNAs, guanylyl transferase catalyzes the addition of _________________ derived from ______________ to the 5' end of the growing transcript. What is liberated?
guanylyl residue, GTP, PPi is liberated from GTP and the terminal phosphate is removed from the primary transcript
What is done to the third phosphate group on the 5' end of the primary transcript?
a phosphatase removes it
Guanylyl transferase next brings in ____________, which goes on the ____________ end. Once ______________ is added, _____________ is eliminated
GTP, 5', GTP, pyrophosphate (PPi)
What adds a methyl group to the guanine on the 5' end?
guanine 7-methyltransferase
The 5' cap is recognized by
cap binding proteins
The 5' cap distinguishes mRNA from other types of RNA molecules such as
RNA molecules produced from RNA pol I and pol III. They each produce uncapped RNAs
What RNA pols produce capped RNAs?
only RNA pol II --> mRNA
What do mRNAs have to have for export from the nucleus?
a cap and a poly A tail
Is a 5' cap necessary for translation?
yes
What does the 5' cap of mRNA do for the mRNA in the cytoplasm?
stabilizes it and prevents it from being degraded
When does termination of transcription occur?
only after RNA pol has transcribed a concensus AAUAAA sequence (polyA signal)
What is the polyA signal?
AAUAAA
10-30 nucleotides after the polyA signal, what happens to the mRNA?
it is cleaved and a string of ~200 adenine residues is added to the mRNA transcript --> polyA tail
Enzyme that adds the adenine residues to produce a polyA tail
polyA polymerase
polyA tail bound by _____________ stimulates translation and governs the stability of mRNA
PABP
polyA binding proteins
Where does polyA addition occur?
3' end of transcripts about 10-35 nucleotides downstream from the polyA signal (AAUAAA)
What binds to the polyA signal and mediates looping of the 3' end of the transcript through interactions with a G/U rich sequence even further downstream?
CPSF
cleavage and polyA specificity factor
What do cleavage factors do?
bind and bring about the endonucleolytic cleavage of the transcript to create a new 3' end 10-35 nucleotides down from the polyA signal
Does polA addition require a template?
no
Is the polyA tail encoded in the genome?
no
it is added by polyA polymerases
What is the function of the polyA tail?
by interacting with PABP, it is necessary for efficient translation and protection from mRNA degradation
First amino acid of all proteins
methionine
AUG
In the nucleus, pre-mRNA forms _____________ by associating with a characteristic set of nuclear proteins
ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs)
What do the nuclear proteins help maintain pre-mRNA as?
untangled and accessible
Where does splicing occur?
nucleus
Substrate for splicing
capped, polyadenylated RNA in the form of a RNP complex
What happens in splicing?
the introns are excised and the exons are sewn together to form mature mRNA
What is the 5' end of an intron in higher eukaryotes?
GU
What is the 3' end of an intron in higher eukaryotes?
AG
What is present about 18-40 nucleotides upstream of introns' 3'?
branch site
The branch site is essential to what?
splicing
Branch site is usually
YNYRAY
Y= pyrimidine
R=purine
N=anything
A covalently closed loop of RNA is formed by attachment of the _________ of the intron's invariant 5'-G to the 2'-OH at the branch A site
5'-P
Splicing depends on what ribonucleoprotein particles?
snRNPs
A snRNP consists of
small nuclear RNA and about 10 different proteins
Spliceosome
snRNPs and pre-mRNA
Lariat intermediate
the 2' OH of the branch point adenine attacks the donor sequence, cleaving the 5' splice site
Splicing occurs when what come together?
various snRNPs come together with the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome
What does the assembly of the spliceosome require?
ATP
snRNP U1 binds to
5' splice site
snRNP U2 binds to
branch site
Interaction between U1 and U2 snRNP does what?
brings the 5' and 3' splice sites together so lariat can form and exon ligation can occur
5 different snRNAs
U1, U2, U4, U5, U6
The 5 snRNAs are rich in
uridine
What is associated with each of the snRNAs to form snRNPs?
proteins
U1 snRNP binds at the ____________, followed by the association of U2 snRNP with ________________
5'-splice site, UACUAA branch point sequence
The _____________ replaces U1 at the 5' splice site and directs the __________ of the branch point sequence with the 5' splice site, where ________________ is released
triple U4/U6-U5 snRNP complex, juxtaposition, U4
Constitutive splicing
every intron is removed and every exon is kept in the mature mRNA
produces a single form of mature mRNA from the primary transcript
How might eukaryotic genes give rise to multiple forms of mature RNA transcripts?
using different promoters
selecting different polyA sites
alternative splicing of the primary transcript
OR A COMBO OF ALL 3
Alternative mRNA splicing
different cell types express distinct isoform
Alternative splicing expands the
coding potential of the genome
Are bacterial mRNAs unstable or stable?
unstable
Bacteria can/cannot adapt quickly to environmental changes?
can
Most eukaryotic mRNAs are more/less stable than prokaryotic mRNAs?
more
What removes the polyA tail?
polyA nuclease
mRNA is thought to be circularized by its interaction with
eIF4E, eIF4G, and PABP
PABP, EIF4E and EIF4G circularizing the mRNA does what for the mRNA?
protects the 5' and 3' ends from attack by decay enzymes and stimulates translation
RNA editing
process that changes one or more nucleotides in an RNA transcript by deaminating a base
either A-->I or C--> U
A to I RNA editing is carried out by
ADAR
adenosine deaminase acting on RNA
General decay pathway of most mRNAs
Slow polyA shortening
decapping
5'-->3' degradation