Threats to Marine Biodiversity
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Marine Bio Exam 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Invasive species
introduced species that survive and reproduce, and then negatively affect the habitats they invade, ecologically or economically
What regions do invasive species originate in
regions with similar abiotic conditions (ex salinity) This enables the invaders to survive while their population numbers are still low
Invasive species often achieve __
large body sizes and high population densities
Escape from the effects of natural enemies
Invasive parasite species in native and introduced ranges
Parasite species richness (left) and prevalence (right) was greater in native than in introduced populations
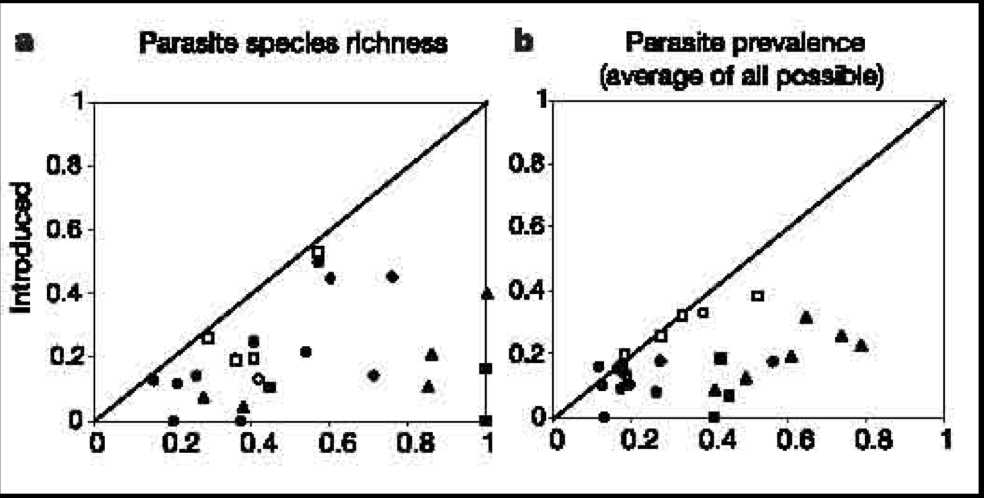
What makes communities more resistant against invasion?
Theory predicts that systems that are more diverse should be more resistant to invasion
High Species richness resists invasion …
increased species richness significantly decreased invasion success (A)
This is because more species rich communities, more completely and efficiently use limiting resources
declining biodiversity facilitates invasion, further accelerating loss of biodiversity
Communities are prone to invasion because
additional stress to community
Annual recruitment of introduced species was positively related to water temperature, whereas recruitment of native species was negatively related to water temperature
introduced species grew faster than native species at warmer temperatures (not pictured)
Causes of invasion
invasive species must be able to cross barriers that it would not naturally cross
related to frequency with which potential invaders arrive ex BALLAST WATER OF SHIPS provide frequent source of movement across long distances
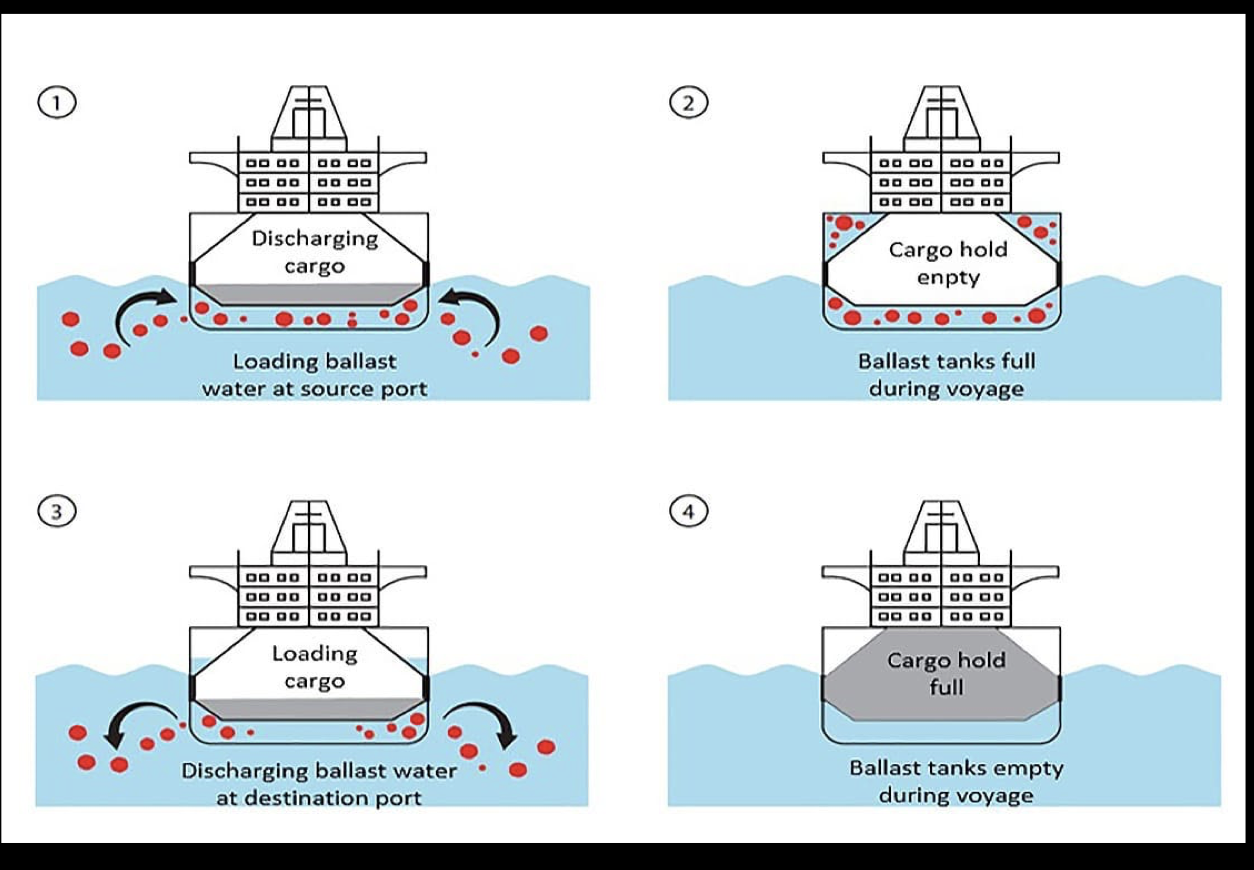
What action can be taken? (Ballast Water)
Ballast water exchange involves replacing coastal water with open ocean water during a voyage
Process reduces the density of coastal organisms in ballast tanks that might invade recipient port
Major Causes of Pollution
a. Toxic substances - Metals
- Pesticides
- PCBs
- Oil
b. Nutrient sources - Sewage
- Fertilizers
- Animal waste
- Atmospheric sources
c. Debris sources - Fishing gear
- Plastics
d. Noise
Heavy Metals Mercury
reaches the ocean in low concentrations through natural weathering of rocks and volcanic activity
Discharges from industries, cities, and coal burning have increased the concentration of mercury in marine environment
Combines with organic chemicals to form organic compounds such as methyl mercury, which are particularly toxic
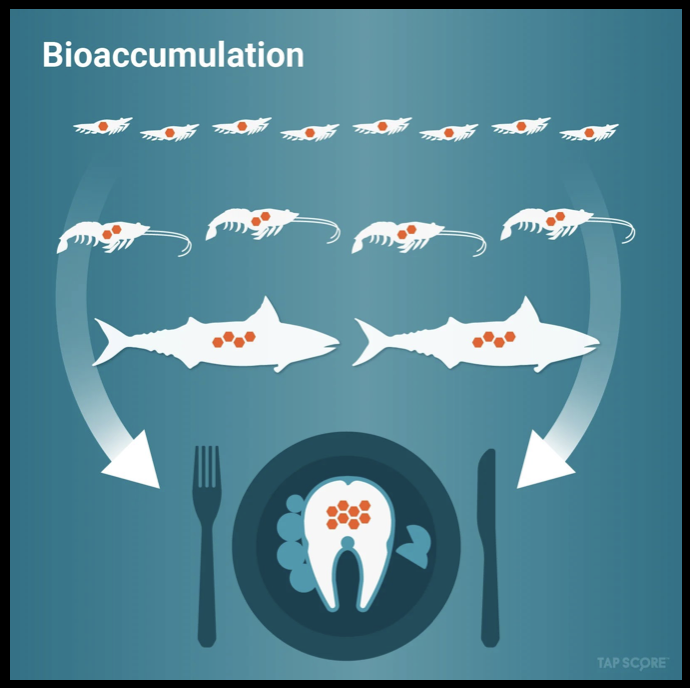
Methyl Mercury
accumulates in food chain. Older fish, higher in food chain, have higher mercury levels due to bioaccumulation.
humans eat fish containing mercury, they may suffer neurological disorders, paralysis and death
Other Heavy Metals
Cadmium – batteries and computers
Lead – batteries, paints, fuel additive
Copper – wood treatment other industries
Pesticides
usually designed to kill terrestrial insects, but they are carried to ocean by rivers (runoff)
As with heavy metals, they are taken up by plankton, then bioaccumulate and are magnified further up the food chain
Effect of Pesticides DDT on sea birds
High concentrations accumulate in body fat, interfere with reproduction, specifically deposition of calcium in eggs shells
some birds such as brown pelican and osprey faced extinction in 1970s
Polychlorinated biphenyls PCBs
derive from industrial activities and pose a major toxicity problem, especially in estuarine environments
bioaccumulates in food chains - cause reproductive failures

Oil
682 million tons of oil and derivatives enter each year as a result of pollution
584 million tons of oil enters the world oceans each year via natural seepage
Almost 85% of the polluting oil in US comes from storm water, river runoff, and fuel from small craft
Oil effects
short-term and long-term effects
Birds and mammals are particularly affected – many die of exposure
because oil covered fur and feathers loses its insulating propertiesRecovery estimates vary from 5 to 70 years
Minimizing oil pollution
Double-hulled tankers minimize loss of cargo in the event of minor accidents
Nutrient Sources
large additions of dissolved nutrients to coastal waters.
Principal known sources include:
• Sewage treatment outfall pipes
• Storm sewer overflows
• Commercial fertilizer – runoff from agricultural lands • Animal waste – runoff from agricultural lands
• Atmospheric deposition
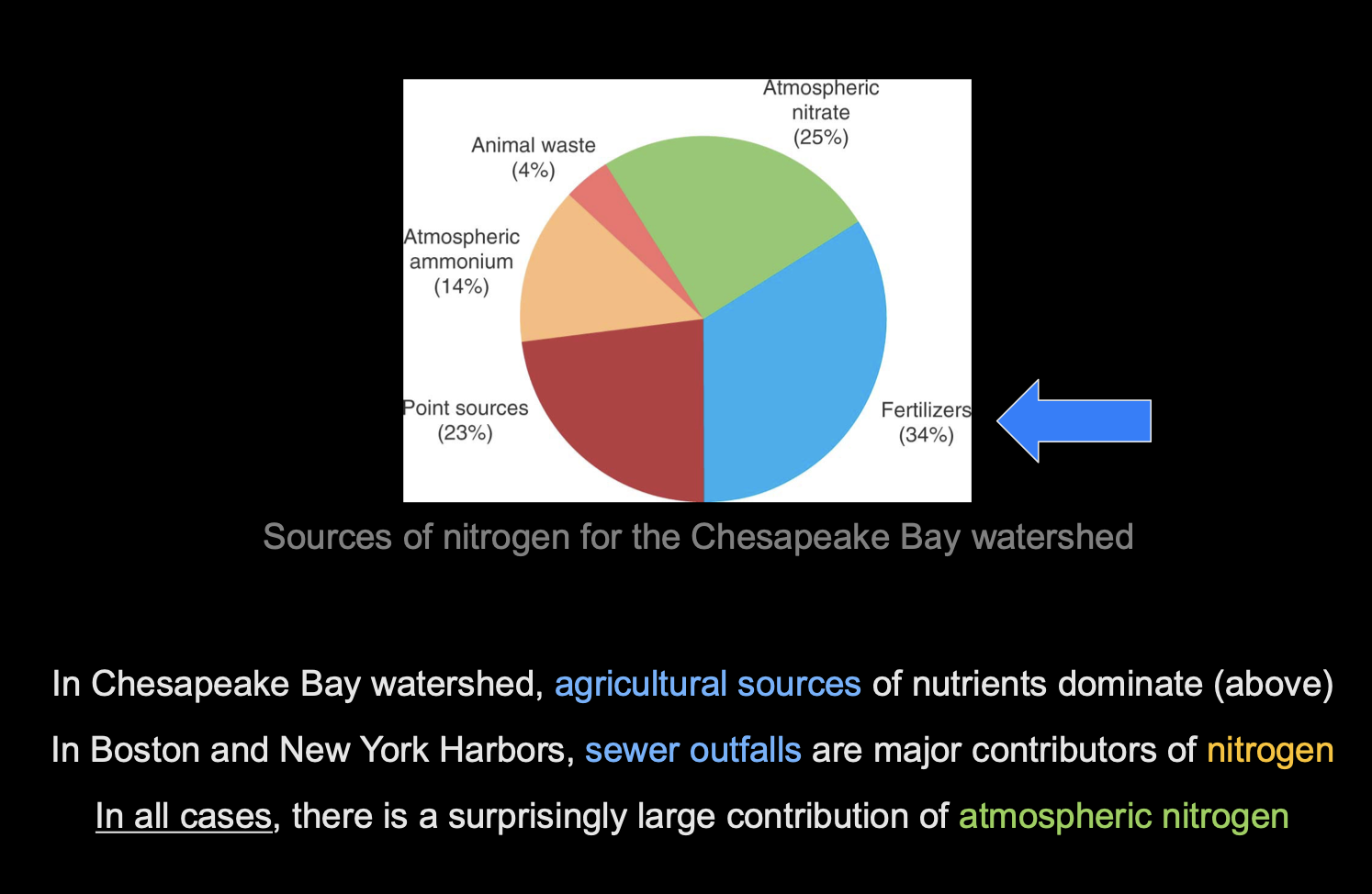
Atmospheric Nitrogen
major source of nutrient addition to the ocean
Fossil fuel combustion is a major source of nitrogen oxide emissions
Gaseous emissions return to earth as soluble nitrates in precipitation
Eutrophication
ecosystem response to the addition of dissolved nutrients
ex phytoplankton bloom followed by hypoxia or anoxia - leads to crashes in population of zooplankton and nekton (die offs)
Development of die-off in an estuary:
a) Normal situation: phytoplankton is grazed and bottom waters are oxygenated
(b) Nutrient input stimulates phytoplankton growth and dead phytoplankton sink
– bacterial decomposition reduces oxygen content of water (hypoxia)
(c) Oxygen is removed (anoxia) from bottom waters and
benthic organisms die
Dead zones are a result of __
Nutrient addition to coastal waters
Reducing nutrient inputs by
Eliminating ocean dumping of solid sewage waste and better treatment of sewage before wastewaters are released into the coastal zone can abate eutrophication
treatment of sewage includes __
Primary treatment removes solids;
Secondary treatment removes toxic compounds;
Tertiary treatment removes nitrates and phosphates
But... it is expensive
Ghost Nets
fishing nets that have been abandoned or lost. Marine animals can still get caught and die (drown);
Nets and ropes can drag and destroy reefs and sessile organisms
Micro Plastics
tiny plastic particles (<5 mm) that result from both commercial product development and the breakdown of larger plastics.
Plastic is
non-biodegradable- it never does away, just gets smaller.
Microplastics have also been found to facilitate the transfer __
f contaminants when ingested.
noise pollution
can harm whales by damaging their hearing,
and in extreme cases, cause internal bleeding and death.
can cause behavioral changes
Major causes of habitat destruction
Coastal development: dredging; dumping of silt and mud; landfilling
Major drivers: growing cities; increased tourism; industrial development
major causes of habitat destruction beaches
Dredging/ Sand Mining:
Decimates communities living within sediment; suspends sedimentation in the area; buries top layer of sensitive beach communities
Major drivers: Beach grooming/ replenishment; digging out shipping routes
Major causes of habitats destruction mangroves
Mangrove removal: Destruction of mangrove forests; removing whole communities and ecosystem services (including coastline protection, flooding prevention)
Major drivers: Ocean view resorts, tourism; Vacation homes (typically not only home)
Trawling
trawls are dragged along the bottom to supply fish and shrimp to markets
Major drivers: government subsidies and customer demand for trawl caught fish
Deep sea mining:
excavating and harvesting resources from the deep sea bed Major drivers: precious metals, minerals and alternative energy sources for sustainable, electronic technology