Semester 2 Exam Chem
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
1
New cards
Reaction Stoichiometry
The study of materials consumed & produced in chemical reactions
2
New cards
In stoichiometry, what do you use to balance equations?
Coefficients
3
New cards
Mole rations are known as _____?
Conversion factors
4
New cards
What do mole ratios help predict?
The amount of reactants & products in a balanced equation
5
New cards
How are mole ratios formed?
Coefficients
6
New cards
4 Steps to Stoichiometry Calculations
1. Balance The Equation
2. Convert Given into Moles
3. Use Coefficients for Mole Ratio
4. Convert the Substance Needed Into Grams
7
New cards
Limiting Reactant
The reactant that is consumed (runs out) first; limits the amount of **products** formed
8
New cards
Excess Reactant
The reactant that does not run out
9
New cards
Steps for determining limiting & excess reactants
1. Write a **balanced** chemical equation
2. Identify all given **quantities**
3. Solve for **one** of the products based on all given quantities
4. Cross out the **larger** amount of the products produced
5. **Larger** amounts indicate the **excess** reactants
6. The **smaller** amount of the product indicates the **limiting** reactant
7. The **smaller** amount of the product is the **theoretical yield**
10
New cards
Theoretical Yield
The maximum produced from a balanced chemical equation based on 100% efficiency
11
New cards
Actual Yield
The amount obtained in a **laboratory** setting. Rarely **100%** due to sources of error.
12
New cards
Percent Yield Equation
Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield x 100
13
New cards
Heat
A measure of the total kinetic energy of a system
14
New cards
Temperature
A measure of the average amount of kinetic energy of a system
15
New cards
Phase Diagram
A graph of pressure versus temperature that shows the conditions under which phaSes of a substance exist
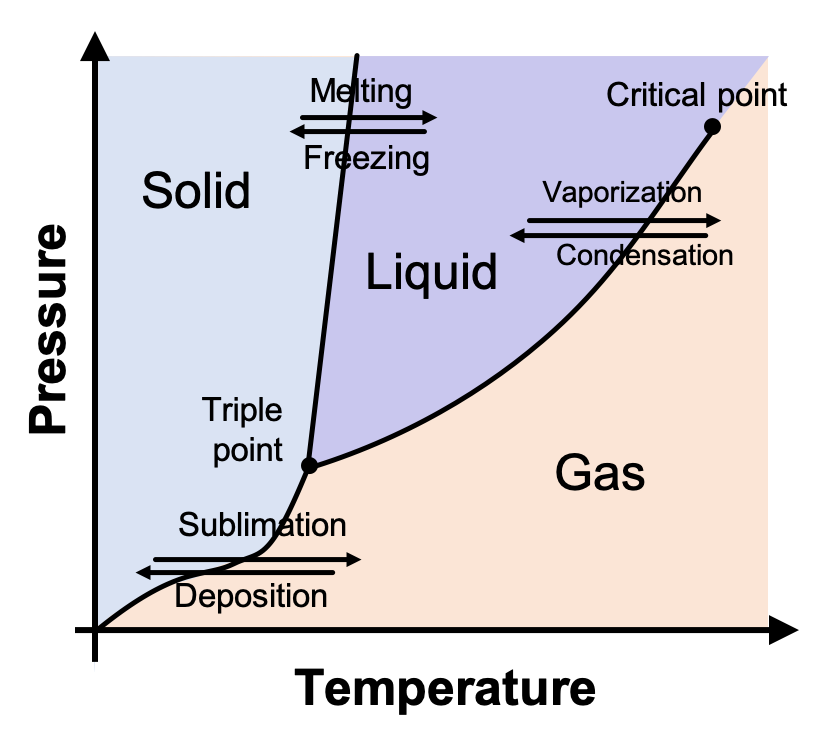
16
New cards
Triple Point
Indicates the temperature and pressure at which a solid, liquid & gas can coexist at equilibrium
17
New cards
Critical Point
The critical temperature and pressure
18
New cards
Critical Temperature
The temperature above which the substance cannot exist in a liquid state
19
New cards
Critical Pressure
The lowest pressure at which the substance can exist as a liquid at it’s critical temperature
20
New cards
Melting Phase
Solid → Liquid
21
New cards
Vaporization Phase
Liquid → Gas
22
New cards
Sublimation Phase
Solid → Gas
23
New cards
Condensation Phase
Gas → Liquid
24
New cards
Crystallization Phase
Liquid → Solid + Crystals
25
New cards
Deposition
Gas → Solid
26
New cards
Endothermic
Absorption of heat/energy
27
New cards
Exothermic
Release of heat/energy
28
New cards
When will a liquid boil?
When vapor pressure = atmospheric pressure
29
New cards
Boiling Point
The temperature at which the equilibrium vapor pressure of the liquid equals the atmospheric pressure
30
New cards
Heating Curve
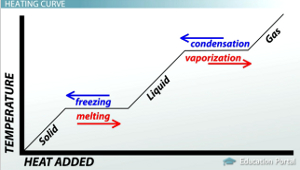
31
New cards
Heating Curve Equations
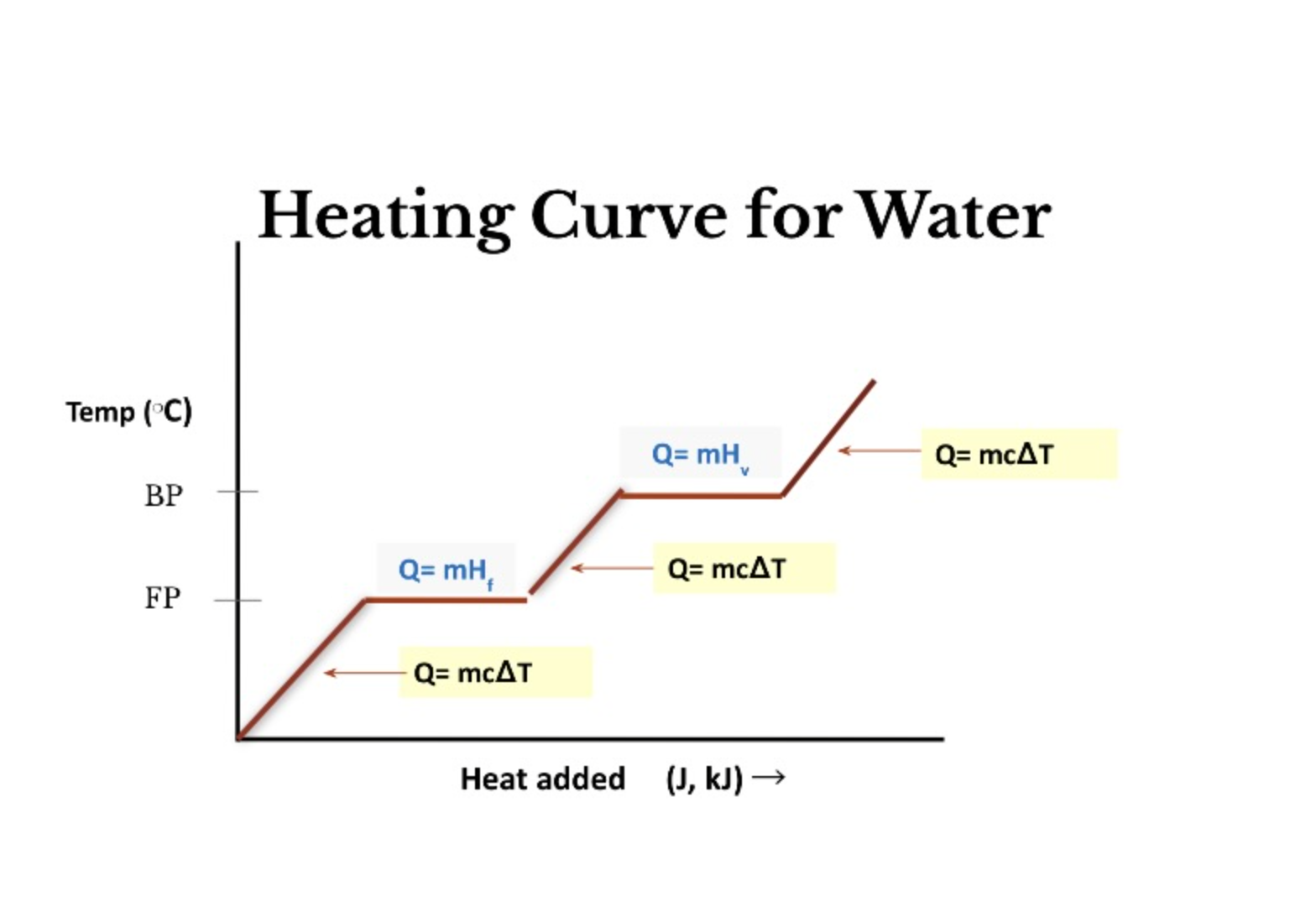
32
New cards
Heat Lost = Heat Gained Equation
m x c △ t = m x c △ t
33
New cards
What are the 3 most common physical states of matter?
1. Solid
2. Liquid
3. Gas
34
New cards
What does the kinetic molecular theory state about the make-up of matter?
Particles of matter are always in motion
35
New cards
What 2 properties is the kinetic molecular theory based upon?
1. Energy of particles
2. Forces between particles
36
New cards
Ideal Gas
A hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory
37
New cards
The five assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory of gases
1. Gases consist of many particles that are spread apart relative to their __**size**__
2. Collisions between particles and the walls of the container are __**elastic**__
3. Gas particles are in continuous, rapid, random motion and therefore have __**kinetic energy**__
4. There are __**NO forces of attraction or repulsion**__ between gas particles
5. The average amount of kinetic energy depends on the __**temperature**__ of the gas
38
New cards
Do Ideal Gases exist?
No
39
New cards
Why are gases and liquids considered to be fluids?
Gas particles slide past one another
40
New cards
Why do gases have such low density as compared to solids or liquids?
The particles are very far apart compared to solids & liquids and the volume is greater
41
New cards
Why are gases compressible?
Volume can be reduced
42
New cards
Diffusion
Mixing of gases in air
43
New cards
Effusion
Mixing of gases in a piece of lab glassware particles passing through a tiny opening
44
New cards
What is a real gas?
A gas that does not behave completely according to the kinetic molecular theory
45
New cards
What four measurable quantities are needed to describe a gas fully?
1. Moles
2. Volume
3. Temperature
4. Pressure
46
New cards
Volume
The amount of space an object occupies
47
New cards
Pressure
The amount of force applied per area on a surface
48
New cards
What are the SI units for pressure?
1. atm (atmosphere)
2. mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
3. Pa (pascal)
4. Torr (torr)
49
New cards
Barometer
Measures the atmospheric pressure
50
New cards
Who introduced the first barometer?
Evangelista Torricelli
51
New cards
What are STP conditions?
0° & 1 atm
52
New cards
Standard Units of Pressure Conversions
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 101.325 kPa
53
New cards
What are gas laws?
Mathematical relationships between the 4 variables for gases: Pressure, Temperature, Volume, Moles
54
New cards
Boyle’s Law
Volume and pressure are **inversely** related with a constant temperature & number of moles
__**Equation:**__ P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
__**Equation:**__ P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
55
New cards
Charle’s Law
Volume and temperature are **directly** related with a constant pressure & number of moles
__**Equation:**__ V1/T1 = V2/T2
__**Equation:**__ V1/T1 = V2/T2
56
New cards
Before calculating, the temperature must be in ____?
Kelvin
57
New cards
How do you find Kelvin?
Kelvin (K) = °C + 273
58
New cards
How do you find °C?
°C = Kelvin - 273
59
New cards
Gay-Lussac’s Law
Pressure and temperature are **directly** related with a constant volume & number of moles
__**Equation:**__ P1/T1 = P2/T2
__**Equation:**__ P1/T1 = P2/T2
60
New cards
Combined Gas Law
Expresses all variables with a constant of number of moles
__**Equation:**__ P1 x V1 / T1 = P2 x V2 / T2
__**Equation:**__ P1 x V1 / T1 = P2 x V2 / T2
61
New cards
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
The total pressure of a mixture is equal to the sum of all partial pressures
__**Equation**__: PT = P1 + P2 + P3 …
__**Equation**__: PT = P1 + P2 + P3 …
62
New cards
Dalton’s Formula
PT = P Gas + P H2O
63
New cards
Gay-Lussac noticed gas volume relationships at a constant ____ and ____
temperature, pressure
64
New cards
Gay-Lussac noticed (small whole number ratios, one whole number ratios) by volume for the reaction of gases
small whole number ratios
65
New cards
Gay-Lussac’s Law of Combining Volumes
At a constant **temperature** and **pressure**, the **volumes** of reactants & products can be expressed as small whole-number ratios
66
New cards
Equal volumes of all gases under the same conditions of temperature & pressure contain the same number of ____?
molecules
67
New cards
Avagadro proved a direct relationship existed between volume and the number of ____?
moles
68
New cards
Standards Molar Volume of a Gas at STP
1 mole gas = 22.4 L
69
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
A mathematical relationship that helps describe gas behavior
70
New cards
Variables Needed in the Ideal Gas Law
1. P
2. V
3. T
4. n (# of moles)
71
New cards
Ideal Gas Law Equations
1. PV = nRt (n= moles)
2. PV = mRt/M (m = mass (g) & M = molar mass)
3. D = MP/RT (D= density)
72
New cards
Ideal Gas Law Constant
R
* R = 0.0821 atm/mol k
* R = 8.314 kPa/mol k
* R = 62.4 mmHg/mol k
* R = 0.0821 atm/mol k
* R = 8.314 kPa/mol k
* R = 62.4 mmHg/mol k
73
New cards
Graham’s Law
Rate A / Rate B = √Molar Mass B / √Molar Mass A
74
New cards
Homogeneous Solution
Mixture of 2 or more substances that appear to look the same
75
New cards
Can particles be seen?
No
76
New cards
Solute
Substance being dissolved
77
New cards
Solvent
Substance doing the dissolving
78
New cards
Soluable
Capable of dissolving
79
New cards
Insoluable
Not capable of dissolving
80
New cards
Suspensions
* The particles are so large that they settle out of the solvent in not constantly stirred
* Can be filtered
* __**Example:**__ Muddy water
* Can be filtered
* __**Example:**__ Muddy water
81
New cards
Colloids
The particle is intermediate in size between those of suspension and those of a solution
82
New cards
Heterogeneous
Microscopic scale under a microscope
83
New cards
Homogeneous
Macroscopic scale under a microscope
84
New cards
The Tyndall Effect
Colloids scatter light, making a beam visible
85
New cards
Can solutions scatter light?
No
86
New cards
Electrolyte
A substance whose aqueous solution conducts an electric current
87
New cards
Nonelectrolyte
A substance whose aqueous solution does not conduct an electric current
88
New cards
Why do some compounds conduct electricity in solution but others don’t?
It is determined by the type of bond for the compound
89
New cards
Dissociation
The seperation of ions. The ions are already present at the beginning due to the ionic bond.
90
New cards
Can ionic compounds dissociate?
Yes
91
New cards
Ionization
The formation of ions
92
New cards
Can polar-covalent compounds ionize?
Yes
93
New cards
What is the general rule for solute-solvent interactions?
Like dissolves like
94
New cards
Like dissolves like examples
* Polar dissolves polar
* Non-polar dissolves non-polar
* Polar also dissolves **ionic**
* Non-polar dissolves non-polar
* Polar also dissolves **ionic**
95
New cards
Hydration
The attraction between water molecules and the ions dissolved
96
New cards
Immiscible
Liquids that are not soluble in each other
97
New cards
Miscible
Liquids that dissolve freely in each in any proportion
98
New cards
Factors Effecting Solubility
1. **Increasing** surface area, stirring/shaking, or temperature **increases the rate of dissolution** (dissolving)
2. **Solution Equilibrium**- dissolving and crystallizing at the same rate in a closed system
99
New cards
Saturated Solution
A solution that contains the **maximum** amount of solute that may be dissolved under existing conditions
100
New cards
Unsaturated Solution
A solution that contains **less solute** than a saturated solution under existing conditions