acids and bases (chap 8) -olevel pure chem
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is an acid
an acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions, H+, when dissolved in water
what are the properties of acids
acids have a sour taste
acids produce ions when dissolved in water. these ions allow the resulting aqueous solution to conduct electricity
acids turn blue litmus paper red
acids react with reactive metals
acids react with bases (metal oxides or hydroxides)
acids react with carbonates
what is the result of:
acid + base
acid + metal
acid + carbonate
acid + base —> salt + water
acid + metal —> salt + hydrogen
acid + carbonate —> salt + carbon dioxide + water
why does lead appear not to react with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid?
it forms an layer of lead chloride or lead sulfate around the metal which is both insoluble, preventing the metal from further reaction with the acid
what are some unreactive metals
copper
silver
gold
what is the difference between a strong and weak acid
strong acid- completely ionised in an aqueous solution
weak acid- partially ionised in an aqueous solution, reversible reaction
what is the difference between the strength of an acid and the concentration of an acid
strength of acid: its degree of ionisation
concentration of acid: the number of acid molecules present in a given volume of water
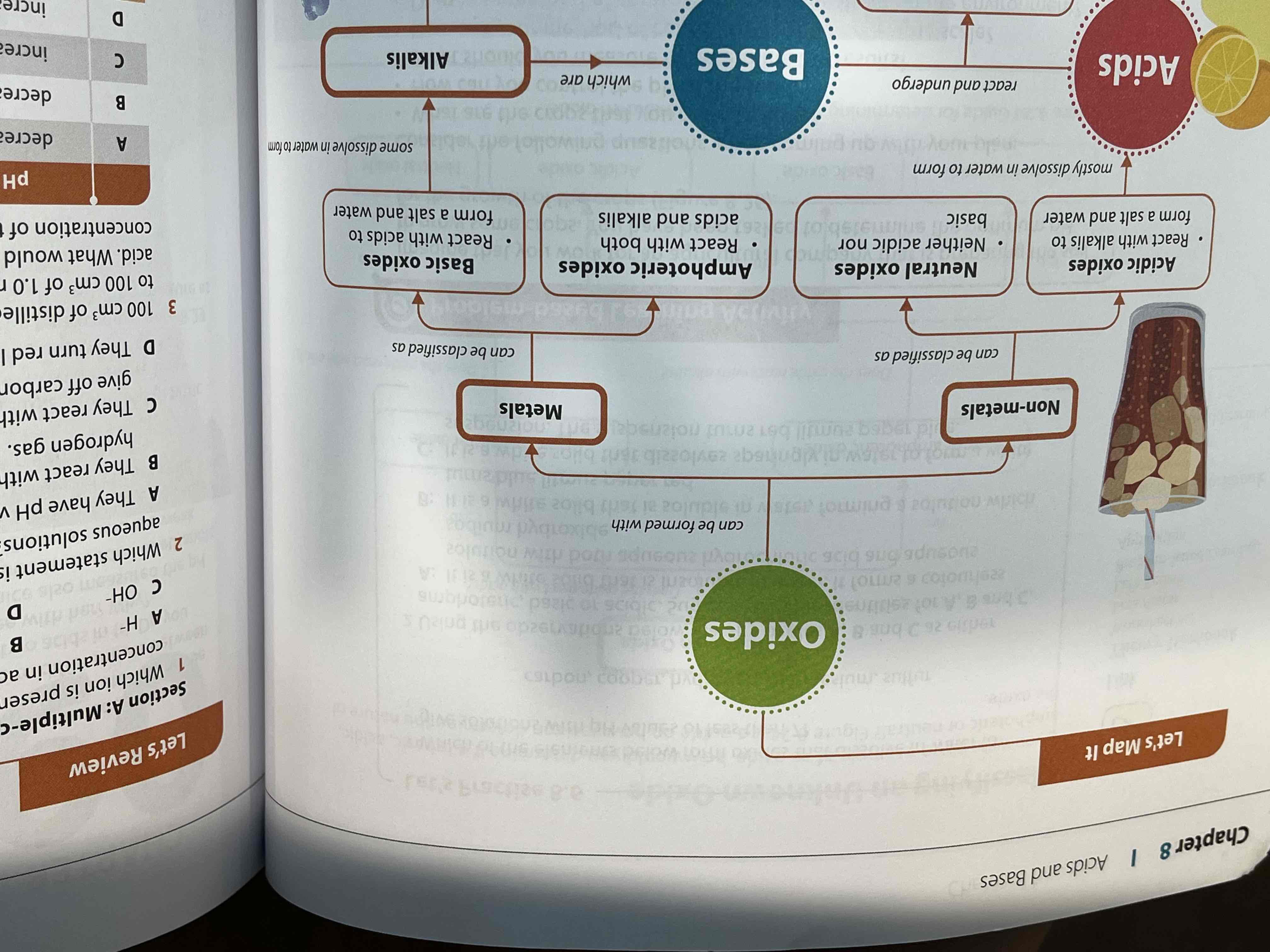
what is a base
any metal oxide or hydroxide
what is the differences between bases and alkalis
like acids, bases can also be strong or weak depending on their degree of ionisation
bases:
mostly insoluble in water
alkali:
produces OH- ions when dissolved in water
soluble in water eg:
group 1 hydroxides
ammonium hydroxide
calcium hydroxide
what is the ionic equation for any neutralisation reaction
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) —> H2O (l)
what are some properties of alkalis
alkalis taste bitter
alkalis feel slippery and soapy
alkalis dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity
alkalis turn red litmus paper blue
alkalis react with acids
alkalis react with ammonium salts
alkali + ammonium salt —> salt + water + ammonia
what are the color changes of the following indicators
methyl orange
screened methyl orange
litmus
thymophthalein
universal
methyl orange
acidic: red
alkaline: yellow
range where color changes: 3-5
screened methyl orange
acidic: violet
alkaline: green
range where color changes: 3-5
litmus
acidic: red
alkaline: blue
range where color changes: 5-8
thymophthalein
acidic: colorless
alkaline: blue
range where color changes: 9-10.5
universal
acidic: red-yellow
alkaline: green-violet
neutral: green
what is pH a measure of
pH is a measure of the concentration difference of H+ ions and OH- ions
why is fertilisers added to soil to control its pH
soil tends to be more acidic due to natural factors such as acid rain. most plants grow best when the soil is neutral, so fertiliser is added to neutralise the acidic soil and make it neutral so that the plant can grow optimally
what are some common elements for soil fertilisers
nitrogen
phosphorus
potassium
calcium hydroxide (slaked lime)
ammonia
types of oxides